Abstract
More than fifteen million women with the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection are of childbearing age world-wide. Due to improved and affordable access to antiretroviral therapy (ART), the number of in utero antiretroviral drug (ARV)-exposed children has exceeded a million and continues to grow. While most recommended ART taken during pregnancy suppresses mother to child viral transmission, the knowledge of drug safety linked to fetal neurodevelopment remains an area of active investigation. For example, few studies have suggested that ARV use can be associated with neural tube defects (NTDs) and most notably with the integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) dolutegravir (DTG). After risk benefit assessments, the World Health Organization (WHO) made recommendations for DTG usage as a first and second-line preferred treatment for infected populations including pregnant women and those of childbearing age. Nonetheless, long-term safety concerns remain for fetal health. This has led to a number of recent studies underscoring the need for biomarkers to elucidate potential mechanisms underlying long-term neurodevelopmental adverse events. With this goal in mind, we now report the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) activities by INSTIs as an ARV class effect. Balanced MMPs activities play a crucial role in fetal neurodevelopment. Inhibition of MMPs activities by INSTIs during neurodevelopment could be a potential mechanism for adverse events. Thus, comprehensive molecular docking testing of the INSTIs, DTG, bictegravir (BIC), and cabotegravir (CAB), against twenty-three human MMPs showed broad-spectrum inhibition. With a metal chelating chemical property, each of the INSTI were shown to bind Zn++ at the MMP’s catalytic domain leading to MMP inhibition but to variable binding energies. These results were validated in myeloid cell culture experiments demonstrating MMP-2 and 9 inhibitions by DTG, BIC and CAB and even at higher degree than doxycycline (DOX). Altogether, these data provide a potential mechanism for how INSTIs could affect fetal neurodevelopment.
Keywords: HIV-1, pregnancy, antiretroviral drugs, integrase strand transfer inhibitors, neurodevelopment, drug-induced adverse events
Introduction
Pregnant women and women of child bearing age infected with the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infection have benefited by antiretroviral therapy (ART) in the reduction of maternal fetal viral transmission (The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2015; World Health Organization (WHO), 2019a). Currently, more than 15.5 million women of child-bearing age are HIV-1 infected, worldwide (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), 2021a). In 2020, eighty five percent of HIV-1-infected pregnant women were on ART (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), 2021a). Due to such broad usage of ART during pregnancy, the rate of vertical transmission of HIV-1 has reduced to less than 1% (The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 2018; Peters et al., 2017; Schnoll et al., 2019; Rasi et al., 2022; The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), 2021b). This includes resource-limited countries (RLCs), which currently hold up to two-thirds of the world’s total HIV-1 infected population (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), 2021b). However, along with the significant benefits in reducing infection-associated morbidities and mortalities, there remains risks of ART-linked adverse events (Hill et al., 2018). As over a million ARV-exposed HIV-1 uninfected children are born each year (Ramokolo et al., 2019; Crowell et al., 2020), an appreciation of adverse pregnancy events, in particular, related to ARVs is certainly warranted.
Herein, we particularly focused on HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), a relatively new class of ARVs. Raltegravir (RAL), elvitegravir (EVG), dolutegravir (DTG), bictegravir (BIC), and cabotegravir (CAB) are the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved INSTIs for the treatment of HIV-1 infected patients (Smith et al., 2021). In recent years, widespread usage of INSTIs have emerged related to their efficacy and high barrier to viral drug resistance (Smith et al., 2021). Indeed, these antiretrovirals are currently part of preferred first- and second-line ART regimens (World Health Organization (WHO), 2016; Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS), 2022). Moreover, increasing pretreatment resistance to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in RLCs, especially in women, increases usage of INSTI-based regimens (World Health Organization (WHO), 2019a; World Health Organization (WHO), 2019b). During pregnancy, DTG and RAL are preferred drugs in combination therapy with a preferred dual-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) backbone. EVG, BIC or CAB are not recommended during pregnancy due to limited safety data (The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2015). Recently DTG was found to be potentially associated with birth defects (NTDs) and postnatal neurodevelopmental abnormalities (Hill et al., 2018; Cabrera et al., 2019; Zash et al., 2019; Crowell et al., 2020; Mohan et al., 2020; Bade et al., 2021). Given the widescale usage of DTG as a part of first-line regimens worldwide (Hill et al., 2018; Dorward et al., 2018; World Health Organization (WHO), 2018; The Lancet, 2020) and emerging potent INSTIs such as BIC and CAB, uncovering any INSTIs-associated adverse effects and thus, the underlying mechanisms is of importance.
Pre-clinical and clinical research have served to evaluate interaction between folate levels or transport pathways and DTG or other INSTIs for any developmental toxicity (Cabrera et al., 2019; Chandiwana et al., 2020; Gilmore et al., 2022). However, results have failed to conclusively establish cause-and-effect relationships (Cabrera et al., 2019; Chandiwana et al., 2020; Gilmore et al., 2022). No other biomarker linked to INSTI drug-induced adverse events has been explored. We demonstrated that DTG is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) (Bade et al., 2021). MMPs are known to play a role in many neurodevelopmental processes, including, but not limited to axonal growth and guidance, synaptic development and plasticity (Ethell and Ethell, 2007; Agrawal et al., 2008; Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; De Stefano and Herrero, 2017). Therefore, dysregulation of their activities could affect fetal neurodevelopment (Reinhard et al., 2015; Bade et al., 2021). Docking assessments against five MMPs showed that DTG binds to Zn++ at the catalytic domain of an MMP to inhibit the enzyme’s activity. Moreover, such MMPs inhibition can affect mice fetal neurodevelopment following DTG administration to pregnant dams at the time of conception. Clinical reports of adverse events associated with INSTIs have demonstrated class effects. Therefore, it is prudent to determine whether other ARVs from the INSTI class are inhibitors of MMPs and consider this as a potential mechanism of INSTIs-related adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. Moreover, such biomarker discovery against MMP enzymes will help to understand potential genetic susceptibility. Herein, we show, for the first time, comprehensive computational molecular docking assessments of DTG, BIC or CAB against each one of the twenty-three human MMP enzymes. Further, inhibition potency of each INSTI was validated using a cell culture model. To this end, we show that inhibition of MMPs activities is an INSTI class effect and warranting assessments to determine the effect of drug-induced effects on the gestational environment and fetal neurodevelopment.
Methods
Molecular docking
Homology models of all 23 known human MMPs (MMP-1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, and 28) were generated. This was done on a template of MMP-2 (PDB ID: 1HOV) using the Homology Modeling module of the YASARA Structure program package (Krieger and Vriend, 2014). The Schrodinger software suite release 2020–4 (New York, NY) was used for all molecular dynamic simulations and molecular docking calculations. All molecules were parametrized using the OPLS3e force field (Harder et al., 2016). Each homology model was placed in an orthorhombic box of TIP4P water with periodic boundaries; at least 10 Å from any solute molecule. The simulation cells were neutralized with the addition of Na + or Cl− ions. Production molecular dynamics were run for 500 ns with default settings. The representative structure of the largest cluster from each simulation was chosen for docking calculations. Induced-fit binding as implemented in Schrodinger was used with default settings, except that the high-accuracy XP mode was chosen for Glide docking. All ranked poses were required to have at least one bond with the active site zinc ion; other poses were not considered.
Gelatin zymography
Gelatin zymography was performed to assess MMP-9 and -2 activity following treatment of THP-1 cells with DTG, CAB, BIC, or DOX. This assay was used as preliminary confirmation of the inhibition of MMPs by individual INSTIs. Due to the nature of this assay, only the gelatinases, MMP-2 and -9, could be assessed. Cells were plated at a density of 1 × 106 in 12 well plates and treated with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) for 24 h. This was done to promote cell differentiation to stimulate MMP secretion. Following PMA treatment, cells were treated with DTG, CAB, BIC, or DOX at concentrations of 25, 50, 75, or 100 µM or control vehicle for 24 h. In our previous study, no DTG-induced cytotoxicity was recorded in PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells up to 100 µM (Bade et al., 2021). Thus, for comparative assessments among different INSTIs (DTG, BIC, and CAB) and DOX (positive control) drug concentrations of up to 100 µM were utilized. Each of the experimental tests were performed in triplicate. Following treatment, media was collected and centrifuged at 15,000 x g for 10 min at 4°C. Supernatant was collected and stored at −80°C for further analysis. For gelatin zymography, 3 µg of protein from cell medium was loaded in a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel containing 0.1% gelatin. Gels were ran at 55 V until the loading dye passed through its bottom. The gel was then removed and washed with water for 15 min, then incubated with renaturation buffer [2.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 in Milli-Q water] for 90 min at room temperature. The used renaturation buffer was replaced with fresh buffer every 30 min. Renaturation buffer was then replaced with developing buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 5 mM CaCl2, 0.2 M NaCl, and 0.02% Brij-35) and the gel was incubated at 37°C in a shaker (Innova 42, New Brunswick Scientifc, Edison, NJ) for 48 h. After 48 h, the gel was washed with water for 15 min and then stained using 0.2% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA) for 1 h. After staining, the gel was washed with water for 15 min before washing with destaining solution (30% methanol, 10% acetic acid, 60% water) for 45 min. The gel was then washed with water for 20 min to remove any destaining solution. Finally, the stained gel was imaged using the iBright 750 Imaging System (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). ImageJ software was used to quantitate band density recorded as a measure of relative MMP activity.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (La Jolla, CA). Data from in vitro studies were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) with a minimum of 3 biological replicates. A one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s or Dunnett’s test was used to compare three or more groups. Statistical significance was denoted as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Results
INSTIs chelate Zn++ at the catalytic domain of MMPs
Molecular dockings were completed using Schrodinger’s software to identify the mechanism through which each INSTI interacts with the catalytic domain structures of the human MMPs. Here, we used DTG, BIC and CAB for assessments. MMPs are Zn++ dependent endopeptidases. INSTIs possess a prominent metal-binding pharmacophore (MBP) also, referred to as a metal-binding group or MBG in their chemical structure. Based on these chemical abilities for binding to the metal ions we hypothesized that DTG, BIC or CAB can inhibit MMPs activities by binding to Zn++ at the catalytic domain of the protein structure. Herein, induced fit docking used a combination of the Glide and Prime programs in the Schrodinger suite. All docking scores used the highest accuracy Glide XP mode. Previously, we reported interaction of DTG with five MMPs, MMP-2, 8, 9, 14, and 19 and interaction of CAB or BIC with MMP-2 and -14 as proof-of-concept evaluations (Bade et al., 2021). Herein, as 23 MMPs are known to be found in humans, molecular docking interaction was tested against each of these enzymes to find the highest binding interaction for DTG, BIC or CAB and determine whether any individual MMP could have genetic susceptibility against these INSTIs.
DTG formed a metal coordination complex with Zn++. This was recorded in the catalytic domain of each of the MMPs tested. Metal coordination of DTG with Zn++ occurred at Zn 166, 166, 479, 269, 469, 709, 478, 490, 472, 473, 584, 671, 609, 605, 510, 485, 571, 485, 647, 564, 263, 515, and 522 receptors of MMP-1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, and 28, respectively. DTG also formed other interactions with Zn++, which included cation pi interactions. These interactions occurred at Zn 490, 605, and 522 receptors of MMP-11, 17, and 28 respectively. Other interactions included pi stacking and hydrogen bonding. Pi stacking occurred with histidine amino acids of all tested MMPs except MMP-7, 9, 19, and 27. Pi stacking also occurred with tyrosine amino acids, but only with MMP-3, 11, and 16. Hydrogen bond interactions occurred at glutamate amino acid residues of MMP-1, 3, 10, 12, 15, 16, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, and 26; alanine amino acid residues of MMP-2, 7, 8, 11, 14, 17, and 19; leucine amino acid residues of MMP-7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 20, 23, 24, 25, and 26; glycine amino acid residues of MMP-9 and 27; tyrosine amino acid residues of MMP-9 and 27; asparagine 170 amino acid residue of MMP-8; proline 421 amino acid residue of MMP-9; phenylalanine 249 of MMP-21; and glutamine 247 of MMP-21. The distances of all the receptor-ligand bonds are shown in the respective DTG-MMP interaction table (Table 1). Docking simulation of DTG into individual MMP showed binding energy of −6.032, −6.450, −6.253, −7.243, −8.330, −9.430, −6.686, −6.210, −6.713, −6.461, −9.040, −5.885, −7.325, −6.810, −7.130, −6.097, −6.179, −6.213, −6.917, −6.865, −7.198, −7.427 or −6.012 kcal/mol for MMP-1 to −28, respectively (Table 4). Overall, observed high binding energies from the docking simulation validated docking interactions in Table 1. Moreover, these docking assessments confirmed that DTG is a broad-spectrum inhibitor, and it inhibits all MMPs activities by chelating Zn++ at the catalytic domain.
TABLE 1.
Dolutegravir (DTG)- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) Interactions.
| MMP-1 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 218 | Pi stacking | 3.60 |
| NH | Glu 219 | Hydrogen bond | 1.98 |
| O2 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.01 |
| MMP-2 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 120 | Pi stacking | 3.59 |
| NH | Ala 84 | Hydrogen bond | 2.28 |
| O1 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.19 |
| O2 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.21 |
| MMP-3 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 218 | Pi stacking | 3.57 |
| Ar1 | Tyr 240 | Pi stacking | 5.32 |
| NH | Glu 219 | Hydrogen bond | 2.36 |
| O2 | Zn 479 | Metal coordination | 2.13 |
| MMP-7 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 176 | Hydrogen bond | 2.02 |
| O1 | Ala 177 | Hydrogen bond | 2.07 |
| O2 | Zn 269 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| MMP-8 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 217 | Pi stacking | 3.8 |
| O1 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.93 |
| O1 | Ala 181 | Hydrogen bond | 2.32 |
| O2 | Zn 469 | Metal coordination | 2.02 |
| O5 | Asn 170 | Hydrogen bond | 1.91 |
| MMP-9 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| NH | Gly 186 | Hydrogen bond | 1.87 |
| O1 | Try 423 | Hydrogen bond | 1.96 |
| O3 | Pro 421 | Hydrogen bond | 2.09 |
| O4 | Zn 709 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| O5 | Leu 188 | Hydrogen bond | 2.80 |
| MMP-10 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 217 | Pi stacking | 3.42 |
| NH | Glu 218 | Hydrogen bond | 1.99 |
| O1 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 2.67 |
| O2 | Zn 478 | Metal coordination | 2.15 |
| MMP-11 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 215 | Pi stacking | 4.03 |
| Ar1 | Tyr 237 | Pi Stacking | 5.48 |
| Ar1 | Zn 490 | Cation pi | 4.63 |
| NH | Ala 178 | Hydrogen bond | 1.91 |
| O2 | Zn 490 | Metal coordination | 2.13 |
| MMP-12 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 218 | Pi stacking | 3.75 |
| NH | Glu 219 | Hydrogen bond | 2.22 |
| O1 | Leu 181 | Hydrogen bond | 2.1 |
| O2 | Zn 472 | Metal coordination | 2.13 |
| MMP-13 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 222 | Pi stacking | 3.72 |
| O2 | Zn 473 | Metal coordination | 2.07 |
| MMP-14 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar2 | His 239 | Pi stacking | 3.49 |
| O3 | Ala 258 | Hydrogen bond | 1.87 |
| O4 | Zn 584 | Metal coordination | 2.12 |
| MMP-15 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 259 | Pi stacking | 3.4 |
| NH | Glu 260 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| O1 | Leu 219 | Hydrogen bond | 2.22 |
| O2 | Zn 671 | Metal coordination | 2.06 |
| MMP-16 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 246 | Pi stacking | 3.34 |
| Ar1 | Tyr 268 | Pi Stacking | 5.43 |
| NH | Glu 247 | Hydrogen bond | 2.11 |
| O1 | Leu 206 | Hydrogen bond | 2.07 |
| O2 | Zn 609 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| MMP-17 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 259 | Pi stacking | 3.89 |
| Ar1 | Zn 605 | Cation pi | 4.72 |
| NH | Ala 208 | Hydrogen bond | 1.89 |
| O2 | Zn 605 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| MMP-19 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Zn 510 | Metal coordination | 2.10 |
| O3 | Ala 231 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| O4 | Glu 235 | Hydrogen bond | 2.14 |
| MMP-20 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 226 | Pi stacking | 3.49 |
| NH | Glu 227 | Hydrogen bond | 2.06 |
| O1 | Leu 189 | Hydrogen bond | 2.26 |
| O2 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| MMP-21 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 283 | Pi stacking | 3.52 |
| NH | Glu 284 | Hydrogen bond | 2.00 |
| O1 | Phe 249 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| O2 | Zn 571 | Metal coordination | 2.11 |
| O5 | Gln 247 | Hydrogen bond | 2.60 |
| MMP-23 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 226 | Pi stacking | 3.59 |
| NH | Glu 227 | Hydrogen bond | 2.18 |
| O1 | Leu 189 | Hydrogen bond | 2.23 |
| O2 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| MMP-24 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 282 | Pi stacking | 3.44 |
| NH | Glu 283 | Hydrogen bond | 2.19 |
| O1 | Leu 242 | Hydrogen bond | 2.20 |
| O2 | Zn 647 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| MMP-25 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 233 | Pi stacking | 3.43 |
| NH | Glu 234 | Hydrogen bond | 2.63 |
| O1 | Leu 192 | Hydrogen bond | 2.06 |
| O2 | Zn 564 | Metal coordination | 2.02 |
| MMP-26 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 208 | Pi stacking | 3.41 |
| NH | Glu 209 | Hydrogen bond | 2.6 |
| O1 | Leu 171 | Hydrogen bond | 2.46 |
| O2 | Zn 263 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| MMP-27 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| NH | Gly 177 | Hydrogen bond | 2.08 |
| O1 | Tyr 238 | Hydrogen bond | 1.79 |
| O3 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.22 |
| O4 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.27 |
| MMP-28 interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 240 | Pi stacking | 3.87 |
| Ar1 | Zn 522 | Cation pi | 4.75 |
| O2 | Zn 522 | Metal coordination | 2.12 |
TABLE 4.
Binding energies for each MMP with DTG, CAB or BIC.
| Structure | DTG [Energy (kcal/mol)] | CAB [Energy (kcal/mol)] | BIC [Energy (kcal/mol)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-1 | −6.032 | −14.251 | −14.55 |
| MMP-2 | −6.450 | −8.588 | −10.972 |
| MMP-3 | −6.253 | −15.222 | −15.082 |
| MMP-7 | −7.243 | −12.305 | −11.385 |
| MMP-8 | −8.330 | −14.337 | −15.771 |
| MMP-9 | −9.430 | −14.222 | −13.415 |
| MMP-10 | −6.686 | −14.592 | −16.021 |
| MMP-11 | −6.210 | −10.352 | −12.143 |
| MMP-12 | −6.713 | −12.19 | −13.482 |
| MMP-13 | −6.461 | −11.798 | −12.73 |
| MMP-14 | −9.040 | −12.983 | −14.539 |
| MMP-15 | −5.885 | −9.632 | −8.877 |
| MMP-16 | −7.325 | −12.249 | −14.625 |
| MMP-17 | −6.810 | −11.666 | −12.409 |
| MMP-19 | −7.130 | −12.718 | −11.695 |
| MMP-20 | −6.097 | −12.413 | −11.923 |
| MMP-21 | −6.179 | −14.389 | −12.698 |
| MMP-23 | −6.213 | −13.109 | −12.25 |
| MMP-24 | −6.917 | −15.339 | −10.181 |
| MMP-25 | −6.865 | −11.62 | −11.716 |
| MMP-26 | −7.198 | −12.381 | −11.971 |
| MMP-27 | −7.427 | −12.614 | −12.54 |
| MMP-28 | −6.012 | −10.11 | −10.823 |
Notably, CAB also formed a metal coordination complex with Zn++ in the catalytic domain of all tested MMPs. Metal coordination of CAB with Zn++ occurred at Zn 471, 166, 479, 269, 469, 709, 478, 490, 472, 473, 584, 671, 609, 605, 510, 485, 571, 392, 647, 564, 263, 515, and 522 receptors of MMP-1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, and 28, respectively. However, CAB also formed salt bridges with Zn++ of all tested MMPs. In addition, salt bridge interactions occurred with glutamate amino acids of MMP-1, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 17, 19, 21, 23, 24, and 26. Salt bridges with Zn++ or with other amino acids were not observed with any of DTG-MMP interactions. Other interactions between CAB and MMPs were cation pi, pi stacking and hydrogen bonding. Cation pi interactions occurred at histidine 263 and phenylalanine 205 of MMP-15 and 16 respectively. Pi stacking interactions occurred with histidine amino acids of MMP-1, 2, 11, 12, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, and 28; phenylalanine amino acids of MMP-1 and 16; tyrosine amino acids of MMP-2, 14, and 19. Hydrogen bonding of CAB with tested MMPs was found, except MMP-17. Like DTG, CAB was found to produce hydrogen bonding with leucine, alanine, glutamate, phenylalanine, glycine, proline, asparagine, and tyrosine amino acid residues. However, other hydrogen bonding occurred at serine 239 amino acid residue of MMP-1, valine 233 amino acid residue of MMP-19, and arginine 240 amino acid residue of MMP-23. The distances of all the receptor-ligand bonds are shown in the respective CAB-MMP interaction table (Table 2). Docking simulation of CAB into individual MMP showed binding energy of −14.251, −8.588, −15.222, −12.305, −14.337, −14.222, −14.592, −10.352, −12.19, −11.798, −12.983 −9.632, −12.249, −11.666, −12.718, −12.413, −14.389, −13.109, −15.339, −11.62, −12.381, −12.614, or −10.11 kcal/mol for MMP-1 to −28, respectively (Table 4). Altogether, observed high binding energies from the docking simulation and docking interactions (Table 1; Table 4) evaluations confirmed that CAB is a broad-spectrum inhibitor, and it inhibits all MMPs activities by binding to Zn++ at the catalytic domain.
TABLE 2.
Cabotegravir (CAB)- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) Interactions.
| MMP-1 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 218 | Pi stacking | 4.9 |
| Ar1 | Phe 242 | Pi stacking | 5.28 |
| O2 | Ser 239 | Hydrogen bond | 2.28 |
| O2 | Zn 471 | Salt bridge | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 471 | Metal coordination | 2.08 |
| O3 | Zn 471 | Salt bridge | 2.08 |
| N2 | Glu 219 | Salt bridge | 4.91 |
| MMP-2 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 120 | Pi stacking | 3.34 |
| Ar1 | Tyr 142 | Pi stacking | 5.07 |
| O1 | Leu 83 | Hydrogen bond | 1.99 |
| O1 | Ala 84 | Hydrogen bond | 2.40 |
| O2 | Glu 121 | Hydrogen bond | 1.92 |
| O2 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.25 |
| O3 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O3 | Zn 166 | Salt bridge | 2.05 |
| MMP-3 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 181 | Hydrogen bond | 1.76 |
| N1 | Pro 238 | Hydrogen bond | 1.96 |
| O2 | Zn 479 | Metal coordination | 2.41 |
| O3 | Zn 479 | Metal coordination | 2.00 |
| O3 | Zn 479 | Salt bridge | 2.00 |
| MMP-7 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 176 | Hydrogen bond | 2.05 |
| O1 | Ala 177 | Hydrogen bond | 2.1 |
| O2 | Glu 215 | Hydrogen bond | 2.14 |
| O2 | Zn 269 | Metal coordination | 2.39 |
| O3 | Zn 269 | Metal coordination | 2.01 |
| O3 | Zn 269 | Salt bridge | 2.01 |
| MMP-8 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Asn 170 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| O3 | Zn 469 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 469 | Salt bridge | 2.14 |
| N2 | Glu 218 | Salt bridge | 4.78 |
| O4 | Zn 469 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O5 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.76 |
| MMP-9 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| N1 | Pro 421 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| O1 | Leu 188 | Hydrogen bond | 1.95 |
| O2 | Zn 709 | Metal coordination | 2.24 |
| N2 | Glu 402 | Salt bridge | 4.73 |
| O3 | Zn 709 | Metal coordination | 1.98 |
| O3 | Zn 709 | Salt bridge | 1.98 |
| MMP-10 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| N1 | Pro 237 | Hydrogen bond | 2.24 |
| O1 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.95 |
| O2 | Zn 478 | Metal coordination | 2.37 |
| O3 | Zn 478 | Metal coordination | 1.92 |
| O3 | Zn 478 | Salt bridge | 1.92 |
| N2 | Glu 218 | Salt bridge | 4.77 |
| MMP-11 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 215 | Pi stacking | 3.98 |
| O1 | Leu 177 | Hydrogen bond | 2.2 |
| O2 | Zn 490 | Metal coordination | 2.08 |
| O3 | Zn 490 | Metal coordination | 2.10 |
| O3 | Zn 490 | Salt bridge | 2.10 |
| MMP-12 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 183 | Pi stacking | 4.16 |
| O3 | Zn 472 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O3 | Zn 472 | Salt bridge | 2.05 |
| N2 | Glu 219 | Salt bridge | 4.27 |
| O4 | Zn 472 | Metal coordination | 2.23 |
| O5 | Leu 181 | Hydroen bond | 1.94 |
| MMP-13 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| N1 | Pro 242 | Hydrogen bond | 2.11 |
| O1 | Leu 185 | Hydrogen bond | 2.11 |
| O2 | Zn 473 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| O3 | Zn 473 | Metal coordination | 1.92 |
| O3 | Zn 473 | Salt bridge | 1.92 |
| MMP-14 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 239 | Pi stacking | 3.76 |
| Ar1 | Tyr 261 | Pi stacking | 5.36 |
| Ar2 | His 239 | Pi stacking | 4.98 |
| O2 | Zn 584 | Metal coordination | 2.33 |
| O3 | Zn 584 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O3 | Zn 584 | Salt bridge | 2.05 |
| O5 | Ala 202 | Hydrogen bond | 2.42 |
| N1 | Glu 240 | Hydrogen bond | 2.15 |
| N2 | Glu 240 | Salt bridge | 3.15 |
| MMP-15 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | Tyr 223 | Pi stack | 4.84 |
| O1 | Ala 222 | Hydrogen bond | 1.94 |
| O2 | Glu 260 | Hydrogen bond | 2.23 |
| O3 | Zn 671 | Metal coordination | 1.96 |
| O3 | Zn 671 | Salt bridge | 1.96 |
| N2 | His 263 | Cation pi | 5.84 |
| O4 | Zn 671 | Metal coordination | 2.29 |
| MMP-16 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 206 | Hydrogen bond | 2.17 |
| O1 | Ala 207 | Hydrogen bond | 1.84 |
| O2 | Glu 247 | Hydrogen bond | 1.74 |
| O2 | Zn 609 | Metal coordination | 2.49 |
| Ar2 | Phe 205 | Pi stacking | 4.25 |
| O3 | Zn 609 | Metal coordination | 2.03 |
| O3 | Zn 609 | Salt bridge | 2.03 |
| N2 | Phe 205 | Cation pi | 3.97 |
| MMP-17 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 248 | Pi stacking | 4.3 |
| O2 | Zn 605 | Metal coordination | 1.98 |
| O3 | Zn 605 | Salt bridge | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 605 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| N2 | Glu 249 | Salt bridge | 4.98 |
| MMP-19 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O2 | Val 233 | Hydrogen bond | 1.53 |
| Ar2 | His 212 | Pi stacking | 3.92 |
| Ar2 | Tyr 234 | Pi stacking | 4.27 |
| O3 | Zn 510 | Metal coordination | 2.13 |
| O3 | Zn 510 | Salt bridge | 2.13 |
| N2 | Glu 213 | Salt bridge | 3.36 |
| O4 | Zn 510 | Metal coordination | 2.42 |
| MMP-20 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 189 | Hydrogen bond | 1.86 |
| O1 | Ala 190 | Hydrogen bond | 2.1 |
| O2 | Glu 227 | Hydrogen bond | 1.94 |
| O2 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 2.37 |
| O3 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 2.15 |
| O3 | Zn 485 | Salt bridge | 2.15 |
| MMP-21 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 283 | Pi stacking | 4.76 |
| N1 | Glu 284 | Hydrogen bond | 1.69 |
| O1 | Phe 249 | Hydrogen bond | 2.1 |
| O2 | Zn 571 | Metal coordination | 2.11 |
| O3 | Zn 571 | Metal coordination | 2.15 |
| O3 | Zn 571 | Salt bridge | 2.15 |
| N2 | Glu 248 | Salt bridge | 4.83 |
| O5 | Arg 240 | Hydrogen bond | 1.87 |
| MMP-23 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 211 | Pi stacking | 4.19 |
| O1 | Leu 168 | Hydrogen bond | 2.01 |
| O2 | Ala 169 | Hydrogen bond | 2.48 |
| O2 | Glu 212 | Hydrogen bond | 2.25 |
| O3 | Zn 392 | Metal coordination | 2 |
| O3 | Zn 392 | Salt bridge | 2 |
| N2 | Glu 167 | Salt bridge | 3.36 |
| MMP-24 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 242 | Hydrogen bond | 2.14 |
| O2 | Zn 647 | Metal coordination | 2.28 |
| O3 | Zn 647 | Salt bridge | 2.12 |
| O3 | Zn 647 | Metal coordination | 2.12 |
| N2 | Glu 283 | Salt bridge | 4.63 |
| MMP-25 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 233 | Pi stacking | 3.52 |
| O1 | Leu 192 | Hydrogen bond | 1.79 |
| O1 | Ala 193 | Hydrogen bond | 2.02 |
| O2 | Glu 234 | Hydrogen bond | 1.72 |
| O2 | Zn 564 | Metal coordination | 2.18 |
| O3 | Zn 564 | Salt bridge | 2.06 |
| O3 | Zn 564 | Metal coordination | 2.06 |
| MMP-26 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O3 | Zn 263 | Metal coordination | 1.99 |
| O3 | Zn 263 | Salt bridge | 1.99 |
| N2 | Glu 209 | Salt bridge | 4.9 |
| O4 | Zn 263 | Metal coordination | 2.22 |
| O5 | Leu 171 | Hydrogen bond | 1.92 |
| MMP-27 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Gly 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.99 |
| O2 | Glu 217 | Hydrogen bond | 1.66 |
| O2 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.48 |
| O3 | Zn 515 | Salt bridge | 2.11 |
| O3 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.11 |
| MMP-28 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 240 | Pi stacking | 3.92 |
| O1 | Leu 205 | Hydrogen bond | 2.01 |
| O1 | Ala 206 | Hydrogen bond | 2.41 |
| O2 | Ala 206 | Hydrogen bond | 2.57 |
| O2 | Glu 241 | Hydrogen bond | 2.34 |
| O2 | Zn 522 | Metal coordination | 2.35 |
| O3 | Zn 522 | Metal coordination | 2.19 |
| O3 | Zn 522 | Salt bridge | 2.19 |
Further, docking simulation confirmed that BIC formed a metal coordination complex with Zn++ in the catalytic domain of all tested MMPs, validating that all INSTIs possess chemical abilities to inhibits MMPs activities by chelating Zn++ at the catalytic domain. Metal coordination of BIC with Zn++ occurred at Zn 471, 166, 479, 269, 469, 709, 478, 490, 472, 473, 584, 671, 609, 605, 510, 485, 571, 392, 647, 564, 263, 515, and 522 receptors of MMP-1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, and 28, respectively. Like CAB, BIC also formed salt bridges with Zn++ of all tested MMPs. Along with Zn++, BIC was found to form salt bridge interactions with glutamate amino acids of all tested MMPs except MMP-2, 13, 15, 24 and 26. Cation pi interactions occurred only at phenylalanine 241 of MMP-24. Pi stacking interactions occurred with histidine amino acids of MMP-1, 9, 14, 17, 24, 26, 27, and 28; tyrosine amino acids of MMP-3, 10, 16, and 19, phenylalanine amino acids of MMP-12 and 24; tryptophan amino acid of MMP-26. Hydrogen bonding of BIC was observed with all MMPs except MMP-2, 19, 28. Like DTG and CAB, BIC was found to form hydrogen bonds with asparagine, histidine, leucine, alanine, proline, glutamate, valine, phenylalanine, glycine, and arginine amino acid residues. The distances of all the receptor-ligand bonds are shown in the respective BIC-MMP interaction table (Table 3). Docking simulation of BIC into individual MMP showed binding energy of −14.55, −10.972, −15.082, −11.385, −15.771, −13.415, −16.021, −12.143, −13.482, −12.73, −14.539, −8.877, −14.625, −12.409, −11.695, −11.923, −12.698, −12.25, −10.181, −11.716, −11.971, −12.54, and −10.823 kcal/mol for MMP-1 to −28, respectively (Table 4). Observed high binding energies and docking interactions (Table 1; Table 4) confirmed that BIC is a broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitor.
TABLE 3.
Bictegravir (BIC)- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) Interactions.
| MMP-1 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 183 | Pi stacking | 4.4 |
| O1 | Asn 179 | Hydrogen bond | 1.99 |
| O1 | His 183 | Hydrogen bond | 2.64 |
| O3 | Zn 471 | Metal coordination | 1.99 |
| O3 | Zn 471 | Salt bridge | 1.99 |
| O4 | Zn 471 | Metal coordination | 2.2 |
| O4 | Glu 219 | Salt bridge | 4.4 |
| O5 | Leu 181 | Hydrogen bond | 2.38 |
| MMP-2 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O2 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.24 |
| O3 | Zn 166 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O3 | Zn 166 | Salt bridge | 2.05 |
| MMP-3 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | Tyr 185 | Pi stacking | 5.35 |
| O3 | Zn 479 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| O3 | Zn 479 | Salt bridge | 2.09 |
| N2 | Glu 219 | Salt bridge | 4.64 |
| O4 | Zn 479 | Metal coordination | 2.13 |
| O5 | Leu 181 | Hydrogen bond | 2.25 |
| MMP-7 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Ala 179 | Hydrogen bond | 2.06 |
| N2 | Glu 215 | Salt bridge | 4.86 |
| O3 | Zn 269 | Metal coordination | 2.04 |
| O3 | Zn 269 | Salt bridge | 2.04 |
| O4 | Zn 269 | Metal coordination | 2.07 |
| MMP-8 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Asn 170 | Hydrogen bond | 2.19 |
| O3 | Zn 469 | Metal coordination | 2.04 |
| O3 | Zn 469 | Salt bridge | 2.04 |
| N2 | Glu 218 | Salt bridge | 4.71 |
| O4 | Zn 469 | Metal coordination | 2.29 |
| O5 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 2.3 |
| MMP-9 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 401 | Pi stacking | 3.84 |
| O2 | Pro 421 | Hydrogen bond | 2.28 |
| O2 | Zn 709 | Metal coordination | 2.29 |
| O3 | Zn 709 | Metal coordination | 2.01 |
| O3 | Zn 709 | Salt bridge | 2.01 |
| N2 | Glu 402 | Salt bridge | 4.3 |
| MMP-10 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | Tyr 184 | Pi stacking | 5.01 |
| O1 | Ala 183 | Hydrogen bond | 2.03 |
| N2 | Glu 218 | Salt bridge | 4.58 |
| O3 | Zn 478 | Metal coordination | 1.96 |
| O3 | Zn 478 | Salt bridge | 1.96 |
| O4 | Zn 478 | Metal coordination | 2.11 |
| O5 | Leu 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.96 |
| MMP-11 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Ala 180 | Hydrogen bond | 1.91 |
| O3 | Zn 490 | Metal coordination | 2.26 |
| O3 | Zn 490 | Salt bridge | 2.26 |
| N2 | Glu 216 | Salt bridge | 4.69 |
| O4 | Zn 490 | Metal coordination | 2.21 |
| O5 | Leu 177 | Hydrogen bond | 1.9 |
| MMP-12 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | Phe 171 | Pi stacking | 5.1 |
| O1 | His 172 | Hydrogen bond | 2.01 |
| O3 | Zn 472 | Metal coordination | 2.03 |
| O3 | Zn 472 | Salt bridge | 2.03 |
| N2 | Glu 219 | Salt bridge | 4.44 |
| O4 | Zn 472 | Metal coordination | 2.02 |
| O5 | Leu 181 | Hydrogen bond | 1.91 |
| MMP-13 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 185 | Hydrogen bond | 1.92 |
| O1 | Ala 186 | Hydrogen bond | 1.85 |
| O2 | Glu 223 | Hydrogen bond | 1.98 |
| O3 | Zn 473 | Metal coordination | 1.99 |
| O3 | Zn 473 | Salt bridge | 1.99 |
| MMP-14 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 239 | Pi stacking | 3.69 |
| O1 | Leu 199 | Hydrogen bond | 2.61 |
| O2 | Zn 584 | Metal coordination | 2.24 |
| O3 | Zn 584 | Metal coordination | 2.07 |
| O3 | Zn 584 | Salt bridge | 2.07 |
| N1 | Glu 240 | Hydrogen bond | 2.64 |
| N2 | Glu 240 | Salt bridge | 3.61 |
| MMP-15 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O1 | Leu 219 | Hydrogen bond | 1.92 |
| O2 | Zn 671 | Metal coordination | 2.19 |
| O3 | Zn 671 | Metal coordination | 2.18 |
| O3 | Zn 671 | Salt bridge | 2.18 |
| MMP-16 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | Tyr 210 | Pi stacking | 5.02 |
| O3 | Zn 609 | Metal coordination | 2.01 |
| O3 | Zn 609 | Salt bridge | 2.01 |
| N2 | Glu 247 | Salt bridge | 4.06 |
| O4 | Zn 609 | Metal coordination | 2.18 |
| O5 | Leu 206 | Hydrogen bond | 2.05 |
| MMP-17 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 209 | Pi stacking | 4.62 |
| O3 | Zn 605 | Metal coordination | 2.09 |
| O3 | Zn 605 | Salt bridge | 2.09 |
| N2 | Glu 249 | Salt bridge | 4.63 |
| O4 | Zn 605 | Metal coordination | 2.02 |
| O5 | Val 207 | Hydrogen bond | 2.33 |
| MMP-19 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O2 | Zn 510 | Metal coordination | 2.03 |
| Ar2 | Tyr 234 | Pi stacking | 4.39 |
| O3 | Zn 510 | Metal coordination | 2.04 |
| O3 | Zn 510 | Salt bridge | 2.04 |
| N2 | Glu 213 | Salt bridge | 3.79 |
| MMP-20 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O3 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 1.99 |
| O3 | Zn 485 | Salt bridge | 1.99 |
| N2 | Glu 227 | Salt bridge | 4.19 |
| O4 | Zn 485 | Metal coordination | 2.07 |
| O5 | Leu 189 | Hydrogen bond | 2.27 |
| MMP-21 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| N1 | Glu 248 | Hydrogen bond | 1.93 |
| O3 | Zn 571 | Metal coordination | 2 |
| O3 | Zn 571 | Salt bridge | 2.2 |
| N2 | Glu 248 | Salt bridge | 3.33 |
| N2 | Glu 284 | Salt bridge | 4.15 |
| O4 | Zn 571 | Metal coordination | 2.2 |
| O5 | Phe 249 | Hydrogen bond | 2.23 |
| MMP-23 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| N1 | Glu 167 | Hydrogen bond | 1.99 |
| O3 | Zn 392 | Metal coordination | 2.15 |
| O3 | Zn 392 | Salt bridge | 2.15 |
| N2 | Glu 212 | Salt bridge | 4.47 |
| O4 | Zn 392 | Metal coordination | 2.24 |
| O5 | Leu 168 | Hydrogen bond | 1.87 |
| MMP-24 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 282 | Pi stacking | 4.35 |
| O1 | Leu 242 | Hydrogen bond | 2.14 |
| O1 | Ala 243 | Hydrogen bond | 2.64 |
| O2 | Glu 283 | Hydrogen bond | 2.14 |
| O2 | Zn 647 | Metal coordination | 2.34 |
| Ar2 | Phe 241 | Pi stacking | 3.99 |
| O3 | Zn 647 | Metal coordination | 2.08 |
| O3 | Zn 647 | Salt bridge | 2.08 |
| N2 | Phe 241 | Cation pi | 3.62 |
| MMP-25 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| O3 | Zn 564 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 564 | Salt bridge | 2.14 |
| N2 | Glu 234 | Salt bridge | 4.33 |
| O4 | Zn 564 | Metal coordination | 2.05 |
| O5 | Leu 192 | Hydrogen bond | 2.35 |
| MMP-26 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 208 | Pi stacking | 4.05 |
| Ar1 | Trp 231 | Pi stacking | 5.45 |
| O1 | Gly 172 | Hydrogen bond | 1.94 |
| O2 | Glu 209 | Hydrogen bond | 1.94 |
| O2 | Zn 263 | Metal coordination | 2.29 |
| O3 | Zn 263 | Metal coordination | 1.96 |
| O3 | Zn 263 | Salt bridge | 1.96 |
| MMP-27 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 181 | Pi stacking | 3.71 |
| O1 | Arg 170 | Hydrogen bond | 1.95 |
| O3 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 515 | Salt bridge | 2.14 |
| N2 | Glu 217 | Salt bridge | 4.14 |
| O4 | Zn 515 | Metal coordination | 2.28 |
| O5 | Leu 179 | Hydrogen bond | 2.13 |
| MMP-28 Interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand | Receptor | Type | Distance (Å) |
| Ar1 | His 240 | Pi stacking | 4.07 |
| O2 | Zn 522 | Metal coordination | 2.14 |
| O3 | Zn 522 | Metal coordination | 1.92 |
| O3 | Zn 522 | Salt bridge | 1.92 |
| N2 | Glu 241 | Salt bridge | 4.79 |
For comparative evaluations, docking simulations were also performed using the known broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitor DOX. DOX is the only US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitor. These were performed against five MMPs. These included MMP-2, 8, 9, 14, and 19. These MMPs were selected as INSTIs have higher binding energies with these enzymes compared to others and each enzyme represented different class of the MMP family. DOX was found to form metal coordination with Zn++ for all tested MMPs. These metal co-ordinations occurred at Zn 166, 469, 709, 584, and 510 receptors of MMP-2, 8, 9, 14, and 19 respectively. Pi stacking interactions occurred with histidine amino acids of MMP-2 and 14. Hydrogen bonding of DOX occurred with all five MMPs tested. DOX was found to form hydrogen bonds with glutamate, alanine, aspartic acid, tyrosine, asparagine, serine, and proline amino acid residues. The distances of receptor-ligand bonds are shown in the DOX-MMP interaction table (Supplementary Table S1). Further, docking simulations of DOX into individual MMPs showed binding energies of −6.595, −7.024, −7.658, −7.114, and −6.488 kcal/mol for MMP-2, 8, 9, 14, and 19 respectively. In comparison to DOX, all three INSTIs (DTG, CAB and BIC) showed higher binding energies with each tested MMP. Interestingly, both, CAB and BIC, showed significantly higher energies compared to DOX and DTG, suggesting CAB or BIC may have comparatively stronger inhibition effect on MMPs (Supplementary Table S2).
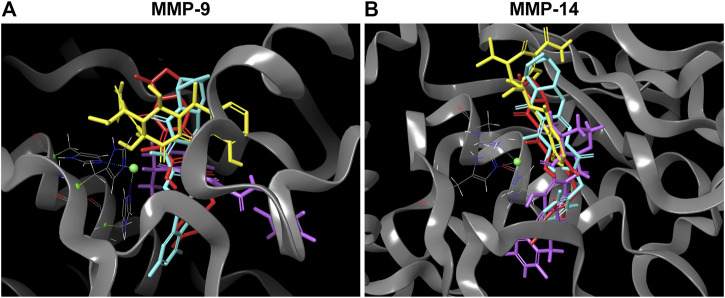
The lower binding energy of DOX compared to INSTIs can be explained by its fit within the catalytic binding site. An overlay of the docked DTG, CAB, BIC and DOX on catalytic domain of MMP-9 and -14 showed that DOX (yellow color) has more solvent exposed area than DTG (magenta color), BIC (light blue color) and CAB (red color) (Figure 1). Further, solvent accessible surface area (SASA) calculations confirmed the higher solvent exposure of DOX compared to any of the INSTI (Supplementary Table S3). The higher SASA values of docking complex indicate that the DOX is interacting at lesser extent with MMP’s structural binding site and has a higher affinity to form bonds with the solvent compared to INSTIs. These data confirmed that INSTIs fit the MMP binding pocket with greater efficiency than DOX.
FIGURE 1.
Superior affinity of DTG, CAB, BIC compared to DOX at MMPs catalytic binding site. (A and B) 3D representative images of overlapping molecular docking complexes of DTG, CAB, BIC, and DOX on MMP-9 or -14 catalytic domain containing Zn++ (green ball) are shown in ribbon (gray color) format. The color scheme utilized for drugs is as follows: DTG - Magenta; CAB - Red; BIC - Light blue; and DOX - Yellow.
INSTIs-induced inhibition of MMPs activities
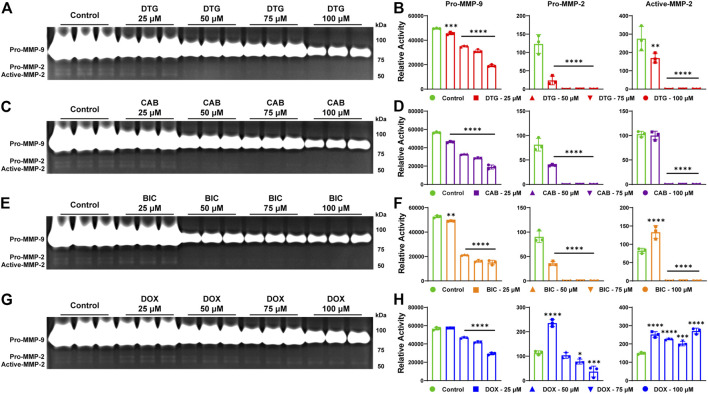
To affirm that inhibition of MMPs activity is an INSTI class effect, gelatin zymography, a commonly used assay to study MMPs activity and their inhibitors, was performed. For gelatin zymography, cell culture of THP-1 cells was utilized. Cells were treated with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA) to induce differentiation of THP-1 cells into macrophage like cells and to promote MMPs secretion. Herein, PMA-stimulated THP-1 cells were treated with escalating concentrations (25, 50, 75 or 100 µM) of DTG, CAB or BIC for 24 h in serum-free culture medium. Further, to validate the outcome, DOX was utilized as an MMP inhibitor control and the same treatment conditions were employed. To determine the proteolytic activity of MMP-2 and -9 (gelatinases), equal amount of protein (3 µg) from cell culture medium was loaded on SDS-PAGE containing gelatin. Gel area digested by both MMPs was visualized using Coomassie blue stain (Figures 2A, C, E). A decrease in activity of MMP-2 and -9 was observed following treatment with all three INSTIs compared to vehicle-treated controls on gelatin zymogram (Figures 2A, C, E). Relative activity of the pro forms of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was significantly decreased in a concentration-dependent manner at each tested concentration after treatment with DTG, CAB or BIC compared to controls (Figures 2B, D, F). Relative activity of the active form of MMP-2 was significantly reduced at all concentrations of DTG. However, for CAB and BIC, relative activity of the active form of MMP-2 was significantly reduced at 75 or 100 µM. Interestingly, there was a significant increase in relative activity of the active form of MMP-2 at 25 µM BIC compared to controls. Further, DOX treatment, showed a significant decrease in relative activity of pro-form of MMP-9 in a concentration dependent manner (Figures 2G, H). However, variable inhibition of MMP-2 was observed after DOX treatment (Figures 2G, H). Relative activity of the pro form of MMP-2 was significantly increased at 25 µM DOX, but significantly decreased in a concentration-dependent manner at 75 and 100 µM concentrations. Relative activity of the active form of MMP-2 was significantly increased at all treatment concentrations of DOX. When comparing DOX and INSTIs at the same treatment concentration, DTG, CAB, and BIC showed higher MMP inhibition compared to DOX (Supplementary Figure S1A–H). Overall, gelatin zymography results confirmed that inhibition of MMPs activities is an INSTI class effect. These results demonstrated that INSTIs inhibit MMP at a higher degree than the known broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor, DOX.
FIGURE 2.
Inhibition of MMPs by INSTIs. (A, C, E, and G) Gelatin zymogram. Activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 was evaluated in serum-free medium of THP-1 cells following treatment with DTG, CAB, BIC or DOX (25, 50, 75 or 100 µM). Vehicle treated cells were used as controls. (B, D, F, and H) Relative activity of MMP-9 or -2 was measured following treatment with DTG, CAB, BIC or DOX. A one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used to compare activity of individual MMP between each treatment concentration of individual drug and respective control (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, N = 3 biological replicates. Experiments were repeated independently three times with equivalent results.
Discussion
The risk of pre- or post-natal neurodevelopmental deficits due to gestational exposure to ARVs remains possible (Hill et al., 2018; Cassidy et al., 2019; Zash et al., 2019; Crowell et al., 2020; Williams et al., 2020). Works outlined in this report provide unique insights into the underlying mechanisms linked to such adverse events. Recently, clinical and pre-clinical studies reported a potential association between DTG usage at the time of conception and NTDs (Hill et al., 2018; Raesima et al., 2019; Zash et al., 2019; Kreitchmann et al., 2021) and postnatal neurological abnormalities(Crowell et al., 2020). Due to mass usage of DTG-based regimens worldwide, reports highlighted the need to find an underlying mechanism of potential DTG-related adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. With the introduction of new potent ARVs from the INSTI class to treatment regimens, it is essential to establish if such mechanism can be linked to other ARVs from the INSTI class. Herein, we show that INSTIs including DTG, CAB, and BIC possess chemical abilities to interact with Zn++ at the catalytic domain of all twenty-three MMPs observed in humans and thus, can be classified as broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitors. Such secondary mechanism of MMPs inhibition introduces potential for adverse effects, especially during critical periods of fetal brain development.
All ARVs from the INSTI class possess metal-binding pharmacophore, MBP in their chemical structure. This chemical property enables INSTIs to interact with active metal ion (Mg++) sites in the HIV-1 integrase enzyme to block its action of insertion of the viral genome into the host cellular DNA (Smith et al., 2021). With such inherent metal chelating chemical property, INSTIs have potential to interact with other metalloenzymes that are critical for normal cellular functions such as cell proliferation, differentiation, cell signaling, protein cleavage, etc. MMPs are well recognized Zn++ dependent metalloenzymes (Ethell and Ethell, 2007; Page-McCaw et al., 2007; Agrawal et al., 2008; van Hinsbergh and Koolwijk, 2008; Loffek et al., 2011; Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; Rempe et al., 2016; Small and Crawford, 2016; De Stefano and Herrero, 2017; Shinotsuka et al., 2018; Kanda et al., 2019). The active site of these enzymes is highly conserved, and comprised of three histidine residues that are bound to the catalytic zinc (Laronha and Caldeira, 2020). Dysregulation of activities of MMPs through chelation of Zn++ can cause detrimental effects on structural and functional development of the CNS. The chemical property of INSTIs to chelate divalent cations enables them to engage with Zn++ in the catalytic domain of all twenty-three human MMPs. Our comprehensive molecular docking assessments confirmed that inhibition of MMPs activity is an INSTI class effect. Notably, interaction of individual DTG, CAB or BIC with each MMP was variable with different binding energy. Thus, studies evaluating drug-induced inhibitions of individual MMPs under biological conditions is needed in the future to identify the susceptibility of individual MMP enzymes under normal and genetic polymorphism conditions.
The role of MMPs in normal neural development is of critical importance. MMPs expression is at high levels during early CNS development and decreases into adulthood (Vaillant et al., 1999; Ayoub et al., 2005; Ulrich et al., 2005; Larsen et al., 2006; Bednarek et al., 2009; Aujla and Huntley, 2014; Reinhard et al., 2015). Due to their proteolytic activities, MMPs are ubiquitously expressed during neural development and their expression has been majorly studied in hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum (Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; Small and Crawford, 2016; Beroun et al., 2019). The principal function of MMPs is to degrade extracellular matrix components (Lukes et al., 1999). However, it is well recognized that MMPs functions are essential for the regulation of several neurodevelopmental processes including neurogenesis, neurite outgrowth, migration of newly born neurons, myelination, axonal guidance, synaptic plasticity and angiogenesis (Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; Small and Crawford, 2016). Dysregulation of MMPs activities during critical periods of fetal brain development during gestation could significantly affect these processes, resulting in adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes (Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; Small and Crawford, 2016). Notably, previously we observed that DTG inhibits MMPs activities in rodent embryo brain during gestation leading to neuroinflammation and neuronal injury in the CNS of mice pups during postnatal assessments (Bade et al., 2021). This study identified DTG-induced inhibition of MMPs activities as a neurotoxicity biomarker. However, the previous study was proof of concept and mainly focused on DTG, but comprehensive docking assessments for consideration of each of MMP was missing. The current study confirmed that all INSTIs possess abilities to inhibit MMPs activities. Therefore, drug-induced differences in MMP activities or MMP expression levels could serve as a biomarker for INSTI-associated neurodevelopmental impairments. In addition to pregnancy outcomes, INSTIs also have been recognized to be associated with neuropsychiatric adverse events (NPAEs) in adults (Yombi, 2018; Amusan et al., 2020; Senneker and Tseng, 2021) and clinically significant weight-gain, especially in females (NAMSAL ANRS 12313 Study Group et al., 2019; Venter et al., 2019; Bourgi et al., 2020; Caniglia et al., 2020; Sax et al., 2020). Impaired MMPs activity, expression and related cellular pathways have been identified as biomarkers in both disorders (Vandenbroucke and Libert, 2014; Jaoude and Koh, 2016; Shinotsuka et al., 2018; Beroun et al., 2019; Ruiz-Ojeda et al., 2019; Gorwood et al., 2020; Li et al., 2020). Further, due to critical functions of MMPs, their dysregulation has also served as a biomarker for several types of tumors and atherosclerosis (Goncalves et al., 2015; Huang, 2018). Thus, this work provides a potential mechanistic biomarker for neurodevelopmental assessments following in utero exposure to ART regimens with an INSTI component.
Identifying the roles of the MMPs and impact of their independent or broad-spectrum inhibition in physiological or pathological conditions is complex. This has reflected in cessation of clinical trials of more than fifty broad-spectrum MMP inhibitors due to adverse events following prolonged treatment (Vandenbroucke and Libert, 2014). Thus, an understanding of the inhibitory effect of INSTIs against each MMP enzyme is essential to define the mechanism linked to neurodevelopment. The INSTIs utilized for testing in this study DTG, CAB and BIC showed strong binding energy with the catalytic domains of all twenty-three MMPs. Moreover, comparison assessments against DOX, a clinically used broad-spectrum inhibitor of MMPs, confirmed the high potency of DTG, CAB or BIC against MMPs. For example, binding energies (kcal/mol) with the catalytic domain of MMP-9 were −9.430 (DTG), −14.222 (CAB), and −13.415 (BIC) against −7.658 (DOX). These molecular docking assessment differences against MMP-9 were further apparent on the confirmatory gelatin zymography biological tests. Interestingly, CAB and BIC exhibited higher binding energies for all tested MMPs compared to DTG, suggesting that these newer INSTIs may be more potent MMPs inhibitors. Such observations will need biological validations along with determination of half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of each INSTI against individual enzymes in the future.
Of the twenty-three human MMPs, few MMPs are well characterized for their role during neurodevelopment. MMP-2 and MMP-9 have been studied extensively and are shown to be essential for the neuronal development, migration, axonal guidance and synaptic plasticity (Ethell and Ethell, 2007; Page-McCaw et al., 2007; Agrawal et al., 2008; Fujioka et al., 2012; Reinhard et al., 2015; Small and Crawford, 2016; De Stefano and Herrero, 2017). Widespread expression of MMP-3 has been identified in neurons in the brain and spinal cord of rodents during critical timepoints of axonal outgrowth (Van Hove et al., 2012a). Moreover, MMP-24 is also expressed in neurons in the brain and spinal cord during development, signifying its role in neuronal development, and MMP-2 and -14 are involved in angiogenesis and in establishment and/or maintenance of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) (Girolamo et al., 2004; Lehti et al., 2005; Lehti et al., 2009; Ikonomidou, 2014; Rempe et al., 2016; Kanda et al., 2019). Knock out or knockdown models of the mentioned MMPs have proved that deficiency in these MMPs can affect neurodevelopmental processes (Oh et al., 2004; Luo, 2005; Van Hove et al., 2012b; Kanda et al., 2019). Interestingly, MMPs are expressed abundantly in neural stem cells (Frolichsthal-Schoeller et al., 1999). Inhibition of MMPs activity by synthetic inhibitors was shown to reduce proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells (Szymczak et al., 2010; Wojcik-Stanaszek et al., 2011). Thus, identifying the impact of INSTI-induced inhibition of MMPs activities on neurodevelopment and unravelling genetic susceptibility increasing the severity of adverse effects will be critical.
Clinical and pre-clinical studies showed high levels of transplacental transfer of INSTI drugs (Schalkwijk et al., 2016; Mulligan et al., 2018; Mandelbrot et al., 2019; Waitt et al., 2019; Bollen et al., 2021; Bukkems et al., 2021). Studies of DTG have found high placental transfer of DTG from mother to fetus with median cord blood to maternal blood drug level ratios from 1.21 up to 1.29 (Schalkwijk et al., 2016; Mulligan et al., 2018; Mandelbrot et al., 2019; Waitt et al., 2019; Bollen et al., 2021). Further, DTG was also found to accumulate in the fetus with noted prolonged elimination of drug from infants after birth (Mulligan et al., 2018; Waitt et al., 2019). Although few studies have addressed placental transfer of CAB and BIC, evidence does suggest that these INSTIs also cross the placental barrier (Pencole et al., 2020; Bukkems et al., 2021; Le et al., 2022). Our previous work investigated pharmacokinetic (PK) and biodistribution (BD) of DTG during pregnancy in mice and confirmed that DTG levels are detectable in brain tissues of embryos following daily oral administration at supratherapeutic dosage (Bade et al., 2021). Our work validated clinical reports of high placental transfer of DTG and was the first to show drug levels in the fetal developing brain during gestation. Such transplacental transfer of DTG indicated that direct exposure of the embryo brain to DTG during critical periods of development could have an adverse impact on neurodevelopment. Therefore, understanding the PK and BD profiles of new INSTIs during pregnancy and their effects on neurodevelopmental processes is needed for better mechanistic assessments.
It is acknowledged that despite the occurrence of birth defects has been a concern, both the United States Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and World Health Organization recommend DTG as a preferred first-line ARV during pregnancy (The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2015; World Health Organization (WHO), 2019a). This decision was based on risk benefit ratios offered by DTG as an ARV compared to rate of associated risk. These included fewer mother-to-child HIV-1 transmission and maternal deaths, and cost-effective (Dugdale et al., 2019; Phillips et al., 2020). Moreover, DTG’s high genetic barrier to drug resistance would address the critical problem of rising pretreatment resistance (PDR) to non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) in RLCs, especially in women (World Health Organization (WHO), 2019a; World Health Organization (WHO), 2019b). Moreover, most updated data from Tsepamo study (Botswana) reported declined rate of birth defects and was comparative between DTG and other ARVs at the time of conception in late breaking abstract at the 24th International AIDS Conference, 2022. Nonetheless, assessment of birth defects in Botswana is an ongoing study and recommended guidelines were based on higher benefits offered by DTG. Yet, risk of long-term neurodevelopmental deficits persists. Particularly, there is a research gap of known adverse events reflecting DTG-associated long-term impact on postnatal neurodevelopment. Therefore, with large number of fetuses being exposed to DTG worldwide, continuous research efforts are critical to uncover any adverse effects of DTG exposures on pre- or post-natal neurodevelopment and elucidate underlying mechanism.
Although the current study provides evidence of an INSTI class effect on the inhibition of MMPs, it was limited to laboratory cell-based assessments. Future studies are necessary in order to affirm mechanistic links between altered MMP activities and adverse developmental outcomes following in utero INSTI exposures. Dose dependent effects of each INSTI on MMPs activities at different stages of neurodevelopment during gestation and early postnatal period need to be studied in animal models. This work would need to include detailed BD drug profiles within the fetal CNS and related MMPs activities. Moreover, with a metal chelating motif, INSTIs possess potential to inhibit other metalloenzymes required for fetal brain development such as Zn++ dependent a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) family members (Jorissen et al., 2010; Vandenbroucke and Libert, 2014). Whether inhibition of these metalloenzymes, even at minimal extent, in addition to MMPs could augment the developmental adverse events needs consideration. Thus, comprehensive computational modeling against other metalloenzymes along with biological validations are critical in the future. Moreover, development of ultra-long acting nanoformulations of DTG and assessment of these as a safe drug delivery system for neuroprotective outcomes will be the focus our own future work. We hypothesize that neuroprotective effect would be the outcome of lower drug biodistribution in the embryo brain preventing MMPs inhibition. Such lower drug biodistribution in fetal brain while maintaining therapeutic drug levels in maternal blood is expected due to long-acting pharmacological properties of formulations and lower total drug administration compared to daily oral drug administration. For example, the 8-week cumulative dose of daily oral CAB (VOCABRIA) is 1,680 mg. Whereas, a 600 mg bi-monthly single intramuscular injection of LA-CAB (CABENUVA or APRETUDE) results in a 3-fold reduction in drug exposure with equivalent duration of action (US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 2021; US Food and Drug Adminis tration (FDA), 2021). Importantly, scientific exchange between basic science mechanistic findings and the clinical assessment of INSTI-exposed children will be required in the future to provide cross-validation of scientific findings and rigorous assessments of neurodevelopment. Overall, it is timely to elucidate any potential ARV-induced secondary effects during pregnancy, in order to provide effective care for women and their fetuses. This study confirms that INSTIs are broad-spectrum MMPs inhibitors. As balanced regulation of MMP activities are crucial for neurodevelopment, the enzyme’s inhibition could underlie INSTI-related adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank the technical support from UNMC Computational Chemistry Core facility.
Funding Statement
This study is supported by NIH grants R21HD106842, R21MH128123, R01AI145542, and R01AI158160.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
EF: performed experiments, collected, analyzed and interpreted data sets, co-wrote, edited and reviewed the manuscript; NP: performed molecular docking experiments, collected, analyzed data sets, YL: provided overall project and technical guidance and edited the manuscript; BE: provided overall project and technical guidance and edited the manuscript; HG: provided overall project and technical guidance, edited and reviewed the manuscript; AB: conceived project, devised central hypothesis and the project’s scientific approach, analyzed and interpreted data, co-wrote, edited and reviewed the manuscript and provided funding acquisition. All authors critically evaluated and approved the final manuscript prior to submission.
Conflict of interest
HG and BE are Co-founders of Exavir Therapeutics, Inc., a biotechnology company focused on the development of long-acting antiretroviral medicines and HIV-1 cure strategies.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/ftox.2023.1113032/full#supplementary-material
References
- Agrawal S. M., Lau L., Yong V. W. (2008). MMPs in the central nervous system: Where the good guys go bad. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 19 (1), 42–51. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.06.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amusan P., Power C., Gill M. J., Gomez D., Johnson E., Rubin L. H., et al. (2020). Lifetime antiretroviral exposure and neurocognitive impairment in HIV. J. Neurovirol 26 (5), 743–753. 10.1007/s13365-020-00870-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aujla P. K., Huntley G. W. (2014). Early postnatal expression and localization of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 during establishment of rat hippocampal synaptic circuitry. J. Comp. Neurol. 522 (6), 1249–1263. 10.1002/cne.23468 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub A. E., Cai T. Q., Kaplan R. A., Luo J. (2005). Developmental expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their potential role in the histogenesis of the cerebellar cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 481 (4), 403–415. 10.1002/cne.20375 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bade A. N. M. J., Liu Y., Edagwa B. J., Gendelman H. E. (2021). Dolutegravir inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases affects mouse neurodevelopment. Mol. Neurobiol. 58, 5703–5721. 10.1007/s12035-021-02508-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarek N., Clement Y., Lelievre V., Olivier P., Loron G., Garnotel R., et al. (2009). Ontogeny of MMPs and TIMPs in the murine neocortex. Pediatr. Res. 65 (3), 296–300. 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181973aee [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beroun A., Mitra S., Michaluk P., Pijet B., Stefaniuk M., Kaczmarek L. (2019). MMPs in learning and memory and neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 76 (16), 3207–3228. 10.1007/s00018-019-03180-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen P., Freriksen J., Konopnicki D., Weizsacker K., Hidalgo Tenorio C., Molto J., et al. (2021). The effect of pregnancy on the pharmacokinetics of total and unbound dolutegravir and its main metabolite in women living with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 72 (1), 121–127. 10.1093/cid/ciaa006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgi K., Rebeiro P. F., Turner M., Castilho J. L., Hulgan T., Raffanti S. P., et al. (2020). Greater weight gain in treatment-naive persons starting dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 70 (7), 1267–1274. 10.1093/cid/ciz407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukkems V. E., Hidalgo-Tenorio C., Garcia C., van Hulzen A. G. W., Richel O., Burger D. M., et al. (2021). First pharmacokinetic data of bictegravir in pregnant women living with HIV. AIDS 35 (14), 2405–2406. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera R. M., Souder J. P., Steele J. W., Yeo L., Tukeman G., Gorelick D. A., et al. (2019). The antagonism of folate receptor by dolutegravir: Developmental toxicity reduction by supplemental folic acid. AIDS 33 (13), 1967–1976. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caniglia E. C., Shapiro R., Diseko M., Wylie B. J., Zera C., Davey S., et al. (2020). Weight gain during pregnancy among women initiating dolutegravir in Botswana. EClinicalMedicine 29-30, 100615. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy A. R., Williams P. L., Leidner J., Mayondi G., Ajibola G., Makhema J., et al. (2019). In utero efavirenz exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes in HIV-exposed uninfected children in Botswana. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 38 (8), 828–834. 10.1097/INF.0000000000002332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandiwana N. C., Chersich M., Venter W. F., Akpomiemie G., Hill A., Simmons B., et al. (2020). Unexpected interactions between dolutegravir and folate: Randomised trial evidence from south Africa. AIDS 35 (2), 205–211. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002741 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell C. S., Williams P. L., Yildirim C., Van Dyke R. B., Smith R., Chadwick E. G., et al. (2020). Safety of in-utero antiretroviral exposure: Neurologic outcomes in children who are HIV-exposed but uninfected. AIDS 34 (9), 1377–1387. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stefano M. E., Herrero M. T. (2017). The multifaceted role of metalloproteinases in physiological and pathological conditions in embryonic and adult brains. Prog. Neurobiol. 155, 36–56. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) (2022). Panel on antiretroviral guidelines for adults and adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents living with HIV. Available at: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- Dorward J., Lessells R., Drain P. K., Naidoo K., de Oliveira T., Pillay Y., et al. (2018). Dolutegravir for first-line antiretroviral therapy in low-income and middle-income countries: Uncertainties and opportunities for implementation and research. Lancet HIV 5, e400–e404. 10.1016/S2352-3018(18)30093-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugdale C. M., Ciaranello A. L., Bekker L. G., Stern M. E., Myer L., Wood R., et al. (2019). Risks and benefits of dolutegravir- and efavirenz-based strategies for South African women with HIV of child-bearing potential: A modeling study. Ann. Intern Med. 170 (9), 614–625. 10.7326/M18-3358 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ethell I. M., Ethell D. W. (2007). Matrix metalloproteinases in brain development and remodeling: Synaptic functions and targets. J. Neurosci. Res. 85 (13), 2813–2823. 10.1002/jnr.21273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolichsthal-Schoeller P., Vescovi A. L., Krekoski C. A., Murphy G., Edwards D. R., Forsyth P. (1999). Expression and modulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in human embryonic CNS stem cells. Neuroreport 10 (2), 345–351. 10.1097/00001756-199902050-00025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka H., Dairyo Y., Yasunaga K., Emoto K. (2012). Neural functions of matrix metalloproteinases: Plasticity, neurogenesis, and disease. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 789083. 10.1155/2012/789083 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore J. C., Hoque M. T., Dai W., Mohan H., Dunk C., Serghides L., et al. (2022). Interaction between dolutegravir and folate transporters and receptor in human and rodent placenta. EBioMedicine 75, 103771. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103771 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolamo F., Virgintino D., Errede M., Capobianco C., Bernardini N., Bertossi M., et al. (2004). Involvement of metalloprotease-2 in the development of human brain microvessels. Histochem Cell Biol. 122 (3), 261–270. 10.1007/s00418-004-0705-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves I., Bengtsson E., Colhoun H. M., Shore A. C., Palombo C., Natali A., et al. (2015). Elevated plasma levels of MMP-12 are associated with atherosclerotic burden and symptomatic cardiovascular disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 35 (7), 1723–1731. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305631 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorwood J., Bourgeois C., Pourcher V., Pourcher G., Charlotte F., Mantecon M., et al. (2020). The integrase inhibitors dolutegravir and raltegravir exert pro-adipogenic and profibrotic effects and induce insulin resistance in human/simian adipose tissue and human adipocytes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, e549–e560. 10.1093/cid/ciaa259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder E., Damm W., Maple J., Wu C., Reboul M., Xiang J. Y., et al. (2016). OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like Small molecules and proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 12 (1), 281–296. 10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Clayden P., Thorne C., Christie R., Zash R. (2018). Safety and pharmacokinetics of dolutegravir in HIV-positive pregnant women: A systematic review. J. Virus Erad. 4 (2), 66–71. 10.1016/s2055-6640(20)30247-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. (2018). Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: Recent advances. Sensors (Basel) 18 (10), 3249. 10.3390/s18103249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonomidou C. (2014). Matrix metalloproteinases and epileptogenesis. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 1 (1), 6. 10.1186/s40348-014-0006-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaoude J., Koh Y. (2016). Matrix metalloproteinases in exercise and obesity. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 12, 287–295. 10.2147/VHRM.S103877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorissen E., Prox J., Bernreuther C., Weber S., Schwanbeck R., Serneels L., et al. (2010). The disintegrin/metalloproteinase ADAM10 is essential for the establishment of the brain cortex. J. Neurosci. 30 (14), 4833–4844. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5221-09.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda H., Shimamura R., Koizumi-Kitajima M., Okano H. (2019). Degradation of extracellular matrix by matrix metalloproteinase 2 is essential for the establishment of the blood-brain barrier in Drosophila. iScience 16, 218–229. 10.1016/j.isci.2019.05.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitchmann R., Oliveira F. R., Sprinz E. (2021). Two cases of neural tube defects with dolutegravir use at conception in south Brazil. Braz J. Infect. Dis. 25 (2), 101572. 10.1016/j.bjid.2021.101572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger E., Vriend G. (2014). YASARA View - molecular graphics for all devices - from smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 30 (20), 2981–2982. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laronha H., Caldeira J. (2020). Structure and function of human matrix metalloproteinases. Cells 9 (5), 1076. 10.3390/cells9051076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. H., DaSilva A. G., Conant K., Yong V. W. (2006). Myelin formation during development of the CNS is delayed in matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -12 null mice. J. Neurosci. 26 (8), 2207–2214. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1880-05.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le M. P., Ferre V. M., Mazy F., Bourgeois-Moine A., Damond F., Matheron S., et al. (2022). Bictegravir pharmacokinetics in a late-presenting HIV-1-infected pregnant woman: A case report. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 77 (3), 851–853. 10.1093/jac/dkab424 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehti K., Allen E., Birkedal-Hansen H., Holmbeck K., Miyake Y., Chun T. H., et al. (2005). An MT1-MMP-PDGF receptor-beta axis regulates mural cell investment of the microvasculature. Genes Dev. 19 (8), 979–991. 10.1101/gad.1294605 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehti K., Rose N. F., Valavaara S., Weiss S. J., Keski-Oja J. (2009). MT1-MMP promotes vascular smooth muscle dedifferentiation through LRP1 processing. J. Cell Sci. 122 (1), 126–135. 10.1242/jcs.035279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Zhao Y., Chen C., Yang L., Lee H. H., Wang Z., et al. (2020). Critical role of matrix metalloproteinase 14 in adipose tissue remodeling during obesity. Mol. Cell Biol. 40 (8), e00564-19. 10.1128/MCB.00564-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffek S., Schilling O., Franzke C. W. (2011). Series "matrix metalloproteinases in lung health and disease": Biological role of matrix metalloproteinases: A critical balance. Eur. Respir. J. 38 (1), 191–208. 10.1183/09031936.00146510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes A., Mun-Bryce S., Lukes M., Rosenberg G. A. (1999). Extracellular matrix degradation by metalloproteinases and central nervous system diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 19 (3), 267–284. 10.1007/BF02821717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J. (2005). The role of matrix metalloproteinases in the morphogenesis of the cerebellar cortex. Cerebellum 4 (4), 239–245. 10.1080/14734220500247646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbrot L., Ceccaldi P. F., Duro D., Le M., Pencole L., Peytavin G. (2019). Placental transfer and tissue accumulation of dolutegravir in the ex vivo human cotyledon perfusion model. PLoS One 14 (8), e0220323. 10.1371/journal.pone.0220323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan H., Lenis M. G., Laurette E. Y., Tejada O., Sanghvi T., Leung K. Y., et al. (2020). Dolutegravir in pregnant mice is associated with increased rates of fetal defects at therapeutic but not at supratherapeutic levels. EBioMedicine 63, 103167. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan N., Best B. M., Wang J., Capparelli E. V., Stek A., Barr E., et al. (2018). Dolutegravir pharmacokinetics in pregnant and postpartum women living with HIV. AIDS 32 (6), 729–737. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001755 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAMSAL ANRS 12313 Study Group; Kouanfack C., Mpoudi-Etame M., Omgba Bassega P., Eymard-Duvernay S., Leroy S., Boyer S., et al. (2019). Dolutegravir-based or low-dose efavirenz-based regimen for the treatment of HIV-1. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 (9), 816–826. 10.1056/nejmoa1904340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh J., Takahashi R., Adachi E., Kondo S., Kuratomi S., Noma A., et al. (2004). Mutations in two matrix metalloproteinase genes, MMP-2 and MT1-MMP, are synthetic lethal in mice. Oncogene 23 (29), 5041–5048. 10.1038/sj.onc.1207688 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page-McCaw A., Ewald A. J., Werb Z. (2007). Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8 (3), 221–233. 10.1038/nrm2125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pencole L., Le M. P., Bouchet-Crivat F., Duro D., Peytavin G., Mandelbrot L. (2020). Placental transfer of the integrase strand inhibitors cabotegravir and bictegravir in the ex-vivo human cotyledon perfusion model. AIDS 34 (14), 2145–2149. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H., Francis K., Sconza R., Horn A., Peckham C. S., Tookey P. A., et al. (2017). UK mother-to-child HIV transmission rates continue to decline: 2012-2014. Clin. Infect. Dis. 64 (4), 527–528. 10.1093/cid/ciw791 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. N., Bansi-Matharu L., Venter F., Havlir D., Pozniak A., Kuritzkes D. R., et al. (2020). Updated assessment of risks and benefits of dolutegravir versus efavirenz in new antiretroviral treatment initiators in sub-saharan africa: Modelling to inform treatment guidelines. Lancet HIV 7 (3), e193–e200. 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30400-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raesima M. M., Ogbuabo C. M., Thomas V., Forhan S. E., Gokatweng G., Dintwa E., et al. (2019). Dolutegravir use at conception - additional surveillance data from Botswana. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 (9), 885–887. 10.1056/NEJMc1908155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramokolo V., Goga A. E., Slogrove A. L., Powis K. M. (2019). Unmasking the vulnerabilities of uninfected children exposed to HIV. BMJ 366, l4479. 10.1136/bmj.l4479 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi V., Peters H., Sconza R., Francis K., Bukasa L., Thorne C., et al. (2022). Trends in antiretroviral use in pregnancy in the UK and Ireland. HIV Med. 23 (4), 397–405. 10.1111/hiv.13243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard S. M., Razak K., Ethell I. M. (2015). A delicate balance: Role of MMP-9 in brain development and pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 9, 280. 10.3389/fncel.2015.00280 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rempe R. G., Hartz A. M. S., Bauer B. (2016). Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 36 (9), 1481–1507. 10.1177/0271678X16655551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Ojeda F. J., Mendez-Gutierrez A., Aguilera C. M., Plaza-Diaz J. (2019). Extracellular matrix remodeling of adipose tissue in obesity and metabolic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (19), 4888. 10.3390/ijms20194888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sax P. E., Erlandson K. M., Lake J. E., McComsey G. A., Orkin C., Esser S., et al. (2020). Weight gain following initiation of antiretroviral therapy: Risk factors in randomized comparative clinical trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71 (6), 1379–1389. 10.1093/cid/ciz999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk S., Greupink R., Colbers A. P., Wouterse A. C., Verweij V. G., van Drongelen J., et al. (2016). Placental transfer of the HIV integrase inhibitor dolutegravir in an ex vivo human cotyledon perfusion model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71 (2), 480–483. 10.1093/jac/dkv358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnoll J. G., Temsamrit B., Zhang D., Song H., Ming G. L., Christian K. M. (2019). Evaluating neurodevelopmental consequences of perinatal exposure to antiretroviral drugs: Current challenges and new approaches. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 16, 113–129. 10.1007/s11481-019-09880-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senneker T., Tseng A. (2021). An update on neuropsychiatric adverse effects with second-generation integrase inhibitors and nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 16 (6), 309–320. 10.1097/COH.0000000000000705 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinotsuka N., Yamaguchi Y., Nakazato K., Matsumoto Y., Mochizuki A., Miura M. (2018). Caspases and matrix metalloproteases facilitate collective behavior of non-neural ectoderm after hindbrain neuropore closure. BMC Dev. Biol. 18 (1), 17. 10.1186/s12861-018-0175-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small C. D., Crawford B. D. (2016). Matrix metalloproteinases in neural development: A phylogenetically diverse perspective. Neural Regen. Res. 11 (3), 357–362. 10.4103/1673-5374.179030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zhao X. Z., Passos D. O., Lyumkis D., Burke T. R., Jr., Hughes S. H. (2021). Integrase strand transfer inhibitors are effective anti-HIV drugs. Viruses 13 (2), 205. 10.3390/v13020205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymczak P., Wojcik-Stanaszek L., Sypecka J., Sokolowska A., Zalewska T. (2010). Effect of matrix metalloproteinases inhibition on the proliferation and differentiation of HUCB-NSCs cultured in the presence of adhesive substrates. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. (Wars) 70 (4), 325–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2018). HIV and pregnant women, infants, and children. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/gender/pregnantwomen/index.html . [Google Scholar]
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) (2021). Global HIV & AIDS statistics fact sheet— 2021. [Google Scholar]
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) (2021). Start free, stay free, AIDS free final report on 2020 targets. Available at: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2021/start-free-stay-free-aids-free-final-report-on-2020-targets . [Google Scholar]
- The Lancet H. (2020). End resistance to dolutegravir roll-out. Lancet HIV 7 (9), e593. 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30231-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (2015). Recommendations for the use of antiretroviral drugs in pregnant women with HIV infection and interventions to reduce perinatal HIV transmission in the United States. Available at: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/Perinatal_GL.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich R., Gerhauser I., Seeliger F., Baumgartner W., Alldinger S. (2005). Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the developing mouse brain and spinal cord: A reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction study. Dev. Neurosci. 27 (6), 408–418. 10.1159/000088455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2021). FDA approves first injectable treatment for HIV pre-exposure prevention. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-injectable-treatment-hiv-pre-exposure-prevention . [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2021). FDA approves cabenuva and vocabria for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv/fda-approves-cabenuva-and-vocabria-treatment-hiv-1-infection . [Google Scholar]
- Van Hove I., Verslegers M., Buyens T., Delorme N., Lemmens K., Stroobants S., et al. (2012). An aberrant cerebellar development in mice lacking matrix metalloproteinase-3. Mol. Neurobiol. 45 (1), 17–29. 10.1007/s12035-011-8215-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant C., Didier-Bazes M., Hutter A., Belin M. F., Thomasset N. (1999). Spatiotemporal expression patterns of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the postnatal developing rat cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 19 (12), 4994–5004. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-12-04994.1999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Koolwijk P. (2008). Endothelial sprouting and angiogenesis: Matrix metalloproteinases in the lead. Cardiovasc Res. 78 (2), 203–212. 10.1093/cvr/cvm102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hove I., Lemmens K., Van de Velde S., Verslegers M., Moons L. (2012). Matrix metalloproteinase-3 in the central nervous system: A look on the bright side. J. Neurochem. 123 (2), 203–216. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07900.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroucke R. E., Libert C. (2014). Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13 (12), 904–927. 10.1038/nrd4390 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter W. D. F., Moorhouse M., Sokhela S., Fairlie L., Mashabane N., Masenya M., et al. (2019). Dolutegravir plus two different prodrugs of tenofovir to treat HIV. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 (9), 803–815. 10.1056/NEJMoa1902824 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitt C., Orrell C., Walimbwa S., Singh Y., Kintu K., Simmons B., et al. (2019). Safety and pharmacokinetics of dolutegravir in pregnant mothers with HIV infection and their neonates: A randomised trial (DolPHIN-1 study). PLoS Med. 16 (9), e1002895. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Yildirim C., Chadwick E. G., Van Dyke R. B., Smith R., Correia K. F., et al. (2020). Association of maternal antiretroviral use with microcephaly in children who are HIV-exposed but uninfected (SMARTT): A prospective cohort study. Lancet HIV 7 (1), e49–e58. 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30340-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcik-Stanaszek L., Sypecka J., Szymczak P., Ziemka-Nalecz M., Khrestchatisky M., Rivera S., et al. (2011). The potential role of metalloproteinases in neurogenesis in the gerbil hippocampus following global forebrain ischemia. PLoS One 6 (7), e22465. 10.1371/journal.pone.0022465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2016). Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: Recommendations for a public health approach. Second edition. Available at: https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/arv/chapter4.pdf?ua=1 . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2018). Dolutegravir (DTG) and the fixed dose combination (FDC) of tenofovir/lamivudine/dolutegravir (TLD): Briefing note. Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/arv/DTG-TLD-arv_briefing_2018.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2019). HIV drug resistance report 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) (2019). Update of recommendations on first- and second-line antiretroviral regimens. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/325892/WHO-CDS-HIV-19.15-eng.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- Yombi J. C. (2018). Dolutegravir neuropsychiatric adverse events: Specific drug effect or class effect. AIDS Rev. 20 (1), 14–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zash R., Holmes L., Diseko M., Jacobson D. L., Brummel S., Mayondi G., et al. (2019). Neural-tube defects and antiretroviral treatment regimens in Botswana. N. Engl. J. Med. 381 (9), 827–840. 10.1056/NEJMoa1905230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.