Abstract
Recently, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are deployed in Novel Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) vaccine distribution process. To address issues of fake vaccine distribution, real-time massive UAV monitoring and control at nodal centers (NCs), the authors propose SanJeeVni, a blockchain (BC)-assisted UAV vaccine distribution at the backdrop of sixth-generation (6G) enhanced ultra-reliable low latency communication (6G-eRLLC) communication. The scheme considers user registration, vaccine request, and distribution through a public Solana BC setup, which assures a scalable transaction rate. Based on vaccine requests at production setups, UAV swarms are triggered with vaccine delivery to NCs. An intelligent edge offloading scheme is proposed to support UAV coordinates and routing path setups. The scheme is compared against fifth-generation (5G) uRLLC communication. In the simulation, we achieve and 86% improvement in service latency, 12.2% energy reduction of UAV with 76.25% more UAV coverage in 6G-eRLLC, and a significant improvement of
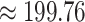 % in storage cost against the Ethereum network, which indicates the scheme efficacy in practical setups.
% in storage cost against the Ethereum network, which indicates the scheme efficacy in practical setups.
Keywords: 6G, blockchain, COVID-19, edge offloading, Solana chain, UAV swarms, ultra-reliable low latency communications, unmanned aerial vehicles
I. Introduction
World health organization (WHO) emergency response programs are constantly working across Asia, Pacific, and European regions to support essential health services, early Novel Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) detection, and advance pandemic preparedness [1]. COVID-19 has taken more than 1.5 million lives worldwide due to unavailability of required vaccine [2]. To gear up the vaccine distribution, WHO has started the initiative for efficacious deployments of COVID-19 vaccines global access (COVAX) in collaboration with epidemic preparedness innovations (CEPI) [3]. The clinical trial indicates
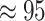 % efficiency of Pfizer/BioNTech to prevent COVID-19 infection [4]. Thus, massive vaccine development and its distribution are required globally. A recent report by Research & Markets estimates that COVID-19 and generic immunity builds to tackle future pandemics is expected to reach over 5.8 billion USD by 2025 [5]. Thus, large scale massive vaccine generation and distribution schemes are required to target high vaccination coverage across the globe.
% efficiency of Pfizer/BioNTech to prevent COVID-19 infection [4]. Thus, massive vaccine development and its distribution are required globally. A recent report by Research & Markets estimates that COVID-19 and generic immunity builds to tackle future pandemics is expected to reach over 5.8 billion USD by 2025 [5]. Thus, large scale massive vaccine generation and distribution schemes are required to target high vaccination coverage across the globe.
On the distribution side, the pharmaceutical supply chain plays a vital role in providing critical medical support in hospitals and aids emergency activities/operations, human missions, and other allied services. However, due to the worldwide lockdown, the supply chain was severely disrupted [6] which affected production, distribution, and safety standards. Vaccine supply chains require secure and smooth operations among multiple suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to deliver the vaccine to the end-user. The vaccine generation, maintenance, and production at vaccine manufacturing labs (VML) and production warehouses (PWs) requires effectiveness and stability, which is achieved through cold-chain process to maintain a standard temperature of
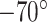 for dose administration. The vaccine containers, after packaging at PWs are shipped to nodal centers (NCs), that have the registered list of potential users eligible for vaccination. Due to high round trip times (RTTs) of logistics cargo shipments via land, water, and air, the container stability is heavily affected, and thus it jeopardizes the effectiveness of the cold-chain process. Moreover, different countries have their national and international boundary regulations on the movement of vaccine cargo, which hampers vaccine stability. The records of potential vaccination users are maintained through the national population register (NPR), and once the user is vaccinated, the record is maintained on either centralized or distributed servers [7].
for dose administration. The vaccine containers, after packaging at PWs are shipped to nodal centers (NCs), that have the registered list of potential users eligible for vaccination. Due to high round trip times (RTTs) of logistics cargo shipments via land, water, and air, the container stability is heavily affected, and thus it jeopardizes the effectiveness of the cold-chain process. Moreover, different countries have their national and international boundary regulations on the movement of vaccine cargo, which hampers vaccine stability. The records of potential vaccination users are maintained through the national population register (NPR), and once the user is vaccinated, the record is maintained on either centralized or distributed servers [7].
Owing to the challenges, critical steps are required to address the timeliness in vaccine deliveries and reduce supply costs with minimal human interventions. Thus, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are considered a viable choice due to their lower round trip time (RTT) than traditional shipments, optimal cargo capacity management, lower cost, and travel to adverse climatic and habitat zones [8]. UAVs also act as Ground Controllers (GCs) to provide seamless connectivity in remote rural locations. Modern UAVs are equipped with global positioning system (GPS) transceivers coupled with localization techniques and routing protocols making it easier to navigate easily through an unknown area for delivery services [9], [10]. Benefits of UAVs include minimizing carbon footprints,human efforts, and improved flexibility and speed. Thus, UAVs make an agile choice for efficient delivery compared to traditional truck-based delivery. Potential UAV applications in healthcare are based to emergency response, improving the lab testing, delivery, and surveillance operation. To support the operations, Table I presents the existing healthcare drones deployed in practical use-case setups. The UAV type differs in weight, cargo, and in-flight operations for the specific application. The article focuses on the delivery aspect of UAVs, potentially to vaccine delivery. UAV assures
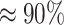 vaccine deliveries from VMLs to PWs before the cold-chain expiration [11].
vaccine deliveries from VMLs to PWs before the cold-chain expiration [11].
TABLE I. Comparison of Existing UAV Projects in Medical Delivery Scenarios.
| Drone | Year | Highlighted | Company | Application | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wing Drone | 2016 | Medical aid to people in emergency | Medical aid, medicine, baby food | 20 km in range with live update of estimated arrival time | |
| HQ-40 UAV | 2017 | Large distance transportation of blood with temperature monitoring in Arizona desert | Johns Hopkins University | Blood delivery | Resilient drone build to cover long distances |
| HiRo | 2018 | Specially designed to provide faster access to life-saving medical aid for critically injured people in dangerous and hostile environments | William Carey University | Integrated rescue operations | |
| Ehang AAV | 2020 | China-based company world-first autonomous UAV capable of transporting patients from one location to another | EHang Holdings | Transportation of donated organs to all over the places | Load-carrying capability excellent |
| Kite | 2021 | An advanced aircraft designed for a range of tasks, from delivering medical supplies and disaster responses | Swoop Aero | Delivery of medical supplies and supply chain management | Enhanced load carrying capacity, real-time tracking with digital twin technology. Speed of 200km/h across a range of more than 180 km flight |
| Wingcopter 198 | 2021 | German-based company to provide commercial, medical services with 110km/hr speed an up to 100km range | Wingcopter | Transportation of blood samples, medicines, diagnostic kits | Heavy payload delivery, all-weather capability, compact size |
In the UAV communication network (UAV-N), both human-to-machine (H2M), and machine-to-machine (M2M) links require fast response time, high-reliability, and very low end-to-end (EE) latency. Tactile internet (TI) provides haptic and sensory feedback, low RTT (< 10 ms), and high availability (99.99999%). 5G-TI vision is to provide ultra-reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) service and EE latency of < 1 ms, with 99.99999% availability.
However, delivery-UAVs communicate in UAV-N at high mobility. To maintain the flight path set-up and trajectory information, a swarm controller module is set-up at GCs to precisely monitor the UAV-N movements. 5G-eRLLC spectrum communication has a transmission time interval of
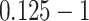 ms for control connection set-up, limiting the real-time EE latency for mission-critical applications. However, with the rise in massive and dense H2M and M2M connections, delivery-UAVs require effective resource orchestration from edge nodes at proximity range where the EE delay cannot exceed 1 ms, and packet loss probability should be less than 10-7, with 99.9999999 % availability in the radio access network (RAN) core.
ms for control connection set-up, limiting the real-time EE latency for mission-critical applications. However, with the rise in massive and dense H2M and M2M connections, delivery-UAVs require effective resource orchestration from edge nodes at proximity range where the EE delay cannot exceed 1 ms, and packet loss probability should be less than 10-7, with 99.9999999 % availability in the radio access network (RAN) core.
6G-eRLLC (enhanced uRLLC) service sets with guaranteed delay bounds of < 0.1 ms, and over-the-air latency of
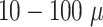 s, 1 Tbps user-experienced data rate, and would maximize Quality-of-Experience (QoE) to overcome the above bottleneck. With artificial intelligence (AI)-supported RAN core, 6G-eRLLC would support resource provisioning to UAV-N through edge nodes. 6G-RAN core collects network information as training samples and improves network reliability, EE delay bounds, trajectory set-up, path planning, collision avoidance, route optimization, and precise localization of UAVs in UAV-N utilizing deep neural network models.
s, 1 Tbps user-experienced data rate, and would maximize Quality-of-Experience (QoE) to overcome the above bottleneck. With artificial intelligence (AI)-supported RAN core, 6G-eRLLC would support resource provisioning to UAV-N through edge nodes. 6G-RAN core collects network information as training samples and improves network reliability, EE delay bounds, trajectory set-up, path planning, collision avoidance, route optimization, and precise localization of UAVs in UAV-N utilizing deep neural network models.
As mentioned above, 6G-eRLLC furnishes end-to-end delivery and distribution of vaccines from VMLs to the registered user (based on the priority list, vaccine type, age, and service occupation) through NPR. The distribution is a complex task owing to the challenges of illegal drug counterfeiting, limited raw material for drugs, drug caching, and huge price variation between the manufacturer and supplier, which finally increases the cost of supply-chain [12]. Employing traditional database management for storing records results in heterogeneity in record maintenance, asynchronous data, and duplicity. Blockchain (BC) based vaccine registrations thus provide trust, provenance, chronology, and transparency in the entire supply chain with no duplication [13].
The above discussions highlight the need for a holistic scheme to address practical challenges in vaccine distribution, network management, and the improvement of UAV communication parameters. Thus, we present the design goals of our scheme, SanJeeVni, that integrates 6G and BC in UAV delivery scenarios. Figure 1 presents the design goals of the scheme. Via BC, the scheme assures transparency in the vaccine supply chain from VMLs to NC. BC also mitigates security attacks on UAV swarms and allows trusted vaccine registration among users. We design an intelligent task offloading scheme from edge servers in close proximity at the networking front. The scheme uses 6G-eRLLC scheme to propose embedded task intelligence, which optimizes the swarm management. Also, 6G-eRLLC has low EE latency, which ensures vaccine stability and expiration conditions are met during the delivery process. to address massive registration and distribution on BC network, we preferred a Solana chain over Ethereum owing to the high transaction rate and included interplanetary file systems (IPFS) to store the user information. IPFS allows content information to be fetched through the IPFS key, and only meta-information is maintained on the main BC ledger. This minimizes the transaction size on the main BC. The vaccine payloads and supplier information is registered in the Solana network. The scheme also forms an intelligent traffic offloading (TO) to optimize the swarm route and traffic condition, which orchestrates the swarm management during flights. As part of the experimental discussion, the proposed results indicate the scheme’s effectiveness in terms of network rate, minimized task size, packet loss, and transaction throughput.
Fig. 1.
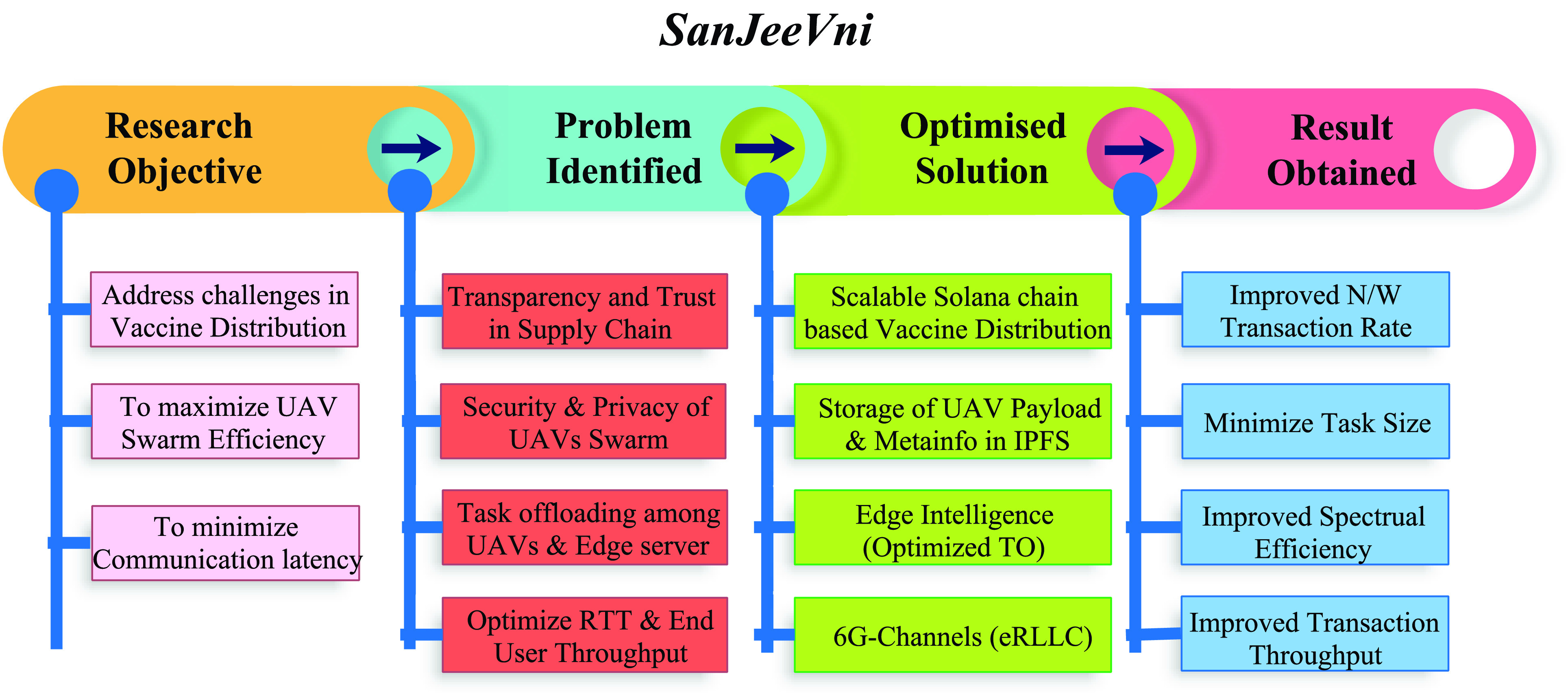
Design goals for SanJeeVni.
A. Research Contributions
Based on the design goals, we highlight the research contributions of the article as follows.
-
•
A UAV swarm setup is proposed at the backdrop of 6G-eRLLC setup, which addresses the stringent EE latency of vaccine deliveries from SAs to NCs. This addresses our objective of optimizing RTT cycles, which allows a single UAV to have multiple in-flight operations in a day.
-
•
To address the issues of task offloading, a 6G-eRLLC TO scheme is proposed. A swarm controller initiates high computing intensive tasks to nearby edge servers. To optimize the task processing, different training samples are collected from UAVs, and short term and long term predictors are generated that simplify the UAV traffic and network management.
-
•
To address issues of transparency and throughput of BC, we propose a permissioned Solana BC between VMLs, PWs, and NCs for vaccine tracking and registration. User vaccine registration is done on BC through unique identification numbers (UIN). A permissioned Solana Chain DApp infrastructure is preferred that assures on-chain clock verification, global consensus through effective Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus, and directly forward of unconfirmed transactions to validators instead of storage into mempool.
-
•
A case study of our proposed scheme with comparative analysis over 5G-uRLLC scheme is presented. The scheme performance is analyzed for metrics like BC transaction throughput, gas fees, energy consumption of UAV swarms, UAV covered range, spectral efficiency, and edge servicing latency. The obtained results indicate the scheme’s efficacy in real-world setups.
B. Article Layout
The structure of the article is as follows. Section II presents a discussion on existing state-of-the-art scheme in vaccine and medical distribution via UAVs. A comparative analysis is also outlined with the proposed scheme. Section III presents the background information of key technical drivers. Section IV presents the entity description and the data flow model in the proposed scheme. Section V presents the key entities and operating process of SanJeeVni scheme. Section VI highlights the open issues and challenges in the proposed integration. Section VII presents a case study of the proposed scheme. Section VIII presents a discussion on the obtained results, the significant impacts, challenges, and future aspects of the study. Finally, Section IX concludes the paper.
II. State-of-the-Art
A few recent studies focus on the deployment of UAVs in vaccine and healthcare deliveries. For example, Huang et al. [22] discussed UAV co-operative path-planning using ant colony and grey wolf optimizations. They considered the service capability of heterogeneous nodes at different demand points. The numerical results analyze the scalability for resource and area dimensions. However, the scheme complexity increased many folds. The authors present a simplified view in [23], where they proposed a self-sovereign identity framework that identifies and authorizes UAVs, with transactional ledger states in BC. The setup is considered on an edge-assisted delivery process. Gupta et al. [14] proposed a scheme VaHaK, which is based on an ethereum BC-based outdoor healthcare supply scheme that prioritizes healthcare supplies based on patient criticality. The scheme ensures smart contract (SC) execution through payment wallets over the backdrop of 5G-TI communication reliability. Zuhair et al. [16] proposed an improvement of the scheme over 6G communication channels. The scheme is named as BloCoV6, and it integrates 6G and BC in UAV communication for massive COVID-19 patient surveillance in dense regions. A contact-tracing ecosystem is designed on BC, where the collected patient thermal data are sent to GC through 6G channel. To address the scalability factor, authors in [24] studied BC-based COVID-19 vaccination that utilizes SCs to induce automation and handle impersonation attacks. The scheme proposed algorithms for beneficiary registration, vaccine tracking, handling rule-sets, and production condition over the entire vaccine supply-chain.
In vaccination delivery scenarios, to improve scalability and transaction rates, recent works have used permissioned setups. For example, Rathee et al. [25] proposed a permissioned BC-based vaccine distribution ecosystem, with a three-level distributed architecture for secure distribution of vaccines among different supply-chain points. Verma et al. [26] proposed VaCoChain, a scheme that integrates BC and 5G-TI based UAV services to support resilient vaccine distribution with reduced RTT delays from PW to NCs. However, the scheme fails to address compromised nodes in the supply chain. To address the issue, Cheema et al. [17] proposed a UAV based delivery system that utilizes BC for authentication of participating entities, medical centers, and UAV swarm nodes. The scheme is developed using ethereum based SC and a machine learning (ML) enabled intrusion detection system for robust communication performance. The authors in [18] propose an automated UAV based secured real-time traffic management scheme. The scheme utilizes BC, mobile edge computing (MEC), and deep learning (DL) algorithm for two-factor authentication and low latency communication in pair-wise UAVs. It achieves robust performance in terms of security, UAV training, end-to-end throughput, and energy consumption. The authors in [27] proposes a hybrid reinforcement learning based vaccine distribution scheme. The scheme develops an optimal trajectory for UAVs to deliver test kits to patients with a high probability of COVID-19 infection in a short time. Rani et al. [19] explored various UAV enabled societal applications and proposed a secured delivery system that utilizes a voice-based authentication system and provides various features such as image recognition, voice recognition, location-based tracking, and security. Table II presents a comparative analysis of the proposed scheme against the existing state-of-the-art.
TABLE II. Comparative Analysis of the Proposed Scheme With Existing State-of-the-Art.
| Author | Year | Objective | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gupta et al. [14] | 2020 | BC based medical supply scheme with priority queue to expedite delivery to critical patients | Y | N | Y | N | A criticality score assessment is proposed and smart contracts are embedded between healthcare stakeholders | Does not discuss the security issues in UAV communication |
| Das et al. [15] | 2021 | Proposes a BC, AI and IoMT enabled vaccine distribution scheme for COVID-19 disease in Internet-of-Medical-Things environment | N | N | Y | N | Utilizes BC for storing health assets of patients at cloud end through threat models and AI based analytic | Does not discusses computation offloading through edge based communication network |
| Zuhair et al. [16] | 2021 | Proposes a UAV-enabled, 6G-assisted contact tracing scheme for COVID-19 patient | Y | Y | Y | N | Explores usage of UAV for identifying potentially affected COVID-19 patients and storing their records on BC at the backdrop of 6G communication network | Does not explain the edge offloading phenomena for UAVs with high dynamics |
| Cheema et al. [17] | 2022 | Explores UAV based secured delivery of medical aids using BC | Y | N | Y | N | Proposes a BC based scheme for registering delivery agents and utilizes machine learning-based intrusion detection system for securing UAVs during in-flight operations | Does not explores communication network between UAVs and ground entities |
| Masuduzzaman et al. [18] | 2022 | Proposes an automated real-time surveillance scheme using UAV | Y | N | N | Y | Utilizes deep learning-based vehicle detection & two factor authentication for faster and secured verification | Does not discuss radio communication network between UAVs and server |
| Rani et al. [19] | 2022 | Discusses societal applications of UAV for secured and authentic delivery | Y | N | N | N | Discusses technologies like voice based authentication, GPS navigation tracking and visual detection | Does not discuss the end-to-end communication requirement with server and adversary attacks |
| Johannessen et al. [20] | 2022 | Discusses the assessment of time and cost saving for sample transport using UAVs | Y | N | N | N | Provides an analytical study on time savings of drone transport compared to ground, differing distance & route frequency, and elements to assess the UAV transportation cost | The proposed approach does not dictate assessments in heavy traffic and battery limitations of UAVs |
| Sham et al. [21] | 2022 | Examines the attitude of rural health care workers towards drone delivery | Y | N | N | N | Classifies the attitude of participants or healthcare workers based on different classes | Explores theoretical calculations based on limited factors. |
| Proposed | 2022 | Proposes a generic scheme to integrate UAV, 6G, and BC for secured vaccine distribution | Y | Y | Y | Y | Utilizes SC and 6G-enabled edge offloading technologies for handling high end UAV computations, provides very low latency compared to 5G counterpart | – |
1-UAV, 2-6G, 3-BC, 4-Edge Offloading, Y-shows parameter is considered, N-shows parameter is not considered.
The aforementioned schemes of UAV-based vaccine distributions do not address the issues of stringent EE delay constraints, edge-based UAV resource provisioning, and the integration of BC at the backdrop of 6G-service sets. Thus, the proposed scheme integrates the mentioned technologies and provides a secured vaccine distribution network with improved transaction throughput and improved spectral efficiency compared to 5G counterparts, which ensures smooth coordination among vaccine administrative entities.
III. Background of Key Technical Drivers
The Section discusses the key technical drivers of the proposed architecture.
A. 6G-eRLLC Enabled UAV
UAVs are primarily used for medical aid supplies to remote hospitals, such as first aid kits, pharmacies, blood transfusions, and sample collections in the healthcare sector. It is estimated that UAVs reduce the shipping costs by
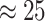 % in comparison to conventional logistics [28].
% in comparison to conventional logistics [28].
UAV-N experiences bottlenecks in battery consumption, energy management, routing paths, flying control, wing-torque, and control operations at GC with increased UAV density and high request load. 6G envisions 50 times higher peak achievable data rate (1 Tbps),
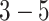 times higher spectrum efficiency,
times higher spectrum efficiency,
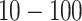 times higher UAV connection density (due to increased usage of heterogeneous networks (HetNets)), 10 times higher energy efficiency (due to effective AI radio management), with an area traffic capacity of 1 GB/s/
times higher UAV connection density (due to increased usage of heterogeneous networks (HetNets)), 10 times higher energy efficiency (due to effective AI radio management), with an area traffic capacity of 1 GB/s/
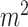 compared to 5G counterparts. 6G-eRLLC enabled communication supports high UAV mobility of 1000 km/h, which would induce shorter RTT delays during vaccination trips. Moreover, 6G-eRLLC UAV channels support open UAV-UAV (U2U) links, and UAV-to-ground (U2G) links to facilitate both H2M and M2M communication and provide high directivity slight path loss, less blockage, and scattering due to atmospheric absorption and channel fading.
compared to 5G counterparts. 6G-eRLLC enabled communication supports high UAV mobility of 1000 km/h, which would induce shorter RTT delays during vaccination trips. Moreover, 6G-eRLLC UAV channels support open UAV-UAV (U2U) links, and UAV-to-ground (U2G) links to facilitate both H2M and M2M communication and provide high directivity slight path loss, less blockage, and scattering due to atmospheric absorption and channel fading.
To support intelligent offloading, 6G-eRLLC enabled UAVs would communicate with multiple egde nodes through AI-based intelligent UAV sensing and transmission mechanisms. It provides dynamic orchestration of networking, caching, and computing resources. 6G enables iterative UAV sensing, swarm mobility model (Manhattan model), and transfer of vaccine payload data to destination NCs based on routing control algorithms.
B. UAV-N Swarm Network
A UAV swarm network is formed by scaling multi UAV networks through ubiquitous 6G connectivity U2U and U2G links. The advantages of a UAV swarm network include maximization of the operational altitude, communication, coverage, and computing capabilities, wider coverage range, high probability of line-of-sight (LOS) links, directed fly path, and many others. Leader-based selection algorithms are used to elect swarm controllers in the coverage range of UAVs to form cooperative relays. After controller setup at GC, it communicates with UAV-N through the H2M link. The Manhattan grid mobility model (MGM) randomizes UAV mobility patterns to prevent malicious attacks. In MGM, random patterns are mapped to random numbers, so malicious eavesdroppers do not intercept UAV-N mobility patterns [29].
Once it is done, the swarm controller module sets up aerial maps and flight control parameters, UAV-N stabilization parameters, initial flying measurements (start and end map coordinates), horizontal and angular speed, and wing angular momentum. 6G-eRLLC service enables UAV swarm setup and oral propagation message delivery in 0.125 ms & 0.02 ms, respectively. The swarm network manages oral updates to maintain paths, avoid collisions, and connect to heterogeneous radio links. The computational task can be scheduled to close mobile edge devices while caching the required contents at their end.
C. 6G-Enabled Edge UAV Offloading
In 6G-eRLLC networks, UAV swarms require task offloading based on edge intelligence (EI), owing to a huge amount of ingested data. EI predicts UAV coordinates, the number of UAV task offload requests, the time of the request, UAV path precision, and the flying time of the UAV swarm. Once the task offloading request is received, EI encompasses the time-series data through various models, which measure the channel temporal characteristics to form the task offload grant to UAVs. Based on communicated messages over 6G-eRLLC links, the EI node predicts the potential hotspots of overloaded UAV routes and assists UAVs to make topology selection nodes and optimize battery management and route map planning with swarm nodes. EI also allows ubiquitous UAV connectivity at large scales and monitors the environment perception based on real-time classification.
D. Solana Chain, Vaccine Registrations and Prioritization
Solana is the native fastest BC. It is designed as an alternative to Ethereum DApp platform. Table III highlights the advantages of preferring the Solana Chain in terms of node parameters over other similar chains. Solana uses Proof-of-History (PoH) in contrast to Ethereum’s Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which allows a verified sequence of computation between two events in time which is verified cryptographically through hashes to generate the consensus output.
TABLE III. Comparisons of Different BC Network.
| BC/Parameter | Solana | Ethereum | Smart chain | Polkadot | Cardano | Tron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction per second | 55,000 | 15 | 100 | 1000 | 270 | 1000 |
| Avg. transaction fee | 0.0015
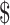
|
15
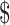
|
0.01
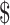
|
1
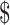
|
0.25
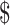
|
– |
| Transaction latency | 0.4 sec | 5 min | 75 sec | 2 min | 10 min | 3 sec |
| Number of validators | 702 |
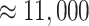 |
21 | 297 | 2376 | 27 |
| Consensus mechanism | Proof-of-Stack | Proof-of-Work | Proof-of-Authority | Nominated PoS | Proof-of-Stack | Delegated PoS |
| Overall transactions | 15 billion | 1.07 billion | 227 million | 1.7 million | 5.9 million | 1.7 billion |
Solana has a single-state chain with no shards; it offers decentralization, very low transaction cost (around 0.0001 US dollars), and a high transaction rate (65000 transactions/s (TPS)) which solves scalability issues of BC. Solana uses Turbine and Gulf Stream, a block propagation protocol and forwarding protocol, respectively, which do not refer to the mempool.
In comparison, Ethereum uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus that selects validators in proportion to the stake (or quantity) of cryptocurrency they hold. PoS suffers from a nothing-at-stake issue, where malicious validators present alternate copies of the chain and allow issues like double-spending on the forged chain. Ethereum 2.0 uses PoS consensus and sharding to create sidechains that link to the main Ethereum chain to increase the transaction speed. Ethereum 2.0 has a transaction rate of 100 transactions/s (TPS). Owing to the above advantages, we utilize a permissioned and public version of Solana Chain to handle fast transaction requests between VMLs, PWs, & NCs, ensure complete fairness and transparency in vaccine registration at NCs and maintain scalability. Moreover, U2U and U2G transactions meta-information is also stored in Solana. Before registration, we consider a priority queue
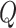 , which signifies the priority of vaccination assignment. Thus, once a user registers through public DApp via
, which signifies the priority of vaccination assignment. Thus, once a user registers through public DApp via
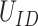 , the age, and the profession is fetched from government NPRs. Based on this, a priority score
, the age, and the profession is fetched from government NPRs. Based on this, a priority score
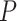 is assigned to every user, and
is assigned to every user, and
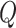 is initiated.
is initiated.
IV. SanJeeVni: Entities and the Data Flow Model
In this section, we outline the entities and the communication and data flow among them. Figure 2 presents the introduction to the entities in the scheme and the data flow among the entities.
Fig. 2.
SanJeeVni: The data flow among entities.
The complete scheme is divided into three working layers-namely the Vaccine infrastructure layer, UAV & communication layer, and Distribution layer. We consider an entity set
 , that represents the hospitals, vaccine research centers, state administration, VMLs, PWs, and NCs, respectively.
, that represents the hospitals, vaccine research centers, state administration, VMLs, PWs, and NCs, respectively.
 is responsible for developing vaccines with better efficacy and based on National Population Register (NPR) data. The data flow among the entities is formulated as follows.
is responsible for developing vaccines with better efficacy and based on National Population Register (NPR) data. The data flow among the entities is formulated as follows.
-
1)
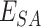 computes the number of vaccine doses
computes the number of vaccine doses
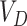 required to meet the supply demands for vaccine users in a region, which is calculated from the NPR
required to meet the supply demands for vaccine users in a region, which is calculated from the NPR -
2)
Based on the computed
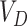 quantity, a request is placed to
quantity, a request is placed to
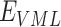 , which represents the amount of
, which represents the amount of
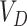 , that summarizes the need of each
, that summarizes the need of each
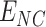 which comes under
which comes under
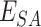
-
3)
Each entity is registered in consortium Solana BC, based on the vaccine request a SC between
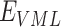 and
and
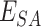 is executed to initiate the vaccine delivery
is executed to initiate the vaccine delivery -
4)
Based on
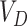 , vaccine supplies is transported to
, vaccine supplies is transported to
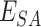 by
by
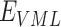 , based on the shared coordinates mentioned in the SC
, based on the shared coordinates mentioned in the SC -
5)
Once
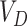 reaches to
reaches to
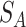 , depending on quantity and UAV payload, UAV swarms are initialized with vaccine payload and location coordinates to target
, depending on quantity and UAV payload, UAV swarms are initialized with vaccine payload and location coordinates to target
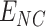
-
6)
Once the computed vaccine doses
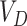 reaches to
reaches to
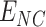 , a notification is sent to all beneficiaries
, a notification is sent to all beneficiaries
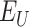 about the vaccination slot and time
about the vaccination slot and time -
7)
UID is verified at
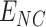 , and vaccine is administered to
, and vaccine is administered to
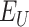
-
8)
Post the vaccine dosage, the
 UID along with dosage meta-information about the beneficiary is added in the IPFS, and the content reference from IPFS is stored in Solana BC ledgers
UID along with dosage meta-information about the beneficiary is added in the IPFS, and the content reference from IPFS is stored in Solana BC ledgers
V. SanJeeVni: The Proposed Scheme
As outlined in Section IV, Figure 3 presents the proposed three-layered scheme, SanJeeVni, that integrates BC and 6G-eRLLC to handle massive vaccine distributions for COVID-19, and future pandemics. The details are presented as follows.
Fig. 3.
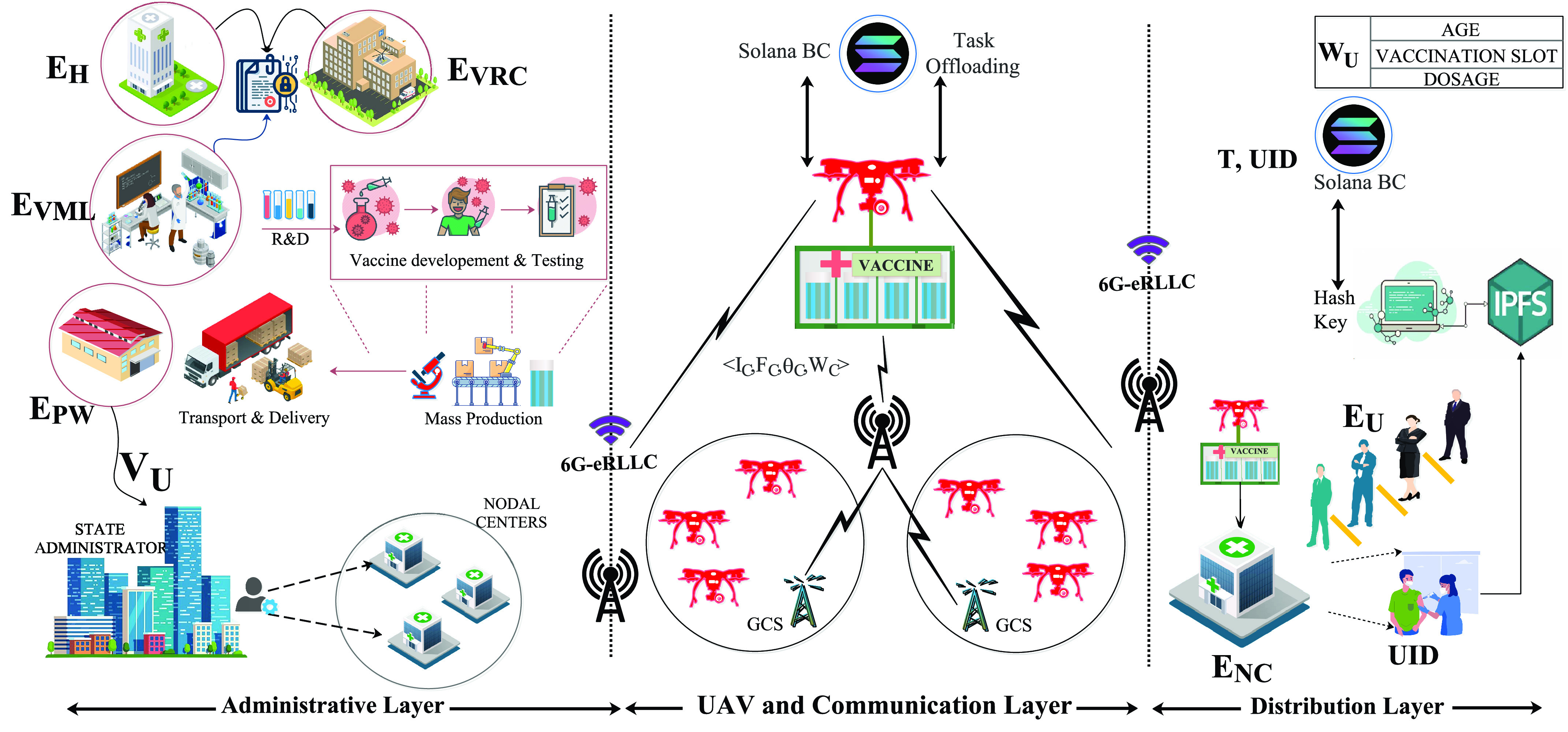
SanJeeVni: The proposed architecture to handle massive vaccine distributions.
A. Vaccine Infrastructure Layer
At this layer, we consider the vaccine infrastructure and basic entities that are involved in the manufacturing, design, and packaging of the vaccines based on cold-chain operating conditions. Initially,
 builds the list of possible demographics (locations), to decide on requirements of
builds the list of possible demographics (locations), to decide on requirements of
 at each location. Normally, based on fetched information from
at each location. Normally, based on fetched information from
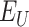 UIDs, which are denoted as
UIDs, which are denoted as
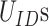 , we compute the number of NCs required to meet the vaccine coverage requirements.
, we compute the number of NCs required to meet the vaccine coverage requirements.
At every NC, we compute the received vaccine requests, which is denoted by a mapping
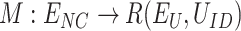 i.e. each
i.e. each
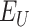 with their
with their
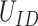 is eligible for immunization program. Based on requests, the vaccine dose requirements are calculated as
is eligible for immunization program. Based on requests, the vaccine dose requirements are calculated as
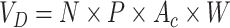 , where
, where
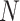 is the required number of vaccine doses to be administered to each
is the required number of vaccine doses to be administered to each
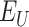 in multiple phases,
in multiple phases,
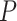 is the overall target population at NC to be vaccinated,
is the overall target population at NC to be vaccinated,
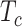 represents the formulated target coverage, and
represents the formulated target coverage, and
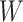 is the expired vaccines during the cold-chain process. As per WHO guidelines, 2 vaccine dosage is required to be administered to each
is the expired vaccines during the cold-chain process. As per WHO guidelines, 2 vaccine dosage is required to be administered to each
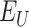 , with a preferred time gap of
, with a preferred time gap of
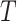 , depending on vaccine type. To demonstrate the formulation, we consider the sample space of 1000 users, with considered value of
, depending on vaccine type. To demonstrate the formulation, we consider the sample space of 1000 users, with considered value of
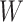 to 1.21, and we would like to coverage of 85% target population then
to 1.21, and we would like to coverage of 85% target population then
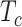 would be 0.85, and based on the formula the estimated
would be 0.85, and based on the formula the estimated
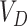 required is 2057.
required is 2057.
Based on
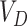 estimation, the request is forwarded by
estimation, the request is forwarded by
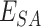 to
to
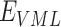 for required vaccines.
for required vaccines.
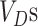 are sent in packed containers via road logistics. We consider permissioned SCs deployed at every point in the Solana supply chain to automate the system. Once
are sent in packed containers via road logistics. We consider permissioned SCs deployed at every point in the Solana supply chain to automate the system. Once
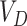 reaches
reaches
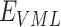 , it is forwarded with cold-chain packed containers, and forwarded via UAVs to
, it is forwarded with cold-chain packed containers, and forwarded via UAVs to
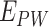 . At
. At
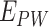 , we maintain the cold-chain conditions, and through
, we maintain the cold-chain conditions, and through
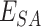 , we forward the vaccines to
, we forward the vaccines to
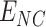 via UAV setups.
via UAV setups.
B. 6G-UAV Communication Layer
In our proposed approach, we deploy the UAVs to collect vaccine payloads from
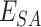 to
to
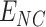 , with transactional entries recorded in permissioned Solana Chains. At each supply point, we estimate the required number of UAVs based on
, with transactional entries recorded in permissioned Solana Chains. At each supply point, we estimate the required number of UAVs based on
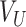 requests at
requests at
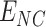 . The UAVs are selected based on UAV type
. The UAVs are selected based on UAV type
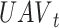 , payload size
, payload size
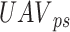 , and destination route
, and destination route
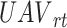 to
to
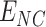 . In a particular coverage drone-cell range, denoted as
. In a particular coverage drone-cell range, denoted as
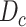 , we initiate the UAV swarm selection.
, we initiate the UAV swarm selection.
The UAV swarm selection algorithm initiates inside a coverage range
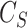 . We consider a service-controller mechanism at GCs, denoted as
. We consider a service-controller mechanism at GCs, denoted as
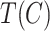 , that initiates the parameters for swarm controller
, that initiates the parameters for swarm controller
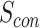 . For all
. For all
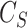 and
and
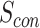 , the service-parameter setup is
, the service-parameter setup is
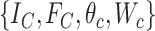 , where
, where
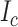 denotes the initial flying coordinates,
denotes the initial flying coordinates,
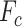 denotes the final destination coordinates,
denotes the final destination coordinates,
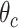 denotes the flying Euler angle of UAVs, and
denotes the flying Euler angle of UAVs, and
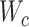 denotes the amount of computational work involved in the process. Any
denotes the amount of computational work involved in the process. Any
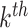 UAV-N,
UAV-N,
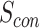 identify the swarm leader
identify the swarm leader
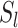 through leader selection algorithms [30].
through leader selection algorithms [30].
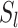 manages cooperative paths and route planning through optimization.
manages cooperative paths and route planning through optimization.
During the in-transit phase, the UAV flocks follow the MGM mobility model, where we position all UAVs in a
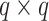 grid. We assume that the position of any
grid. We assume that the position of any
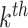 UAV be
UAV be
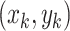 . The next move can be at any of the four-possible quadrants, namely,
. The next move can be at any of the four-possible quadrants, namely,
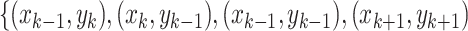 . The selection of the particular grid depends on the computed joint probability
. The selection of the particular grid depends on the computed joint probability
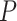 of all UAVs in
of all UAVs in
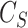 .
.
The UAVs are encapsulated with
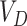 and packet header
and packet header
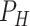 . 6G-eRLLC allows 10 times higher mobility than 5G-uRLLC U2U links. To support the computational requirements, the UAV swarms can initiate an intelligent task offloading process, as depicted in Figure 4.
. 6G-eRLLC allows 10 times higher mobility than 5G-uRLLC U2U links. To support the computational requirements, the UAV swarms can initiate an intelligent task offloading process, as depicted in Figure 4.
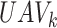 offloads high-compute intensive tasks to nearby edge-node
offloads high-compute intensive tasks to nearby edge-node
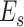 if required. The task, denoted as
if required. The task, denoted as
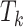 , is depicted as
, is depicted as
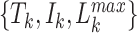 , where
, where
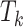 denotes the task size (in bytes),
denotes the task size (in bytes),
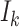 denotes the edge-CPU instruction cycles, and
denotes the edge-CPU instruction cycles, and
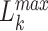 denotes the maximum permissible latency. To optimize the task processing, training samples
denotes the maximum permissible latency. To optimize the task processing, training samples
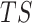 , collected from different UAV swarms and fed to a learning model
, collected from different UAV swarms and fed to a learning model
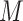 . The generated output by
. The generated output by
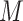 is
is
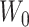 , which contains two sets of predictions, a short term predictor sequence
, which contains two sets of predictions, a short term predictor sequence
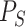 , and a long term predictor, denoted as
, and a long term predictor, denoted as
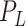 for
for
 .
.
Fig. 4.
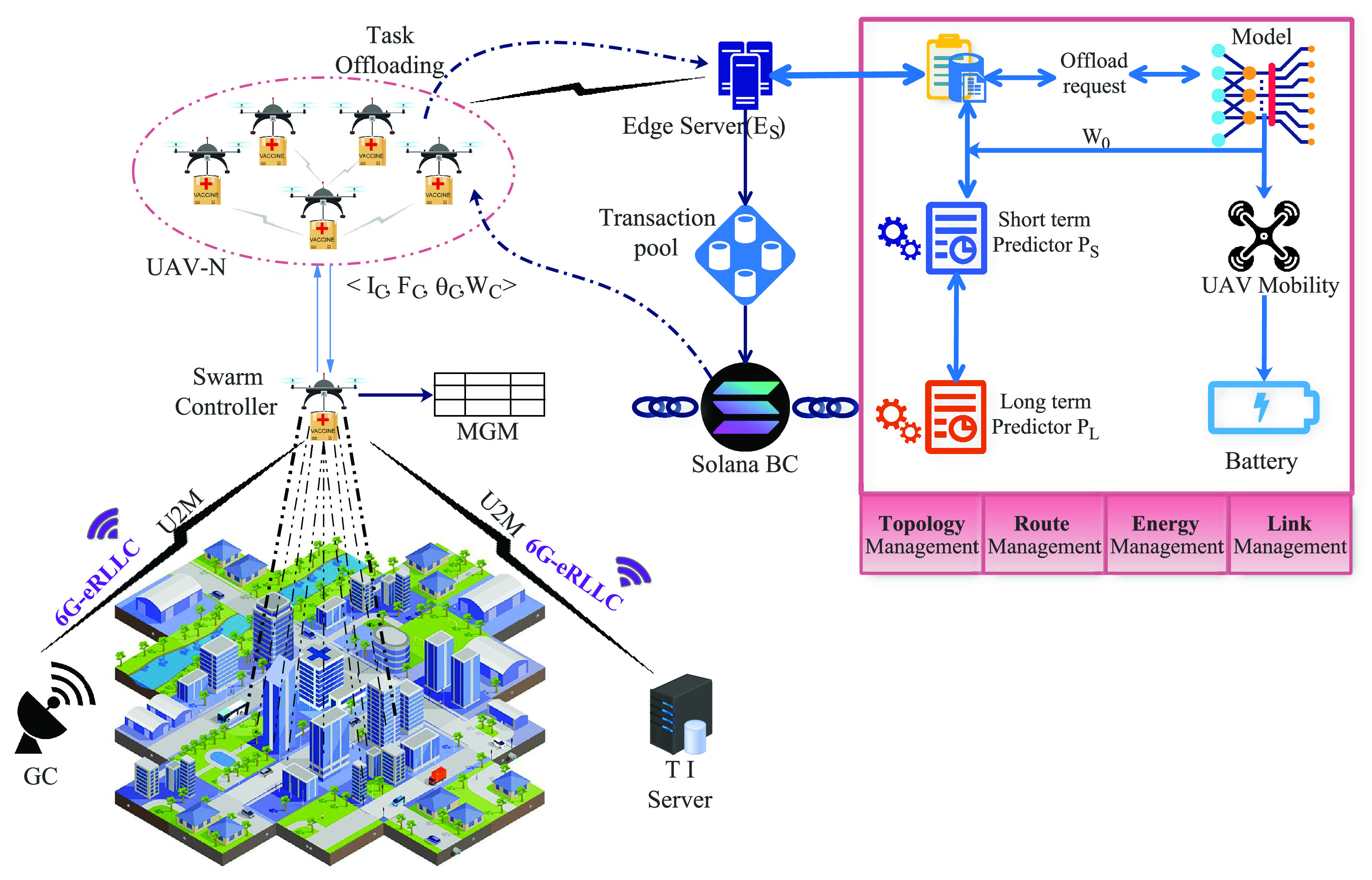
The intelligent tO process by
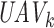 at edge servers
at edge servers
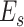 .
.
Based on
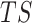 ,
,
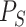 focuses on relationships among task offload requests
focuses on relationships among task offload requests
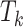 , and patterns of task context for any
, and patterns of task context for any
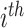 time slot, denoted as
time slot, denoted as
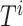 . For example, UAV distributions in
. For example, UAV distributions in
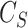 , vaccine load
, vaccine load
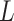 , channel state
, channel state
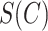 , and UAV event information to predict the number of task offload requests for the next slot,
, and UAV event information to predict the number of task offload requests for the next slot,
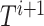 . This approach is termed optimal task offloading (TO), as it measures the micro-estimations of requests over a time window
. This approach is termed optimal task offloading (TO), as it measures the micro-estimations of requests over a time window
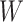 . In
. In
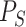 ,
,
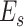 learns about task request patterns that are slow parameters, with less drift rate over a specific period. The model
learns about task request patterns that are slow parameters, with less drift rate over a specific period. The model
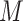 estimates the UAV locations through map regions and input data distribution to predict the max peak and off periods.
estimates the UAV locations through map regions and input data distribution to predict the max peak and off periods.
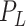 signifies the macro-estimation models. The model also communicates the prediction results to improve the topology, route, energy dissipation, and link-state management. The offload request-response is managed over 6G-eRLLC up-link and down-link channels. We assume that
signifies the macro-estimation models. The model also communicates the prediction results to improve the topology, route, energy dissipation, and link-state management. The offload request-response is managed over 6G-eRLLC up-link and down-link channels. We assume that
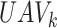 offloads
offloads
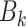 bits to
bits to
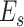 through up-link, and
through up-link, and
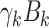 bits are sent as a response from
bits are sent as a response from
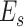 to
to
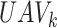 , with constraint
, with constraint
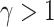 . The controller node is assumed stationary to assist in offloading.
. The controller node is assumed stationary to assist in offloading.
C. Vaccination Layer
In this layer, based on
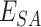 regulations, the vaccines
regulations, the vaccines
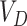 are delivered at
are delivered at
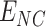 . Beneficiary
. Beneficiary
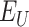 , registers to Solana BC. We consider a DApp that registers
, registers to Solana BC. We consider a DApp that registers
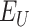 . The registration is processed through the NCs wallet identifier
. The registration is processed through the NCs wallet identifier
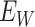 . The vaccine requirements
. The vaccine requirements
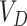 are recorded into a permissioned version of Solana Chain, at every supply point of the delivery, i.e. between
are recorded into a permissioned version of Solana Chain, at every supply point of the delivery, i.e. between
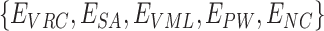 . This eliminates the fake and illegal vaccination generation and dissemination by intermediaries. Once
. This eliminates the fake and illegal vaccination generation and dissemination by intermediaries. Once
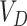 is registered in the chain, the vaccine availability and slot information are displayed to
is registered in the chain, the vaccine availability and slot information are displayed to
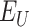 through the DApp via a push notification. At this point, we consider a priority-based scenario of vaccination, where a priority queue
through the DApp via a push notification. At this point, we consider a priority-based scenario of vaccination, where a priority queue
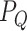 is formed by the assignment of the priority score of each user. The scores are recorded in the permissioned chain and depends on age, and occupation type i.e. senior citizens, healthcare workers, front line workers, and administrative task force.
is formed by the assignment of the priority score of each user. The scores are recorded in the permissioned chain and depends on age, and occupation type i.e. senior citizens, healthcare workers, front line workers, and administrative task force.
Once user
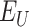 is vaccinated with the first dose, the meta-records are reflected in the permissioned Solana chain, to estimate the time interval of the next dosage. The transaction is represented as
is vaccinated with the first dose, the meta-records are reflected in the permissioned Solana chain, to estimate the time interval of the next dosage. The transaction is represented as
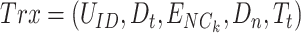 where
where
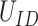 is the unique identity of the citizen,
is the unique identity of the citizen,
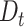 is the date,
is the date,
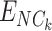 is the identity of the
is the identity of the
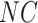 ,
,
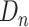 is the dose number and
is the dose number and
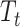 is the vaccination time-stamp. As Solana Chain has a high transaction rate, it can process the transaction meta-information easily, which handles the scalability issue of BC. Moreover, the information overhead can be further reduced by publishing the transaction to IPFS, which acts as a distributed storage handle. IPFS returns a hash key to access that record
is the vaccination time-stamp. As Solana Chain has a high transaction rate, it can process the transaction meta-information easily, which handles the scalability issue of BC. Moreover, the information overhead can be further reduced by publishing the transaction to IPFS, which acts as a distributed storage handle. IPFS returns a hash key to access that record
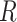 that is then recorded in the public chain.
that is then recorded in the public chain.
To summarize the process, algorithm 1 presents the schematics of vaccine request and delivery. Lines 2–10 formulate the
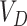 estimation. We check if vaccine stock is available to deliver, a SC will execute between
estimation. We check if vaccine stock is available to deliver, a SC will execute between
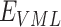 ,
,
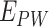 , and
, and
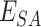 , and deduct the stock count by
, and deduct the stock count by
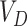 units. We initiate the delivery at
units. We initiate the delivery at
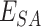 , and record the delivery status.
, and record the delivery status.
Algorithm 1:
VD Request and Delivery
Once
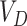 reaches
reaches
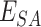 , we initiate the UAV swarm initial parameters to deliver vaccines to
, we initiate the UAV swarm initial parameters to deliver vaccines to
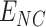 . Any
. Any
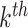 UAV is loaded with data {
UAV is loaded with data {
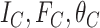 ,
,
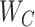 }, and the status of the
}, and the status of the
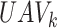 changes to IN_TRANSIT, the same is represented with Line 11-14. Lines 15–17 depict the condition, If the UAV reaches the final coordinates
changes to IN_TRANSIT, the same is represented with Line 11-14. Lines 15–17 depict the condition, If the UAV reaches the final coordinates
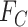 , then the status of the
, then the status of the
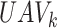 is changed to DELIVERED, and the notification is sent to each
is changed to DELIVERED, and the notification is sent to each
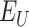 . Line 18–23 depicts, For every
. Line 18–23 depicts, For every
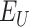 that belongs to
that belongs to
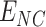 , the notification is verified before administrating vaccine dose
, the notification is verified before administrating vaccine dose
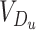 . Once the vaccine is administered to beneficiary
. Once the vaccine is administered to beneficiary
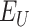 , details of the same is stored in the IPFS server, and a hashed content reference key
, details of the same is stored in the IPFS server, and a hashed content reference key
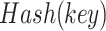 is returned that is added to the transaction list
is returned that is added to the transaction list
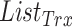 . Finally,
. Finally,
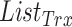 will be appended in the block of transactions along with timestamp
will be appended in the block of transactions along with timestamp
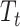 and merkle root
and merkle root
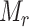 . Due to the inclusion of 6G-eRLLC and Solana BC, a large number of
. Due to the inclusion of 6G-eRLLC and Solana BC, a large number of
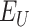 are registered in the network, and the swarm network is supported by
are registered in the network, and the swarm network is supported by
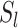 , which communicates with intelligent
, which communicates with intelligent
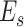 . This leverages a massive distribution framework support that maximizes the vaccine coverage at
. This leverages a massive distribution framework support that maximizes the vaccine coverage at
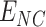 .
.
VI. Open Issues and Challenges
In this section, we discuss the potential issues and challenges in the deployment of the proposed scheme. The details are presented as follows.
A. Congestion and Scalability Issues in Large-Scale Networks
In 6G networks, owing to the intelligent protocol stack, optimization algorithms perform well for small-scale networks. However, in the proposed scenario of mass vaccine distributions, we require a large number of networked UAV swarms to effectively orchestrate the logistics. With more UAVs, the networks tend to become dense, and thus they force the developers to add more optimization variables and constraints to the scenario to maintain similar efficiency. Thus, the complexity and scalability increase many folds and become a challenging issue. A possible solution is to explore simpler optimization algorithms that can operate with fewer variables and fewer iterations to improve the overall complexity.
B. Variations in Successive Control Packet Arrivals at UAVs
UAVs have to maintain stringent latency requirements over large distances. Thus, stability and control operations supplied by GC and TI controllers are crucial for maintaining UAV swarm stability. However, this requires high arrival rates, and in some cases, the time to process the control information of the packet at the network layer is more than successive packet arrivals. Due to this, the instruction control by the TI controller would be different for different routers, which is a race condition in networks, and it results in unpredicted behaviour of UAV swarms. The behavior also gives rise to induced jitter, which increases the overall propagation delay over large distances and might create bottlenecks in the network. Thus, software-defined UAV flow mechanisms is a preferred approach, where packets would follow a defined control designated by the flow switch and not the underlying network.
C. Pre-Offloading Scenarios
The proposed vaccination scheme considers the backdrop of 6G communication networks, where UAV mobility is crucial. As UAV mobility is relatively high, the resource offloading to a stationary edge is affected. Thus, a challenging aspect is to send a request for pre-offloading to those edge nodes that fall in the selective paths of MGM. This would increase the computing capability when the UAVs move to the grid coordinates where the edge node is present, as handshaking between UAV-Edge is completed prior. However, distributing the MGM grids to map edge nodes prior to the UAV movements is an open issue and requires investigation. A possible direction is to map all proximity edge nodes as MGM and map the two MGMs to decide the edge coordinates.
D. Task Offloading Split for UAV Swarms
Owing to the high mobility of UAV swarms, a cooperative task model among all UAV sets is generally preferred, which is communicated to the edge node by the swarm leader. However, the challenge is to split the results of the coherent tasks obtained from the edge into smaller-sized subtasks, which can be communicated back to the individual UAVs. To determine the split, we need to administer the UAV location at all times, which is challenging owing to high mobility. Moreover, this induces an additional overhead on the swarm leader to locate and coordinate the results back to all UAVs, which consumes a lot of power.
E. UAV Swarm Coordination
In UAV swarms, the UAVs are directed to complete the vaccine delivery task to the scheduled NCs. However, in cases of poor network communication, the aerial 3D road layouts become unclear, owing to the collective fading in the wireless channels, which increases the signal dropouts. In such scenarios, the UAV swarm coordination is affected as UAV radio communication among U2U links is affected. Thus, selective mechanisms to handle the link dropouts to monitor the UAV swarm control is a challenge. Given this, accurate channel modeling and signal distribution model are required to handle the channel issues in order to maintain consistent bandwidth for swarm communication.
F. Solana Consensus: The BC Trilemma
Solana project is designed to handle the BC trilemma, i.e. trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization. However, to manage the high TPS rate, Solana compromises with its consensus approach and the validator requirements. Owing to the high TPS rate, validators in Solana are powerful machines and thus require a high cost to build and maintain such machine sets. Thus, in Solana Chains, selective nodes are elected as validators, which tend to centralize networks. In case validators are not powerful, the Solana network experiences instability, and thus fair and optimized PoH consensus should be designed to manage the trade-off of scalability, and decentralization, at desired security levels.
VII. Performance Evaluation: A Case Study
In this section, we consider the vaccine distribution ecosystem at the backdrop of 5G-assisted UAV communications. Currently, vaccine registrations are managed as distributed database systems, that manages
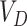 requirements from
requirements from
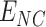 . We have considered 5G-uRLLC U2U and U2M links, with peak rates of 20 Gbps, and RTT latency of < 10 ms. The details of the simulation parameters are presented in Table IV. We considered the Solana v1.7.12, with prebuilt binaries in Linux.
. We have considered 5G-uRLLC U2U and U2M links, with peak rates of 20 Gbps, and RTT latency of < 10 ms. The details of the simulation parameters are presented in Table IV. We considered the Solana v1.7.12, with prebuilt binaries in Linux.
TABLE IV. Simulation Parameters.
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Communication Standard | 6G-eRLLC and 5G-uRLLC |
| Link setups | U2U and U2M |
| Channel Multiplexing | 5G-OFDM |
| No. of GC | 2 |
| UAV Coverage area |
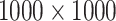 m m |
| UAV Swarms | 4 |
| UAV Placement | Random |
| GC range | 1 km of UAV swarms |
| Transmission Power | 32 mW, 197 mW |
| TS | [200 kB, 1 MB] |
| CPU-cycles |
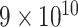 instructions instructions |
| UAV Payload | 10 kg |
| Validators | 10 |
| Network Switch | 10 GbE |
| Mining setup | NVDIA RTX 1650 graphics |
| RAM | 8 GB |
| Processor | Intel® Core
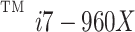
|
| Operating frequency | 3.2 GHz |
| UAV flying altitude | 120 kms |
| UAV air drag resistance | 20 m/s |
For traditional UAV vaccine delivery ecosystems, we have considered the architecture proposed by Verma et al. [26]. The paper proposes an Ethereum-based vaccine registration ecosystem, at the backdrop of 5G-TI communication, with uRLLC channel RTT latency of < 1 ms. The authors considered 5G-uRLLC multiplexed channels via OFDM that operates at 20 Gbps. Figure 5 presents the details.
Fig. 5.
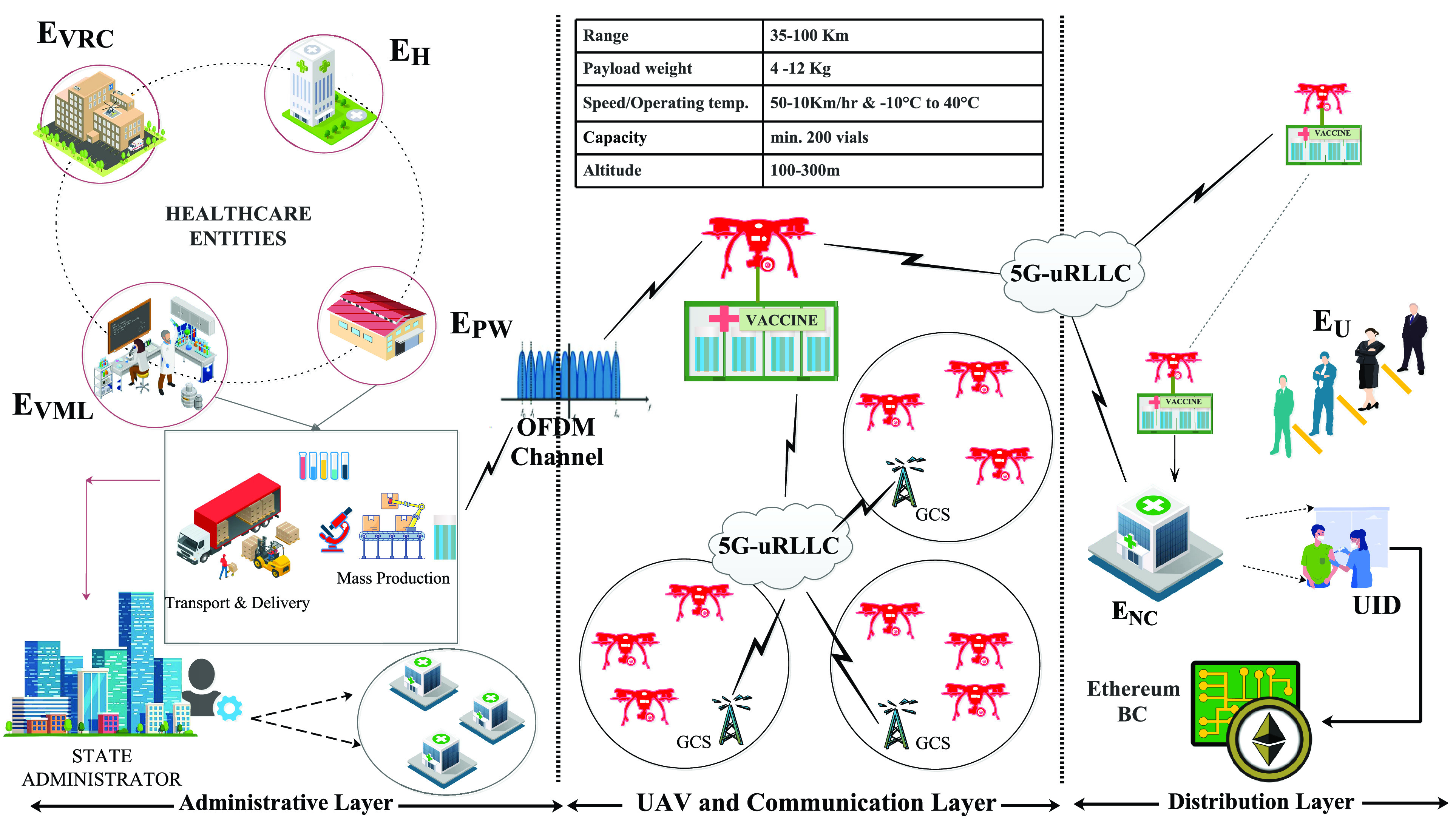
Case Study: Permissioned 5G-UAV assisted traditional vaccine delivery [26].
A. Effectiveness of SanJeeVni in the Case-Study
In this section, we discuss the advantages of the deployment of our proposed scheme in the traditional setup. We discuss the effectiveness in terms of three key parameters, namely, the scalability of vaccine registrations, benefits of 6G-eRLLC assisted UAVs, and impact of EI to support optimal TO. The details are presented as follows.
1). Impact of BC in Maintaining Vaccine Record:
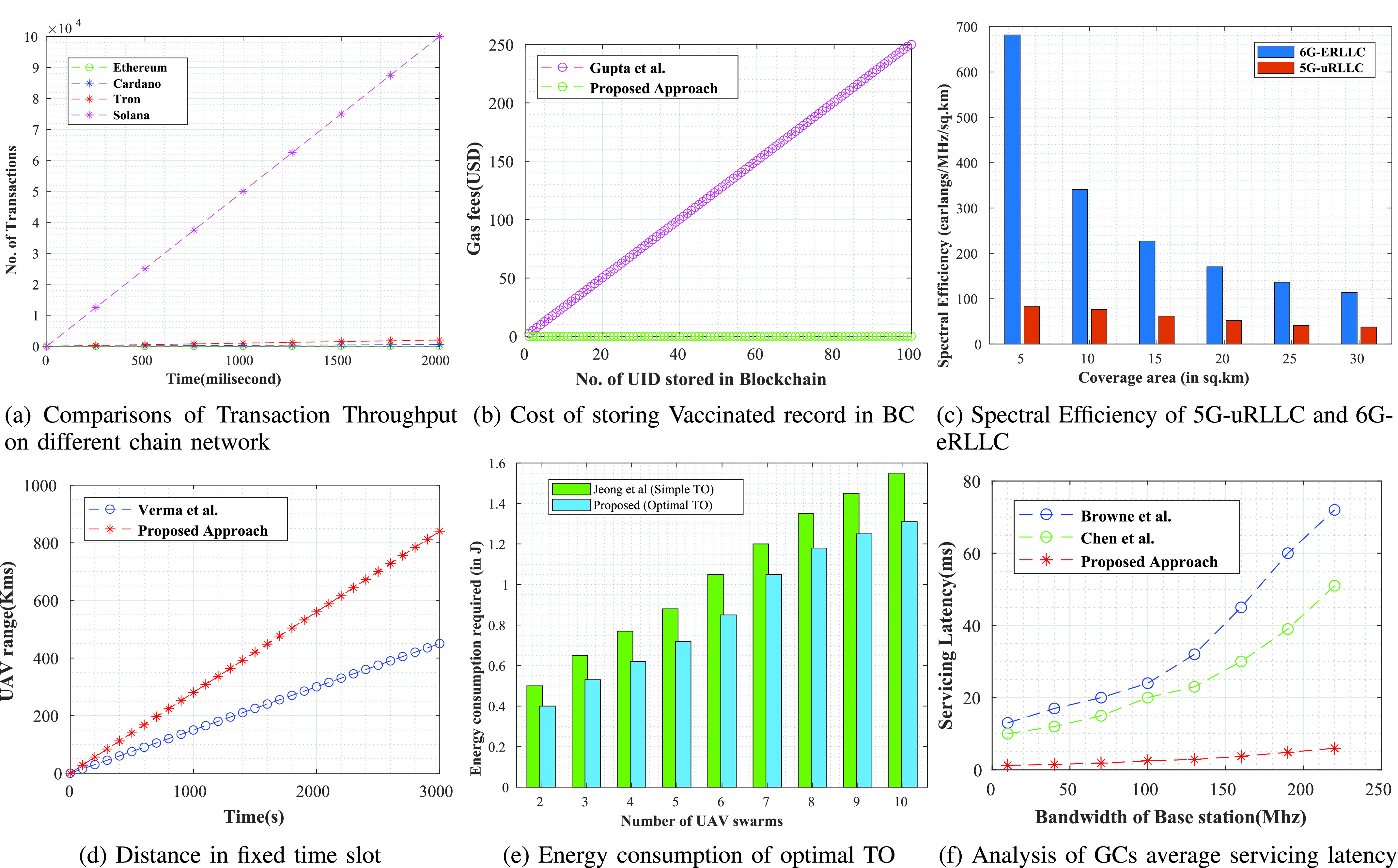
In the proposed ecosystem, we have considered Solana Chain for
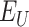 vaccine registration and dose administration. Figure 6a presents the details of transaction throughput in comparison to other legacy networks. As indicated, for 55,000 transactions, Solana Chain takes
vaccine registration and dose administration. Figure 6a presents the details of transaction throughput in comparison to other legacy networks. As indicated, for 55,000 transactions, Solana Chain takes
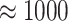 ms, or 1 s, compared to 15 transactions in ethereum, 100 in Smart Chain, 1000 in Polkadot, and 270 in Cardano. Moreover, the average transaction fee of Solana is 0.0015 USD, with a low transactional latency of 0.4 secs.
ms, or 1 s, compared to 15 transactions in ethereum, 100 in Smart Chain, 1000 in Polkadot, and 270 in Cardano. Moreover, the average transaction fee of Solana is 0.0015 USD, with a low transactional latency of 0.4 secs.
Fig. 6.
Case study: Deployment of SanJeeVni scheme in vaccine distributions against future pandemics.
Once the
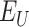 vaccinated with its dose, the
vaccinated with its dose, the
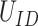 and meta information such as will be forwarded to IPFS server such as
and meta information such as will be forwarded to IPFS server such as
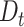 ,
,
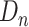 ,
,
 and
and
 . The server will generate one fixed length unique content reference, that will be added as a part of the transaction in the BC. To store one transaction in Ethereum network in odd hrs is
. The server will generate one fixed length unique content reference, that will be added as a part of the transaction in the BC. To store one transaction in Ethereum network in odd hrs is
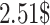 on Etherscan, whereas Solana network in peak hrs is
on Etherscan, whereas Solana network in peak hrs is
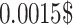 . Figure 6b represents the cost of storing
. Figure 6b represents the cost of storing
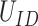 in after vaccination in Solana chain and the cost of storing the medical aid details on Ethereum chain [14]. There is a significant improvement of
in after vaccination in Solana chain and the cost of storing the medical aid details on Ethereum chain [14]. There is a significant improvement of
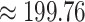 % in storage cost 0.15
% in storage cost 0.15
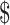 and 250
and 250
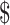 for storing the 100 vaccinated
for storing the 100 vaccinated
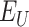 .
.
2). Potential of 6G-eRLLC UAV Management:
Next, we present the analysis of spectral efficiency of 6G-eRLLC channels over 5G counterpart. Figure 6c presents the details. 6G-eRLLC envisions a low RTT latency of < 0.1 ms. If we fix the UAV delivery in the 15 sq. km range, the servicing latency of 5G-uRLLC channels is
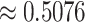 ms. However, the value is
ms. However, the value is
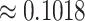 ms in the case of 6G-eRLLC U2U swarm setups. 6G channels have higher spectral efficiency than 5G channels, where the spectral coefficient
ms in the case of 6G-eRLLC U2U swarm setups. 6G channels have higher spectral efficiency than 5G channels, where the spectral coefficient
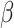 is defined as
is defined as
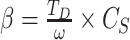 , where
, where
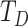 represents the total data traffic by UAV swarms, and
represents the total data traffic by UAV swarms, and
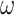 denotes the U2U channel bandwidth. As depicted, at
denotes the U2U channel bandwidth. As depicted, at
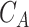 = 20 sq.km, the value of
= 20 sq.km, the value of
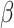 for 6G-U2U link is 52.112 earlangs/MHz, compared to 170.4 Earlangs/MHz in 5G-uRLLC. Thus, 6G servicing antennas have a higher lifetime and can communicate over distanced UAV-N to support real-time operations and control.
for 6G-U2U link is 52.112 earlangs/MHz, compared to 170.4 Earlangs/MHz in 5G-uRLLC. Thus, 6G servicing antennas have a higher lifetime and can communicate over distanced UAV-N to support real-time operations and control.
The main problem with 5G-eRLLC is less spectral efficiency as compared to 6G-eRLLC, and that divides the overall coverage of
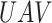 in a fixed amount of time. Figure 6d presents the covered distance by UAV in given time slots. In 1000 seconds, Verma et al.
[26] covers
in a fixed amount of time. Figure 6d presents the covered distance by UAV in given time slots. In 1000 seconds, Verma et al.
[26] covers
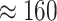 Km whereas the proposed scheme covers
Km whereas the proposed scheme covers
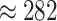 Km, that shows an improvement of
Km, that shows an improvement of
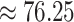 % in UAV coverage. This shows that 6G-eRLLC enabled UAVs are capable of more vaccine round trips from
% in UAV coverage. This shows that 6G-eRLLC enabled UAVs are capable of more vaccine round trips from
 to
to
 , which shortens the time duration of vaccination dosage to eligible
, which shortens the time duration of vaccination dosage to eligible
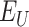 .
.
3). Impact of 6G-eRLLC Enabled Edge Intelligence:
We consider that any
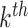 UAV offload its task
UAV offload its task
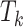 to edge node
to edge node
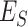 in
in
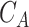 . In simple TO, as presented by Jeong et al.
[31], the authors assumed that tasks are collected in UAV-N, and are sent to closest
. In simple TO, as presented by Jeong et al.
[31], the authors assumed that tasks are collected in UAV-N, and are sent to closest
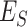 from leader
from leader
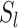 . The drawback of a simple TO scheme is that the processor capability is not considered, whereas in the proposed scheme, we consider intelligent TO supported by EI in 6G networks. Figure 6e presents the results. Each
. The drawback of a simple TO scheme is that the processor capability is not considered, whereas in the proposed scheme, we consider intelligent TO supported by EI in 6G networks. Figure 6e presents the results. Each
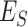 runs two local predictor models,
runs two local predictor models,
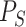 , and
, and
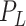 , that depend on the relationship among
, that depend on the relationship among
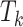 , and other patterns of similar tasks in that
, and other patterns of similar tasks in that
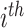 slot unit. For 5 UAV swarm networks, the proposed energy consumption of simple TO, as presented in Guo et al. is
slot unit. For 5 UAV swarm networks, the proposed energy consumption of simple TO, as presented in Guo et al. is
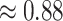 Joules (J), compared to 0.72 in the proposed scheme. Overall, we observe a significant improvement in the energy reduction of UAVs and
Joules (J), compared to 0.72 in the proposed scheme. Overall, we observe a significant improvement in the energy reduction of UAVs and
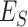 , with an average drop of 12.2 % over the U2M uplink and downlink channels.
, with an average drop of 12.2 % over the U2M uplink and downlink channels.
Figure 6f represents the analysis of impact of bandwidth on GC against the latency in-service performance of Browne et al. [32], and Chen et al. [33]. We assume that the request generated from each UAV per time slot is in the form of Poisson Distribution, and the computing capability of the edge server is clocked at 12.70 Mhz. In the figure, we observe that less time is required to offload data, which improves the servicing latency. The service latency in Browne et al. [32] decreases from 72 ms to 11 ms when we increase frequency from 10 to 220 MHz, while in Chen et al. [33], the servicing latency drops to 9 ms from 51 ms at the same conditions. In the proposed approach, the servicing latency only drops from 5.98 to 1.25 ms when we increase the bandwidth from 10 to 220 Mhz. An improvement of 88% is observed against Browne et al. [32], and 86% improvement against Chen et al. [33] respectively.
VIII. Discussion and Future Aspects
As discussed in Section VII, and the obtained results, some key technical improvements are discussed in the section. As the scheme uses a scalable and permissioned Solana BC for vaccine registration and distribution, the cost of transaction storage of vaccinated records improves drastically. Moreover, 6G-eRLLC based UAV setups greatly orchestrate the covered distance, spectral efficiency, and servicing latency, that justifies its effectiveness in real setups.
However, in practical healthcare scenarios, the deployment of SanJeeVni is challenged by a large number of users worldwide. First, a shift is required from a permissioned approach to a public BC, to make vaccination records fully transparent to end-users. In current public BC setups, Ethereum networks are mostly used. Owing to a large number of transaction networks, it is not a feasible option. Solana BC has a high TPS rate, which is suitable for public networks. Secondly, vaccine distribution is facilitated by 6G channels to minimize the communication latency. However, 6G practical deployments are still in their infancy. Although a large volume of literature is proposed on 6G, but there are critical challenges in the commercial adoption of 6G, due to lack of uniform standards.
6G envisions a low latency of
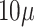 s at the PHY layer, but as the majority of the core communication follows legacy networks, the compatibility and flow control between devices is a challenge. Also, effective AI provisioning to envision a real-time EI is a complex task, owing to the heterogeneity in link formations. Thus, the effective realization of THz bandwidth is far-fetched in reality [34]. More stability in semiconductor design and open standards at PHY and MAC layers might envision the 6G service design to operate at desired frequencies in the near future. Finally, UAV flight operations are restricted into non-flying zones or personnel airspace, which restricts the scheme’s utility in case of long flights. Moreover, UAV acceptance over human presence is still not acceptable by healthcare stakeholders. Thus, the openness toward UAVs in the general public is still in the early phases.
s at the PHY layer, but as the majority of the core communication follows legacy networks, the compatibility and flow control between devices is a challenge. Also, effective AI provisioning to envision a real-time EI is a complex task, owing to the heterogeneity in link formations. Thus, the effective realization of THz bandwidth is far-fetched in reality [34]. More stability in semiconductor design and open standards at PHY and MAC layers might envision the 6G service design to operate at desired frequencies in the near future. Finally, UAV flight operations are restricted into non-flying zones or personnel airspace, which restricts the scheme’s utility in case of long flights. Moreover, UAV acceptance over human presence is still not acceptable by healthcare stakeholders. Thus, the openness toward UAVs in the general public is still in the early phases.
IX. Conclusion
COVID-19 vaccine distribution and registration requires a timely, supportive framework to manage transparency in massive supply chains. Thus, the article proposed a scheme, SanJeeVni, that fuses BC and 6G in vaccine setups to assure trusted logistics while meeting the requirements of stringent EE delay. The scheme proposes a UAV swarm network where path setup and swarm mobility is managed via intelligent edge. With 6G-eRLLC, UAV trip times are bounded, which assures timely vaccine coverage to users. For scalability, we integrate a permissioned Solana network for high transaction throughput, with simplified registrations and dosage maintenance at NCs. Extensive experiments were performed on UAV swarm and GC controller setup, and a significant improvement in storage cost and UAV coverage is obtained. Conclusively, the proposed scheme simplifies the UAV flight operations, owing to 6G-eRLLC setup, and supports an intelligent TO to reduce energy requirements for longer flight duration. As part of the future scope, an extension to the scheme would be investigated for security in UAV swarm communication. An anonymous and secured quantum key distribution channel would be set up, which allows perfect secrecy and privacy of user communication for massive dense networks.
Biographies

Ashwin Verma received the M.Tech. degree in CSE from NIT, Jaipur, India. He is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in the healthcare domain. He is employed as an Assistant Professor with the Computer Science and Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Nirma University. He has seven years of teaching and academic experience and has authored and coauthored more than six articles in leading SCI journals and IEEE conferences. Some of his top findings are published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, Journal of Information Security and Applications (Elsevier), and IEEE-ICIEM-2021. His research interests lie in healthcare 4.0, federated learning, blockchain technology, and 5G and beyond communications.

Pronaya Bhattacharya received the Ph.D. degree in optical switching networks. He has over eight years of teaching experience. He is employed as an Assistant Professor with the Computer Science and Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad, India. He has authored or coauthored more than 60 research papers in leading SCI journals and top core IEEE COMSOC A* conferences. Some of his top-notch findings are published in reputed SCI journals like IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, IEEE Access, ETT (Wiley), Expert Systems (Wiley), FGCS (Elsevier), OQEL (Springer), WPC (Springer), ACM-MOBICOM, IEEE-INFOCOM, IEEE-ICC, IEEE-CITS, IEEE-ICIEM, IEEE-CCCI, and IEEE-ECAI. His research interests include healthcare analytics, optical switching and networking, federated learning, blockchain, and the IoT. He is a Reviewer of 17 reputed SCI journals like IEEE Internet of Things Journal, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, IEEE Access, IEEE Network, ETT (Wiley), IJCS (Wiley), MTAP (Springer), OSN (Elsevier), and WPC (Springer).

Deepti Saraswat is pursuing the Ph.D. degree with the Dhirubhai Ambani Institute of Information and Communication Technology (DA-IICT), Gandhinagar, India. She is employed as an Assistant Professor with the Computer Science and Engineering Department, Institute of Technology, Nirma University, Ahmedabad, India. She had more than five years of industrial experience at the Samsung Research and Development Research Institute, Bengaluru, India, where she had worked on implementation of web browsers and the Internet of Things (IoT). Her research interests include data security and privacy, blockchain technology, optimization techniques, and the IoT.

Sudeep Tanwar (Senior Member, IEEE) received the Ph.D. degree in computer science and engineering from Mewar University, India. He is working as a Professor with Nirma University, India; and was a Visiting Professor with Jan Wyzykowski University, Polkowice, Poland, and the University of Piteşti, Piteşti, Romania. He has authored/coauthored more than 270 research papers in leading journals and conferences of repute and has edited/authored 20 books published in leading publication houses like IET and Springer. His research interests include WSN, blockchain technology, fog computing, and smart grid. He is an Associate Editor of IJCS, Security and Privacy journal (Wiley), and Computer Communications (Elsevier).

Neeraj Kumar (Senior Member, IEEE) received the Ph.D. degree in CSE from SMVD University, India. He was a Postdoctoral Research Fellow with Coventry University, U.K. He is working as a Professor with the Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, India. He has more than 300 research papers in leading journals and conferences of repute. He is an Associate Editor/Technical Editor of IEEE Communications Magazine, IEEE Network magazine, IJCS (Wiley), JNCA (Elsevier), Computer Communications (Elsevier), Security and Privacy (Wiley), IEEE Systems Journal, and ACM Computing Surveys.

Ravi Sharma is working as a Professor with the Centre for Inter-Disciplinary Research and Innovation, University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Dehradun, India. Dr. Sharma is passionate in the field of business analytics and worked in various MNC’s as a Leader of various software development groups. He has contributed various articles in the area of business analytics, prototype building for a startup, and artificial intelligence. He is leading academic institutions as a Consultant to uplift research activities ininterdisciplinary domains.
Contributor Information
Ashwin Verma, Email: ashwin.verma@nirmauni.ac.in.
Pronaya Bhattacharya, Email: pronoya.bhattacharya@nirmauni.ac.in.
Deepti Saraswat, Email: deepti.saraswat@nirmauni.ac.in.
Sudeep Tanwar, Email: sudeep.tanwar@nirmauni.ac.in.
Neeraj Kumar, Email: neeraj.kumar@thapar.edu.
Ravi Sharma, Email: ravisharmacidri@gmail.com.
References
- [1].(2021). Operational Update on COVID-19. Accessed: Aug. 7, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports
- [2].Worldometer.(2020). COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. Accessed: Apr. 30, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
- [3].Kwok K. O., Li K.-K., Wei W. I., Tang A., Wong S. Y. S., and Lee S. S., “Influenza vaccine uptake, COVID-19 vaccination intention and vaccine hesitancy among nurses: A survey,” Int. J. Nursing Stud., vol. 114, Feb. 2021, Art. no. 103854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Ramasamy M. N.et al. , “Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): A single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial,” Lancet, vol. 396, no. 10267, pp. 1979–1993, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].(2021). COVID-19 Vaccine Market—Global Outlook and Forecast 2021–2024. Accessed: Aug. 11, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5306516/covid-19-vaccine-market-global-outlook
- [6].Wang J., Zhao L., and Huchzermeier A., “Operations-finance interface in risk management: Research evolution and opportunities,” Prod. Oper. Manage., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 355–389, Feb. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- [7].Fusco A., Dicuonzo G., Dell’Atti V., and Tatullo M., “Blockchain in healthcare: Insights on COVID-19,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 17, no. 19, p. 7167, Sep. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Deng J., Hua J., Gyamfi B. A., and Shaw R., Drones Activity in Epidemic Prevention and Prospects in the Post-COVID-19. Singapore: Springer, 2022, pp. 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- [9].Arafat M. Y. and Moh S., “Localization and clustering based on swarm intelligence in UAV networks for emergency communications,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 8958–8976, Oct. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- [10].Baek J., Han S. I., and Han Y., “Optimal UAV route in wireless charging sensor networks,” IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 1327–1335, Feb. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- [11].Triche R. M., Greve A. E., and Dubin S. J., “UAVs and their role in the health supply chain: A case study from Malawi,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Unmanned Aircr. Syst. (ICUAS), Athens, Greece, Sep. 2020, pp. 1241–1248. [Google Scholar]
- [12].Khurshid A., “Applying blockchain technology to address the crisis of trust during the COVID-19 pandemic,” JMIR Med. Informat., vol. 8, no. 9, Sep. 2020, Art. no. e20477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Chamola V., Hassija V., Gupta V., and Guizani M., “A comprehensive review of the COVID-19 pandemic and the role of IoT, drones, AI, blockchain, and 5G in managing its impact,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 90225–90265, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- [14].Gupta R.et al. , “VAHAK: A blockchain-based outdoor delivery scheme using UAV for healthcare 4.0 services,” in Proc. Conf. Comput. Commun. Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Toronto, ON, Canada, Jul. 2020, pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- [15].Das A. K., Bera B., and Giri D., “AI and blockchain-based cloud-assisted secure vaccine distribution and tracking in IoMT-enabled COVID-19 environment,” IEEE Internet Things Mag., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 26–32, Jun. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- [16].Zuhair M., Patel F., Navapara D., Bhattacharya P., and Saraswat D., “BloCoV6: A blockchain-based 6G-assisted UAV contact tracing scheme for COVID-19 pandemic,” in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Intell. Eng. Manage. (ICIEM), London, U.K., Apr. 2021, pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- [17].Cheema M. A.et al. , “Blockchain-based secure delivery of medical supplies using drones,” Comput. Netw., vol. 204, Feb. 2022, Art. no. 108706. [Google Scholar]
- [18].Masuduzzaman M., Islam A., Sadia K., and Shin S. Y., “UAV-based MEC-assisted automated traffic management scheme using blockchain,” Future Gener. Comput. Syst., vol. 134, pp. 256–270, Sep. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- [19].Rani S. S., Deshmukh V. M., Pradeep S., Dinesh R. M., and Prabhu S. G., “Securing technology enabled services using unmanned aerial vehicles,” in Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Smart Syst. Inventive Technol. (ICSSIT), Tirunelveli, India, Jan. 2022, pp. 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- [20].Johannessen K. A., “A conceptual approach to time savings and cost competitiveness assessments for drone transport of biologic samples with unmanned aerial systems (drones),” Drones, vol. 6, no. 3, p. 62, Feb. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- [21].Sham R.et al. , “Drone usage for medicine and vaccine delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic: Attitude of health care workers in rural medical centres,” Drones, vol. 6, no. 5, p. 109, Apr. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- [22].Huang Y., Han H., Zhang B., Su X., and Gong Z., “Supply distribution center planning in UAV-based logistics networks for post-disaster supply delivery,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. E-Health Netw., Appl. Services (HEALTHCOM), Mar. 2021, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- [23].Dong C., Jiang F., Li X., Yao A., Li G., and Liu X., “A blockchain-aided self-sovereign identity framework for edge-based UAV delivery system,” in Proc. IEEE/ACM 21st Int. Symp. Cluster, Cloud Internet Comput. (CCGrid), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, May 2021, pp. 622–624. [Google Scholar]
- [24].Antal C., Cioara T., Antal M., and Anghel I., “Blockchain platform for COVID-19 vaccine supply management,” IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc., vol. 2, pp. 164–178, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- [25].Rathee G., Garg S., Kaddoum G., and Jayakody D. N. K., “An IoT-based secure vaccine distribution system through a blockchain network,” IEEE Internet Things Mag., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 10–15, Jun. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- [26].Verma A., Bhattacharya P., Zuhair M., Tanwar S., and Kumar N., “VaCoChain: Blockchain-based 5G-assisted UAV vaccine distribution scheme for future pandemics,” IEEE J. Biomed. Health Informat., vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 1997–2007, May 2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Xing Y., Carlson C., and Yuan H., “Optimize path planning for UAV COVID-19 test kits delivery system by hybrid reinforcement learning,” in Proc. IEEE 12th Annu. Comput. Commun. Workshop Conf. (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, Jan. 2022, pp. 0177–0183. [Google Scholar]
- [28].Gupta R., Kumari A., Tanwar S., and Kumar N., “Blockchain-envisioned softwarized multi-swarming UAVs to tackle COVID-I9 situations,” IEEE Netw., vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 1–8, Mar. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- [29].Kabilan K., Bhalaji N., Selvaraj C., Kumaar B M., and Karthikeyan P. T. R., “Performance analysis of IoT protocol under different mobility models,” Comput. Electr. Eng., vol. 72, pp. 154–168, Nov. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- [30].D’Ursol F., Grasso C., Santoro C., Santoro F. F., and Schembra G., “The tactile internet for the flight control of UAV flocks,” in Proc. 4th IEEE Conf. Netw. Softwarization Workshops (NetSoft), Montreal, QC, Canada, Jun. 2018, pp. 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- [31].Jeong S., Simeone O., and Kang J., “Mobile edge computing via a UAV-mounted cloudlet: Optimization of bit allocation and path planning,” IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., vol. 67, no. 3, pp. 2049–2063, Mar. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- [32].Browne C. B.et al. , “A survey of Monte Carlo tree search methods,” IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–43, Mar. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- [33].Chen J., Chen S., Luo S., Wang Q., Cao B., and Li X., “An intelligent task offloading algorithm (iTOA) for UAV edge computing network,” Digit. Commun. Netw., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 433–443, Nov. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- [34].Tataria H., Shafi M., Dohler M., and Sun S., “Six critical challenges for 6G wireless systems: A summary and some solutions,” IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 16–26, Mar. 2022. [Google Scholar]



