Abstract
Background
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) p-tau235 is a novel biomarker highly specific of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, CSF p-tau235 has only been studied in well-characterized research cohorts, which do not fully reflect the patient landscape found in clinical settings. Therefore, in this multicentre study, we investigated the performance of CSF p-tau235 to detect symptomatic AD in clinical settings and compared it with CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231.
Methods
CSF p-tau235 was measured using an in-house single molecule array (Simoa) assay in two independent memory clinic cohorts: Paris cohort (Lariboisière Fernand-Widal University Hospital Paris, France; n=212) and BIODEGMAR cohort (Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, Spain; n=175). Patients were classified by the syndromic diagnosis (cognitively unimpaired [CU], mild cognitive impairment [MCI] or dementia) and their biological diagnosis (amyloid-beta [Aβ]+ or Aβ ). Both cohorts included detailed cognitive assessments and CSF biomarker measurements (clinically validated core AD biomarkers [Lumipulse CSF Aβ1–42/40 ratio, p-tau181 and t-tau] and in-house developed Simoa CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231).
Results
High CSF p-tau235 levels were strongly associated with CSF amyloidosis regardless of the clinical diagnosis, being significantly increased in MCI Aβ+ and dementia Aβ+ when compared with all other Aβ− groups (Paris cohort: P ˂0.0001 for all; BIODEGMAR cohort: P ˂0.05 for all). CSF p-tau235 was pronouncedly increased in the A+T+ profile group compared with A−T− and A+T− groups (P ˂0.0001 for all). Moreover, CSF p-tau235 demonstrated high diagnostic accuracies identifying CSF amyloidosis in symptomatic cases (AUCs=0.86 to 0.96) and discriminating AT groups (AUCs=0.79 to 0.98). Overall, CSF p-tau235 showed similar performances to CSF p-tau181 and CSF p-tau231 when discriminating CSF amyloidosis in various scenarios, but lower than CSF p-tau217. Finally, CSF p-tau235 associated with global cognition and memory domain in both cohorts.
Conclusions
CSF p-tau235 was increased with the presence of CSF amyloidosis in two independent memory clinic cohorts. CSF p-tau235 accurately identified AD in both MCI and dementia patients. Overall, the diagnostic performance of CSF p-tau235 was comparable to that of other CSF p-tau measurements, indicating its suitability to support a biomarker-based AD diagnosis in clinical settings.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s13195-023-01201-0.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, CSF, Biomarkers, p-tau235, p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231, Memory clinic
Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by the accumulation of aggregated amyloid-beta (Aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau protein into extracellular Aβ plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), respectively [1, 2]. These two immunohistochemical findings, together with gross atrophy and synaptic and neuronal loss, represent the hallmarks of AD and post-mortem examination demonstrating the presence of these proteinopathies is required for definitive diagnosis [3]. Validated imaging and fluid biomarkers increasingly support the clinical assessment and diagnosis of AD during life. Imaging biomarkers include positron emission tomography (PET) using radio-ligands capable of specifically binding Aβ and tau aggregates, whereas widely validated fluid biomarkers currently include Aβ1–42 (or Aβ1–42/40 ratio), total tau (t-tau) and phosphorylated tau at threonine 181 (p-tau181), all measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) [4–7] often by full-automated instruments.
Recently, the field of fluid biomarkers in neurodegeneration has undergone a remarkable expansion, particularly with regard to biomarkers measuring different variants of tau protein. This has resulted in a wide range of novel p-tau biomarkers, measured with different methods and platforms (fundamentally immunoassays and mass spectrometry) [8–11]. Different p-tau residues may change in different stages of the Alzheimer’s continuum. For example, p-tau231 is the first p-tau residue increasing in preclinical AD, confirming the earliest underlying AD processes [11, 12] whereas p-tau217, with its pronounced fold changes and strong association with AD pathological hallmarks, appears to be the most suitable p-tau biomarker for AD diagnosis and patient monitoring [13, 14]. Moreover, different p-tau epitopes may provide different information about the disease and some of them be more suited as a state, stage, or prognostic biomarkers. The most recent p-tau biomarker to demonstrate potential utility in relation to AD is p-tau235 [15], a phosphorylation site that has been found to be a prominent feature in paired helical filaments (PHFs) [16–19]. Recently, using a targeted mass spectrometry method, our group has demonstrated that p-tau235 is highly increased in neuropathologically confirmed AD brain when compared with control cases [15]. These findings align with previous studies, indicating that phosphorylation at serine 235 hampers tubulin assembly, compromising normal microtubules dynamics [20, 21]. We developed a single molecule array (Simoa) assay capable of measuring p-tau235 in CSF, demonstrating that this novel biomarker is highly specific for AD and that it increases during preclinical stages, when only subtle abnormalities in CSF Aβ1–42/40 can be detected [15]. Interestingly, when examining post-mortem brain samples, phosphorylation at serine 235 appears to occur only when preceded by nearby phosphorylation at threonine 231, in what appears to be a sequential phosphorylation event. Due to the translatability of this sequential phosphorylation event from the brain into CSF, p-tau235 has been previously proposed as a potentially useful staging biomarker of preclinical AD (CSF p-tau235 positivity being indicative of late asymptomatic AD stage) [15]. With clinical trials increasingly focusing their intervention at the earliest stages of AD, CSF p-tau235 may be useful to discriminate early from late preclinical AD cases and to evaluate if novel compounds effectively prevent disease progression.
In order to further characterize this novel p-tau biomarker and contextualize its performance with other CSF p-tau species, we previously compared CSF p-tau235 with CSF p-tau217 and p-tau231 in a well-characterized research cohort including the AD continuum and a preclinical AD cohort. We demonstrated that CSF p-tau235 displays a statistically equal performance to that of CSF p-tau217 and p-tau231 when discriminating cognitively impaired CSF Aβ-positive cases from cognitively impaired CSF Aβ-negative cases. However, the cases enrolled in that study belonged to a well-characterized research cohort, which does not fully reflect the patients from daily clinical practice including atypical AD, other dementia and comorbidities. Therefore, evaluating the performance of CSF p-tau235 in the routine practice of a memory clinic is much needed, since in these settings patients present with a higher heterogeneity in demographics, comorbidities and disease presentations [22–25]. As a secondary aim, we tested whether CSF p-tau235 was associated with cognitive performance.
To this end, we measured this novel p-tau biomarker in two independent memory clinic cohorts, compared its performance with N-terminal directed Simoa immunoassays targeting CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231, and assessed its relation with cognitive status.
Methods
Study participants
Paris cohort
Paris cohort enrolled a total of 212 patients who had undergone CSF analysis at the Centre of Cognitive Neurology at Lariboisière Fernand-Widal University Hospital between March 2014 and December 2019, including participants with subjective cognitive decline (SCD, n=21), non-AD mild cognitive impairment (non-AD MCI, n=45), AD-MCI (n=40), AD dementia (n=75) and non-AD dementia (n=31). Non-AD dementia patients encompassed patients with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB, n=12), frontotemporal dementia (FTD, n=15), vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID, n=3) and Creutzfeldt Jakob disease (n=1). Patients underwent a thorough clinical examination involving personal medical and family histories, treatment, neurological examination, extensive neuropsychological assessment, APOE genotyping, brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) extensive neuropsychological evaluation, MRI, APOE genotyping, blood and CSF analysis and fluid sampling for collection (blood and CSF). The diagnosis for each patient was made during multidisciplinary consensus meetings (including neurologists, neuropsychologists, gerontologists, neuroradiologist and biochemists) considering results of validated CSF biomarkers and according to clinical diagnostic criteria for AD dementia [3], MCI due to AD (AD-MCI) [26], DLB [27] and FTD [28]. AD patients displayed CSF biomarkers on the AD continuum [3]. MCI of other causes (non-AD MCI) included patients with psychiatric disorder, sleep apnea, or systemic disease. Non-AD MCI presented with normal CSF biomarkers or suspected non-Alzheimer pathophysiology (normal Aβ1-42/40, high p-tau and/or high t-tau). Included SCD participants were individuals with several years of clinical follow-up for a clinical complaint, presenting with normal cognitive testing and no abnormalities at imaging and CSF examinations [29, 30].
BIODEGMAR cohort
The BIODEGMAR cohort is an observational longitudinal study that enrolls patients with neurodegenerative diseases visiting the Cognitive Decline and Movement Disorders Unit of Hospital del Mar (Barcelona, Spain). The procedures of the BIODEGMAR study include extensive neuropsychological evaluation, MRI, APOE ε4 genotyping, lumbar puncture for CSF collection and blood sampling. Clinical evaluation was performed by a neurologist, including anamnesis, physical examination and clinical diagnosis. Neuropsychological evaluation was performed by a neuropsychologist and consisted of a series of standardized cognitive tests and functional scales. A comprehensive description of the BIODEGMAR cohort has been previously published, with further details on the inclusion and exclusion criteria and on core AD CSF biomarker procedures, including assay details and cutoff determination [31, 32]. In this study, 175 patients of the BIODEGMAR cohort were included from 27 April 2017 to 24 July 2020. The clinical diagnoses included SCD (n=18, similar diagnostic criteria as for Paris cohort), MCI (n=74) and, for subjects with moderate to severe cognitive impairment, possible AD dementia (n=11), probable AD dementia (n=43), LBD (n=2), extrapyramidal syndrome (n=2), vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID; n=4), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP; n=2), corticobasal syndrome (n=4), behavioral variant of FTD (bvFTD; n=4), primary progressive aphasia (PPA; n=8) and cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA; n=3).
Cohort stratification
Patient data from the Paris cohort and the BIODEGMAR cohort was examined using two stratification criteria: (i) according to clinical syndrome (cognitively unimpaired [CU], MCI, or dementia) and CSF amyloid status (Aβ−/Aβ+, as defined by Lumipulse CSF Aβ1-42/40, Supplementary Table 3), resulting in six groups: CU Aβ−, CU Aβ+, MCI Aβ−, MCI Aβ+, dementia Aβ− and dementia Aβ+ (clinical diagnosis included in each group are available in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2); (ii) based on the Aβ (A) and tau (T) status defined using CSF Aβ1–42/40 and p-tau181, respectively (Lumipulse®) into A−T−, A+T− and A+T+ (the A−T+ group considered suspected non-AD pathology [SNAP] was not included in the statistical analysis, but is depicted in the boxplots). The clinical diagnoses included in each group are available in Supplementary Tables 5 and 6). Additionally, CSF p-tau235 levels across clinical diagnostic groups for both cohorts are available in Supplementary Figure 1.
Neuropsychological assessment
All included participants were evaluated using the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). Detailed cognitive assessment was available for a subsample of participants in both the Paris cohort (total n=135: CU [n=14], MCI patients [n=64], dementia patients [n=57]) and the BIODEGMAR cohort (total n=139: CU [n=18], MCI [n=59], dementia [n=62]). In the Paris cohort, memory domain scores were evaluated using total immediate and delayed recall of Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test (FCSRT), and the delayed matching-to-samples 48 test (DMS 48) for visual memory testing. Executive function was assessed using forward and backward digit span, frontal assessment battery and letter and animal fluencies. The language domain was evaluated using the Dénomination Orale 80 test, a naming test. In BIODEGMAR cohort, memory domain was evaluated using total immediate and delayed recall of FCSRT and the Memory Impairment Screen; executive functions, with backward digit span, TMT A and B; language domain, with the Boston naming test. Z-scores were computed from the control group scores as a reference. Domain scores were obtained by averaging z-scores of the individual tests available results within that domain and the global cognition score by averaging the 3 domains’ z-scores.
Biomarker measurements
In the Paris cohort, core AD CSF biomarkers (Aβ1–42/40 ratio, p-tau181 and t-tau) were measured using the clinically validated Lumipulse® G1200 assay (Fujirebio) [33]. Biomarker measurements for CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231 were performed using in-house Simoa assays. CSF p-tau181 and p-tau217 measurements were previously reported [34] and were included here in order to allow the comparison with novel CSF p-tau235. In the BIODEGMAR cohort, core AD CSF biomarkers (Aβ1–42/40 ratio, p-tau181 and t-tau) were measured at Laboratori de Referència de Catalunya (LRC) with Lumipulse G600II (Fujirebio). Cutoff values for biomarkers and their ratios (Aβ1–42/40, p-tau181, t-tau) were previously defined in the CORCOBIA study [31]. Biomarker measurements for CSF p-tau181 and p-tau231 were performed using in-house Simoa assays and were previously reported [32].
CSF p-tau235 measurements
CSF p-tau235 measurements were performed at the Clinical Neurochemistry Laboratory at the University of Gothenburg using a Simoa HD-X instrument (Quanterix), and all samples were blinded. Prior to the analysis, samples were allowed to thaw at room temperature for 45 min. Thawed samples were subsequently vortexed for 15 s, after which they were plated and diluted 1:2 using Tau2.0 sample assay diluent (Quanterix). Due to sample volume availability, CSF samples from the Paris cohort were run in singlicates, while BIODEGMAR cohort samples were run in duplicates. An eight-point calibration curve was generated using recombinant full-length GSK-3β-phosphorylated tau-441 (SignalChem) and run in duplicates. Two internal quality controls (iQC, low and high) were run at the beginning and end of each plate, also in duplicates. Repeatability (%CVr) and intermediate precision (%CVRw) values for both cohorts were ˂15%. Further details on assay specifications and validation can be found elsewhere [15].
Statistical analysis
Statistics were performed using SPSS (v26, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and Scistat (Ostend, Belgium). Graphs were generated using GraphPad PRISM (v7.03, San Diego, CA, USA) and R version 4.1 (https://www.r-project.org/). Boxplots show the median and interquartile range (IQR), with individual data points for all participants always shown. Statistical analyses were performed using parametric or non-parametric methods when appropriate, based on the normality or not of the data. Group comparisons between two categories were performed using a t-test and Mann-Whitney U test. All comparisons of multiple groups were tested with a one-way ANOVA adjusted for age and sex followed by Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc pairwise comparisons. Adjusted P-values for covariates are indicated as PADJ. For each of the CSF p-tau biomarkers, accuracy for binary outcomes was determined using receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis and area under the curve (AUC). AUC values are accompanied by the 95% confidence interval, abbreviated as CI95%. Performance comparison between different p-tau biomarkers was analysed using DeLong test (MedCalc). Spearman’s rank correlation (rS) was used to determine associations between biomarkers. Association of CSF p-tau biomarkers with global and domain-specific cognitive z-scores was studied with linear regression models adjusted for age, sex and level of education.
Results
Cohort characteristics
A total number of 387 participants were included in this study, which belong to two independent clinical cohorts (Paris cohort [n=212]; BIODEGMAR cohort [n=175]). Demographics and stratification in syndromic groups (CU Aβ−/Aβ+, MCI Aβ−/Aβ+ and dementia Aβ−/Aβ+) are presented in Table 1 for both cohorts. In the Paris cohort, MCI Aβ+ and dementia Aβ+ were older than CU Aβ− group (P<0.0001). There was a weak yet significant association with age in both cohorts (Paris cohort: rS=0.32, P <0.0001; BIODEGMAR cohort: rS =0.17, P <0.05). There were no sex differences between groups (P ≥0.05; χ2 test). In both cohorts, CSF p-tau levels were significantly higher in APOE ε4 carriers (overall P <0.0001). As expected, there were significant differences in MMSE scores across groups in both cohorts (P <0.0001), which, as compared with CU, gradually decreased in MCI and further in patients with dementia.
Table 1.
Demographics and biomarkers levels
| Paris cohort (n = 212) | BIODEGMAR cohort (n =175 ) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CU Aβ− |
MCI Aβ− |
Dementia Aβ− |
MCI Aβ+ |
Dementia Aβ+ |
P-value |
CU Aβ− |
MCI Aβ− |
Dementia Aβ− |
CU Aβ+ |
MCI Aβ+ |
Dementia Aβ+ | P-value | |
| n = 21 | n = 47 | n = 27 | n = 40 | n = 77 | n=11 | n=28 | n=19 | n=7 | n=46 | n=64 | |||
| Age, years |
64.6 (9.42) |
66.30 (9.58) | 66.04 (7.73) | 72.40 (7.96)a | 71.90 (8.61)a | < 0.0001 |
70.4 (5.8) |
71.4 (6.1) |
70.0 (6.1) |
70.1 (4.5) |
74.4 (4.8) |
73.5 (4.5) |
0.009 |
| Male (% male) |
8 (38%) |
16 (34%) |
15 (56%) |
16 (40%) |
30 (39%) |
0.338 |
3 (27%) |
16 (57%) |
6 (32%) |
2 (29%) |
19 (41%) |
25 (39%) |
0.141 |
| APOEε4 carriers |
7/21 (33%) |
5/47 (11%)a |
7/26 (27%) |
22/40 (55%) |
51/76 (67%)a |
< 0.001 |
1/10 (10%) |
4/24 (17%) |
3/18 (17%) |
3/7 (43%) |
24/38 (63%)a | 39/62 (61%)a | < 0.02 |
| Level of education, years | 11.5 (2.4) | 10.7 (2.2) | 11.0 (2.1) | 10.0 (2.5) | 10.6 (2.4) | 0.299 | 10.4 (4.9) | 8.5 (4.6) | 7.75 (4.7) | 11.4 (4.0) | 8.4 (4.6) | 7.7 (3.6) | 0.0267 |
| MMSE score | 27.14 (2.45) | 24.00 (4.01)a | 23.85 (4.87)a | 23.82 (3.84)a | 19.09 (5.74)a | < 0.0001 |
28.4 (2.3) |
25.6 (2.7) |
22.2 (5.8)a |
28.7 (1.5) |
23.3 (3.9)a |
20.4 (4.8)a |
< 0.0001 |
| Core biomarkers Lumipulse | |||||||||||||
| CSF Aβ1–42 |
1060.95 (245.23) |
1090.66 (468.75) | 1027.78 (354.02) | 553.00 (209.36)a | 497.88 (155.27)a | < 0.0001 |
1186 (357) |
1164 (549) |
986 (449) |
634 (206)a |
556 (178)a |
522 (153)a |
< 0.0001 |
| CSF Aβ1–42/40 |
0.093 (0.010) |
0.088 (0.012) |
0.09 (0.01) |
0.044 (0.009)a | 0.042 (0.009)a | < 0.0001 | 0.091 (0.017) | 0.0879 (0.012) | 0.091 (0.017) | 0.049 (0.008)a | 0.043 (0.009)a | 0.043 (0.008)a | < 0.0001 |
| CSF pTau, pg/mL |
32.25 (8.16) |
40.97 (20.81) |
33.59 (10.50) |
94.80 (47.31)a | 113.53 (60.02)a | < 0.0001 |
56.8 (31.4) |
50.2 (30.9) |
41.0 (24.4) |
59.1 (14.3) |
112 (59.6)a |
121.4 (57.9)a | < 0.0001 |
| CSF t-tau, pg/mL |
236.62 (63.69) |
333,085 (172.630) |
362.26 (341.90) |
594.83 (285.45)a | 722.01 (393.87)a | < 0.0001 |
307 (141) |
357 (230) |
311 (166) |
407 (107) |
669 (323)a |
759 (342)a |
< 0.0001 |
| Biomarker profile | |||||||||||||
| Normal profile | 21 (100%) | 39 (83%) | 25 (92%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (82%%) | 24 (86%) | 17 (89%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| AD continuum | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 40 (100%) | 77 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 7 (100%) | 46 (100%) | 64 (100%) | ||
| A+T− | / | / | / | 7 (18%) | 10 (13%) | / | / | / | 6 (86%) |
11 (24%) |
3 (5%) |
||
| A+T+ | / | / | / | 33 (82%) | 67 (87%) | / | / | / |
1 (14%) |
35 (76%) |
61 (95%) |
||
| SNAP |
0 (0%) |
8 (17%) | 2 (8%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
2 (18%) | 4 (14%) | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| CSF p-tau biomarkers | |||||||||||||
| CSF N-term p-tau181, pg/mL |
224.72 (66.33) |
300.708 (245.52) | 242.23 (110.58) | 965.91 (628.08) a | 1223.94 (802.66)a | < 0.0001 |
427 (110) |
410 (164) |
426 (168) |
494 (129) |
771 (257)a |
871 (343)a |
< 0.0001 |
| CSF N-term p-tau217, pg/mL |
1.84 (0.94) |
2.90 (2.50) |
2.14 (1.67) |
13.88 (9.48)a | 16.62 (9.74)a | < 0.0001 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| CSF N-term p-tau231, pg/mL |
271.93 (64.74) |
325.05 (148.44) | 286.62 (114.72) | 657.64 (205.53)a | 800.58 (640.95)a | < 0.0001 |
313 (211) |
348 (201) |
331 (236) |
541 (144) |
788 (399)a |
893 (469)a |
< 0.0001 |
| CSF N-term p-tau235, pg/mL |
11.19 (2.94) |
12.74 (5.67) | 11.56 (4.30) | 24.75 (8.11)a | 28.03 (11.52)a | < 0.0001 |
17.6 (8.10) |
18.5 (11.3) |
17.4 (7.23) |
23.1 (3.65) |
34.8 (12.9)a |
41.6 (20.0)a |
< 0.0001 |
Data is shown as mean (SD) or n (%), as appropriate. We used Kruskal-Wallis test to compare age between groups and Pearson’s chi-square to compare sex and APOE ε4 frequencies between groups. Fluid biomarkers levels and MMSE were compared with a one-way ANOVA adjusted by age and sex. aP < 0.0001 versus controls. aP < 0.05 versus CU Aβ−
Aβ1-42 β-amyloid 42, Aβ1-40 β-amyloid 40, CSF Cerebrospinal fluid, CU Cognitively unimpaired, MCI Mild cognitive impairment, MMSE Mini-Mental State Examination, N-term N-terminal, p-tau181 Tau phosphorylated at threonine 181, p-tau217 Tau phosphorylated at threonine 217, p-tau231 Tau phosphorylated at threonine 231, p-tau235 Tau phosphorylated at threonine 181, t-tau Total tau
CSF p-tau235 across syndromic and CSF Aβ-positive and CSF Aβ-negative groups
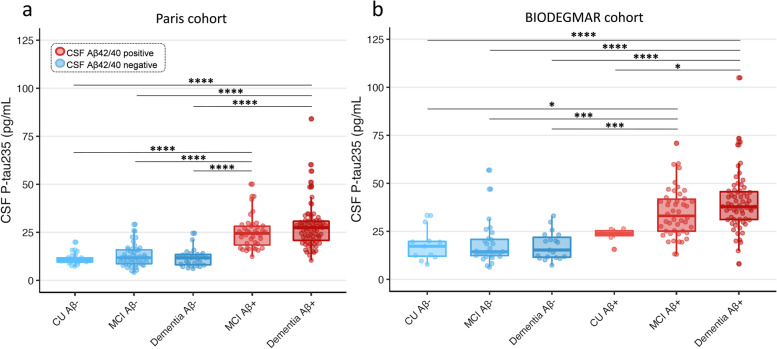
All comparisons of multiple groups were adjusted for age and sex. In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 was significantly higher in MCI Aβ+ and dementia Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ−, MCI Aβ− and dementia Aβ− groups (all PADJ <0.0001) (Fig. 1a). Similarly, in the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 was significantly increased in MCI Aβ+ and dementia Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ−, MCI Aβ− and dementia Aβ− (all PADJ <0.001) (Fig. 1b). CSF p-tau235 was also significantly higher in dementia Aβ+ participants when compared with CU Aβ+ (despite this group being only comprised by seven subjects, PADJ =0.038), but no statistical differences were found between MCI Aβ+ and CU Aβ+. No significant differences were found between CU Aβ− and CU Aβ+, likely due to small sample sizes (eleven and seven cases, respectively), although higher CSF p-tau235 levels in CU Aβ+ were noticeable (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1.
CSF levels of p-tau235 across syndromic groups stratified by CSF amyloidosis. a In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 was significantly increased in both dementia Aβ+ and MCI Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ−, MCI Aβ− and dementia Aβ−. b In the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 was significantly higher in both dementia Aβ+ and MCI Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ−, MCI Aβ− and dementia Aβ−. Additionally, CSF p-tau235 was significantly increased in dementia Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ+. Data information: Boxplots show the median, IQR, and all the participants colour-coded based on the presence (red) or absence (blue) of CSF amyloidosis measured with Lumipulse CSF Aβ Aβ1–42/40. P-values were determined using one-way ANOVA adjusted by age and sex, followed by Bonferroni-corrected post hoc comparison (*P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, ****P <0.0001)
CSF p-tau235 discriminatory accuracy identifying CSF amyloidosis in syndromic groups
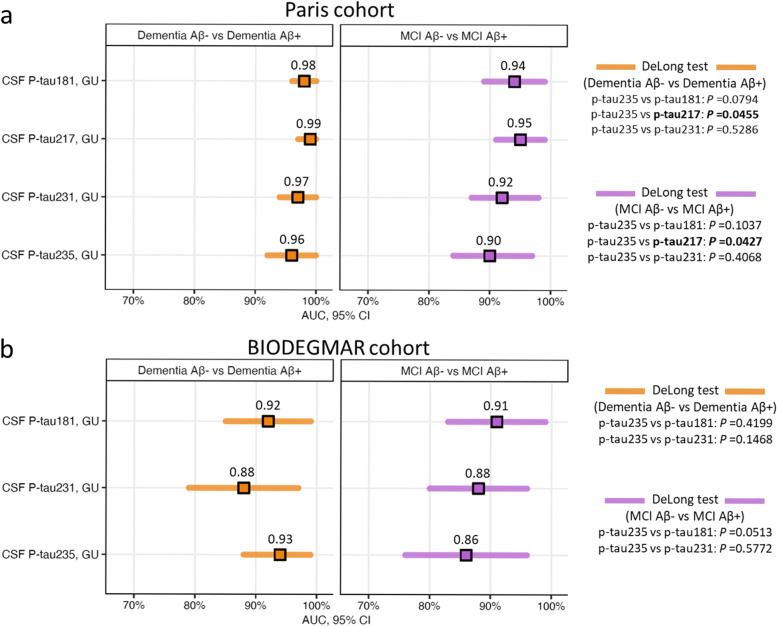
We then investigated the discriminatory accuracies of CSF p-tau235 to detect CSF amyloidosis between each of the syndromic groups and compared its performance with other novel N-terminal directed CSF p-tau biomarkers, specifically p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231 (Fig. 2). In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 displayed high accuracies when discriminating dementia Aβ− from dementia Aβ+ (AUCDementia Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.96, CI95%=0.90–0.99) and MCI Aβ+ from MCI Aβ− (AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.90, CI95%=0.82–0.96) (Fig. 2a). In these two scenarios, CSF p-tau235 performance showed no statistical differences when compared with CSF p-tau181 (AUCDementiaAβ− vs Aβ+=0.98, CI95%=0.93–1.00; AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.94; CI95%=0.86–0.98) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCDementiaAβ− vs Aβ+=0.97, CI95%=0.92–0.99, AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.92, CI95%=0.85–0.97). In contrast, lower accuracies were observed when compared with CSF p-tau217 (AUCDementiaAβ− vs Aβ+=0.99, CI95%=0.94–1.00; AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.95, CI95%=0.88–0.99; both P˂0.05) (Fig. 2a). In the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 showed high performance discriminating dementia Aβ+ from dementia Aβ− (AUCDementia Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.93, CI95%=0.86–0.98) and MCI Aβ+ from MCI Aβ− (AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.86, CI95%=0.76–0.93) (Fig. 2b). When compared with other p-tau species, CSF p-tau235 performance discriminating dementia Aβ+ from dementia Aβ− was equal to CSF p-tau181 (AUCDementiaAβ− vs Aβ+=0.92, CI95%=0.84–0.97) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCDementiaAβ− vs Aβ+=0.88, CI95%=0.79–0.94). On the other hand, the accuracy of CSF p-tau235 distinguishing MCI Aβ+ from MCI Aβ− approached significance compared with CSF p-tau181 (AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.91, CI95%=0.82–0.96; P=0.0513), while matched CSF p-tau231 (AUCMCI Aβ− vs Aβ+=0.88, CI95%=0.78–0.94) (Fig. 2b).
Fig. 2.
Diagnostic performance of CSF p-tau235 when discriminating syndromic groups stratified by CSF amyloidosis. Both in a the Paris cohort and b the BIODEGMAR cohort CSF p-tau235 displayed high accuracies differentiating dementia Aβ+ from dementia Aβ− and MCI Aβ+ from MCI Aβ−, similar to CSF p-tau181 and p-tau231, and lower than CSF p-tau217. Data information: forest plots showing AUC values from ROC analysis (CI95% available in Supplementary Table 4). Comparisons of AUC values between CSF p-tau235 and other available CSF p-tau biomarkers were determined using DeLong test (significance is indicated in bold)
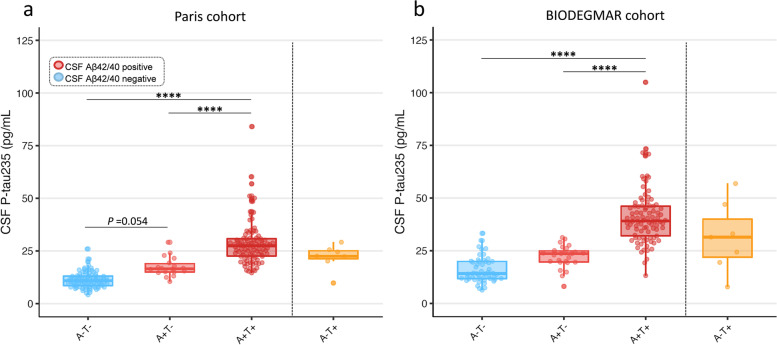
CSF p-tau235 across AT groups
All comparisons of multiple groups were adjusted for age and sex. In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 levels progressively increased across the AD continuum, that is, from A−T− to A+T− and from A+T− to A+T+ (Fig. 3a). A borderline significant increase in CSF p-tau235 levels was observed between A−T− and A+T− (PADJ =0.054). This was followed by a prominent increase between A+T− and A+T+ (PADJ <0.0001). CSF p-tau235 concentration was also significantly higher in A+T+ when compared with A−T− (PADJ <0.0001) (Fig. 3a). In the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 also followed an increasing trajectory across the AD continuum, although no significant differences were found between A−T− and A+T− subjects when performing multiple comparisons (Fig. 3b). On the other hand, the levels of CSF p-tau235 were significantly higher in A+T+ when compared with A−T− and A+T− (PADJ <0.0001 for both) (Fig. 3b). Finally, we stratified patients based on exclusively CSF Aβ, which resulted in CSF p-tau235 being highly increased in A+ cases when compared with A− in both cohorts (P<0.0001 for all) (Supplementary Figure 2).
Fig. 3.
CSF levels of p-tau235 across AT groups. In both a the Paris cohort and b the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 followed an increasing trajectory across the AT continuum. CSF p-tau235 was significantly increased in A+T+ when compared with A−T− and A+T−, and approached significance between A−T− and A+T− in the Paris cohort. Data information: Boxplots show the median, IQR, and all the participants colour-coded based on the presence (red) or absence (blue) of CSF amyloidosis measured with Lumipulse CSF Aβ1–42/40. P-values were determined using one-way ANOVA adjusted by age and sex, followed by Bonferroni-corrected post hoc comparison (*P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, ****P <0.0001)
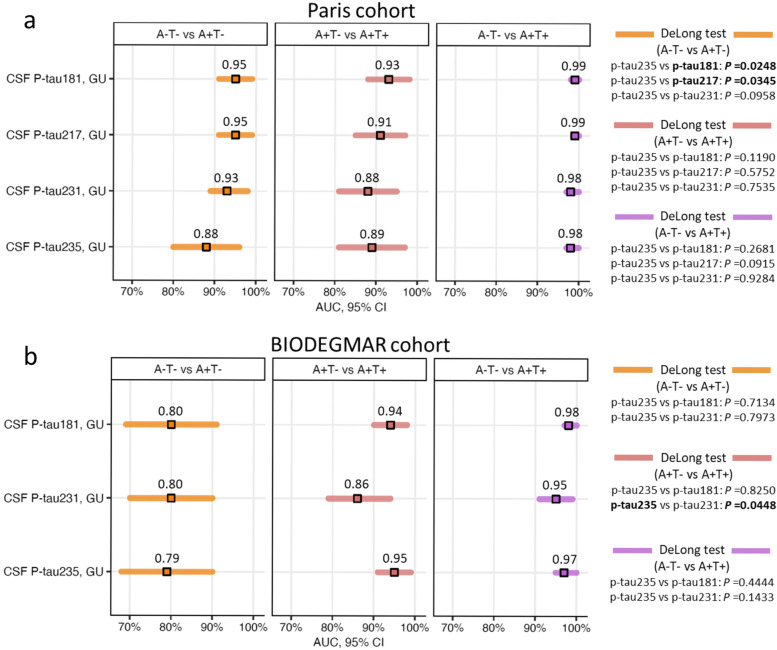
CSF p-tau235 discriminatory accuracy identifying CSF amyloidosis in AT groups
We then examined the performance of CSF p-tau235 for discriminating the AT groups which comprise the AD continuum, that is A−T−, A+T− and A+T+ (Fig. 4). In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 displayed high accuracy discriminating A−T− from A+T− (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.88, CI95%=0.80−0.93), similar to CSF p-tau231 (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.93, CI95%=0.87–0.97), but lower than both CSF p-tau181 (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.95, CI95%=0.89–0.98, P˂0.05) and CSF p-tau217 (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.95, CI95%=0.89–0.98, P˂0.05) (Fig. 4a). CSF p-tau235 showed high accuracy discriminating A+T− from A+T+ participants (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.89, CI95%=0.82–0.94) and A−T− from A+T+ (AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.98, CI95%=0.95–1.00). In both scenarios, CSF p-tau235 performance was statistically equal to that of CSF p-tau181 (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.93, CI95%=0.87–0.97; AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.99, CI95%=0.97–1.00), CSF p-tau217 (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.91, CI95%=0.84–0.96; AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.99, CI95%=0.97–1.00) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.88, CI95%=0.81–0.93; AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.98, CI95%=0.95–1.00) (Fig. 4a).
Fig. 4.
Diagnostic performance of CSF p-tau235 when discriminating AT groups. a In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 showed high accuracies in all three scenarios. CSF p-tau235 performance discriminating A−T− from A+T− was lower than CSF p-tau181 and p-tau217, but matched that of CSF p-tau231. When differentiating A+T− from A+T+ and A−T− from A+T+, CSF p-tau235 matched the performance of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231. b In the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 displayed high accuracies in all three scenarios, equal to those of CSF p-tau181 and p-tau231, slightly outperforming the latter when discriminating A+T− from A+T+. Data information: Forest plots showing AUC values from ROC analysis (CI95% available in Supplementary Table 7). Comparisons of AUC values between CSF p-tau235 and other available CSF p-tau biomarkers were determined using DeLong test (significance is indicated in bold)
In the BIODEGMAR cohort (Fig. 4b), CSF p-tau235 displayed equal accuracies when discriminating A−T− from A+T− (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.79, CI95%=0.68–0.87) as CSF p-tau181 (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.80, CI95%=0.69–0.88) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCA−T− vs A+T−=0.80, CI95%=0.70–0.88). The accuracy of CSF p-tau235 when discriminating A+T− and A+T+ (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.95, CI95%=0.88–0.98) statistically matched that of CSF p-tau181 (AUCA+T- vs A+T+=0.94, CI95%=0.88–0.98) and slightly outperformed that of CSF p-tau231 (AUCA+T− vs A+T+=0.86, CI95%=0.79–0.92, P=0.0448). Finally, CSF p-tau235 showed a nearly perfect accuracy discriminating A−T− and A+T+ (AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.97, CI95%=0.93–0.99), same as that observed for CSF p-tau181 (AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.98, CI95%=0.94–1.00) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCA−T− vs A+T+=0.95, CI95%=0.90–0.98) (Fig. 4b).
Finally, we evaluated the performance of CSF p-tau235 when discriminating Aβ+ from Aβ− individuals (Supplementary Figure 3, Supplementary Table 8). In the Paris cohort, CSF p-tau235 showed high accuracy distinguishing these two groups (AUCAβ− vs Aβ+= 0.94, CI95%=0.90–0.97). When compared with other p-tau species (Supplementary Table 8), CSF p-tau235 performance was significantly lower than CSF p-tau181 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ +=0.97, CI95%=0.93–0.99, P˂0.05) and CSF p-tau 217 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ +=0.98, CI95%=0.95–0.99, P˂0.01), but equal to CSF p-tau231 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ+=0.96, CI95%=0.92–0.98) (Supplementary Figure 3a). In the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ+ =0.89, CI95%=0.83–0.93) matched the performance of both CSF p-tau181 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ+=0.91, CI95%=0.85–0.94) and CSF p-tau231 (AUCAβ− vs Aβ+=0.88, CI95%=0.82–0.92) (Supplementary Figure 3b).
CSF p-tau235 association with cognition
In both cohorts, MMSE score was associated with CSF p-tau235 after adjustment on age, sex and level of education (Paris: β=−0.304, PADJ <0.0001; BIODEGMAR: β=−0.247, PADJ =0.0009). The association remained significant after further adjustment on Aβ1–42/40 ratio (Paris Cohort: β=−0.243, PADJ =0.0012; BIODEGMAR cohort: β=−0.225, PADJ =0.004).
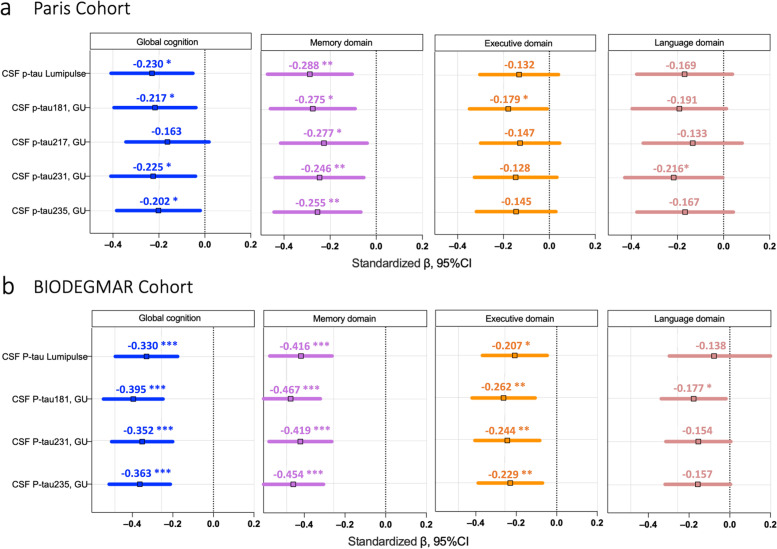
Neuropsychological assessment was available for a subset of patients in the Paris (n=136) and BIODEGMAR cohort (n=139). The cross-sectional associations of CSF p-tau235 levels and other CSF p-tau measurements with global and domain-specific cognition are shown in Fig. 5, after adjustment on age, sex and level of education. CSF p-tau 235 associated with global cognition in both cohorts (Paris β=−0.202, PADJ =0.046; BIODEGMAR β=−0.363, PADJ <0.0001), similar to all CSF p-tau measurements but CSF p-tau217. Regarding specific cognitive domains, the strongest association was found with memory impairment, both for CSF p-tau235 and other p-tau species (CSF p-235: Paris β= −0.255, PADJ =0.0031; BIODEGMAR: β= −0.454, PADJ <0.0001). A weak association was also found with executive domain function but only in BIODEGMAR (β= −0.229, PADJ =0.0051).
Fig. 5.
CSF p-tau 235 association with global cognition and specific cognitive domains. Comparison of CSF p-tau235 and other p-tau markers (p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231) for global and domain-specific cognition in a the Paris and b the BIODEGMAR cohort. Data information: Linear regressions were adjusted for age, sex and level of education. Estimates are presented standardized to allow for comparison in between the different p-tau biomarkers. (*P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, ****P <0.0001)
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the novel CSF biomarker p-tau235 in two independent memory clinic cohorts and compared its diagnostic performance with other relevant p-tau species, specifically CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231. We found that (i) CSF p-tau235 is strongly associated with CSF amyloidosis, regardless of clinical presentation; (ii) high levels of CSF p-tau235 in cognitively impaired patients are highly indicative of MCI or dementia of the AD type; (iii) the main increase in CSF p-tau235 levels occurs between A+T− and A+T+, irrespective of the presence of symptoms or not; (iv) CSF p-tau235 displayed overall the same diagnostic performance as CSF p-tau181 and p-tau231, but a slightly lower diagnostic performance compared with CSF p-tau217; and (v) CSF p-tau235 levels associate with global and specific-domain cognitive decline.
In a previous study, we described CSF p-tau235 across the AD continuum using two research cohorts, demonstrating its high specificity for AD and its comparable performance to other CSF p-tau species [15]. However, these findings cannot be directly translated into the real-world of memory clinics, which is characterized by higher heterogeneity in population (both in social-economic and ethnic terms), clinical presentations and co-pathologies, vastly contrasting with the stringent inclusion/exclusion criteria and detailed pathophysiological characterizations in research cohorts. Thus, the main goal of the present study was to investigate the translatability of previous CSF p-tau235 results into the routine practice of memory clinic. Consistent with our previous findings in selected research cohorts (similarly stratified using Aβ1–42/40) [15], CSF p-tau235 was elevated across CSF Aβ-positive groups in both clinical cohorts. CSF p-tau235 was increased in MCI Aβ+ and dementia Aβ+ showing similar levels between the two groups. This aligns well with previous results in a preclinical AD cohort in which CSF p-tau235 measurements seemingly plateau between MCI Aβ+ and AD Aβ+ [15]. Moreover, in the BIODEGMAR cohort, CSF p-tau235 was noticeably higher in CU Aβ+ when compared with CU Aβ−, and despite lacking sufficient statistical power (eleven and seven cases, respectively), it approached significance. Hence, these results from clinical practice are concordant with our previous results in research cohorts, where CSF p-tau235 was increased in Aβ+ subjects both in preclinical and symptomatic AD [15]. Furthermore, these results indicate that high levels of CSF p-tau235 are strongly associated with CSF amyloidosis and highly indicative of MCI or dementia of an AD type. In terms of diagnostic accuracy identifying Aβ+ in MCI and dementia, CSF p-tau235 showed equal performance to that of CSF p-tau181 and p-tau231, but slightly lower than CSF p-tau217. Because these differences were very marginal, with almost fully overlapping 95% confidence intervals, and together with the lack of CSF p-tau217 measurements in the BIODEGMAR cohort to corroborate these results, this should be cautiously interpreted.
CSF p-tau235 followed an increasing trajectory across AT groups, which was characterized by a minor increment between A−T− and A+T−, followed by a prominent increase from A+T− to A+T+. These differences across AT groups are similar to those previously reported in preclinical AD [15], despite the fact that the cohorts analysed here are memory clinic-based, and thus included proportionally more symptomatic cases. Therefore, this suggests that the increase in CSF p-tau235 is more prominent when abnormalities in CSF Aβ and p-tau are established (i.e. A+T+ cases), regardless of these cases being symptomatic, as shown here, or asymptomatic, like previously reported [15]. CSF p-tau235 showed high performance discriminating all three AT groups and was, for the most part, comparable to other CSF p-tau biomarkers. When compared with CSF p-tau181, CSF p-tau235 was outperformed when discriminating A-T- from A+T-, but only in the Paris cohort. This may suggest that N-terminal p-tau181 species emerge earlier in response to Aβ pathology than N-terminal p-tau235 species (which in turn start increasing earlier than mid-region p-tau181) [15, 35]. CSF p-tau217 also outperformed CSF p-tau235 in the same scenario (A−T− vs A+T−) in the Paris cohort, which aligns well with previous results indicating that CSF p-tau217 emerges prior to CSF p-tau235 [15]. On the other hand, no differences in performance could be found between CSF p-tau235 and CSF p-tau231, except when discriminating A+T− and A+T+ in the BIODEGMAR cohort, where CSF p-tau235 slightly outperformed CSF p-tau231. The marginal difference observed is likely due to the fact that CSF p-tau231 emerges very early in preclinical stages, and tends to plateau later on the continuum AD, thus rendering a lower discrimination between A+T− and A+T+ groups [12]. Finally, CSF p-tau235 showed a high diagnostic accuracy discriminating Aβ− and Aβ+, however, slightly lower than CSF p-tau181 and clearly lower than CSF p-tau217. Despite this, CSF p-tau235 exhibited the same performance as CSF p-tau231 in both the Paris and BIODEGMAR cohorts. In our previous publication, CSF p-tau235 started to increase in A+T− cases; however, the magnitude or extent of this increase was smaller than for other CSF p-tau species, whereas the increase was more pronounced between A+T− and A+T+ [15]. The same was observed here in this study, and the resulting overlap between the levels of CSF p-tau235 in A−T− and A+T−groups rendered the lower performance of this novel biomarker species identifying CSF amyloidosis. Thus, despite its high performance, other p-tau biomarkers emerge earlier than CSF p-tau235 in response to CSF amyloidosis and, therefore, provide a superior performance discriminating A−T− from A+T− and Aβ− from Aβ+.
Higher CSF p-tau235 levels were associated with lower global cognition and memory function in both cohorts, which had not been previously investigated. CSF p-tau181 and CSF p-tau217 have been reported to associate with global cognition and memory impairment cross-sectional and longitudinally, with p-tau217 showing stronger associations with cognitive decline [36]. In our study, CSF p-tau235 performed overall similarly to other p-tau species. We observed modest differences between assays; however, we cannot determine if this reflects differences in the analytical performances of the assays or differences in the biology underlying tau phosphorylation association with cognition.
Limitations/strengths
The strengths of this study include the use of two independent memory clinic-based cohorts, allowing us to validate and confirm our findings in two different clinical settings. Secondly, both cohorts had clinically validated biomarker measurements available, which enabled the detailed stratification of participants and the subsequent investigation of CSF p-tau235 in syndromic or AT groups. Moreover, the studied cohorts included measurements of other novel p-tau species, specifically N-terminal directed CSF p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231 (all measured in the same analytical platform), making possible a head-to-head comparison between different p-tau residues. However, this study does not go without limitations. CSF p-tau217 measurements were not available in the BIODEGMAR cohort, and therefore, the biomarker comparison with CSF p-tau235 could only be explored in the Paris cohort. Another limitation is that CU Aβ+ cases were limited to the BIODEGMAR cohort, and their sample size was rather small. Considering that CSF p-tau235 increases late during preclinical AD [15], it is expected that in cohorts richer in CU cases (especially A+T−), other CSF p-tau biomarkers that abnormally emerge earlier in the AD continuum (such as p-tau231 and p-tau217) [15] would provide a superior performance identifying CSF amyloidosis in asymptomatic individuals. This would subsequently affect the A−T− vs A+T- analysis, where CSF p-tau235 discriminatory accuracy would likely be lower than that of other CSF p-tau biomarkers. A limited number of patients in non-AD dementia group also warranted further studies.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our memory-clinic-based study including two well-characterized cohorts brings further evidence that p-tau235 is a novel and specific CSF biomarker for AD diagnosis, both at MCI and dementia stages. Comparison with other CSF p-tau species, including p-tau181, p-tau217 and p-tau231, supports that CSF p-tau235 should be suitable for use in clinical settings. In addition, significant association with cognitive decline adds an argument to its relevance as a clinical tool to identify and monitor CSF amyloidosis along the whole AD continuum. Future studies will aim to elucidate whether CSF p-tau235 can predict cognitive decline in longitudinal samples and attempt to measure p-tau235 in blood samples.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Supplementary Figure 1. CSF levels of p-tau235 across clinical diagnosis. Supplementary Figure 2. CSF levels of p-tau235 in Aβ+ and Aβ- cases. Supplementary Figure 3. CSF p-tau235 diagnostic performance discriminating Aβ+ from Aβ- cases. Supplementary Table 1. Clinical diagnosis included in each syndrome group in Paris cohort. Supplementary Table 2. Clinical diagnosis included in each syndrome group in BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 3. CSF AD biomarkers cut-offs for BIODEGMAR and Paris Cohort. Supplementary Table 4. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when identifying CSF amyloidosis in dementia and MCI cases in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 5. Clinical diagnosis included in each AT group in Paris cohort. Supplementary Table 6. Clinical diagnosis included in each AT group in BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 7. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when discriminating AT groups in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 8. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when discriminating Aβ- from Aβ+ in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort.
Abbreviations
- AD
Alzheimer’s disease
- AD-MCI
Mild cognitive impairment due to AD
- Aβ
Amyloid beta
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- AUC
Area under the curve
- Aβ1–40
Aβ peptide 1–40
- Aβ1–42
Aβ peptide 1–42
- Aβ1–42/40
Ratio Aβ1–42/Aβ1–40
- bvFTD
Behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia
- CAA
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- CBS
Corticobasal syndrome
- CJD
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CU
Cognitively unimpaired
- CU Aβ−
Cognitively unimpaired Aβ negative
- CU Aβ−
Cognitively unimpaired Aβ positive
- CI95%
95% confidence interval
- CV
Coefficient of variation
- DLB
Dementia with Lewy bodies
- FTD
Frontotemporal dementia
- IP-MS
Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry
- MCI
Mild cognitive impairment
- MCI Aβ−
Mild cognitive impairment Aβ negative
- MCI Aβ+
Mild cognitive impairment Aβ positive
- MMSE
Mini-Mental State Examination
- MS
Mass spectrometry
- NFT
Neurofibrillary tangles
- PPA
Primary progressive aphasia
- PSP
Progressive supranuclear palsy
- p-tau181
Tau phosphorylated at threonine 181
- p-tau217
Tau phosphorylated at threonine 217
- p-tau231
Tau phosphorylated at threonine 231
- p-tau235
Tau phosphorylated at serine 235
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic curve
- SCD
Subjective cognitive decline
- rS
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient
- Simoa
Single molecule array
- t-tau
Total tau
- ULOQ
Upper limit of quantification
- VCID
Vascular contributions to cognitive impairments and dementia
Authors’ contributions
JLR, AV, AFL, HZ, MSC, CP, and KB created the concept and design. Data acquisition was performed by JLR, AFL, AV, EC and JD. JLR, AV and AFL performed data analysis. JLR, AV, AFL, POR, AES, LGM, WSB, EC, JD, APJ, ING, GGE, TK, EV, NJA, HZ, MSC, CP, KB contributed to sample selection and/or interpretation of data. JLR, AV and AFL drafted the manuscript and all authors revised. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Open access funding provided by University of Gothenburg. This study was funded by the Swedish Research Council (#2017-00915 and #2022-00732), the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA (#RDAPB-201809-2016615), the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation (#AF-742881), Hjärnfonden, Sweden (#FO2017-0243), the Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the County Councils, the ALF-agreement (#ALFGBG-715986), the European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders (JPND2019-466-236) and the National Institute of Health (NIH), USA, (grant #1R01AG068398-01). AV is supported by Fondation Ophtalmologique Adolphe de Rothschild and Fondation Vaincre Alzheimer. AES was supported by the Paulo Foundation, the Orion Research Foundation sr, and currently holds a postdoctoral fellowship from the Academy of Finland (#341059). TKK was funded by the Swedish Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet #2021-03244), the Alzheimer’s Association Research Fellowship (#AARF-21-850325), the Aina (Ann) Wallströms and Mary-Ann Sjöbloms stiftelsen and the Emil och Wera Cornells stiftelsen. HZ is a Wallenberg Scholar supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council (#2018-02532), the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101053962, Swedish State Support for Clinical Research (#ALFGBG-71320), the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA (#201809-2016862), the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer’s Association (#ADSF-21-831376-C, #ADSF-21-831381-C and #ADSF-21-831377-C), the Bluefield Project, the Olav Thon Foundation, the Erling-Persson Family Foundation, Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor, Hjärnfonden, Sweden (#FO2022-0270), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 860197 (MIRIADE), the European Union Joint Programme – Neurodegenerative Disease Research (JPND2021-00694) and the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL (UKDRI-1003). MSC receives funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (Grant agreement No. 948677), Project “PI19/00155”, funded by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) and co-funded by the European Union, and from a fellowship from “la Caixa” Foundation (ID 100010434) and from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 847648 (LCF/BQ/PR21/11840004).
Availability of data and materials
Bulk anonymized data can be shared by request from qualified investigators, providing data transfer is in agreement with EU legislation and decisions by the institutional review board of each participating center.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients or their legal relatives in case of severe dementia gave written informed consent to their participation in this study. Collection and analysis of samples were approved by the ethic committee of Bichat University, Paris, France (CEERB GHU Nord n°10-037) for Paris cohort and by the local ethics committee (CEIC PSMAR, project code 2018/7805I) for the BIODEGMAR cohort.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
KB has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu. Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). MSC has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics International Ltd and has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Roche Diagnostics, S.L.U and Roche Farma, S.A. MSC was granted with a project funded by Roche Diagnostics International Ltd; payments were made to the institution (BBRC). EVM is cofounder of ADx NeuroSciences.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Juan Lantero-Rodriguez, Agathe Vrillon and Aida Fernández-Lebrero contributed equally as first authors.
References
- 1.Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00308809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thal DR, et al. Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology. 2002;58(12):1791–800. doi: 10.1212/WNL.58.12.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jack CR, Jr, et al. NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14(4):535–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Blennow K, Vanmechelen E, Hampel H. CSF total tau, Abeta42 and phosphorylated tau protein as biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2001;24(1–3):87–97. doi: 10.1385/MN:24:1-3:087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ashton NJ, et al. Update on biomarkers for amyloid pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Biomark Med. 2018;12(7):799–812. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Molinuevo JL, et al. Current state of Alzheimer’s fluid biomarkers. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;136(6):821–853. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1932-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scholl M, et al. Biomarkers for tau pathology. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019;97:18–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barthelemy NR, et al. Tau phosphorylation rates measured by mass spectrometry differ in the intracellular brain vs. extracellular cerebrospinal fluid compartments and are differentially affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019;11:121. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Karikari TK, et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(5):422–433. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Palmqvist S, et al. Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA. 2020;324(8):772–781. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ashton NJ, et al. Plasma p-tau231: a new biomarker for incipient Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2021;141(5):709–724. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02275-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ashton NJ, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau231 as an early indicator of emerging pathology in Alzheimer's disease. EBioMedicine. 2022;76:103836. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Janelidze S, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1683. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15436-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ashton NJ, et al. Differential roles of Abeta42/40, p-tau231 and p-tau217 for Alzheimer’s trial selection and disease monitoring. Nat Med. 2022;28(12):2555–2562. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02074-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lantero-Rodriguez J, et al. P-tau235: a novel biomarker for staging preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(12):e15098. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202115098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hasegawa M, et al. Protein sequence and mass spectrometric analyses of tau in the Alzheimer's disease brain. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(24):17047–54. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)41890-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hoffmann R, et al. Unique Alzheimer’s disease paired helical filament specific epitopes involve double phosphorylation at specific sites. Biochemistry. 1997;36(26):8114–24. doi: 10.1021/bi970380+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Singer D, et al. Neighbored phosphorylation sites as PHF-tau specific markers in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;346(3):819–28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hanger DP, et al. Novel phosphorylation sites in tau from Alzheimer brain support a role for casein kinase 1 in disease pathogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(32):23645–54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703269200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sengupta A, et al. Phosphorylation of tau at both Thr 231 and Ser 262 is required for maximal inhibition of its binding to microtubules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;357(2):299–309. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1998.0813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cho JH, Johnson GV. Primed phosphorylation of tau at Thr231 by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) plays a critical role in regulating tau's ability to bind and stabilize microtubules. J Neurochem. 2004;88(2):349–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Van der Mussele S, et al. Behavioral syndromes in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;38(2):319–29. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Valero S, et al. Interaction of neuropsychiatric symptoms with APOE epsilon4 and conversion to dementia in MCI patients in a Memory Clinic. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20058. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77023-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xiong C, et al. Complex interactions underlie racial disparity in the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;16(4):589–597. doi: 10.1002/alz.12060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Santiago JA, Potashkin JA. The impact of disease comorbidities in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:631770. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.631770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment criteria in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative: meeting biological expectations. Neurology. 2021;97(12):597–599. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.McKeith IG, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology. 2017;89(1):88–100. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rascovsky K, et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 9):2456–77. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Molinuevo JL, et al. Implementation of subjective cognitive decline criteria in research studies. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13(3):296–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jessen F, et al. The characterisation of subjective cognitive decline. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30368-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Puig-Pijoan A, et al. The CORCOBIA study: cut-off points of Alzheimer’s disease CSF biomarkers in a clinical cohort. Neurologia (Engl Ed). 2022. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 32.Ashton NJ, et al. Plasma and CSF biomarkers in a memory clinic: head-to-head comparison of phosphorylated tau immunoassays. Alzheimers Dement. 2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Leitao MJ, et al. Clinical validation of the Lumipulse G cerebrospinal fluid assays for routine diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Karikari TK, et al. Head-to-head comparison of clinical performance of CSF phospho-tau T181 and T217 biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17(5):755–767. doi: 10.1002/alz.12236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Snellman A, et al. N-terminal and mid-region tau fragments as fluid biomarkers in neurological diseases. Brain. 2022;145(8):2834–2848. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mielke MM, et al. Comparison of CSF phosphorylated tau 181 and 217 for cognitive decline. Alzheimers Dement. 2022;18(4):602–611. doi: 10.1002/alz.12415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Supplementary Figure 1. CSF levels of p-tau235 across clinical diagnosis. Supplementary Figure 2. CSF levels of p-tau235 in Aβ+ and Aβ- cases. Supplementary Figure 3. CSF p-tau235 diagnostic performance discriminating Aβ+ from Aβ- cases. Supplementary Table 1. Clinical diagnosis included in each syndrome group in Paris cohort. Supplementary Table 2. Clinical diagnosis included in each syndrome group in BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 3. CSF AD biomarkers cut-offs for BIODEGMAR and Paris Cohort. Supplementary Table 4. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when identifying CSF amyloidosis in dementia and MCI cases in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 5. Clinical diagnosis included in each AT group in Paris cohort. Supplementary Table 6. Clinical diagnosis included in each AT group in BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 7. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when discriminating AT groups in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort. Supplementary Table 8. Accuracies of CSF p-tau181, p-tau217, p-tau231 and p-tau235 when discriminating Aβ- from Aβ+ in Paris and BIODEGMAR cohort.
Data Availability Statement
Bulk anonymized data can be shared by request from qualified investigators, providing data transfer is in agreement with EU legislation and decisions by the institutional review board of each participating center.