Abstract
Aims:
Filifactor alocis has recently emerged as a periodontal pathobiont that appears to thrive in the oral cavity of smokers. We hypothesized that identification of smoke-responsive F. alocis genes would provide insight into adaptive strategies and that cigarette smoke would enhance F. alocis pathogenesis in vivo.
Materials and Methods:
F. alocis was grown in vitro and cigarette smoke extract-responsive genes determined by RNAseq. Mice were exposed, or not, to mainstream 1R6F research cigarette smoke and infected with F. alocis, or not, in an acute ligature model of periodontitis. Key clinical, infectious, and immune data were collected.
Results:
In culture, F. alocis growth was unaffected by smoke conditioning and only a small number of genes were specifically regulated by smoke exposure. Reduced murine mass, differences in F. alocis-cognizant antibody production and altered immune profiles as well as altered alveolar bone loss were all attributable to smoke exposure and/or F. alocis infection in vivo.
Conclusions:
F. alocis is well-adapted to tobacco-rich conditions and its pathogenesis is enhanced by tobacco smoke exposure. A smoke-exposed ligature model of periodontitis shows promise as a tool with which to further unravel mechanisms underlying tobacco-enhanced, bacteria-induced disease.
Keywords: Alveolar bone loss, experimental periodontitis, Filifactor alocis, microbiology, tobacco smoking
Introduction:
The development of rapid and inexpensive genetic screening technologies has led to the identification of previously unappreciated periodontal pathogens and, subsequently, to the gradual supersession of classic red complex theory. Among the emergent microbes, the evidence for Filifactor alocis, a Gram-positive, anaerobic rod, is particularly strong with abundance shown to be relatively low in health but high in chronic and aggressive forms of periodontitis [2–20]. F. alocis is associated with deteriorating clinical parameters, including enhanced gingival bleeding (in non-smokers) and increased pocket depth and attachment loss [4, 10, 21–23]. F. alocis may also help predict bone loss in rapidly deteriorating periodontal lesions [24]. Oral F. alocis has been suggested to preferentially colonize children of subjects with periodontitis [25] while, at the same time, F. alocis is more abundant with increasing severity of periodontitis in elderly individuals [26] with the IgG-cognizant F. alocis response increasing with age [27].
Cigarette smokers are more susceptible to a plethora of infectious diseases, compared to non-smokers, not limited to pneumonia, tuberculosis, meningitis and sexually transmitted bacterial infections [28]. Critically, cigarette use is also a, if not the, major risk factor for destructive forms of periodontal disease [29, 30]. Indeed, at the population level, smoking accounts for most cases of periodontitis in adults in developed nations, at least in Scandinavia, New Zealand and the US [31–34]. Tobacco use has been associated with increased disease progression and severity, as well as with refractory disease [35, 36]. Risk appears dose-related [29, 37, 38] while environmental smoke exposure may also be associated with higher risk of destructive periodontitis, as we and others have shown [39–42].
Some components of the oral microbiome are highly resistant to the toxic insults contained in cigarette smoke. One such species may be F. alocis, which has been consistently associated with periodontal diseases epidemiologically and may thrive in tobacco-rich environments, both in vitro and in vivo [20, 43]. While there has been extensive delineation concerning how tobacco smoke influences Porphyromonas gingivalis gene activity, ultrastructure and physiology [44–48], there are obvious fundamental differences between this established Gram-negative pathogen and F. alocis, not least architecturally. The role of F. alocis and, indeed, Gram-positive bacteria in general are not well studied, mechanistically, in the context of periodontal diseases. However, F. alocis is particularly active, from a transcriptional perspective, relative to other members of the oral microbiome [3, 18]. Our overall premise is that cigarette smoke represents an environmental stressor to which F. alocis responds in a manner that will inform as to tobacco-adaptive mechanisms. We further theorize that tobacco exposure may enhance F. alocis pathogenesis and test this hypothesis in a controlled in vivo experimental system that will facilitate future mechanistic insights into this important oral ill-health phenomenon.
Materials and Methods:
Materials
Bacterial strains, animals, consumables and key equipment are noted in the supplementary materials.
Cigarette smoke extract-conditioning of F. alocis growth medium.
F. alocis ATCC 35896 was grown anaerobically at 37°C in pre-reduced brain heart infusion with 0.5% yeast extract, 0.05% L-cysteine and 0.05% arginine (BHI) or in cigarette smoke-conditioned medium (CSE), prepared as described previously [46–48]. Essentially, cigarette smoke from standardized 1R6F research cigarettes was drawn through 100 ml of medium in 40 ml drags performed every 20 seconds. Nicotine, a surrogate dose marker, was determined by GLC and the medium adjusted to physiological relevance (1000 ng/ml nicotine equivalency) at pH 7.2 [46, 48, 49]. F. alocis growth was monitored spectrophotometrically at O.D. 600nm (Biowave CO 8000, Biochrom Ltd, Cambridge, England) and cells harvested during mid-exponential growth.
Transcriptomic analysis of the cigarette smoke-specific response of F. alocis.
F. alocis was grown in pre-reduced BHI then transferred to fresh BHI or CSE, again pre-reduced. Bacterial cells were harvested during mid-exponential growth. RNA was immediately extracted using Qiagen RNeasy kits and RNase-free DNase sets, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A n additional cell lysis procedure was employed using RNase-free Lysing Matrix B tubes and the FastPrep-24 system (MP Bio). RNA quality and quantity was determined using a NanoDrop One system. RNAseq was performed at the DNA Sequencing Core at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, MI). For quality control, the raw sequences were trimmed using Trimmomatic v0.39 and the trimmed read quality assessed using FastQC v0.11.7 and MultiQC v1.1. 2.3. Trimmed sequences were aligned to the F. alocis_ATCC_35896 genome using EDGE-Pro v1.3.1. Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq2 v1.32.0 and normalized based on (rlog) expression values. Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted p values (p <0.05). Preliminary, alignment-derived annotations were augmented using the prokaryote-specific BlastX functions of the KEGG genes database (www.genome.jp/tools/blast/) and/or NCBI (blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
Murine model of F. alocis infection and alveolar bone loss.
In preparation for in vivo animal model studies, we established that F. alocis persists in the murine cavity for ≥42 days, as determined by qPCR (data not shown). A ligature model of bacterial-induced murine periodontitis was employed within a Teague TE-10C cigarette smoke inhalation exposure system. Briefly, Balb/c mice (6–8 weeks, 4 groups of n = 7 per group) were exposed to mainstream cigarette smoke (20 cigarettes per day over 3 hours; mean (s.d.) CO, 170 (9) ppm) or sham-exposed in a parallel ambient air chamber over 15 days. Females only were employed to reduce conflict-related stress within the confines of the exposure chamber. After 7 days, a ligature was applied to the right maxillary second molar under anesthesia with ketamine (50 mg/kg) / dexdomitor (0.5 mg/kg) and mice recovered on a heat pad while under constant observation, including non-invasive infrared monitoring of body temperature. Mice were then orally inoculated with F. alocis (1×109 CFU of live bacteria suspended in 100 μl PBS with 2% carboxymethylcellulose vehicle) or sham infected (vehicle only) directly by gavage needle. Infections were performed three times at 2 d intervals. Power was established using G*Power 2.1 (Heinrich Heine University, Dusseldorf, Germany). Group 1: Sham infection, ambient air, Group 2: F. alocis infection, ambient air; Group 3: Sham infection and smoke exposure; Group 4: F. alocis infection and smoke exposure. Mice were weighed on alternate days and mass differentials between baseline and experimental endpoint established. Mice were euthanized 8 days after ligature placement by CO2 asphyxiation followed by desanguination. Local and systemic immune responses, alveolar bone loss and F. alocis infection were assessed, as described below. All murine procedures were approved by the local IACUC (Study #18359).
Smoke exposure parameters
CO levels in the exposure chamber were monitored continuously over the 3 hr smoking period and maintained, by venting, between 100 and 200 ppm with a target of 150 ppm and recorded 8 times. Total suspended particulates were also measured daily, at the end of three-hour smoking period, and recorded as mass per unit volume (mg/m3). Urinary cotinine (ng/ml) was measured using a commercial ELISA, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
F. alocis colonization of the gingiva
F. alocis was quantified through examination of a 101 bp amplicon from the gyrase B-encoding gene from 2 ml, 24hr anaerobic BHI cultures of buccal, vestibular gingival swabs collected at the time of euthanization. Bacterial lysis and DNA extraction was performed using the ReliaPrep system, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. F. alocis colonization was quantified using the QuanStudio 3 RT-PCR System with QuanStudio Design Analysis 1.4.1 software (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). The F. alocis gyrB primers (F: ACCCTCAAGTTGCCAAAATTATTAT and R: TACTCCCTTTCTTCTGGTTAAATCT), as previously reported [11], were used. qPCR reactions employed 5 μl SYBR green mix, 0.5 μl of each primer and 4 μl sample DNA. F. alocis was quantified using a standard curve prepared using a known gyrB copy number dilution series.
Quantification of systemic immunoglobulins and immune activation biomarkers
F. alocis-cognizant IgM and IgG were measured in murine serum by ELISA. Briefly, paraformaldehyde-fixed and washed bacterial cells were suspended in PBS at an O.D.600nm of 0.3 and 100 μl suspensions aliquoted into 96 well plates and left to adhere overnight at 4°C. Adherent cells were washed (PBST), ELISA blocking diluent supplied, and mouse serum added, at the appropriate dilution, for 2 hr at RT. After washing, HRP-tagged anti-IgM or -IgM antibodies were added (45 min, RT), TMB substrate supplied, and reactions stopped using 1N H2SO4. Absorbance was measured at O.D. 450nm using a SpectramaxID3 spectrophotometer (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA) and F. alocis-cognizant immunoglobulins quantified by extrapolation from standard curves generated using commercially supplied mouse IgM and IgG standards. Systemic immune activation biomarkers were analyzed with the Milliplex MAP mouse cytokine/chemokine magnetic bead panel using the multiplexing service run by The University of Louisville Center for Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE) in Functional Microbiomics, Inflammation and Pathogenicity.
Quantification of alveolar bone loss
Mouse skulls were boiled, de-fleshed and immersed in 3% H2O2 overnight at 4°C. The skulls were then immersed in 1% HOCl for 1 min, washed in water and air dried. Maxillae were stained with 0.5% eosin for 5 min followed by 1% methylene blue for 1 min. Second molar alveolar bone loss was determined as the distance from the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to the alveolar bone crest (ABC), established using a SMZ 800 dissecting microscope fitted with a VIA-170K video image marker measurement system (Boeckeler Instruments Inc, Tucson, AZ).
Statistical analyses
Other than for transcriptomic data, statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software LLC, La Jolla, CA). Unless otherwise stated, ANOVA or t-tests, were utilized, as appropriate, to test for inter-group differences in mean (s.d.) values with significance set at p < 0.05.
Results:
Transcriptomic response of F. alocis to cigarette smoke extract
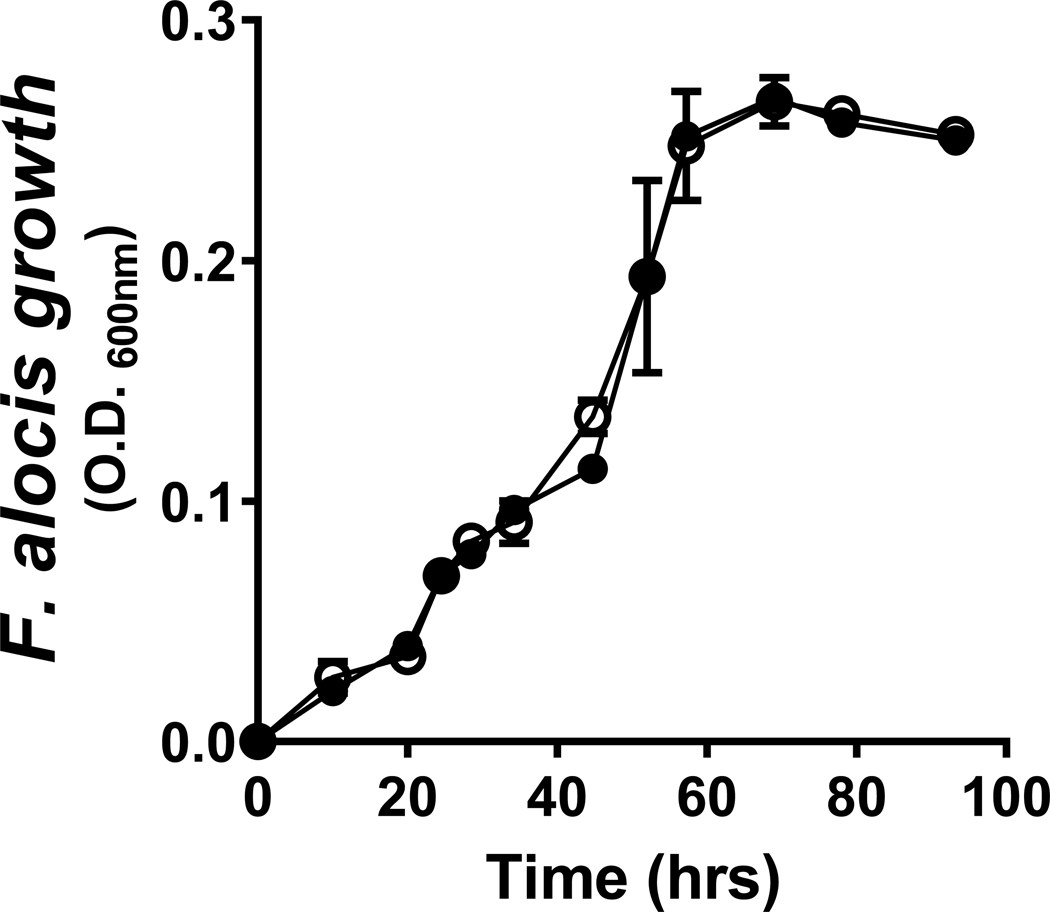
F. alocis was grown anaerobically in BHI (passage 1) and transferred, at mid-log phase, at a 1/100 dilution at 0.D.600nm of 0.200 (0.3 × 107 bacteria) or equivalent, to either fresh BHI or to CSE-conditioned BHI (1000 ng/ml nicotine equivalents). All media were pre-reduced. Passage 2 bacteria were, again, harvested in the middle of exponential growth. As presented in Figure 1, F. alocis is highly tolerant of tobacco smoke, with essentially overlapping growth traits noted for control and CSE-exposed cultures. RNAseq revealed that introduction to fresh medium (BHI or CSE) resulted in the up- and down-regulation of 72 and 143 F. alocis genes (x2 fold; p < 0.05), respectively, that were common to both passage 2 conditions and, therefore, considered not particular to CSE (Table S1). A further 34 and 30 F. alocis genes specific to CSE conditioning, i.e., passage 2 genes differentially regulated in CSE but not BHI, were up- and down-regulated (x2 fold; p < 0.05), respectively (Table S2). The top protein-encoding, annotated F. alocis genes in passage 2 (fold regulation) specific to CSE exposure are presented in Table 1. A volcano plot of the significantly differentially-regulated genes is also presented in Supplemental Figure 1.
Figure 1: Cigarette smoke extract does not influence the growth of F. alocis in culture.
There were no significant differences in the growth characteristics of F. alocis cultured anaerobically in BHI (black circles) or BHI conditioned with 1R6F cigarette smoke (1000 ng/ml nicotine equivalents) (white circles), as assessed spectrophotometrically (O.D.600nm). Data represent mean (s.d.) values.
Table 1:
Functionally relevant F. alocis genes differentially upregulated upon exposure to 1R6F research cigarette smoke extract.
| RNASeq ORF | Annotation | Fold dysregulation | Function | Gene Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS05665 | ssDNA binding protein/ conjugal transfer protein | 3.1 | DNA transfer | HMPREF0389_00666 |
| RS05520 | TrbL-family conjugal transfer protein | 2.9 | DNA transfer | HMPREF0389_00638 |
| RS02715 | dnaJ, heat-shock protein 40 | 2.5 | Molecular chaperone | HMPREF0389_00093 |
| RS02535 | topA, type I DNA topoisomerase | 2.5 | Relaxation of supercoils | HMPREF0389_00129 |
| RS05510 | TpcC-family conjugal transfer protein | 2.4 | DNA transfer | HMPREF0389_00636 |
| RS05560 | Tn5397-family conjugative transposon protein | 2.4 | DNA transfer | HMPREF0389_00645 |
| RS06900 | yesM, Sensor histidine kinase | 2.3 | Response regulator relay | HMPREF0389_00918 |
| RS06910 | msrAB, peptide-methionine-S-oxide reductase | 2.3 | Oxidative damage repair | HMPREF0389_00920 |
| RS02515 | Rrf2-family protein | 2.3 | Transcriptional regulator | HMPREF0389_00133 |
| RS05645 | PrgI family protein, Tn1549-like conjugative transposon | 2.2 | DNA transfer | HMPREF0389_00662 |
Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted pvalues (p< 0.05). The top 10 upregulated regulated F. alocis genes, fold-wise, attributed to 3R4F research cigarette smoke extract exposure and with potential tobacco-related functional annotations are presented. Preliminary, F. alocis 35896 alignment-derived annotations were updated using the prokaryote-specific BlastX functions of the KEGG genes database (www.genome.jp/tools/blast/) and/or NCBI Blast (blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Others, e.g., HMPREF0389_01622, HMPREF0389_00639, HMPREF0389_01597 and HMPREF0389_00134 exhibit 2.9, 2.7, 2.5 and 2.4-fold differentiation, respectively, but do not encode proteins with obvious functional relevance to cigarette smoke adaptation.
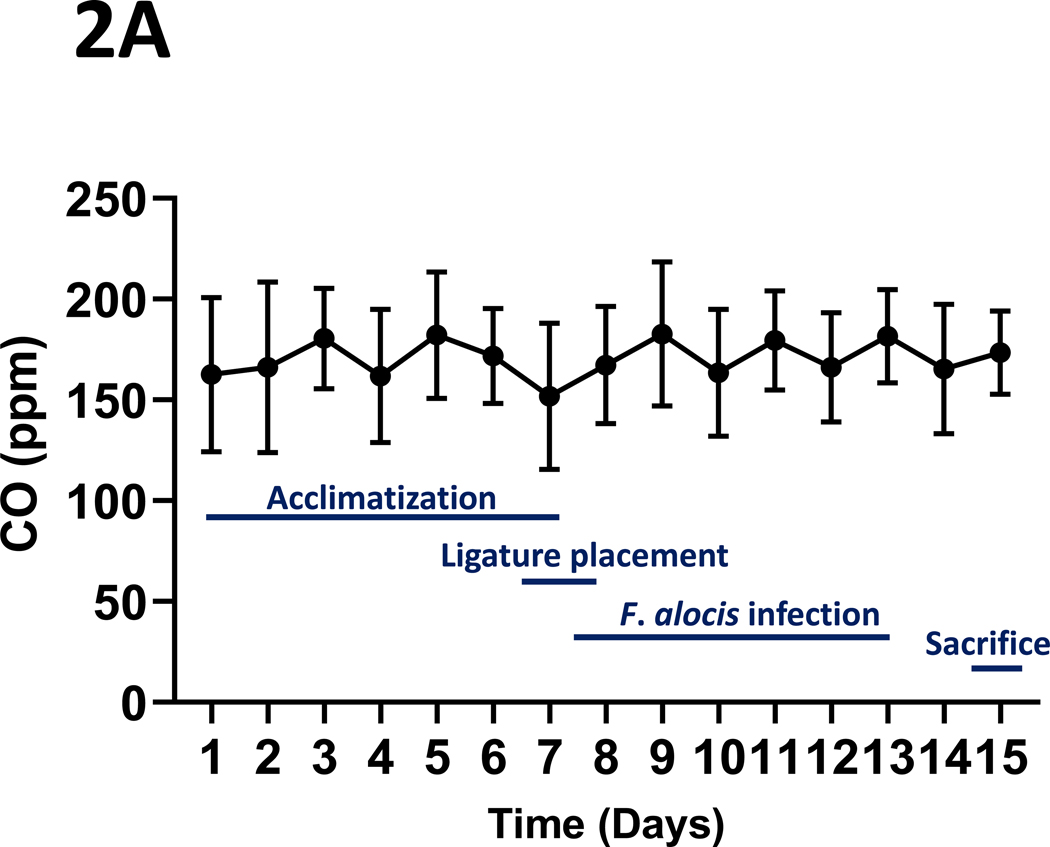
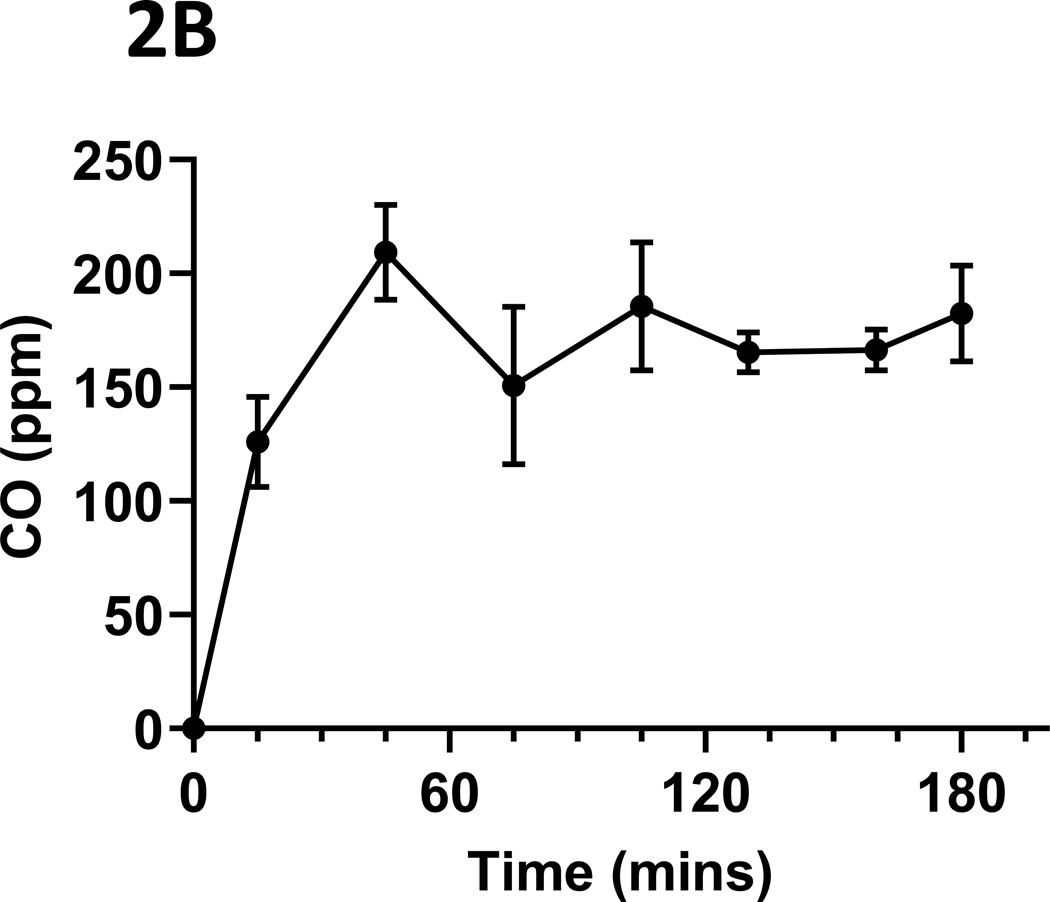
1R6F reference cigarette smoke exposure conditions
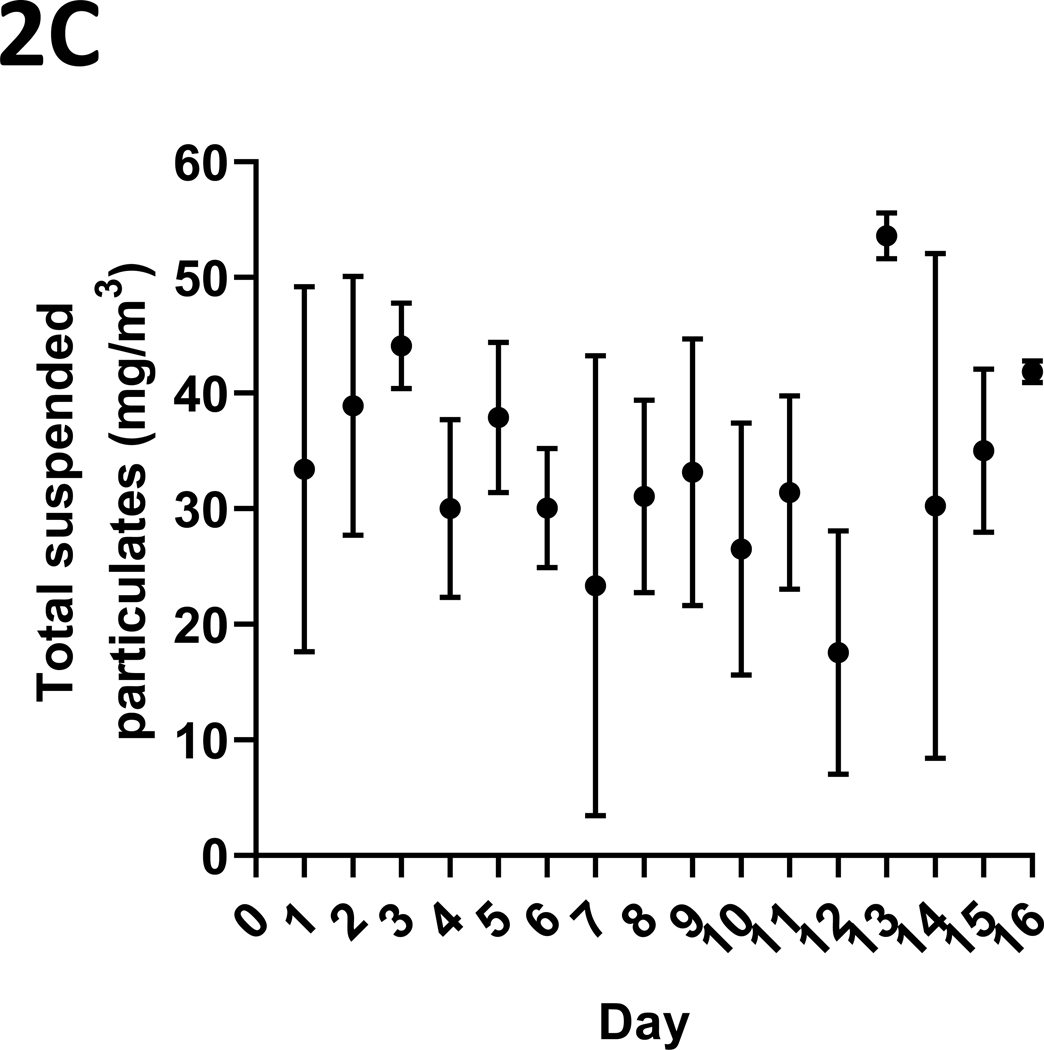
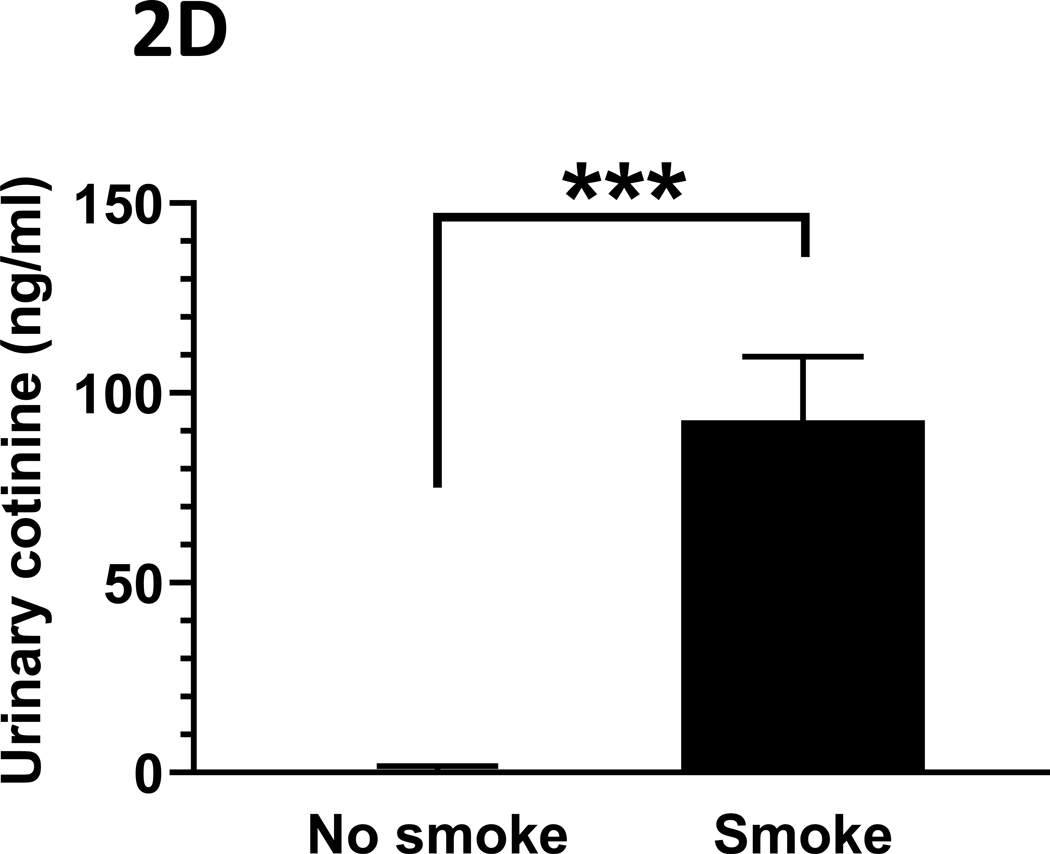
The mean (s.d.) CO concentrations (ppm) over the daily 3-hour exposure periods are presented in Figure 2A. Typical daily exposure levels rose rapidly towards the mean daily level, as shown in Figure 2B. Total suspended particulates (mg/m3) generated over the three-hour daily smoking exposures were also monitored, with the mean (s.d.) levels presented in Figure 2C. Finally, mean (s.d.) urinary concentrations of the primary nicotine metabolite, cotinine, are presented in Figure 2D. Cotinine levels in cigarette smoke-exposed mice were, as expected, significantly elevated relative to those exposed to ambient air (p < 0.001), as measured in a sub-set of mice whose urine could be collected at the end of the exposure period (n = 13, 9 smoke-exposed).
Figure 2: Tobacco smoke exposure indices.
Mice were exposed to mainstream cigarette smoke generated from 1R6F research cigarettes using a Teague TE-10C cigarette smoke inhalation exposure system for 3 hours per day over 15 days. (A) Daily CO concentrations (ppm), as monitored 8 times over the 3-hour exposure period; (B) CO (ppm) fluxes over the 3 hours exposure period; (C) Total suspended particulates (mg/m3) generated daily; and (D) urinary concentrations of the primary nicotine metabolite, cotinine, are presented.
Data represent mean (s.d.) values.
For panel (D), urine was collected from n = 4 control (ambient air-exposed) and n = 9 smoke-exposed mice.
*** p < 0.001.
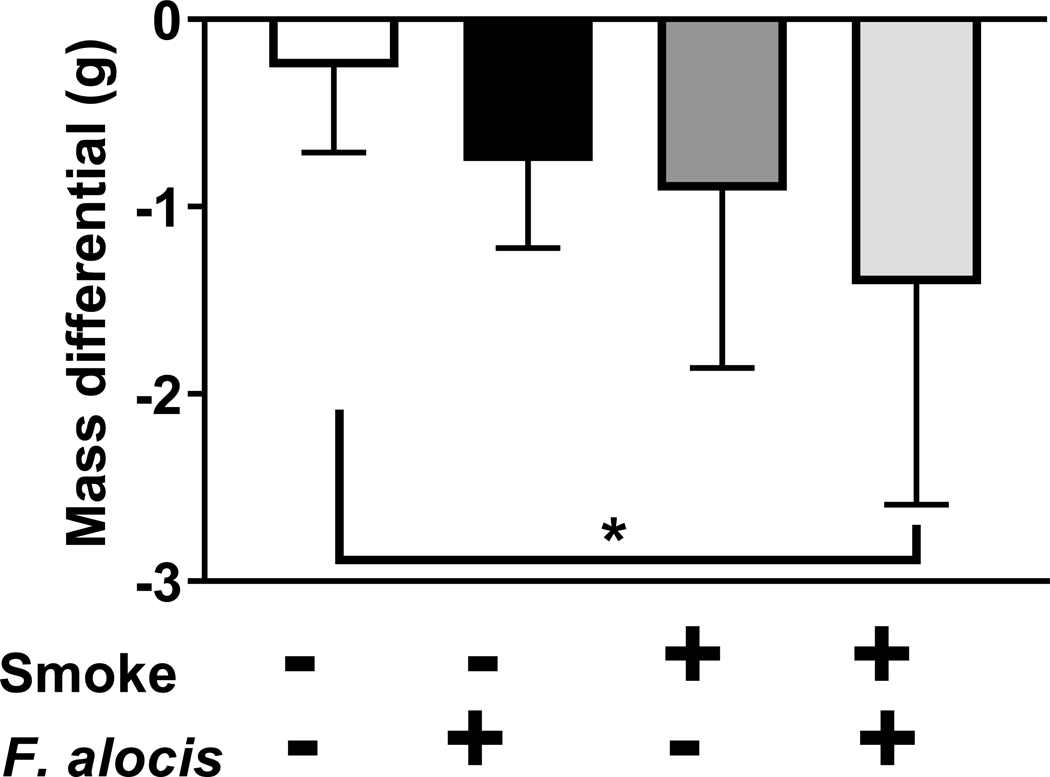
Smoking and F. alocis infection reduce murine mass
There were no significant differences in mouse weight between any of the groups at baseline. However, as shown in Figure 3, the combination of smoke exposure and F. alocis-infection resulted in lower mean murine mass, compared to non-infected, sham-exposed controls at euthanization (p = 0.03). No other significant mass differentials between groups were observed.
Figure 3: 1R6F-smoke and F. alocis-exposure acutely influence murine mass.
The mass (g) of control (non-infected, ambient air-exposed); F. alocis-infected; smoke-exposed; and both smoke-exposed and F. alocis-infected mice were monitored at baseline (20.9 [0.7], 20.6 [1.3], 22.2 [1.3] and 22.1 [1.4], respectively) and after 15 days. Mass differentials over the experimental period are presented.
Data represent the mean [s.d.] of n =7 per group.
* p < 0.05 compared to untreated control mice.
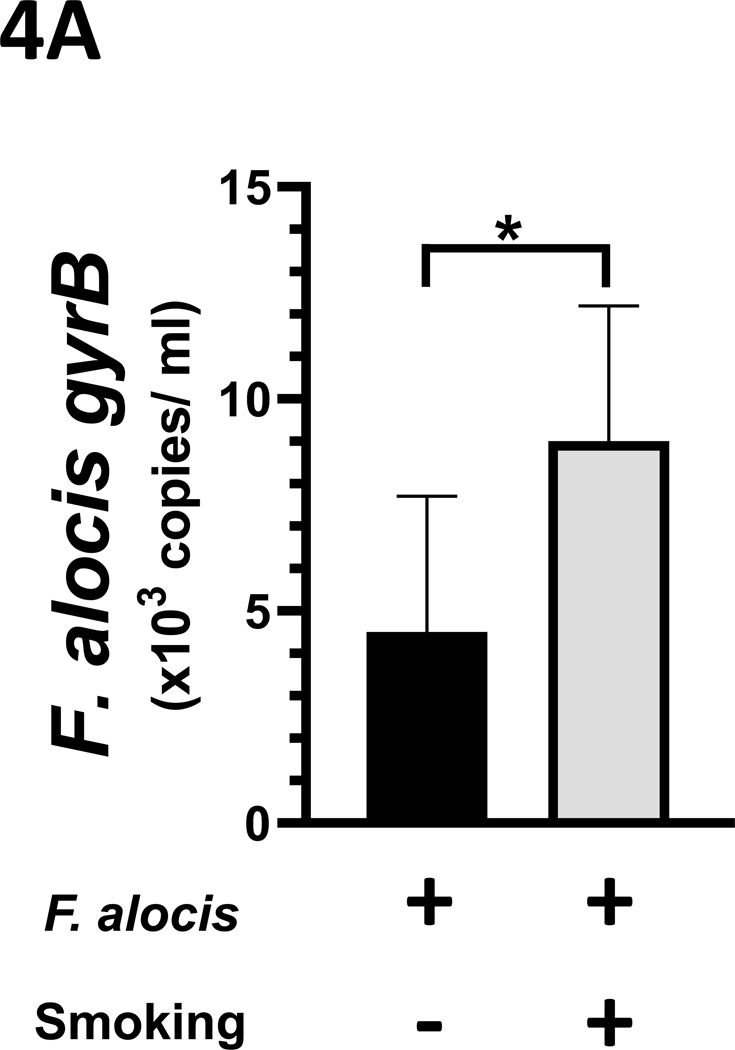
Smoke exposure increases the F. alocis burden
In vivo, F. alocis persistence was established by quantitative PCR targeting the gyrB gene from 24-hr anaerobic BHI cultures of gingival swabs collected at euthanization. As presented in Figure 4A, the mean F. alocis burden was increased in cultures from the smoke-exposed mice (9.0 × 103 [ s.d. 3.2 × 103] copies/ml) compared to the ambient air-exposed mice (4.5 × 103 [ s.d. 3.2 × 103] copies/ml culture), p < 0.05.
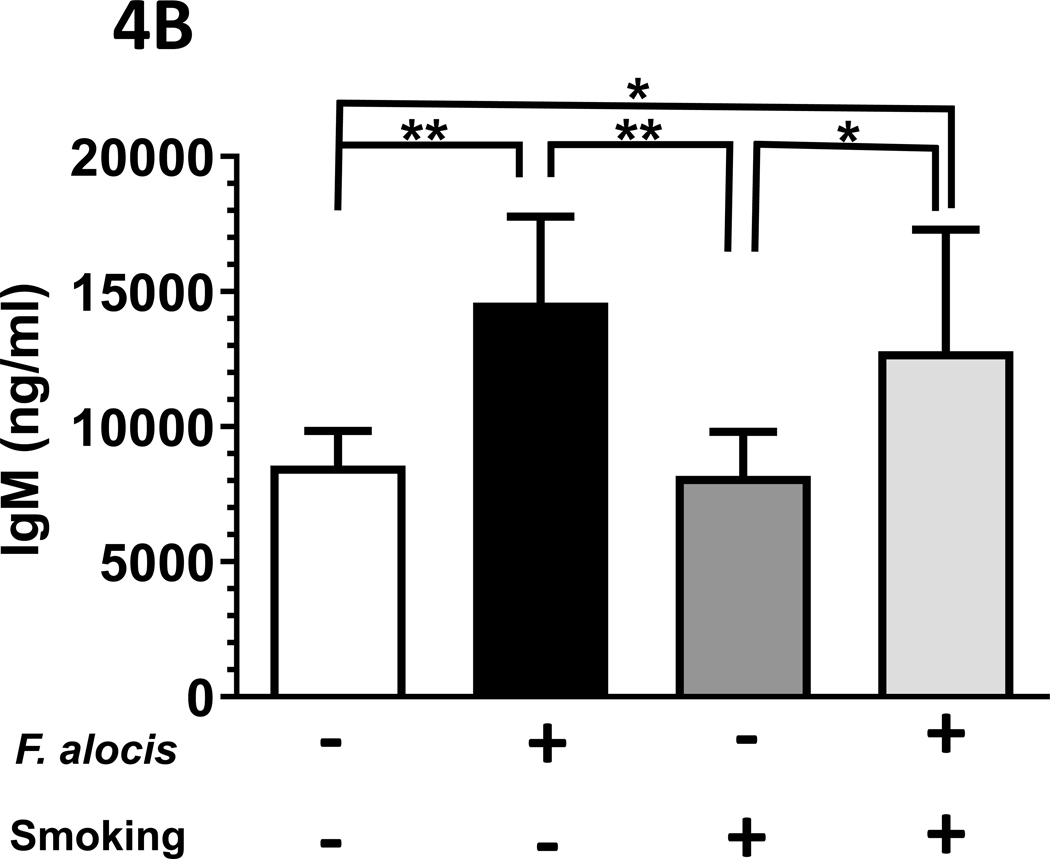
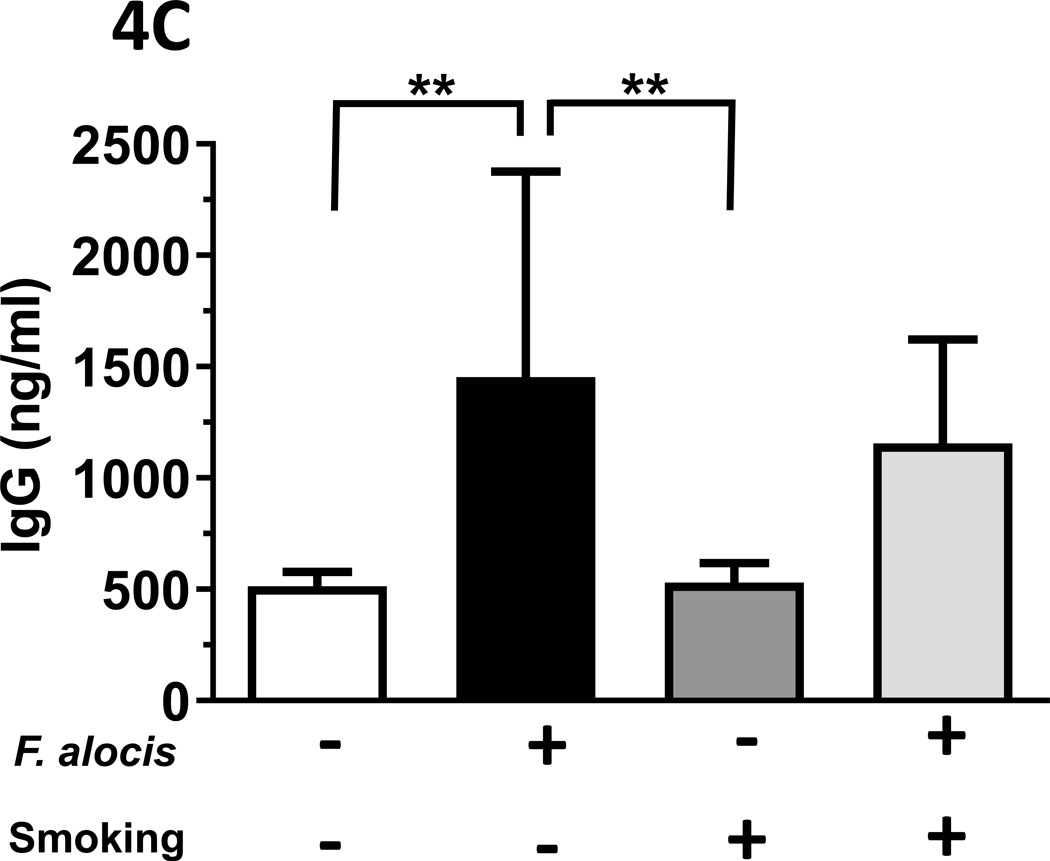
Figure 4: F. alocis is a tobacco-resistant bacterium whose infectivity is enhanced by smoke exposure in vivo.
(A) In vivo, 1R6F smoke exposure enhanced F. alocis infectivity, as assessed by gyrB copy number in anaerobic cultures of gingival swabs collected at euthanization. Further, F. alocis infection led to (B) an increased F. alocis-cognizant IgM signal in both smoke- and ambient air-exposed mice but (C) the F. alocis-cognizant IgG response was significantly elevated in mice exposed to ambient air only.
Data represent mean [s.d.] values.
*/** p < 0.05 and < 0.01, respectively.
Differential F. alocis-cognizant IgM and IgG responses in smoke-exposed mice.
The F. alocis-cognizant IgM signal in each murine group is presented in Figure 4B, as detected in murine serum collected at euthanization. The total F. alocis-cognizant IgG signal is presented in Figure 4C.
Smoking does not exert a profound influence on the inflammatory response to F. alocis.
There were no significant differences between groups in the circulating concentrations of murine G-CSF, IL-1α, IL-5, IL-12 p40, IL-13, IL-15, IL-17, KC, MCP1, MIP1α, MIP1β, MIP2, RANTES or TNF (all p > 0.05), as measured by multiplexing (Table S3). However, an elevated IP-10 (CXCL10) was observed in mice exposed to both cigarette smoke and orally infected with F. alocis, (p < 0.01). The remaining systemic immune biomarkers examined (GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-7, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12 p70) were out of range or not detected. At the mRNA level, the local immune data were also unremarkable (Table 2) in the context of smoke-exposure, with the primary differentials apparently driven by ligature placement.
Table 2.
Relative signal of inflammatory mediators in gingival tissues.
| Mediator | Control | Control (L) | F. alocis | F. alocis (L) | Smoke | Smoke (L) | F. alocis and Smoke | F. alocis and Smoke (L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 1.0 | 16.2 (13.1)* | 0.8 (0.2) | 12.5 (6.1) | 1.0 (0.4) | 10.9 (2.9)# | 1.6 (0.7) | 12.1 (8.7)# |
| MIP-2 | 1.0 | 11.4 (14.4) | 0.6 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.2)### | 0.6 (0.5) | 6.6 (4.0) | 1.7 (2.0) | 5.3 (1.0)# |
| CD14 | 1.0 | 7.5 (7.6) | 0.7 (0.2) | 3.6 (2.5) | 0.6 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.5)## | 1.1 (0.5) | 3.1 (1.8) |
| IL-10 | 1.0 | 7.2 (5.1) | 2.2 (0.9) | 6.5 (3.0) | 1.0 (0.7) | 9.7 (3.2)# | 3.1 (2.6) | 16.1 (6.6)**/# |
| CD45 | 1.0 | 5.5 (6.3) | 1.0 (0.3) | 2.1 (0.4)# | 0.5 (0.7) | 1.5 (1.1) | 0.6 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.5) |
| IL-17α | 1.0 | 7.1 (8.4) | 0.4 (0.2) | 2.1 (1.6) | 0.3 (0.3) | 1.9 (1.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.3)## |
| IL-6 | 1.0 | 13.7 (10.1) | 1.0 (0.5) | 8.4 (4.7) | 0.5 (0.1) | 16.4 (15.5) | 1.8 (1.9) | 5.8 (4.7) |
| MMP8 | 1.0 | 5.9 (4.7) | 0.3 (0.2) | 4.8 (1.9)# | 0.3 (0.2) | 3.7 (2.0)# | 0.3 (1.3) | 3.2 (2.5) |
| MMP9 | 1.0 | 1.4 (1.9) | 1.3 (0.4) | 0.5 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.3) | 0.5 (1.7)# | 0.9 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.1)## |
| TIMP1 | 1.0 | 3.0 (1.7) | 1.1 (0.7) | 32.9 (56.8) | 1.5 (0.6) | 4.1 (0.5)## | 1.9 (0.2) | 6.6 (2.2)# |
The relative expression of key inflammatory mediators in mandibular gingival tissues adjacent to the ligated (L) and unligated second molars are shown. Data represent mean (s.d.) values normalized to GAPDH-encoding gene activity relative to untreated control tissues.
Asterisks represent statistically significant differences between groups compared to the no treatment control mice, as determined by ANOVA.
p < 0.05 and < 0.01, respectively.
Pound symbols represent statistically significant differences between directly comparable ligated and non-ligated sites, as determined by t-test.
p < 0.05, < 0.01 and > 0.001, respectively.
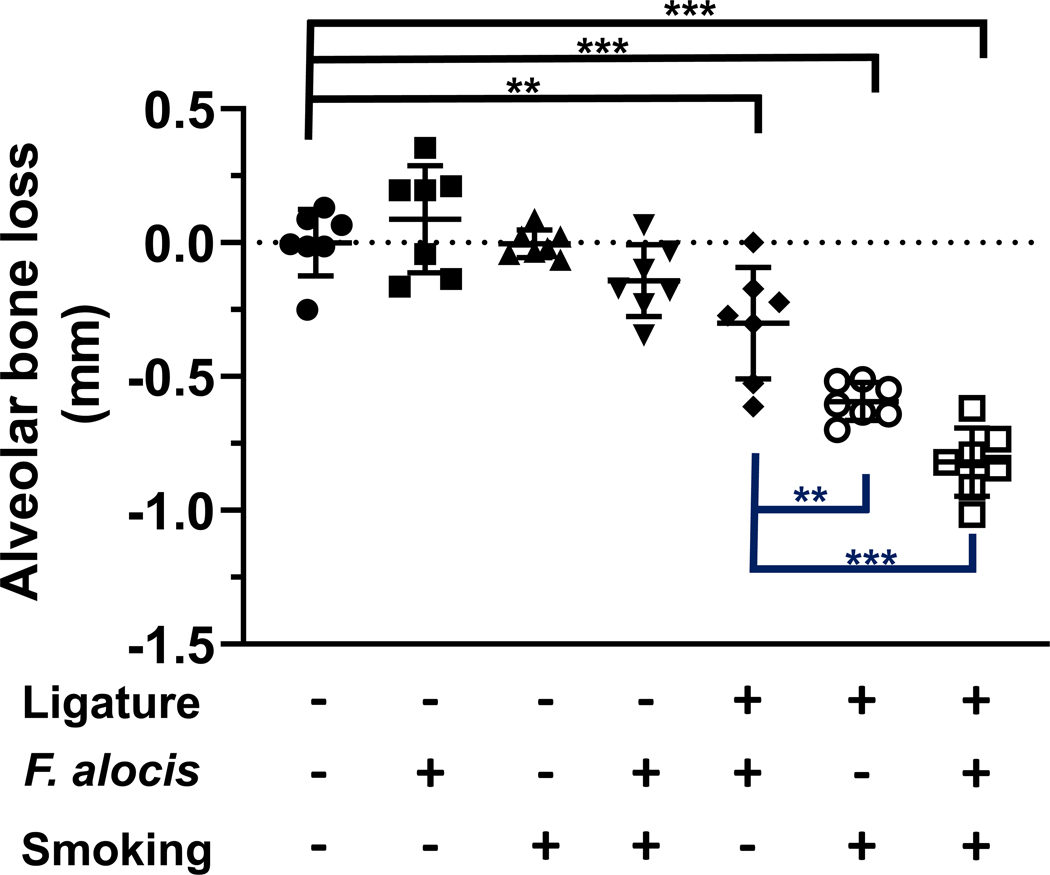
Exposure to cigarette smoke influences bacterial-induced alveolar bone loss.
There were no significant differences in alveolar bone loss at unligated second molar sites between groups (all p < 0.05). However, at ligatured second molars, smoke exposure and adjunctive F. alocis infection (p < 0.001) significantly increased alveolar bone loss, as presented in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Tobacco smoke exposure alters alveolar bone loss in an acute F. alocis-infection model.
Second molar alveolar bone loss was determined microscopically as the distance from the cementoenamel junction to the alveolar bone crest in a model of ligature-induced acute periodontitis.
Data from individual mice are shown with mean (s.d) values represented by long and short black bars, respectively. Black lines represent comparisons to control (no ligature, no F. alocis, no smoke) sites. Blue lines represent comparisons between ligatured second molars.
**/*** p < 0.01 and < 0.001, respectively.
Discussion:
F. alocis infection is associated with periodontal disease progression [2–19, 21–23, 50]. Localization of F. alocis close to the basement membrane or external basal lamina of human gingival epithelium [19], combined with the ability of F. alocis-derived extracellular vesicles to induce TLR2-related long bone resorption in an animal model [51], suggest F. alocis may have the capacity to exert an influence beyond the sulcular environment. Several excellent recent reviews of F. alocis are available [52–55].
Moon et al have shown that F. alocis is enriched in the subgingival plaque of smokers with chronic periodontitis compared to non-smoking controls and that F. alocis is one of a limited number of taxa that individually comprise more than 1% of the total microbiome [20], despite increased microbial diversity in smokers [20, 56, 57]. Re-evaluation of one of our own recent papers [58] discloses increased F. alocis infection in pregnant women (n = 70) who smoke (67%) compared to those who do not (36%, p < 0.05). Critically, Delima et al have shown that F. alocis prevalence and burden decreases upon validated smoking cessation [59]. F. alocis appears to be highly transcriptionally and metabolically active, in situ, relative to many other plaque bacteria [3, 18, 19]. We had anticipated a high degree of transcriptomic activity in response to CSE exposure, a phenomenon previously observed in Porphyromonas gingivalis [46–48]. However, only a relatively small number of F. alocis genes, from a 1.93 Mb, ≅1950 ORF genome [60], were ascribed as being differentially regulated in a CSE-specific manner (n = 64), less than the number of genes differentially (de)activated in common upon passaging from BHI into fresh growth medium, both in BHI and CSE (n = 215). Further, F. alocis growth rates were unaffected by CSE exposure, at 1000 ng/ml nicotine equivalence, in vitro. Therefore, when combined with our data showing increased F. alocis infectivity in the oral cavity of smoke-exposed animals, it would appear that this emergent periodontal pathogen is well-adapted to life in a tobacco-rich niche, in keeping with the relevant clinical data [20, 56–59].
In culture, CSE induced the activity of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein highly orthologous to the TpcC family conjugal transfer proteins of the Gram-positive human pathogens, Clostridioides difficile, Aerococcus christensenii, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae. Another gene with high homology to the TrbL-family conjugal transfer proteins of Enterococcus faecium and C. difficile was also upregulated upon CSE exposure. A third DNA transfer-related gene upregulated in F. alocis upon CSE-exposure was HMPREF0389_00645, most orthologous to genes found in, again, C. difficile and A.christensenii as well as Bacillus sp. BS34A and a bacterium isolated from the female genital tract (Mageeibacillus indolicus). HMPREF0389_00662, which exhibits high homology to a Lachnospiraceae PrgI family protein as well as to a Tn1549-like conjugative transposon protein of C difficile was, again, CSE-regulated as was HMPREF0389_00666, which exhibits considerable homology to putative conjugal transfer proteins of Streptococcus intermedius and Streptococcus anginosis. Thus, tobacco exposure appears to enrich for the expression of DNA transfer-related genes which, should this phenomenon occur in vivo, may assist in the genetic enrichment of F. alocis. It should be stressed that tobacco-enriched F. alocis variants can subsequently be disseminated to the oral cavities of smokers and non-smokers alike.
The F. alocis gene encoding the PMSR-family methionine sulfoxide reductase (msrA / msrB) was induced by CSE. The closest orthologues are found in lesser studied oral and vaginal microbes, including a Lachnospiraceae taxon and Anaerococcus vaginalis. The role of this enzyme group in refunctionalizing oxidated proteins has clear relevance to surviving the considerable oxidative stress inherent to tobacco smoke. Additionally, CSE-induced an Rrf2 family transcriptional regulator whose closest orthologues are found in C. difficile and several aquatic bacteria (Alkaliphilus metalliredigens, Crassaminicella thermophila, Acetoanaerobium sticklandii). The potential gene targets of this regulator are unknown but, considering the lack of activation of other F. alocis genes involved in transcriptome modification, may be of particular interest. The closest orthologues of a F. alocis sensor histidine kinase, yesM, upregulated in CSE, are a Lachnospiraceae isolate, Kurthia sp. 11kri321 and an aquatic microbe, Vallitalea pronyensis. The YesM response regulator partner in Bacillus subtilis is the yesN gene product [61], though the role of this Lyt-family two-component system in environmental monitoring remains poorly understood. CSE induced the expression of two classical stress response genes, dnaJ (heat-shock protein 40, Hsp40) and, just outside of the top 10, groL (GroEL stress response protein) with established roles as environmental sensors [62]. Also just outside of the top 10, the gene encoding HlyD [HMPREF0389_01189], whose nearest relative proteins are annotated as multidrug resistance pumps of the aquatic Gram-positive bacteria, Desulfosporosinus meridiei and Natranaerobius thermophilus, was also significantly upregulated in CSE-exposed F. alocis [x 2.1]. By analogy, it is possible that upregulated HlyD expression is involved in the efflux of tobacco toxins or metabolites.
Annotated down-regulated genes are noted in Supplemental Table 2. Of particular interest is the gene encoding a ranthipeptide (six cys in forty-five residues, SCIFF). Recent evidence suggests that SCIFF peptides may play a role in quorum sensing, at least as ascertained in Clostridium spp, where they are prevalent [63].
Chronic smoking is generally considered to be associated with reduced weight in humans [64, 65] and mimicked in mice [66, 67]. It is noteworthy, then, that the combination of bacterial infection and smoke-exposure led to a significant reduction in murine mass (p < 0.05) over the 15-day experimental period. Indeed, this mean reduction in mass was >1.1 g more than in the non-infected, sham-exposed, control group.
In addition to F. alocis infection per se, the systemic humoral response to gingival infection with F. alocis was also monitored. Compared to uninfected mice, the F. alocis-cognizant IgM signal was elevated in infected mice, irrespective of tobacco exposure status. However, while the total F. alocis-cognizant IgG signal was also elevated in both groups of F. alocis-infected mice, this was only significant for the ambient air-exposed group. Smoking induced reductions in overall systemic IgG production have previously been reported in humans [68, 69]. Thus, alterations to the immunoglobulin response appears to be a further human characteristic reflected in the acute periodontitis model described herein and may, in part, explain increased F. alocis infectivity in this experimental setting.
Clearly, there are any number of F. alocis- and tobacco-related parameters that can be examined in this model system of acute periodontitis in future experiments, such as bacterial dissemination, multispecies infections, histology, and tobacco-related receptor knock out mice. The key outcome measure was bone loss associated with ligation of maxillary second molars. While there were no significant differences in alveolar bone loss at unligated second molar sites between groups (p > 0.05), at ligatured second molars, adjunctive F. alocis infection and smoking (p < 0.001) exhibited the greatest alveolar bone loss, the hallmark of destructive periodontal disease. This augurs well for the future exploitation of the model.
Chronic cigarette use is associated with profound systemic inflammatory dysregulation in humans [70, 71]. Unfortunately, in our acute system, intra-group comparisons of systemic inflammatory biomarker profiles were unremarkable, as monitored by multiplex ELISA. The one exception was IP-10 (CXCL10), a CXCR3-interacting chemokine that functions as a leukocyte attractant, that was significantly elevated in mice exposed to both smoke and F. alocis (p < 0.01). Another important aspect of tobacco-exacerbated periodontal destruction in humans, a dysregulated local inflammatory response [70, 71], was also not apparent in our acute model, at least as assessed at the mRNA level. Instead, ligation itself appears to be the predominant factor in driving immune and disease biomarker profiles in the periodontal tissues, such that any tobacco-related differentials that may exist are swamped. Therefore, a chronic animal model of periodontal disease, most obviously a tobacco-adapted version of the Baker model of periodontitis [72], may be more appropriate for exploring the influence of cigarette smoke on the immune response in mice.
In summary, F. alocis-infected, cigarette smoke-exposed mice may represent a reproducible model of acute tobacco-enhanced periodontitis that reflects multiple tobacco-related phenomena seen in humans (weight loss, increased pathobiont infection, alveolar bone loss, antibody flux), but not all (profound immune dysfunction).
Supplementary Material
CSE-regulated, differentially over- and under-expressed genes of F. alocis ATCC 35896 are presented. Hyperlinks are to the relevant individual genes in the KEGG data base for the appropriate F. alocis strain. The top 10 CSE-upregulated with annotations with clear relevance to tobacco are labeled in red text. Selected CSE-induced genes without obvious functional relevance to surviving a CSE insult and down-regulated genes are noted in green and blue text, respectively. The complete CSE-regulated transcriptome is presented in Supplemental Table 2.
RNAseq revealed that introduction to fresh medium (BHI or CSE) resulted in the up- and down-regulation of 72 and 143 F. alocis genes, respectively, that were common to both passage 2 conditions and, therefore, considered not particular to CSE. Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted p values (p < 0.05).
RNAseq revealed that 34 and 30 F. alocis genes specific to CSE conditioning, i.e., passage 2 genes differentially regulated in CSE but not BHI, were up- and down-regulated, respectively (Table S2). Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted p values (p < 0.05).
Clinical relevance.
Scientific Rationale for Study:
Tobacco-bacterial interactions, and their relevance to periodontal disease etiology, are poorly understood. Herein, we report on the influence of 1R6F research cigarette smoke on the growth and transcriptome of the emergent pathogen, Filifactor alocis, and on F. alocis infection of the murine oral cavity.
Principal Findings:
F. alocis appears resistant to tobacco toxins, the major transcriptional response to tobacco-induced stress appears to be activation of genes involved in genetic mobility, while mainstream cigarette exposure increases F. alocis pathogenicity, at least in in mice.
Practical Implications:
If such phenomena occur in humans, then F. alocis may play an important role in tobacco-induced or -exacerbated periodontitis.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of NIDCR and NIGMS ([DAS] DE028506, DE026963, GM125504) and ([SMU] DE024509).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Data Availability Statement:
The RNAseq data discussed in this publication have been deposited in NCBIs Gene Expression Omnibus [1] and are accessible through Geo Series accession number GSE211505 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=%20GSE211505).
References
- 1.Edgar R, Domrachev M, and Lash AE, Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res, 2002. 30(1): p. 207–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jusko M, et al. , FACIN, a Double-Edged Sword of the Emerging Periodontal Pathogen Filifactor alocis: A Metabolic Enzyme Moonlighting as a Complement Inhibitor. J Immunol, 2016. 197(8): p. 3245–3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Belstrom D, et al. , Metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analysis of saliva reveals disease-associated microbiota in patients with periodontitis and dental caries. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes, 2017. 3: p. 23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Perez-Chaparro PJ, et al. , Do different probing depths exhibit striking differences in microbial profiles? J Clin Periodontol, 2018. 45(1): p. 26–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Deng ZL, et al. , Dysbiosis in chronic periodontitis: Key microbial players and interactions with the human host. Sci Rep, 2017. 7(1): p. 3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goncalves C, et al. , Association of three putative periodontal pathogens with chronic periodontitis in Brazilian subjects. J Appl Oral Sci, 2016. 24(2): p. 181–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shaw L, et al. , Distinguishing the Signals of Gingivitis and Periodontitis in Supragingival Plaque: a Cross-Sectional Cohort Study in Malawi. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2016. 82(19): p. 6057–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Belstrom D, et al. , Microbial profile comparisons of saliva, pooled and site-specific subgingival samples in periodontitis patients. PLoS One, 2017. 12(8): p. e0182992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oliveira RR, et al. , Levels of Candidate Periodontal Pathogens in Subgingival Biofilm. J Dent Res, 2016. 95(6): p. 711–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Camelo-Castillo A, et al. , Relationship between periodontitis-associated subgingival microbiota and clinical inflammation by 16S pyrosequencing. J Clin Periodontol, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Al-hebshi NN, et al. , Quantitative analysis of classical and new putative periodontal pathogens in subgingival biofilm: a case-control study. J Periodontal Res, 2015. 50(3): p. 320–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Belstrom D, et al. , Differences in bacterial saliva profile between periodontitis patients and a control cohort. J Clin Periodontol, 2014. 41(2): p. 104–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Belstrom D, et al. , Influence of periodontal treatment on subgingival and salivary microbiotas. J Periodontol, 2018. 89(5): p. 531–539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Na HS, et al. , Identification of Potential Oral Microbial Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Periodontitis. J Clin Med, 2020. 9(5). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ko Y, et al. , Salivary microbiota in periodontal health and disease and their changes following nonsurgical periodontal treatment. J Periodontal Implant Sci, 2020. 50(3): p. 171–182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ikeda E, et al. , Japanese subgingival microbiota in health vs disease and their roles in predicted functions associated with periodontitis. Odontology, 2020. 108(2): p. 280–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schulz S, et al. , Comparison of the oral microbiome of patients with generalized aggressive periodontitis and periodontitis-free subjects. Arch Oral Biol, 2019. 99: p. 169–176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nemoto T, et al. , Discrimination of Bacterial Community Structures among Healthy, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis Statuses through Integrated Metatranscriptomic and Network Analyses. mSystems, 2021. 6(6): p. e0088621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lee JS, et al. , In Situ Intraepithelial Localizations of Opportunistic Pathogens, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Filifactor alocis, in Human Gingiva. Curr Res Microb Sci, 2020. 1: p. 7–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Moon JH, Lee JH, and Lee JY, Subgingival microbiome in smokers and non-smokers in Korean chronic periodontitis patients. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2015. 30(3): p. 227–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vieira Colombo AP, et al. , Periodontal-disease-associated biofilm: A reservoir for pathogens of medical importance. Microb Pathog, 2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kvarnvik C, et al. , Periodontal disease in a remote Asian population: association between clinical and microbiological parameters. J Investig Clin Dent, 2016. 7(3): p. 246–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen H, et al. , A Filifactor alocis-centered co-occurrence group associates with periodontitis across different oral habitats. Sci Rep, 2015. 5: p. 9053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fine DH, et al. , A consortium of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Streptococcus parasanguinis, and Filifactor alocis is present in sites prior to bone loss in a longitudinal study of localized aggressive periodontitis. J Clin Microbiol, 2013. 51(9): p. 2850–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Monteiro MF, et al. , Parents with periodontitis impact the subgingival colonization of their offspring. Sci Rep, 2021. 11(1): p. 1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Papapanou PN, et al. , Subgingival microbiome and clinical periodontal status in an elderly cohort: The WHICAP ancillary study of oral health. J Periodontol, 2020. 91 Suppl 1: p. S56–S67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Esberg A, et al. , 43-Year Temporal Trends in Immune Response to Oral Bacteria in a Swedish Population. Pathogens, 2020. 9(7). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bagaitkar J, Demuth DR, and Scott DA, Increased susceptibility to bacterial infections in tobacco smokers. Tobacco Induced Diseases, 2008. 4(12). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gonzalez YM, et al. , Serum cotinine levels, smoking, and periodontal attachment loss. J Dent Res, 1996. 75(2): p. 796–802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rheu GB, et al. , Risk assessment for clinical attachment loss of periodontal tissue in Korean adults. J Adv Prosthodont, 2011. 3(1): p. 25–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sanders A. and Slade G, State cigarette excise tax, secondhand smoke exposure, and periodontitis in US nonsmokers. Am J Public Health, 2013. 103(4): p. 740–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bergstrom J, Smoking rate and periodontal disease prevalence: 40-year trends in Sweden 1970–2010. J Clin Periodontol, 2014. 41(10): p. 952–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Haisman-Welsh RJ and Thomson WM, Changes in periodontitis prevalence over two decades in New Zealand: evidence from the 1988 and 2009 national surveys. N Z Dent J, 2012. 108(4): p. 134–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tomar SL and Asma S, Smoking-attributable periodontitis in the United States: findings from NHANES III. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Periodontol, 2000. 71(5): p. 743–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.MacFarlane GD, et al. , Refractory periodontitis associated with abnormal polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis and cigarette smoking. J Periodontol, 1992. 63(11): p. 908–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Soder B, Nedlich U, and Jin LJ, Longitudinal effect of non-surgical treatment and systemic metronidazole for 1 week in smokers and non-smokers with refractory periodontitis: a 5-year study. J Periodontol, 1999. 70(7): p. 761–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Machtei EE, et al. , Longitudinal study of prognostic factors in established periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol, 1997. 24(2): p. 102–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grossi SG, et al. , Effects of smoking and smoking cessation on healing after mechanical periodontal therapy. J Am Dent Assoc, 1997. 128(5): p. 599–607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sutton JD, et al. , Environmental tobacco smoke and periodontitis in U.S. non-smokers. J Dent Hyg, 2012. 86(3): p. 185–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Akinkugbe AA, et al. , Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Association Between Exposure to Environmental Tobacco Smoke and Periodontitis Endpoints Among Nonsmokers. Nicotine Tob Res, 2016. 18(11): p. 2047–2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sutton JD, Salas Martinez ML, and Gerkovich MM, Environmental Tobacco Smoke and Periodontitis in US Non-smokers, 2009 to 2012. J Periodontol, 2017: p. 1–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Danaci G, et al. , Environmental smoke exposure promotes periodontal tissue destruction. Tobacco Induced Diseases, 2019. 19 (59). [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shah SA, et al. , The making of a miscreant: tobacco smoke and the creation of pathogen-rich biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes, 2017. 3: p. 26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Miller DP and Scott DA, Inherently and Conditionally Essential Protein Catabolism Genes of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Trends Microbiol, 2021. 29(1): p. 54–64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hutcherson JA, et al. , Porphyromonas gingivalis genes conferring fitness in a tobacco-rich environment. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2020. 35(1): p. 10–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bagaitkar J, et al. , Tobacco smoke augments Porphyromonas gingivalis - Streptococcus gordonii biofilm formation. PLOS One, 2011. 6(11): p. e27386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bagaitkar J, et al. , Tobacco upregulates P. gingivalis fimbrial proteins which induce TLR2 hyposensitivity. PLoS One, 2010. 5(5): p. e9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bagaitkar J, et al. , Tobacco-induced alterations to Porphyromonas gingivalis-host interactions. Environmental Microbiology, 2009. 11(5): p. 1242–1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Potempa JG and Scott DA, Cigarette smoke-exposed neutrophils die unconventionally but are effectively phagocytosed. Cell Death and Disease, 2011. (in press; ). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Moon JH, Lee JH, and Lee JY, Subgingival microbiome in smokers and non-smokers in Korean chronic periodontitis patients. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kim AS, Lowenstein DH, and Pleasure SJ, Wnt receptors and Wnt inhibitors are expressed in gradients in the developing telencephalon. Mech Dev, 2001. 103(1–2): p. 167–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Aja E, et al. , Filifactor alocis: Recent Insights and Advances. J Dent Res, 2021. 100(8): p. 790–797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Miralda I. and Uriarte SM, Periodontal Pathogens’ strategies disarm neutrophils to promote dysregulated inflammation. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2021. 36(2): p. 103–120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Miralda I, Vashishta A, and Uriarte SM, Neutrophil Interaction with Emerging Oral Pathogens: A Novel View of the Disease Paradigm. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019. 1197: p. 165–178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Aruni AW, et al. , Filifactor alocis--a new emerging periodontal pathogen. Microbes Infect, 2015. 17(7): p. 517–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kumar PS, Smoking and the subgingival ecosystem: a pathogen-enriched community. Future Microbiol, 2012. 7(8): p. 917–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kumar PS, et al. , Tobacco smoking affects bacterial acquisition and colonization in oral biofilms. Infect Immun, 2011. 79(11): p. 4730–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gogeneni H, et al. , Increased infection with key periodontal pathogens during gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Periodontol, 2015. 42(6): p. 506–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Delima SL, et al. , Response of subgingival bacteria to smoking cessation. J Clin Microbiol, 2010. 48(7): p. 2344–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ward D, Earl A, Feldgarden M, Young SK, Gargeya S, Zeng Q,, et al. , Filifactor alocis ATCC 35896, complete genome. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Fabret C, Feher VA, and Hoch JA, Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world. J Bacteriol, 1999. 181(7): p. 1975–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Ghazaei C, Role and mechanism of the Hsp70 molecular chaperone machines in bacterial pathogens. J Med Microbiol, 2017. 66(3): p. 259–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chen Y, et al. , The SCIFF-Derived Ranthipeptides Participate in Quorum Sensing in Solventogenic Clostridia. Biotechnol J, 2020. 15(10): p. e2000136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Molarius A, et al. , Smoking and relative body weight: an international perspective from the WHO MONICA Project. J Epidemiol Community Health, 1997. 51(3): p. 252–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Winslow UC, Rode L, and Nordestgaard BG, High tobacco consumption lowers body weight: a Mendelian randomization study of the Copenhagen General Population Study. Int J Epidemiol, 2015. 44(2): p. 540–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cielen N, et al. , Interaction between Physical Activity and Smoking on Lung, Muscle, and Bone in Mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2016. 54(5): p. 674–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Tam A, et al. , Effects of sex and chronic cigarette smoke exposure on the mouse cecal microbiome. PLoS One, 2020. 15(4): p. e0230932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gonzalez-Quintela A, et al. , Serum levels of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM) in a general adult population and their relationship with alcohol consumption, smoking and common metabolic abnormalities. Clin Exp Immunol, 2008. 151(1): p. 42–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tarbiah N, et al. , Cigarette smoking differentially affects immunoglobulin class levels in serum and saliva: An investigation and review. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2019. 125(5): p. 474–483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Buduneli N. and Scott DA, Tobacco-induced suppression of the vascular response to dental plaque. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2018. 33(4): p. 271–282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Palmer RM, et al. , Mechanisms of action of environmental factors--tobacco smoking. J Clin Periodontol, 2005. 32 Suppl 6: p. 180–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Baker PJ, Evans RT, and Roopenian DC, Oral infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and induced alveolar bone loss in immunocompetent and severe combined immunodeficient mice. Arch. Oral Biol., 1994. 39: p. 1035–1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
CSE-regulated, differentially over- and under-expressed genes of F. alocis ATCC 35896 are presented. Hyperlinks are to the relevant individual genes in the KEGG data base for the appropriate F. alocis strain. The top 10 CSE-upregulated with annotations with clear relevance to tobacco are labeled in red text. Selected CSE-induced genes without obvious functional relevance to surviving a CSE insult and down-regulated genes are noted in green and blue text, respectively. The complete CSE-regulated transcriptome is presented in Supplemental Table 2.
RNAseq revealed that introduction to fresh medium (BHI or CSE) resulted in the up- and down-regulation of 72 and 143 F. alocis genes, respectively, that were common to both passage 2 conditions and, therefore, considered not particular to CSE. Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted p values (p < 0.05).
RNAseq revealed that 34 and 30 F. alocis genes specific to CSE conditioning, i.e., passage 2 genes differentially regulated in CSE but not BHI, were up- and down-regulated, respectively (Table S2). Differentially regulated genes were determined based on log2FoldChange values and adjusted p values (p < 0.05).
Data Availability Statement
The RNAseq data discussed in this publication have been deposited in NCBIs Gene Expression Omnibus [1] and are accessible through Geo Series accession number GSE211505 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=%20GSE211505).