A 72-year-old man was diagnosed with early esophageal cancer and underwent endoscopic resection. After marking the lesion, the size was about 4.0 × 3.0 cm. After submucosal injection, mucosal incision was performed with Endocut Q (Effect 3, Cut duration 2, Cut interval 4), followed by the trimming of the edges with swift coagulation (Effect 3, 45 W), the so-called precutting and trimming technique ( Fig. 1 a ). Because the marginal mucosa had been fully incised, under the condition of continuous water injection, the lesion floated in the water, which allowed it to be completely snared and removed using a 30-mm snare ( Fig. 1 b ). No residual lesion, bleeding, or perforation was observed on the wound ( Fig. 1 c ). The whole operation lasted 20 minutes. Iodine staining after the specimen was stretched and fixed confirmed the presence of all the marks and the size of 4.2 × 3.0 cm ( Fig. 1 d ). The histological findings revealed pathological lamina propria (pT1a-LPM) squamous cell carcinoma with negative horizontal and vertical margins.
Fig. 1.
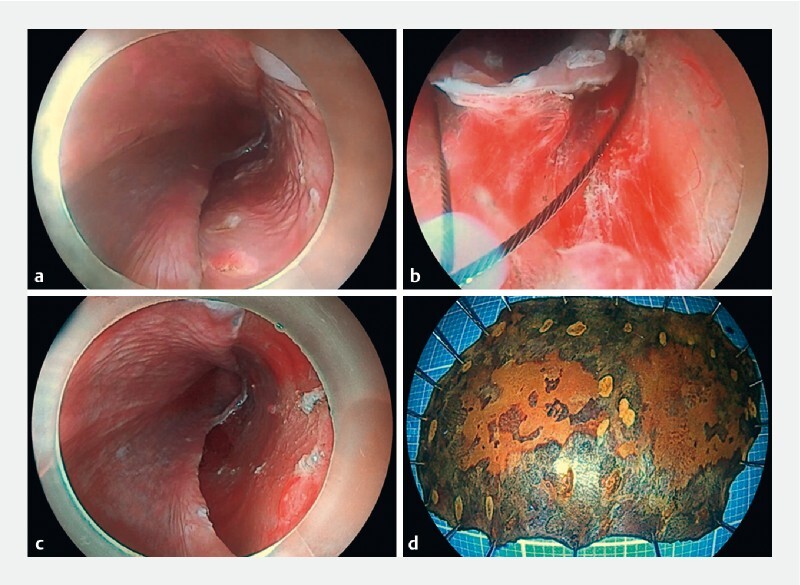
The process of precutting and trimming-assisted underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of large early esophageal cancer. a The marginal mucosa was precut and trimmed. b The lesion floating in the water allowed it to be completely snared. c The wound was clean without bleeding or perforation. d Iodine staining was performed after specimen stretching and fixation.
We previously reported that the spasmodic contraction induced by high-concentration iodine staining assisted underwater endoscopic mucosal resection (UEMR) of early esophageal cancer of 1–2 cm 1 . However, en bloc resection cannot be guaranteed for larger lesions. With esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection, injury to the muscularis propria and even perforation may occur, mainly during the process of submucosal dissection. Therefore, UEMR is performed immediately after precutting and trimming of the edges, which not only saves operation time, but also avoids complications in the process of dissection. This precutting and trimming-assisted UEMR technique can be used for rapid and safe resection of early esophageal cancer in the size range of 3–4 cm ( Video 1 ).
Video 1 Precutting and trimming-assisted underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of large early esophageal cancer.
Endoscopy_UCTN_Code_TTT_1AO_2AG
Footnotes
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Endoscopy E-Videos : https://eref.thieme.de/e-videos .
Endoscopy E-Videos is an open access online section, reporting on interesting cases and new techniques in gastroenterological endoscopy. All papers include a high quality video and all contributions are freely accessible online. Processing charges apply, discounts and wavers acc. to HINARI are available. This section has its own submission website at https://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/e-videos
Reference
- 1.Deng C, Wu S, Xu F et al. Spasmodic contraction induced by high concentration iodine staining to facilitate underwater endoscopic mucosal resection of early esophageal cancer. Endoscopy. 2022;54 02:E952–E953. doi: 10.1055/a-1883-9819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


