Abstract
Heat shock protein 90β (Hsp90β, encoded by Hsp90ab1 gene) is the most abundant proteins in the cells and contributes to variety of biological processes including metabolism, cell growth and neural functions. However, genetic evidences showing Hsp90β in vivo functions using tissue specific knockout mice are still lacking. Here, we showed that Hsp90β exerted paralogue-specific role in osteoclastogenesis. Using myeloid-specific Hsp90ab1 knockout mice, we provided the first genetic evidence showing the in vivo function of Hsp90β. Hsp90β binds to Ikkβ and reduces its ubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation, thus leading to activated NF-κB signaling. Meanwhile, Hsp90β increases cholesterol biosynthesis by activating Srebp2. Both pathways promote osteoclastogenic genes expression. Genetic deletion of Hsp90ab1 in osteoclast or pharmacological inhibition of Hsp90β alleviates bone loss in ovariectomy-induced mice. Therefore, Hsp90β is a promising druggable target for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Subject terms: Endocrine system and metabolic diseases, Drug development
Introduction
Osteoporosis (OP) is mainly characterized by the degradation of bone microstructure and bone mass. The main pathogenesis of osteoporosis is the decline of bone formation by osteoblasts and the enhancement of bone resorption by osteoclasts [1]. Medications that treat OP are characterized as either anabolic to induce bone formation (teriparatide, abaloparatide, romosozumab) [2, 3], or anti-resorptive to decrease the rate of bone resorption (bisphosphonates, estrogens, calcitonin, and denosumab, etc) [4]. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) and receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) stimulate preosteoclasts differentiate from monocyte/macrophage lineage cells [5]. RANKL binds to its receptor RANK (receptor activator of NF-κB), and the intracellular domain of RANK mediates transforming growth factor β Activation of activated kinase 1 (TAK1), together with TNF receptor related factor (TRAF).
Nuclear factor κB (nuclear factor-κB, NF-κB) contains a family of transcription factors that are essential for cell survival, differentiation and apoptosis [6, 7]. Activation of NF-κB pathway promotes osteoclasts differentiation. In the presence of RANKL, TRAF6 binds to RANK and NF-κB is transported into the nucleus, increasing c-FOS expression, which further binds and interacts with NFATC1. NFATC1 starts the transcription of osteoclastogenesis gene, and finally induces the formation of mature osteoclasts [8]. The formation, survival and fusion of osteoclasts are dependent on the presence of cholesterol [9, 10]. Cholesterol lowering drugs greatly reduce the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts [11, 12], thereby reducing the fracture risk associated with OP [13]. In contrast, the use of fiber esters or other lipid-lowering drugs that mainly affect total triglycerides is not associated with a significant reduction in fracture risk [14]. These results suggest that selective reducing cholesterol delays bone loss. Sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP2) is a key transcription factor that regulates cholesterol synthesis, thus affecting osteoclasts differentiation [15, 16]. In addition, NFATC1 is reported as one of the target genes of SREBP2 [17]. Therefore, SREBP2 is considered as a new therapeutic target for OP [15, 18, 19].
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is a member of molecular chaperone family. It is essential for the correct folding of a number of newly synthesized proteins. Meanwhile, HSP90 also helps the re-maturation of denatured or misfolded proteins under stressed conditions. The HSP90 family consists of four paralogs: HSP90AA1 (encoding HSP90α), HSP90AB1 (encoding HSP90β), HSP90B1 (encoding glucose regulatory protein 94) and TRAP 1 (encoding TNF receptor associated protein 1) [20]. Our previous study showed that HSP90β, but not HSP90α, plays an important role in regulating fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism by promoting the ubiquitylation of hepatic SREBPs [21]. We then speculated that suppressing HSP90β might be beneficial against OP. However, the studies on HSP90 inhibition and osteoclastogenesis seem to be controversial. It was reported that 17-AAG, a pan-HSP90 inhibitor that binds to the N-terminal ATP binding pocket and can transiently activate c-Src [22–25]. While another HSP90 inhibitor PF-4928473 with the same binding pocket constitutively suppressed c-Src and prevented osteoclast formation [26]. It should be noted that all of these results were observed in cultured RAW264.7 cells. There is still no genetic evidence on whether HSP90 affects osteoclastogenesis in vivo.
HSP90 inhibition leads to impaired NF-κB activity. In Hodgkin’s lymphoma, HSP90 inhibitor geldanamycin (GA) impaired IκB kinase (IKK) activity, leading to reduced phosphorylation and polyubiquitylation of IκB. NF-κB can not be liberated from stabilized IκB and lose its transcriptional activity [27]. 17-AAG inhibits NF-κB pathway in M1-Polarized macrophages [28] and in human lung microvascular endothelial cells [29]. However, in RAW264.7 cells, 17-AAG affects neither NF-κB nor c-Fos, probably slightly inhibited NFATC1 activity [25]. The divergence of the above research results strongly suggest that more evidence is needed on the role of HSP90 in osteoclasts differentiation. We believe genetic mouse models that the data obtained in osteoclasts-specific HSP90 knockout mice will clarify the puzzle.
Although in pathological conditions, HSP90α [30] or HSP90β [21] are increased, the genetic evidences showing paralog-specific roles of HSP90 are lacking. Meanwhile, the mechanism controlling this HSP90 overexpression remains elusive.
In this study, we found HSP90β is highly expressed in osteoclasts of OVX-mice and OP patients. We then generated osteoclast-specific Hsp90β knockout mice and found that Hsp90β is an osteoclast activator by dual-targeting against Srebp2 and NF-κB. Abnormal high expression of Hsp90β in pathological state of OP is via c-Jun mediated transcriptional activation. Corylin, the active component contained in Psoralea corylifolia, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of OP, binds to HSP90β and simultaneously inhibits Srebp2 and Ikk mediated NF-κB activation to reduce cholesterol synthesis and Nfatc1 mediated osteoclast-forming genes expression.
Materials and methods
Materials
Corylin was purchased from Chengdu Pufei De Biotech co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT), 4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) were purchased from Keygen Biotech (Nanjing, China). RANKL and M-CSF were from R&D Biosystems (Minneapolis, USA). TRAP staining kit was from Wako (Japan). FBS and α-MEM were from GIBCO (Grand Island, New York, USA); TRITC-Phalloidin was from YEASEN (Shanghai, China); MG-132 and Cycloheximide were from MedChem Express (Shanghai, China).
Generation of myeloid Hsp90ab1 knockout mice
Exon1, exon2 and exon3 of the mouse Hsp90ab1 gene were flanked by two LoxP sites to generate a conditional Hsp90ab1 targeting mouse strain (Supplementary Fig. 1). All mice are maintained on C57BL/6 background. An Hsp90ab1 gene sequence containing exon1, exon2 and exon3 was inserted in the targeting vector for generating donor DNA. The resultant donor DNA was confirmed by sequencing and used for generating Hsp90ab1 floxed mice. In order to generate Hsp90ab1 floxed mice, Cas9 nickase, Hsp90ab1-L4 (AGTCAAACTCTTGAACATTGG) and Hsp90ab1-R8 (TATAGAATACAACGTCTAAGG) were transcribed into mRNA and RNA in vitro, with donor DNA were microinjected into the fertilized eggs of mice. Next, these mice were mated with LysM-Cre mice (kindly provided by Prof. Chaojun Li, Nanjing Medical University) to confirm their genotype. For genotyping by PCR, the following primers were used: F1, CCCAATGAGGAGATTGTAGT; R1, CCAGAACAGATGCCCAAA; F2, GAGGCAGCAGGCTACATT; R2, CACCTACAGAGAACAAATCAAG (Supplementary Fig. 1).
Cell culture
The murine monocytic cell line RAW264.7 and 293 T (ATCC, VA) were grown in an incubator with 5% CO2 at 37 °C. The cell lines were cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS, 100 units/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin. The cell lines were not contaminated with mycoplasma. And the source of them was identified by STR profiling.
Preparation and culture of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages
The primary mature osteoclasts were generated from BMMs (bone marrow-derived monocytes), BMMs were flushed from tibias and femora of 6-week-old C57BL/6 mice, as described previously [19]. BMMs were seeded at 2 × 105 into a well of a 24-well plate and 1 × 106 BMMs into a well of a six-well plate. The cells were grown in α-MEM containing 10% FBS, 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 for 4–7 days.
Viability assay
The effect of corylin on viability of RAW264.7 was detected by MTT assay. Briefly, RAW264.7 cells were plated at the density of 2 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates. After 24 h, cells were treated with indicated concentration of corylin for 48 or 96 h. Afterwards, 5 mg/mL MTT was added to each well, and then cells were incubated for 4 h at 37 °C. The cytotoxicity of corylin was determined by microplate reader (Multiskan FC).
Western blotting
Indicated cells were washed with precooling PBS and dissolved with SDS Lysis Buffer. Whole-cell extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose filter (NC) membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk in TBS with Tween-20 (TBST). Then, antibody (Supplementary Table 1) was bound overnight at 4 °C. After washing with TBST, HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (Beyotime Biotechnology, China) was bound for 1 h at room temperature. Immunoreactive signals were detected with Chemi-Lumi One Ultra (Tanon, China).
qRT-PCR
Total RNA was collected from cells using RNA-easy isolation reagent (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA using Hiscript II reverse transcriptase (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Gene expression was measured by quantitative PCR (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using SYBR-green dye (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Gene expression was normalized to Gapdh. The primer sets used were listed in Supplementary Table 2.
Osteoclast formation and TRAP staining
BMMs (2 × 105 cells/well) were cultured in 24-well plates in α-MEM with 10% FBS, 30 ng/ml of M-CSF, 100 ng/ml of RANKL for 5–7 days, as described previously [19]. TRAP staining was used to identify mature OCs that contains more than 3 multinucleated TRAP-positive cells.
Actin-ring formation and pit assay
BMMs cells were stimulated with M-CSF (30 ng/ml) and RANKL (100 ng/ml). Then the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min, after washing with PBS, the cells were incubated with TRITC-Phalloidin for 1 h followed with DAPI staining for 10 min.
Immunofluorescence
Cells were fixed with 4% PFA for 15 min, and then permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 15 min. Immunofluorescence staining was performed as described [19] using primary antibodies and corresponding fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies. Fluorescence signals of stained cells or tissues sections were analyzed with an FV3000 confocal microscope (Olympus).
Reporter gene assay
As previously described [19], RAW264.7 cells were transfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids and β-galactosidase expression plasmids using X-tremeGENE HP DNA Transfection Reagent (Roche) for 24 h. Cells were then exposed to indicated concentrations of corylin. The intensity of β-Gal, as the internal control, and the luciferase activity were measured using a microplate reader.
Micro-computed tomography (μCT) analysis
The tibias from mice were collected, fixed in 4% PFA and scanned using Quantum GX μCT scanner (PerkinElmer, America; 90 kV, 88 μA, 14 min scan time, 18 mm FOV, 36 μm voxel size). The reconstruction of scanned images was performed using the supporting software, followed by generation of three-dimensional models. Three hundred slices of proximal tibial metaphysis starting at 0.6 mm from the end of the growth plate were analyzed using the manufacturer’s evaluation software.
Histology
The femora were fixed in 4% PFA at 4 °C for 1 day, decalcified in 10% EDTA for 4-5 days. Subsequently the femora were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. The femora slices were used for TRAP staining according to manufacturer’s instructions (Sigma, USA), H&E staining, immunohistochemical staining, and immunofluorescence staining.
Animal experiment
Ovariectomy (OVX)-induced osteoporosis mice model was performed 7-week-old female C57BL/6 mice, as previously described [19]. The mice were randomly and blindingly divided into five groups: sham operated mice (Sham), ovariectomized mice treated with vehicle (OVX), OVX mice treated with 0.1 mg/kg E2 (OVX + E2 0.1 mg/kg), OVX mice treated with 30 mg/kg corylin (OVX + corylin 30 mg/kg), and OVX mice treated with 60 mg/kg corylin (OVX + corylin 60 mg/kg). Each group contained six mice, and these mice were intragastrically administrated with vehicle control or corylin for 16 weeks. E2 was injected intraperitoneally once every 2 days for 16 weeks.
Bone resorption assay
BMMs were seeded on the Osteo assay plate (Corning, USA) at a density of 1 × 104 cells/well and stimulated with 30 ng/ml M-CSF and 100 ng/ml RANKL, followed by treatment with indicated concentration of corylin for 7 days. Subsequently, plates were treated with 5% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min to remove the cells. Afterwards, resorption pits on plates were visualized and imaged by an inverted fluorescence microscope (Nikon Ts2R, Japan).
Human bone samples
Human bone samples were obtained either from osteoporosis patients undergoing knee joint replacement (female) or from tibia fracture undergoing Open Reduction Internal Fixation (Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangdong, China and Division of Orthopedic Surgery, the Affiliated Nanjing Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China). This clinical study was approved by the Ethnic Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences) and the Affiliated Nanjing Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, and written informed consents were obtained from the patients before procedure [31].
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed in GraphPad Prism Version 8. Statistical comparisons between two groups were made using the two-tailed Student’s t test; comparisons among multiple groups were made by the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The groups being compared have the similar variance. All experiments were repeated at least three times. All results are presented as the mean ± S.D. In all cases, differences were considered significant at *P < 0.05. P-values are indicated in each figure as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001.
Results
Hsp90β is upregulated during osteoclastogenesis
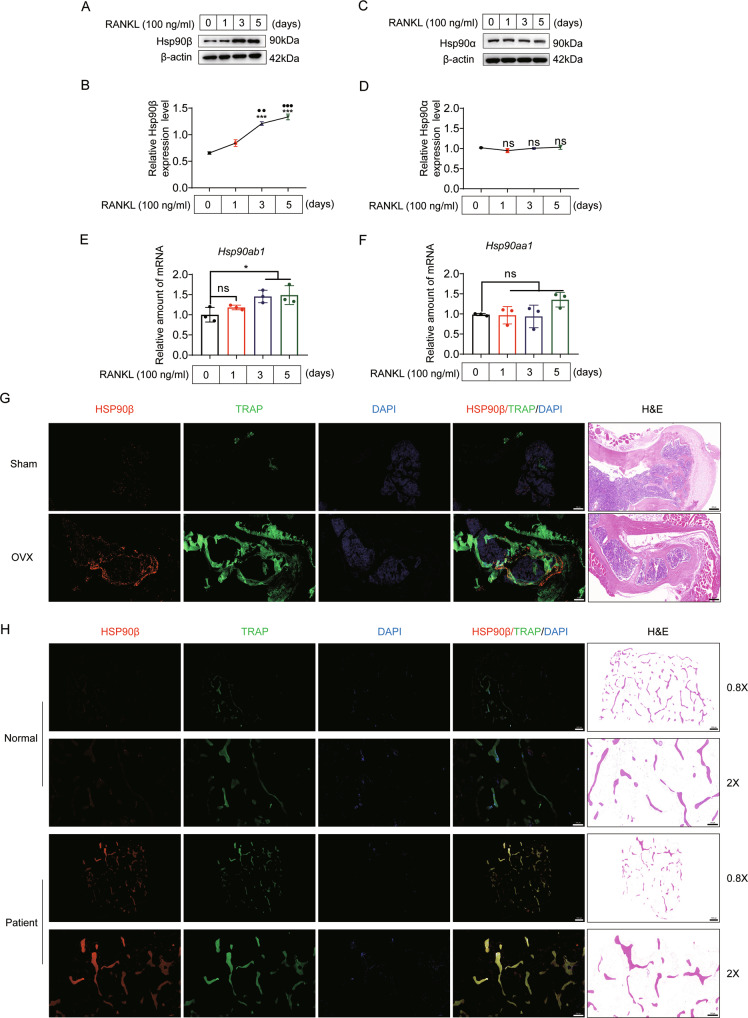
To evaluate potential roles of Hsp90 in the pathogenesis of OP, we first measured Hsp90 protein levels in BMMs treated with RANKL. During RANKL mediated osteoclast differentiation, we observed a significant increase of Hsp90β from the 3rd day (Fig. 1A, B). In contrast, Hsp90α protein level remained unchanged during osteoclastogenesis (Fig. 1C, D). We observed that the mRNA levels of Hsp90ab1, but not Hsp90aa1, was markedly increased during osteoclastogenesis (Fig. 1E, F). Consistently, the distinct overexpression pattern of Hsp90β was also present in osteoclasts (TRAP positive cells) of OVX-group mice (Fig. 1G) or OP patients (Fig. 1H). We therefore considered the possible role of Hsp90β in osteoclastogenesis.
Fig. 1. Hsp90β is upregulated during osteoclastogenesis.
A, B Protein expression of Hsp90β in BMMs in the presence of 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF (*compared with day 0; ● compared with day 1). C, D Protein expression of Hsp90α in BMMs in the presence of 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF. E, F The mRNA level of Hsp90ab1 and Hsp90aa1 during osteoclastogenesis. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times. G TRAP (green) and Hsp90β (red) immunofluorescence staining of femora sections from Sham and OVX mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. H Representative confocal images of TRAP/HSP90β immunofluorescence staining in the tibia of normal and osteoporotic patients (n = 2). Scale bar, 1000 μm and 500 μm, respectively.
Osteoclast Hsp90ab1 deletion reduces osteoporosis phenotypes
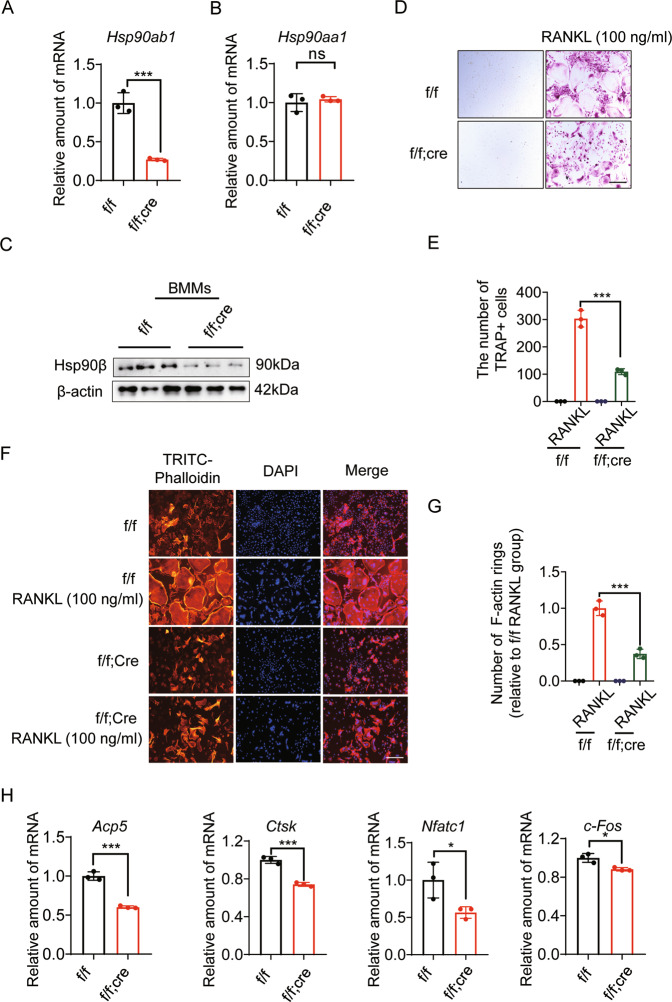
To investigate Hsp90β function in the OP development, we intercrossed floxed Hsp90ab1 (Hsp90ab1f/f) mice with the Lysozyme 2-Cre (LysM-Cre) line to obtain myeloid-specific Hsp90ab1-knockout (Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre) mice. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) were collected to check the expression of HSP90 isoforms. Macrophages in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice showed nice deletion of Hsp90ab1, but did not affect Hsp90aa1 (Fig. 2A, B). Protein level of Hsp90ab1 also decreased in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 2C). To characterize the effects of Hsp90ab1 deletion upon osteoclast formation, we collected primary BMMs cultured with M-CSF and RANKL for 7 days, as described previously [19]. TRAP+ cells with >3 nuclei by light microscopy were counted multinucleated cells (MNCs) or osteoclasts. BMMs from Hsp90ab1f/f mice formed approximately 300 TRAP+ cells. Hsp90ab1 deletion yielded 2/3 reduction of osteoclasts (Fig. 2D, E). Osteoclasts from Hsp90ab1f/f mice formed actin ring structures, which got lost in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 2F, G). Genes involved in osteoclastogenesis, such as acid phosphatase [Acp5 or Trap (tartrate-resistant Acid Phosphatase Type 5)], cathepsin K (Ctsk), nuclear factor of activated T cells, cytoplasmic 1 (Nfatc1) and cellular oncogene Fos (c-Fos) were decreased in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 2H). Taken together, these data suggested that Hsp90β is required for osteoclastogenesis in vitro.
Fig. 2. Osteoclast Hsp90ab1 deletion reduces osteoclastogenesis.
A, B Relative mRNA expression of Hsp90ab1 and Hsp90aa1 in BMMs from Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre (f/f; Cre) mice or Hsp90ab1f/f (f/f) littermates. C Protein level of Hsp90β in BMMs. D TRAP staining of BMMs treated with 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF for 7 days. Scale bars, 100 μm. E Quantification of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells. F BMMs were fixed and stained for F-actin with TRITC-phalloidin. Scale bars, 100 μm. G Number of osteoclasts with actin ring structures. H qRT-PCR was used to quantify relative mRNA expression levels of indicated genes. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
Hsp90ab1 deletion improves ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity
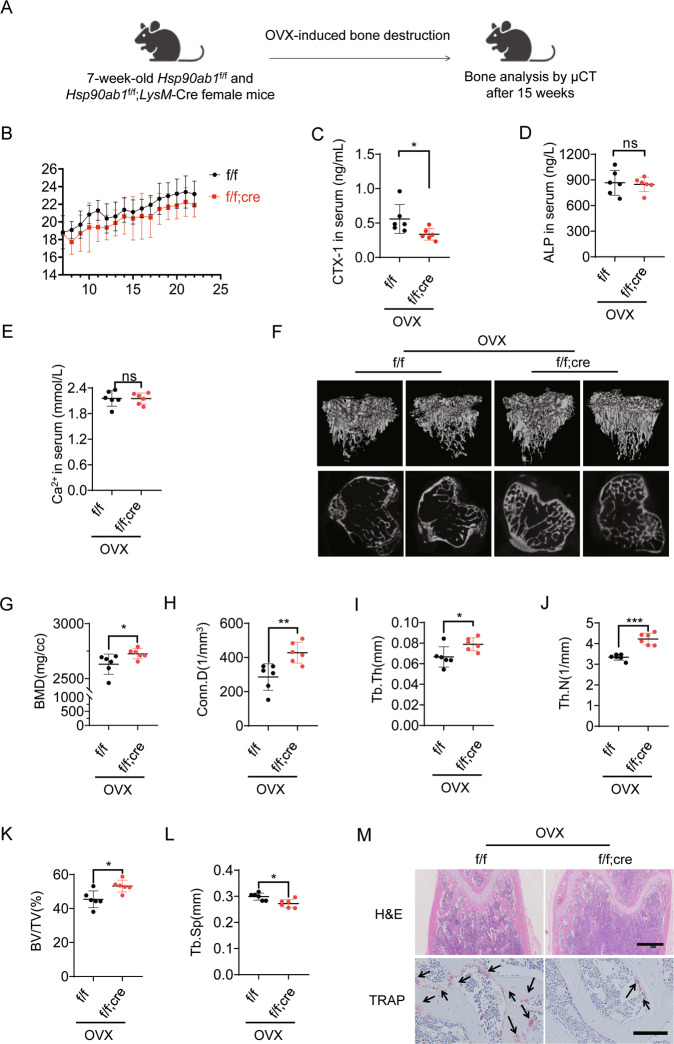
To further evaluate the Hsp90β function in OP development in vivo, female Hsp90ab1f/f or Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice underwent ovariectomy (OVX) at week 7, and recovered for additional 15 weeks (Fig. 3A). Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice exhibited a slight but not significant decrease in bodyweight compared to Hsp90ab1f/f mice (Fig. 3B). The levels of carboxy-terminal crosslinked telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX-1), a bone resorption biomarker [32] decreased in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 3C). Calcium concentration and the bone formation markers, such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP) [32] did not change after Hsp90ab1 deletion (Fig. 3D, E). Quantitative computed tomography (μ-CT) analysis was applied to determine the in vivo effects of Hsp90β within the skeletal system. Trabecular bone mass was significantly increased in OVX Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 3F), confirmed by increased bone mineral density (BMD, Fig. 3G), connectivity density (Conn.D, Fig. 3H), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th, Fig. 3I), trabecular number (Tb.N, Fig. 3J), trabecular bone volume (BV/TV, Fig. 3K) and decreased trabecular spacing (Tb.Sp, Fig. 3L) [33]. H&E staining showed a decreased lipid composition in distal femoral trabecular bones in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice compared to their wildtype littermates. In addition, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining confirmed the decrease of osteoclasts along the surface of trabecular bone in Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Fig. 3M). These results indicated that Hsp90ab1 deletion protected against OVX-induced bone loss, most probably by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. It should be noted that Hsp90β did not express at high level in normal animal osteoclasts (Fig. 1G), therefore, OC knockout of Hsp90β did not cause obvious bone phenotypes (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Fig. 3. Hsp90ab1 deletion improves ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity.
A Schematic for ovariectomy-induced bone loss mice model. B Body weight after OVX was recorded for 15 weeks. C–E Serum CTX-1, ALP and calcium concentration in myeloid Hsp90ab1 knockout mice (n = 6). F Representative reconstructed 3D μCT images of proximal tibia in myeloid Hsp90ab1 knockout mice (n = 6). G–L Quantification of BMD, Conn.D, Tb.Th, Tb.N, BV/TV and Tb.Sp from μCT images. M H&E and TRAP staining of the femora from OVX-mice (black arrows, TRAP-positive cells). Scale bars, 500 μm and 100 μm. Bars represent means ± S.D. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Hsp90ab1 deletion attenuates NF-κB signaling
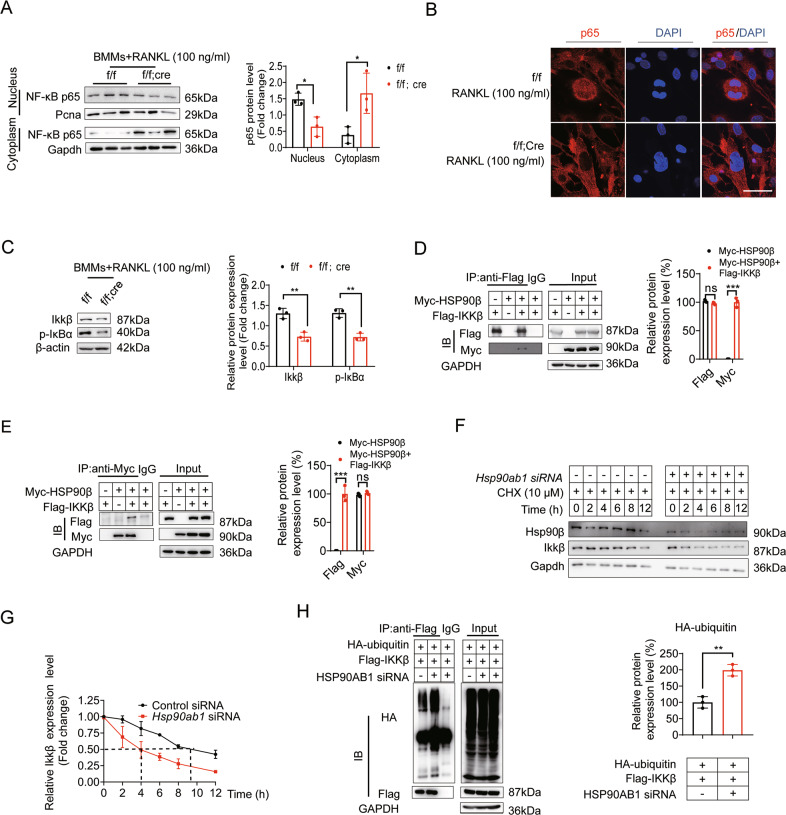
RANKL activated NF-κB signaling is required for osteoclast formation [34]. As such, we next checked NF-κB activity when Hsp90ab1 was genetically inhibited. When treated with 100 ng/ml RANKL, BMMs harvested from Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice have dramatically decreased nuclear NF-κB (p65 subunit). It seems that p65 was sequestered in the cytoplasm (Fig. 4A, B). NF-κB transcription factors are normally kept inactive in the cytoplasm by interaction with their inhibitors called IκBs. IκBs lose their inhibitor effects after being phosphorylated by IKKs (Inhibitor of nuclear factor Kappa B kinase) complex that consists of two catalytic subunits (IKKα and IKKβ) and a regulatory subunit, IKKγ [35]. Hsp90ab1 deletion significantly reduced Ikkβ, subsequently decreased IκB phosphorylation in BMMs (Fig. 4C). There was a direct interaction between Ikkβ and Hsp90β (Fig. 4D, E). When Hsp90ab1 was knocked down by siRNAs, a much quicker turnover rate of Ikkβ was observed (Fig. 4F, G). It seems that the reduced protein stability is due to the increased Ikkβ ubiquitylation after the knockdown of Hsp90ab1 (Fig. 4H).
Fig. 4. Osteoclast Hsp90ab1 deletion attenuates NF-κB signaling.
A BMMs from Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre (f/f; Cre) mice and Hsp90ab1f/f (f/f) littermates were incubated with 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF, p65 expression in the nucleus and cytoplasm was analyzed by western blot. B Nuclear translocation of p65 was visualized using immunofluorescence staining. Scale bars: 100 μm. C Protein expression of Ikkβ and p-IκBα in BMMs treated with 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF. D, E 293 T cells were transfected with Myc-HSP90β, Flag-IKKβ. Flag immunoprecipitates or Myc immunoprecipitates were further analyzed by immunoblotting with corresponding antibodies. F BMMs were transfected with siRNA targeting Hsp90ab1 for 48 h, afterwards, the cells were supplemented with 10 µM cycloheximide following the indicated time. Ikkβ was detected by western blot. G Quantification of Ikkβ protein levels in panel F. H 293 T cells were transfected with Flag-IKKβ and HA-ubiquitin plasmids for 48 h, and the cells were supplemented with control siRNA or siRNA targeting HSP90AB1 for 48 h, the cells were lysed and proteins were detected by WB (left), quantification of indicated protein levels (right). Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
Hsp90ab1 deletion reduces cholesterol biosynthesis
In our previous work, knockdown of Hsp90ab1 blunted de novo lipogenesis in hepatocytes [21]. As Osteoclasts formation, survival and morphology are highly dependent on cholesterol [9], we then checked lipid metabolic features in BMMs from Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) is a master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis [36]. Consistent with former report in liver [21], Srebp2, as well as its downstream target genes involved in cholesterol metabolism, is downregulated in BMMs from Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice (Supplementary Fig. 3A–F). When Hsp90ab1 was knocked down, the trend of total cholesterol content increase by RANKL treatment was fully reversed in BMMs (Supplementary Fig. 3G). Notably, neither RANKL, nor Hsp90ab1 knockdown, changed the total triacylglycerol content (Supplementary Fig. 3H), suggesting that Hsp90ab1 specifically affected cholesterol biosynthesis in BMMs. Meanwhile, the absence of Hsp90ab1 significantly inhibited RANKL-induced nuclear localization of Srebp2 (Supplementary Fig. 3I). Cholesterol is an endogenous ERRα agonist [37], when Hsp90ab1 was abrogated, the expression of ERRα and ERRα target genes significant declined due to reduced cholesterol biosynthesis (Supplementary Fig. 3J–M).
Pathological up-regulation of Hsp90ab1 is transcriptionally regulated by c-Jun
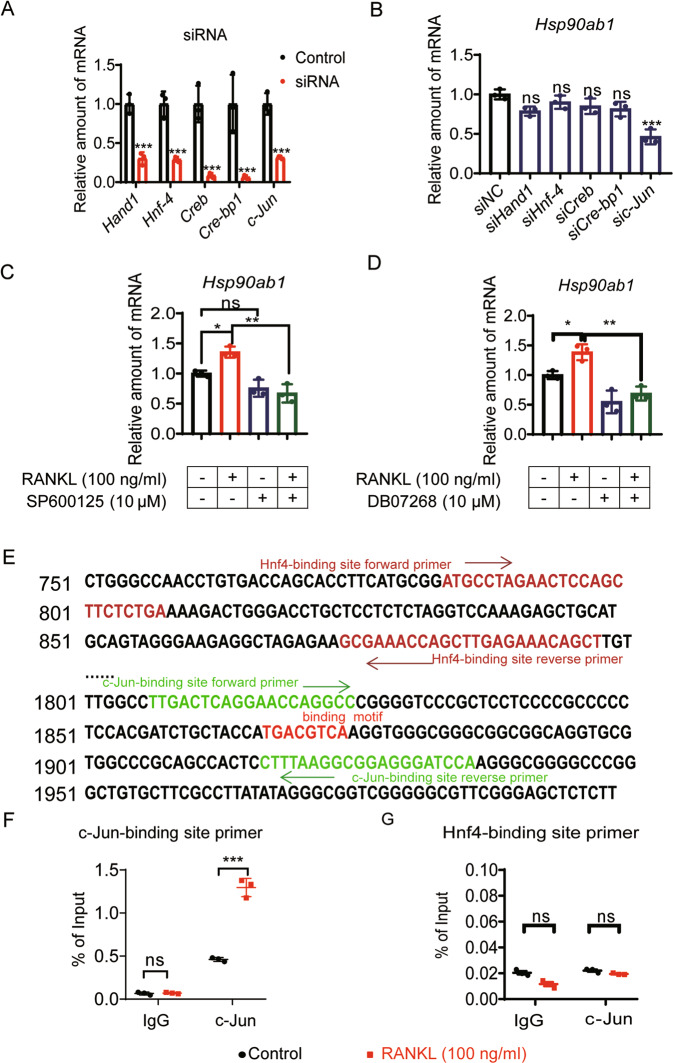
Although lines of evidence prompted pathological relevance between HSP90β and metabolic diseases [21], the underlying mechanisms controlling Hsp90ab1 mis-regulation remain unknown. To unravel the transcriptional regulation of Hsp90ab1, we predicted the transcription factors (TFs) and related TFs binding sites using match tools from TRANSFAC [38]. In the Hsp90ab1 promoter region, we found 6 putative TFs and their binding sites (Supplementary Table 3). We then knocked down each of these TFs using siRNAs (Supplementary Table 4) in BMMs to examine the Hsp90ab1 up-regulation trend by RANKL treatment. Increased trend of Hsp90ab1got diminished only when c-Jun was knocked down (Fig. 5A, B). c-Jun is the substrate for phosphorylation-activated JNKs, thus SP600125 and DB07268, two JNK inhibitors also reversed RANKL-induced Hsp90ab1 upregulation (Fig. 5C, D). To further validate the binding of c-Jun to Hsp90ab1 promoter region, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed. c-Jun was recruited to the 1807-1936 region that contains a predicted c-Jun binding motif in the presence of RANKL (Fig. 5E, F). ChIP results demonstrated that the binding of c-Jun to the promoter region of Hsp90ab1 was significantly decreased in RAW264.7 cells upon c-Jun silencing (Supplementary Fig. 4A). In comparison, RANKL did not affect the binding of Hnf4 that did not affect Hsp90ab1 transcription (Fig. 5G and Supplementary Fig. 4B). In reporter assays, overexpression of Flag-c-Jun induced luciferase expression driven by the genomic fragment containing response elements (TGACGTCA) but not mutants (GGCTTAAC) (Supplementary Fig. 4C). These data suggest that RANKL increases the expression of Hsp90ab1 via c-Jun.
Fig. 5. Pathological up-regulation of Hsp90ab1 is transcriptionally regulated by c-Jun.
A BMMs were transfected with siRNA targeting potential Hsp90ab1 transcription factors for 48 h. qRT-PCR was used to assess the knockdown efficiency of indicated genes. B Hsp90ab1 expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR after transcription factors were knocked down. C, D BMMs were treated with JNK inhibitor SP600125 or DB07268, and the mRNA level of Hsp90ab1 was analyzed by qRT-PCR. E Putative c-Jun and Hnf4 binding sites, ChIP primers in the Hsp90ab1 promoter region. F In the presence/absence of RANKL, the binding of c-Jun to the Hsp90ab1 promoter region was analyzed by ChIP analysis in RAW264.7 cells. G In the presence/absence of RANKL, the binding of Hnf4 to the Hsp90ab1 promoter region was analyzed by ChIP analysis in RAW264.7 cells. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
Corylin inhibits osteoclasts formation and improves ovariectomy-induced bone loss
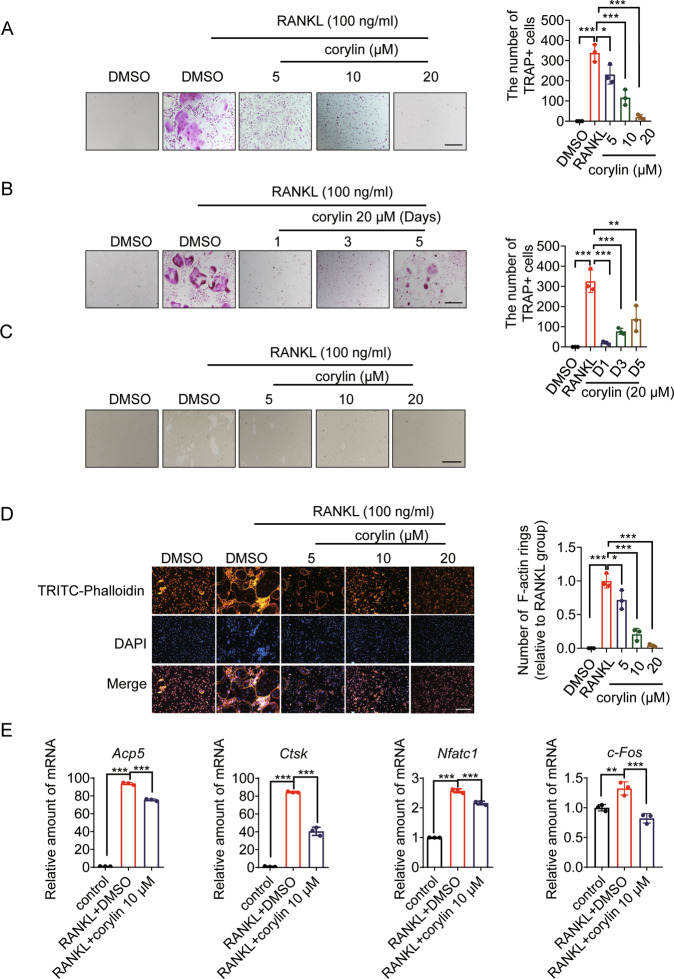
The above results showed that HSP90β is a potent drug target to treat OP. To prove this concept, compounds specifically target HSP90β have therapeutic effects in the treatment of OP. Psoralea Fructus is the fruit of Psoralea corylifolia L., commonly known as “Buguzhi” in Chinese. Psoralea Fructus is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb that is widely used in treating osteoporosis [39]. However, the active components and their therapeutic targets remain largely elusive. We, therefore, performed virtue screening to search compounds from Psoralea Fructus that have higher binding affinity to HSP90β (PDB ID code 3PRY). Among the 30 compounds contained in Psoralea Fructus, 6 compounds were found to bind HSP90β in a Bio-Layer Interferometry method, and corylin exhibited the highest binding affinity (Supplementary Table 5). We then evaluated the anti-osteoclastogenesis effects of corylin in BMMs. RANKL-stimulated the formation of TRAP+ multinucleated osteoclasts were largely disrupted by corylin treatment in dose- and time- dependent manners (Fig. 6A, B). Smaller “resorption pits” in corylin treated osteoclasts were observed (Fig. 6C). Corylin dose-dependently blocked the formation of actin ring structures in the presence of RANKL (Fig. 6D). The expression of osteoclastogenesis related genes that are stimulated by RANKL, including Acp5, Ctsk, Nfatc1 and c-Fos was suppressed by corylin (Fig. 6E). The effects of corylin in vitro were consistent with Hsp90ab1 knockout BMMs.
Fig. 6. Corylin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro.
A Representative TRAP-positive osteoclasts treated with indicated concentrations of corylin followed by stimulation with 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF (left). Scale bars, 100 μm. Quantification of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells (right). B BMMs were treated with 20 μΜ corylin for the indicated days during osteoclastogenesis (left). Scale bars: 100 μm. Quantification of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells (right). C Representative images showing resorption pits in BMMs grown on OsteoAssay plates for 7 days. Scale bars: 100 μm. D BMMs were incubated with or without 100 ng/ml RANKL and 30 ng/ml M-CSF, followed by treatment with indicated concentration of corylin. Cells were fixed and stained for F-actin (left). Scale bars, 100 μm. Osteoclasts having actin rings structures were counted (right). E qRT-PCR was used to assess relative mRNA expression levels of indicated genes. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
Corylin inhibits NF-κB and Srebp2 activities
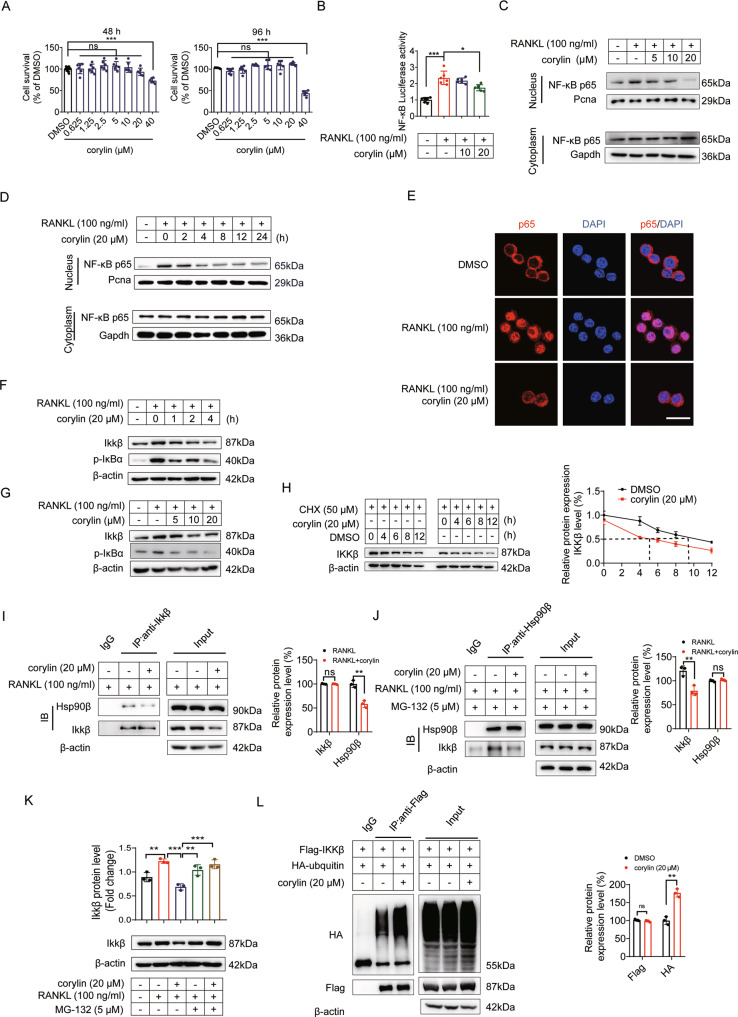
As deletion of Hsp90ab1 led to decreased NF-κB and Srebp2 activities, we next checked whether corylin exhibited similar effects in RAW264.7. Corylin treatment under 20 μM concentrations did not cause obvious cytotoxicity (Fig. 7A). Corylin blocked RANKL-induced NF-κB transcriptional activation corylin (Fig. 7B) by suppression of p65 nuclear localization (Fig. 7C–E). This effect is concentration- and time- dependent. Corylin blunted Ikk complex activity mainly by reducing Ikkβ protein levels. The effect of RANKL on Ikk complex was also mainly manifested in promoting the expression of Ikkβ (Fig. 7F, G), the effect was probably due to corylin increased Ikkβ protein degradation (Fig. 7H). RANKL induced strong interaction between Hsp90β and Ikkβ, which could be disrupted by corylin treatment (Fig. 7I, J). When liberated from Hsp90β protection, Ikkβ was more susceptible to E3 ligase recognition and subsequently was ubiquitylated (Fig. 7L) and degradated in 26 S proteasome, as MG-132, a specific 26 S proteasome inhibitor totally blocked corylin-induced Ikkβ degradation (Fig. 7K).
Fig. 7. Corylin inhibits NF-κB activity.
A Effects of corylin on RAW264.7 cells viability at 48 and 96 h. B The NF-κB luciferase reporter gene assay was performed in the presence of corylin at indicated concentrations. C RAW264.7 cells were incubated with or without 100 ng/ml RANKL, followed by treatment with indicated concentration of corylin for 8 h, relative protein expression of p65 was detected in the nucleus and cytoplasm fractions by western blot. D RAW264.7 cells were treated with 20 µM corylin for indicated time period, relative protein expression of p65 was detected in the nucleus and cytoplasm fractions. E Nuclear translocation of p65 was visualized using immunofluorescence staining. Scale bars: 100 μm. F Expression levels of the indicated proteins in RAW264.7 cells treated with 20 μM corylin for indicated time period. G Expression levels of the indicated proteins in RAW264.7 cells treated with indicated concentration of corylin for 8 h. H 293 T cells were incubated with 50 µM cycloheximide, followed by the treatment of 20 µM corylin for the indicated time period. IKKβ amount was detected by western blot (left). Quantification of IKKβ protein levels (right). I RAW264.7 cells were incubated with 100 ng/ml RANKL, followed by the treatment of 20 µM corylin for 8 h. The cells lysates were immunoprecipitated with Ikkβ and detected by anti-Hsp90β antibody. J RAW264.7 cells were incubated with 5 µM MG-132, followed by the treatment of 100 ng/ml RANKL and 20 µM corylin for 8 h. The cells lysates were immunoprecipitated with Hsp90β and detected by anti-Ikkβ antibody. K RAW264.7 cells were incubated with 5 µM MG-132, followed by treatment with 20 µM corylin for 8 h, expression of Ikkβ was detected. L 293 T cells were transfected with Flag-IKKβ and HA-ubiquitin overexpression plasmids for 48 h, and the cells were supplemented with 20 µM corylin for 48 h, the cells lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag and detected by anti-HA antibody to show the ubiquitylation of IKKβ. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was performed at least three times.
RANKL-induced increase of Srebp2 protein level, as well as its transcriptional activity. Corylin dose-dependently mitigated the increase of Srebp2 protein, its transcriptional activity and the expression of its downstream genes involved in cholesterol synthesis in BMMs (Supplementary Fig. 5A–E). As cholesterol biosynthesis was abrogated, Errα was then less activated (Supplementary Fig. 5F), Errα target gene expression was also decreased (Supplementary Fig. 5G–I). In summary, the effects of corylin in BMMs are similar in regulating NF-κB and Srebp2 activities, comparable to the effect of Hsp90ab1 deletion. These data suggest that interfering Hsp90β activity might be useful to counteract the osteoclastogenesis effects of RANKL.
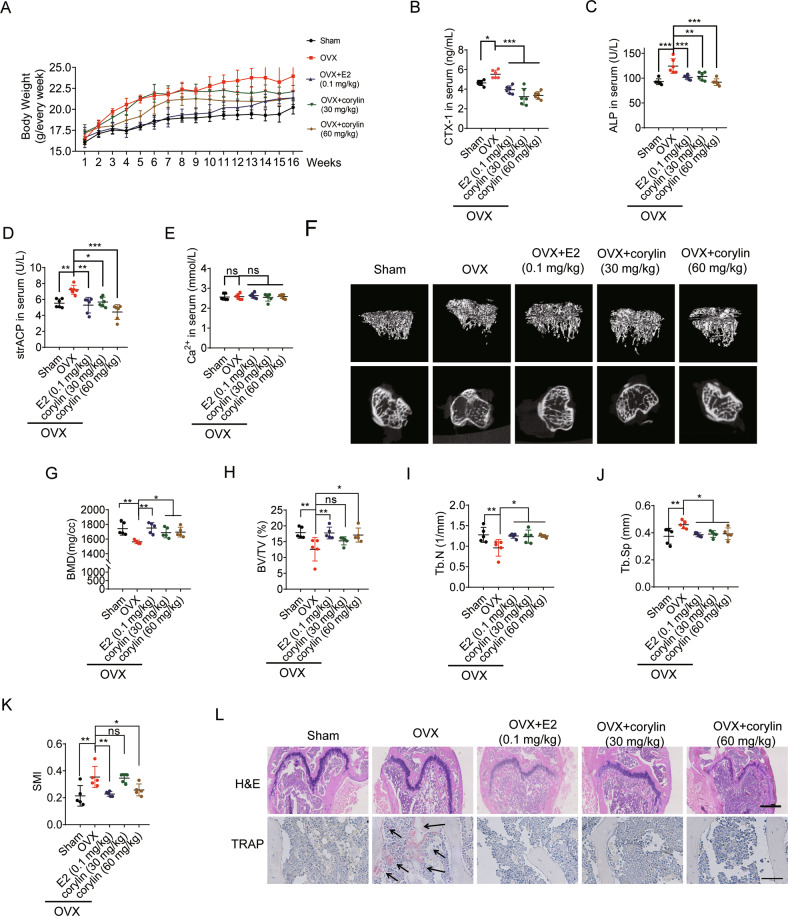
Next, the anti-osteoporosis effect of corylin in vivo was evaluated in an ovariectomy-induced bone loss mouse model. Corylin treatment blunted the bodyweight gain in OVX mice (Fig. 8A) without causing obvious adverse events. Serum CTX-1, ALP and TRAP (strACP) increased significantly in OVX mice. This trend was abrogated dose-dependently by corylin treatment, comparable to estradiol (E2) controls (Fig. 8B–D). All the treatment did not affect serum calcium concentration (Fig. 8E). Representative 3D reconstructions of proximal tibial trabecular bone by μCT showed a decreased bone loss in OVX mice treated with E2 or corylin (Fig. 8F). The histomorphometric of proximal tibial trabecular bone confirmed that corylin significantly increased BMD, BV/TV (%), Tb.N in OVX mice (Fig. 8G–I). In addition, increased Tb.Sp and SMI (Structure model index) in OVX mice were reversed by E2 and corylin treatment (Fig. 8J, K). TRAP positive osteoclasts in OVX mice were dramatically reduced in E2 or corylin treated groups (Fig. 8L). In conclusion, our data demonstrate that corylin protects against OVX-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclasts formation.
Fig. 8. Corylin improves ovariectomy-induced bone loss.
The OVX mice were divided into four groups (n = 6 in each group). The mice were treated with E2 (0.1 mg/kg) or corylin (30, 60 mg/kg) for 16 weeks. A Body weight after OVX was recorded for 16 weeks. B–E Serum CTX-1, ALP, strACP and calcium concentration in five groups of mice (n = 6). F Representative reconstructed 3D μCT images of proximal tibia of five group mice. G–K Quantification of BMD, BV/TV, Tb.N, Tb.Sp, SMI from μCT images of five group mice (n = 5). L H&E and TRAP staining of the femora from five group mice (black arrows, TRAP-positive cells). Scale bars, 500 μm and 100 μm. Bars represent means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Discussion
Bone remodeling is a balance between bone formation and bone resorption. It is the key to maintain bone structural integrity and mineral homeostasis. The dysfunction of osteoclasts is the main cause of osteoporosis and bone loss [1]. Osteoclasts are highly differentiated multinucleated giant cells, mainly derived from monocyte/macrophage hematopoietic stem cell lines. RANK/RANKL/OPG (osteoprotegerin) system plays the central role in regulating the differentiation and maturation of osteoclasts [40]. RANKL stimulates both canonical and non-canonical NF-κB signaling, leading to increased expression of transcription factors involved in osteoclast precursor differentiation, such as c-Fos and NFATC1 [34]. RANKL also stimulates the expression of SREBP2 during osteoclast differentiation [15, 19]. The cross-talk between NF-κB and SREBP2 plays an important role in macrophage foam cell formation [41]. However, there is no sufficient evidence to demonstrate a direct link between the two pathways. In this work, we found that HSP90β is an important upstream activator of both NF-κB and Srebp2 during osteoclastogenesis (Fig. 4 and Supplementary Fig. 3). This finding provides very important evidence for us to understand the relationship between cholesterol and NF-κB, the two important factors downstream RANKL that affect osteoporosis.
HSP90 acts as a molecular chaperone to help protein folding that is important for cell signaling [42]. HSP90 has been considered as a drug target for treating cancer [43], neurodegeneration diseases [44] and metabolic diseases [21, 45]. It should be noted that HSP90α and HSP90β share more than 86% of protein identity and more than 90% of protein similarity. It is very difficult to distinguish paralog-specific roles of HSP90 in different diseases. Homozygous mutation in Hsp90ab1 leads to embryonic lethal [46], while mice without Hsp90α are apparently normal [47]. Although the difference between the gene-trap strategy might contribute to the difference (Hsp90ab1 was trapped in the 9th exon while Hsp90aa1 was trapped in the intron before the last exon). There are still differences in molecular functions between these two proteins, for example, only HSP90β is considered to regulate SREBPs. Knocking down HSP90α, but not HSP90β, affects the stability of their client protein GZMA and H2AFX [21]. According to these research results, it is indeed necessary to use tissue-specific gene knockout mouse model to clarify the paralog-specific function of HSP90. HSP90α and HSP90β are highly expressed in peripheral mononuclear blood of patients with Ankylosing spondylitis [48]. HSP90α is involved in the regulation of rheumatoid arthritis [49] and osteoporosis [50]. FSH stimulates the expression of HSP90α and aggravates osteoporosis through FSHR independent of estrogen [50]. HSP90β regulates a variety of bone diseases, including multiple myeloma [51], rheumatoid arthritis [52], Ankylosing spondylitis [48], and osteoporosis [53]. However, the mechanism by which Hsp90β regulates osteoporosis is not well understood. In this study, we observed abnormally expression of Hsp90β, but not Hsp90α during RANKL-induced osteoclasotogenesis (Fig. 1A–F). Meanwhile, HSP90β is highly expressed in osteoclasts in OP patients (Fig. 1H), suggesting its distinct role in controlling osteoclast formation. For the first time, we constructed Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice. Deletion of Hsp90ab1 was found to hinder the formation of osteoclasts (Fig. 2). Our results are opposite to a former report in which the authors showed that knockdown of Hsp90aa1 and HSP90ab1 by siRNAs or pan-HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG promoted osteoclasotgenesis [54]. In this study, the authors used RAW-D cells (pre-osteoclasts, pre-OCs), selectively cloned from the RAWD264 cell line. We used both RAW264.7 cells and primary BMDMs from both Hsp90ab1f/f and Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice and the results are consistent. Raw264.7 cells are SV40 transformed peritoneal macrophages from a male BALB/c mouse. There are quite differences between RAW264.7 cell lines and primary cells. With continuous culture and passage, phenotypes and functions of the cell lines may change [55]. Therefore, responses observed in a cell line may not reflect normal physiology. In addition, chemical compounds and siRNAs normally have off-target effects [56, 57], 17-AAG and siRNAs induced osteoclastogenesis may not necessarily be caused by targeting HSP90. In Hsp90ab1f/f; LysM-Cre mice, OVX-induced bone loss was greatly reversed (Fig. 3). We also observed reduced TRAP+ osteoclasts in bone (Fig. 3M), consistent with our in vitro data. These evidences suggest that tissue-specific knockout mice models are irreplaceable to clarify the paralog-specific roles of HSP90.
We further looked for the transcription factor of Hsp90ab1 and found that c-Jun may regulate Hsp90ab1 (Fig. 5). JNK induces the activation of AP-1 (activating protein 1, formed by c-Jun/c-Fos heterodimers) [58]. Although activation of JNK1 [59], c-Fos [60] and c-Jun [61] are essential for osteoclastogenesis, the downstream signaling pathway remains elusive. Our results showed that in osteoclast precursors, when RANKL binds with RANK, the activated JNK increases Hsp90ab1 expression in a c-Jun dependent manner (Fig. 5F), subsequently stimulates both cholesterol biogenesis (Supplementary Fig. 3) and NF-κB activation (Fig. 4). These results expand our understanding of how RANKL/RANK pathway regulates osteoclast differentiation and causes osteoporosis.
Finally, by virtue screening, we found corylin, an active compound from Psoralea corylifolia, binds to HSP90β. Corylin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and improves OVX-induced bone loss by inhibiting the entry of NF-κB and Srebp2 into the nucleus (Supplementary Fig. 6). Here, we found increased ubiquitylation Ikkβ and decreased Ikkβ protein levels after the genetic or pharmacological inhibition of Hsp90β. Deceased Ikkβ leads to dephosphorylation and stabilization of IκB, which keeps NF-κB inactive. However, the detailed mechanism that caused the change of Ikkβ still remains elusive. The degradation machinery involved in Ikkβ during osteoclastogenesis needs to be further studied. In conclusion, our study illustrates for the first time how HSP90β participates in the osteoclasts differentiation process. In vivo experiments suggest that HSP90β might be a potential target for the treatment of OP.
Supplementary information
Change of authorship request form-Journals
Acknowledgements
We thank the State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, China Pharmaceutical University for providing experimental instruments. We thank Prof. Chaojun Li (Nanjing Medical University) for providing LysM-Cre mice.
Author contributions
XX, H-MC, ZZ performed research design. H-MC, MX, Y-PZ performed animal experiment. H-MC, MX, WZ, ZL, LL acquired the data. H-MC, MX analyzed the data. XX, H-MC drafted and revised the manuscript. YM, PL, XL, PL provided technical and material support. All authors contributed to the preparation of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Research & Development Program of China for International S&T Cooperation Projects (2018YFE0117800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773957), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2016-I2M-4-001), Beijing Outstanding Young Scientist Program (BJJWZYJH01201910023028), the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (2018RC350004, 2017PT31046).
Data availability
All data in this study are provided in the paper and Supplementary Materials. Additional data related to this study may be obtained from the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Laboratory Animal Management Committee of Jiangsu Province and the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of China Pharmaceutical University (Nanjing, China). This clinical study was approved by the Ethnic Committee of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences) and the Affiliated Nanjing Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, and written informed consents were obtained from the patients before procedure [31].
Footnotes
Edited by M Piacentini
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41418-022-01071-3.
References
- 1.Soysa NS, Alles N. Osteoclast function and bone-resorbing activity: An overview. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2016;476:115–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Starling S. New anti-osteoporosis drug target identified. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17:5–5. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-00441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wei HJ, Xu YH, Wang YB, Xu LT, Mo CY, Li LZ, et al. Identification of fibroblast activation protein as an osteogenic suppressor and anti-osteoporosis drug target. Cell Rep. 2020;33:108252. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Tu KN, Lie JD, Wan CKV, Cameron M, Austel AG, Nguyen JK, et al. Osteoporosis: a review of treatment options. P T. 2018;43:92–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ikebuchi Y, Aoki S, Honma M, Hayashi M, Sugamori Y, Khan M, et al. Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature. 2018;561:195–200. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM. The IKKNF-kappa B system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:17–26. doi: 10.1038/nrd1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clohisy JC, Yamanaka Y, Faccio R, Abu-Amer Y. Inhibition of IKK activation, through sequestering NEMO, blocks PMMA-induced osteoclastogenesis and calvarial inflammatory osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 2006;24:1358–65. doi: 10.1002/jor.20184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boyce BF, Xing LP. Biology of RANK, RANKL, and osteoprotegerin. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9:S1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Luegmayr E, Glantschnig H, Wesolowski GA, Gentile MA, Fisher JE, Rodan GA, et al. Osteoclast formation, survival and morphology are highly dependent on exogenous cholesterol/lipoproteins. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:S108–S118. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sato T, Morita I, Murota S. Involvement of cholesterol in osteoclast-like cell formation via cellular fusion. Bone. 1998;23:135–40. doi: 10.1016/S8756-3282(98)00082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grasser WA, Baumann AP, Petras SF, Harwood HJ, Jr., Devalaraja R, Renkiewicz R, et al. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by statins. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2003;3:53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ruan F, Zheng Q, Wang J. Mechanisms of bone anabolism regulated by statins. Biosci Rep. 2012;32:511–9. doi: 10.1042/BSR20110118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, Chan J, Chen D, Rossini G, et al. Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science. 1999;286:1946–9. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5446.1946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Meier CR, Schlienger RG, Kraenzlin ME, Schlegel B, Jick H. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the risk of fractures. JAMA. 2000;283:3205–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.24.3205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Inoue K, Imai Y. Fatostatin, an SREBP inhibitor, prevented RANKL-induced bone loss by suppression of osteoclast differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852:2432–41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Inoue K, Imai Y. Identification of novel transcription factors in osteoclast differentiation using genome-wide analysis of open chromatin determined by DNase-seq. J Bone Min Res. 2014;29:1823–32. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jie Z, Xie Z, Xu W, Zhao X, Jin G, Sun X, et al. SREBP-2 aggravates breast cancer associated osteolysis by promoting osteoclastogenesis and breast cancer metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865:115–25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zheng ZG, Zhang X, Zhou YP, Lu C, Thu PM, Qian C, et al. Anhydroicaritin, a SREBPs inhibitor, inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation and improves diabetic osteoporosis in STZ-induced mice. Eur J Pharm. 2017;809:156–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zheng ZG, Cheng HM, Zhou YP, Zhu ST, Thu PM, Li HJ, et al. Dual targeting of SREBP2 and ERRalpha by carnosic acid suppresses RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:2048–65. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0484-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Seo YH. Organelle-specific Hsp90 inhibitors. Arch Pharm Res. 2015;38:1582–90. doi: 10.1007/s12272-015-0636-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zheng ZG, Zhang X, Liu XX, Jin XX, Dai L, Cheng HM, et al. Inhibition of HSP90beta improves lipid disorders by promoting mature SREBPs Degradation via the Ubiquitin-proteasome System. Theranostics. 2019;9:5769–83. doi: 10.7150/thno.36505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Koga F, Xu W, Karpova TS, McNally JG, Baron R, Neckers L. Hsp90 inhibition transiently activates Src kinase and promotes Src-dependent Akt and Erk activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:11318–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604705103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yano A, Tsutsumi S, Soga S, Lee MJ, Trepel J, Osada H, et al. Inhibition of Hsp90 activates osteoclast c-Src signaling and promotes growth of prostate carcinoma cells in bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:15541–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805354105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Price JT, Quinn JM, Sims NA, Vieusseux J, Waldeck K, Docherty SE, et al. The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin, enhances osteoclast formation and potentiates bone metastasis of a human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4929–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.van der Kraan AG, Chai RC, Singh PP, Lang BJ, Xu J, Gillespie MT, et al. HSP90 inhibitors enhance differentiation and MITF (microphthalmia transcription factor) activity in osteoclast progenitors. Biochem J. 2013;451:235–44. doi: 10.1042/BJ20121626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lamoureux F, Thomas C, Yin MJ, Kuruma H, Fazli L, Gleave ME, et al. A novel HSP90 inhibitor delays castrate-resistant prostate cancer without altering serum PSA levels and inhibits osteoclastogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2301–13. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Broemer M, Krappmann D, Scheidereit C. Requirement of Hsp90 activity for IkappaB kinase (IKK) biosynthesis and for constitutive and inducible IKK and NF-kappaB activation. Oncogene. 2004;23:5378–86. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhang S, Wang P, Hu B, Liu W, Lv X, Chen S, et al. HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG attenuates nucleus pulposus inflammation and catabolism induced by M1-polarized macrophages. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:796974. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.796974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thangjam GS, Dimitropoulou C, Joshi AD, Barabutis N, Shaw MC, Kovalenkov Y, et al. Novel mechanism of attenuation of LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation by the heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, 17-N-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin, in human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;50:942–52. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0214OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wei W, Zhou J, Chen L, Liu H, Zhang F, Li J, et al. Plasma levels of heat shock protein 90 alpha associated with colorectal cancer development. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:684836. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.684836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fu R, Lv WC, Xu Y, Gong MY, Chen XJ, Jiang N, et al. Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:460. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14076-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kuo TR, Chen CH. Bone biomarker for the clinical assessment of osteoporosis: recent developments and future perspectives. Biomark Res. 2017;5:18. doi: 10.1186/s40364-017-0097-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Muller R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:1468–86. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boyce BF, Xiu Y, Li J, Xing L, Yao Z. NF-kappaB-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2015;30:35–44. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–40. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wei W, Schwaid AG, Wang XQ, Wang XD, Chen SL, Chu Q, et al. Ligand activation of ERR alpha by cholesterol mediates statin and bisphosphonate effects. Cell Metab. 2016;23:479–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, et al. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D108–110. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang X, Zhao W, Wang Y, Lu J, Chen X. The chemical constituents and bioactivities of psoralea corylifolia linn.: a review. Am J Chin Med. 2016;44:35–60. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X16500038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Theoleyre S, Wittrant Y, Tat SK, Fortun Y, Redini F, Heymann D. The molecular triad OPG/RANK/RANKL: involvement in the orchestration of pathophysiological bone remodeling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:457–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li LC, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF, Lee CT, Chen JB, Ruan XZ. Cross-talk between TLR4-MyD88-NF-kappaB and SCAP-SREBP2 pathways mediates macrophage foam cell formation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;304:H874–84. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00096.2012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cowen LE, Lindquist S. Hsp90 potentiates the rapid evolution of new traits: drug resistance in diverse fungi. Science. 2005;309:2185–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1118370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Miyata Y, Nakamoto H, Neckers L. The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:347–65. doi: 10.2174/138161213804143725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sha LZ, Wang XQ, Li J, Shi XZ, Wu LW, Shen Y, et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of Hsp90 to prevent GLT-1 degradation as an effective therapy for epilepsy. J Exp Med. 2017;214:547–63. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kuan YC, Hashidume T, Shibata T, Uchida K, Shimizu M, Inoue J, et al. Heat shock protein 90 modulates lipid homeostasis by regulating the stability and function of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) and SREBP cleavage-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:3016–28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.767277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Voss AK, Thomas T, Gruss P. Mice lacking HSP90beta fail to develop a placental labyrinth. Development. 2000;127:1–11. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Grad I, Cederroth CR, Walicki J, Grey C, Barluenga S, Winssinger N, et al. The molecular chaperone Hsp90 alpha is required for meiotic progression of spermatocytes beyond pachytene in the mouse. Plos One. 2010;5:e15770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Yu Z, Hong X, Zhang X, Zheng F, Liu F, Xu H, et al. Global proteomic analyses reveals abnormal immune regulation in patients with new onset ankylosing spondylitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:838891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang Q, Yao X, Ling Y, Huang Y, Chen C, Hou L, et al. Investigation of the mechanism of periploca forrestii against rheumatoid arthritis with network pharmacology-based analysis. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2022;2022:2993374. doi: 10.1155/2022/2993374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Huang J, Huang J, Hu W, Zhang Z. Heat shock protein 90 alpha and 14-3-3eta in postmenopausal osteoporotic rats with varying levels of serum FSH. Climacteric. 2020;23:581–90. doi: 10.1080/13697137.2020.1758055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Katiyar A, Kaur G, Rani L, Jena L, Singh H, Kumar L, et al. Genome-wide identification of potential biomarkers in multiple myeloma using meta-analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression data. Sci Rep. 2021;11:10957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90424-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rychkov D, Neely J, Oskotsky T, Yu S, Perlmutter N, Nititham J, et al. Cross-tissue transcriptomic analysis leveraging machine learning approaches identifies new biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:638066. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.638066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sun Y, Chen R, Zhu D, Shen ZQ, Zhao HB, Lee WH. Osteoking improves OP rat by enhancing HSP90beta expression. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45:1543–53. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tran MT, Okusha Y, Feng Y, Sogawa C, Eguchi T, Kadowaki T, et al. A novel role of HSP90 in regulating osteoclastogenesis by abrogating Rab11b-driven transport. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021;1868:119096. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Berghaus LJ, Moore JN, Hurley DJ, Vandenplas ML, Fortes BP, Wolfert MA, et al. Innate immune responses of primary murine macrophage-lineage cells and RAW 264.7 cells to ligands of Toll-like receptors 2, 3, and 4. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010;33:443–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2009.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.MacDonald ML, Lamerdin J, Owens S, Keon BH, Bilter GK, Shang Z, et al. Identifying off-target effects and hidden phenotypes of drugs in human cells. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:329–37. doi: 10.1038/nchembio790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jackson AL, Linsley PS. Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2010;9:57–67. doi: 10.1038/nrd3010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Angel P, Allegretto EA, Okino ST, Hattori K, Boyle WJ, Hunter T, et al. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988;332:166–71. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.David JP, Sabapathy K, Hoffmann O, Idarraga MH, Wagner EF. JNK1 modulates osteoclastogenesis through both c-Jun phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:4317–25. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Takayanagi H, Kim S, Matsuo K, Suzuki H, Suzuki T, Sato K, et al. RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-beta. Nature. 2002;416:744–9. doi: 10.1038/416744a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ikeda F, Nishimura R, Matsubara T, Tanaka S, Inoue J, Reddy SV, et al. Critical roles of c-Jun signaling in regulation of NFAT family and RANKL-regulated osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:475–84. doi: 10.1172/JCI200419657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Change of authorship request form-Journals
Data Availability Statement
All data in this study are provided in the paper and Supplementary Materials. Additional data related to this study may be obtained from the authors.