Abstract
How novel genetic interactions evolve, under what selective pressures, and how they shape adaptive traits is often unknown. Here we uncover behavioural and developmental genetic mechanisms that enable water striders to survive attacks by bottom-striking predators. Long midlegs, critical for anti-predator strategy, are shaped through a lineage-specific interaction between the Hox protein Ultrabithorax (Ubx) and a new target gene called gilt. The differences in leg morphologies are established through modulation of gilt differential expression between mid and hindlegs under Ubx control. Furthermore, short-legged water striders, generated through gilt RNAi knockdown, exhibit reduced performance in predation tests. Therefore, the evolution of the new Ubx-gilt interaction contributes to shaping the legs that enable water striders to dodge predator strikes. These data show how divergent selection, associated with novel prey-predator interactions, can favour the evolution of new genetic interactions and drive adaptive evolution.
Introduction
The discovery that distinct lineages share a similar genetic toolkit established that variations within genetic networks could shape the phenotype during development and evolution1,2. An important gap in understanding the origin of phenotypic diversity, however, resides in our poor knowledge about how selection can favour the emergence of novel developmental genetic interactions and ultimately shape phenotypic evolution3-5. Here we focus on the semi-aquatic bugs (Heteroptera, Gerromorpha) to study how divergent selection, associated with a new life style on the water surface6, can drive species diversification. The ancestors of the Gerromorpha transited from terrestrial life to life on the water surface over 200 MY ago6-8. Acquisition of this lifestyle exposes the insects to new challenges including locomotion on fluid and escaping bottom-striking predators. Paramount to their success on water surfaces is the evolution of the shape and size of their legs in association with niche specialization and mode of locomotion6,9,10. Basal lineages, which occupy transitional zones between water and land, retain ancestral character states with midlegs shorter than hindlegs, and employ the ancestral mode of locomotion through alternating leg movements6,7,9,11,12. In contrast, water striders (Gerridae) that specialize in open water zones employ a derived mode of locomotion through simultaneous rowing motion of the midlegs. This rowing mode is enabled by a novel character state where midlegs are now longer than hindlegs6,11-13. A hallmark of the entire lineage of the semi-aquatic bugs, that distinguishes them from closely related terrestrial Heteroptera, is the deployment of the Hox protein Ubx in the second thoracic segment11,13 and a notable increase of Ubx dose in the third thoracic segment12. These changes in Ubx expression and function are associated with changes in leg length across the semi-aquatic bugs11-13. While we are beginning to understand how morphological changes in the appendages are associated with specificities of locomotion and sexual interactions on the fluid water-air interface6,10,14, little is known about how the legs are shaped under selection by aquatic predators. Here we investigated the evolutionary and developmental genetic mechanisms underlying anti-predator strategies in water striders. We found that water striders survive attacks by aquatic predators using a quick jump enabled by their long and slender legs. We demonstrated that the shape of the legs, that are important for this behaviour, is modulated through the evolution of a lineage-specific interaction between Ubx and a new target gene called gilt. Finally, we showed that short-legged individuals, generated through gilt RNAi, exhibit reduced jump performance in predation tests.
Results and discussion
Water striders use quick jump, and not flight, to escape predators
First, we asked how water striders survive in the face of the various predators lurking under the surface15-17 (Supplementary movie 1). Using high-speed videography, we examined the interaction between the water strider Limnoporus dissortis and the stealth surface hunting halfbeak fish Dermogenys sp18. When attacked from beneath, the water strider uses an almost vertical jump in the air to avoid the strike (Figure 1; Supplementary movie 1 section 3). The animal pushes against the water surface with a characteristic bending of the mid and hindlegs, creating dimples without breaking surface tension (Figure 1A; Supplementary movie 1 section 3). The first legs do not seem to contribute. This behaviour results in movement amplification that propels the insect several times higher in the air than the length of its body. The time from the trigger of the strike until when the fish’s jaws reach the water strider is 28.7±3.9 milliseconds, on average (Supplementary Table1). As a result of the jump (Figure 1B), the fish misses (Figure 1C) and the water strider falls back and escapes (Figure 1D; Supplementary Movie 1 section 3). To measure the duration of the jump, we developed a controlled setup where the attack is simulated using a dead backswimmer (Notonecta), a natural predator of water striders17, which we manoeuvred with a wire (Figure 1E). This setup reproduced the water strider jump, with 28.8±1.8 milliseconds from when the jump is triggered until when the legs of the animal lose contact with water surface (Supplementary movie 1 section 3; Supplementary table 1). Therefore, the water strider delivers an anti-predator response that matches the quick strike of the predator. Interestingly, we observed that adult water striders invariably jump to dodge the strike even though they are capable of flight6,19. When we triggered flight (Figure1F, see details in methods and SOM), we found that the water strider takes an average of 124.8±18.6 milliseconds to leave the water surface. Eighty per cent (99.4±18.0 milliseconds) of the flight time is accounted for by the animal flapping its wings, while the remaining twenty per cent (25.4±12.8 milliseconds) represent take-off supported by the legs and the wings (Supplementary movie 2). This indicates that flight is four times significantly slower (one-way ANOVA, n=10, p<0.0001) than the jump, i.e. four times slower than the predatory strike, and thus not suitable as an anti-predator strategy (Supplementary table 1; Supplementary movie 2). Therefore, the jump enabled by the slender long legs is critical for the water strider to survive aquatic predators.
Figure 1. Predation escape strategy and behavioural setups in water striders.
(A) A water strider initiating the escape through a jump triggered by the approaching fish. The midlegs push downwards causing them to bend and form deep depressions (dimples). (B-D) Frames, taken from supplementary movie 1, showing the sequence of interaction between the water strider and the attacking halfbeak fish. The water strider dodges the attack (B) by moving away from the trajectory of the fish’s strike through a quick jump in the air (C), while the fish is carried away by its own momentum, the water strider falls back and skates away (D). (E) Controlled setup used to trigger the jump in adult water striders using a dead backswimmer manoeuvred by the experimentalist with a wire. (F) Flight in water striders triggered by increasing population density and exposure to high light intensity.
Emergence of novel gene expression water striders
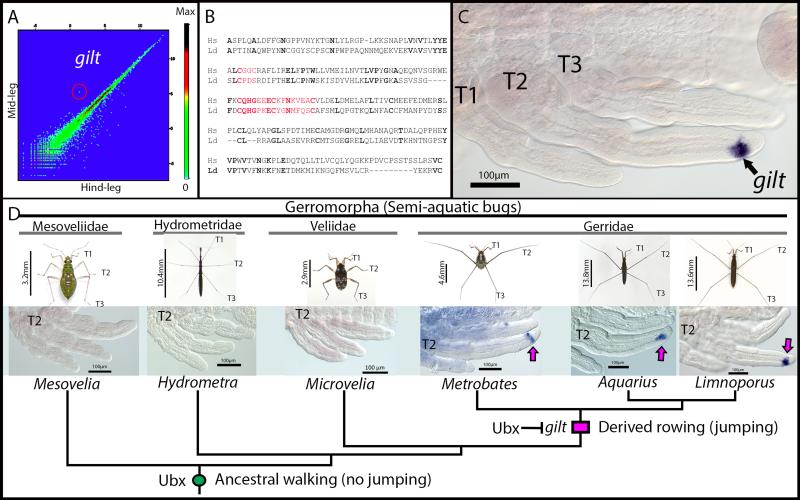
The derived morphology where midlegs are longer than hindlegs is important for this anti-predator behaviour. We therefore wanted to uncover the genetic mechanisms that shape the differences between the legs during development in water striders. A genome-wide comparative analysis of gene expression profiles uncovered 155 differentially expressed transcripts between midlegs and hindlegs of developing Limnoporus embryos (Figure 2A). We further focused on a transcript the expression of which perfectly matched the differences in morphology between the legs, i.e. high in the midlegs and very low in the hindlegs (Figure 2A; Supplementary figure 1a-c). This transcript is homologous to a gene known as gamma interferoninducible thiol reductase (gilt) (Figure 2B), a reducing enzyme required for antigen processing and presentation by the Major Histocompatibility Complex II in mammals 20. A role for Gilt in innate immunity has recently been suggested in flies21, but no known developmental function has ever been associated with this protein. During water strider development, we found that gilt mRNA expression is specific to the midlegs. Its expression begins at ~25% of embryogenesis (Supplementary figure 1d), exclusively in a distinct cell population at the tip of midleg tarsi, and continues through later stages of embryogenesis (Figure 2C; Supplementary figure 1e-f). gilt is exclusively expressed in the midlegs until 45% of embryogenesis, but also appears in the hindlegs during later embryogenesis (Supplementary figure 1b-c). While all Gerridae have the derived leg plan where midlegs are longer than hindlegs, many other Gerromorpha retain the ancestral leg plan where midlegs are shorter than hindlegs6,7,11,12. We therefore cloned gilt from a sample of six species representing the two morphologies (Supplementary figure 1G). We found that gilt is expressed in the tarsus of midlegs in all three species with derived leg plan and absent from all three species that retain an ancestral leg plan (Figure 2D). This indicates that the expression of gilt in the midlegs is characteristic to the derived morphology and that its evolution coincides with the evolution of rowing characteristic of species specialized in open water zones.
Figure 2. gilt expression during development and evolution in the semi-aquatic bugs.
(A) Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles between midlegs and hindlegs during early embryogenesis in Limnoporus dissortis. The transcript corresponding to gilt is encircled. (B) Sequence comparison between Limnoporus dissortis and Homo sapiens Gilt proteins. Gilt active site and signature motif are highlighted in red, identical amino acids are in bold. (C) In situ hybridization detecting gilt mRNA expression in the midlegs of an early Limnoporus embryo (48hours: ~30% development). T1, 2, 3: Thoracic segments 1, 2, 3. (D) Evolution of gilt expression across six semi-aquatic bugs representing four families and both the ancestral and derived leg length plan. gilt expression in the midlegs is detected in species with derived relative leg length plan and absent in species with the ancestral leg plan. The gain of Ubx in midlegs at the base of the Gerromorpha lineage is indicated with green circle and the evolution of gilt expression at the base of the Gerridae with pink rectangle. Scale bars are body sizes of adult individuals are indicated.
Ubx modulates gilt expression in the legs
Previous work has shown a role for Ubx in the acquisition of the novel long midleg body plan, with moderate levels of Ubx lengthening midlegs and six to seven times higher levels of Ubx shortening hindlegs11-13. Interestingly, our comparative transcriptome shows an inverse correlation between Ubx and gilt levels – with low Ubx high gilt in midlegs, and high Ubx low gilt in hindlegs (Supplementary figure 2) – suggesting a regulatory interaction between Ubx and gilt. To test this possible interaction, we contrasted a transcriptome of legs extracted from Ubx RNAi embryos to that of legs from untreated embryos (Figure 3A). We found that in Ubx RNAi embryos gilt expression doubles in the midlegs and appears ectopically in the hindlegs (Figure 3A). Furthermore, in situ hybridization in embryos treated with Ubx RNAi confirms the appearance of gilt expression in the hindlegs (Figure 3B), demonstrating that gilt is no longer repressed when we knock Ubx down. Therefore, Ubx represses gilt partially in the midlegs and entirely in the hindlegs of Limnoporus early embryos, and the extent of this repression is dependent on Ubx levels.
Figure 3. gilt function and interaction with Ubx in Limnoporus dissortis.
(A) Transcriptomics data show that gilt expression doubles in the midleg and appear in the hindlegs of Ubx RNAi embryos, as revealed by the number of reads per kilobase per million (RPKM). (B) In situ hybridization detecting gilt mRNA in an Ubx RNAi early embryo. Note the expansion of gilt in the midlegs and its ectopic expression in the hindleg. T1, T2 and T3: Thoracic segments 1, 2 and 3; A1: Abdominal segment 1; Asterisk (*) indicates an ectopic leg forming on A1 and that is characteristic to Ubx RNAi in water striders12. (C) Control late embryo. (D) gilt RNAi late embryos with shorter midlegs. (E) Tukey box plots showing measurements of the effect of u (Ubx RNAi n=13), g (gilt RNAi n=12), or u+g (double Ubx+gilt RNAi n=21) RNAi on leg length compared to controls (wt untreated n=10 and injected with yfp double stranded RNA n=7). (F) Double Ubx+gilt RNAi late embryo showing drastically shorter midlegs. Scale bars are indicated.
Gilt is required to lengthen the midlegs in water striders
We further tested the role of gilt during embryonic leg development using parental RNA interference11-13. Embryos with depleted gilt transcript (n=12) grow significantly shorter midlegs relative to controls (yfp injected controls n=7 and untreated controls n=10, one-way ANOVA p<0,0001; Figure 3C-D) (The various controls for this experiment are detailed in the Methods and Supplementary figure 3). Statistical analyses of measured leg length revealed that gilt RNAi embryos develop significantly (12%) shorter midlegs compared to controls (Figure 3E). This shortening affects the tarsus, tibia and femur (Supplementary figure 4), suggesting that the role of gilt in leg allometry is cell non-autonomous. gilt expression increases in Ubx RNAi treatments (Figure 3A), whereas either Ubx11-13 or gilt RNAi results in shorter legs (Figure 3D-E). To test whether increased gilt expression impacts leg length in the absence of Ubx, we performed a double Ubx+gilt RNAi experiment (Figure 3E-F) (Details and controls can be found in Methods and Supplementary figure 5). Midlegs in double Ubx+gilt RNAi (n=21) are 7% significantly shorter (one-way ANOVA, p<0,0046) than midlegs of single Ubx RNAi (n=13; Figure 3E). Conversely in the hindlegs, double Ubx+gilt RNAi produces an intermediate effect between single gilt (one-way ANOVA, p<0,0001) and single Ubx (one-way ANOVA, p<0,0001) RNAi (Figure 3E). Therefore, part of the role of Ubx in lengthening the midlegs allows some expression of gilt, and part of its role in shortening the hind legs requires the complete silencing of gilt. Altogether, our data demonstrate that gilt represents a downstream effector of Ubx, whose expression contributes to the long leg phenotype that is associated with the evolution of the anti-predator jump behaviour.
Gilt-free water striders jump lower
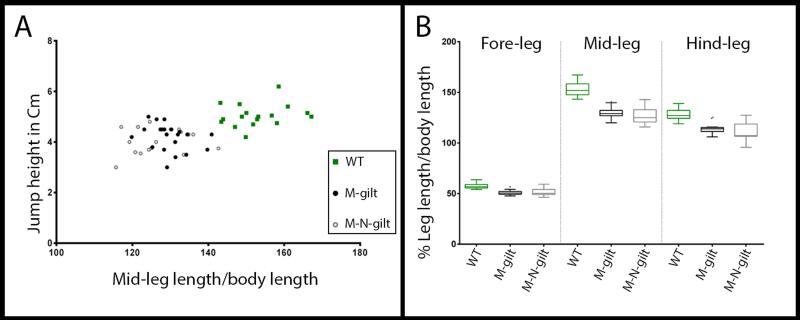
Unlike Ubx, the depletion of gilt does not impair whole body development and instead allows the emergence of viable adults without any apparent defects than the reduction of leg length. gilt RNAi animals therefore provided an exquisite opportunity to directly assay the importance of leg length for anti-predator strategy. To do this, we measured the jump performance of water striders when attacked from beneath using our controlled setup (Figure 4). On average, control individuals (n=17) jumped 5.05±0.46cm (Figure 4A), while gilt RNAi individuals (n=38) jumped 4.13±0.51cm (Figure 4A), i.e., a performance 18% significantly lower than that of normal individuals (one-way ANOVA, p<0,0001; Supplementary movie 3). Interestingly, gilt RNAi animals display a varying degree of leg length reduction (in average 16% and 6% shorter mid and hindlegs, respectively; Figure 4B) and there is a clear correlation between midleg length and jump performance (Figure 4A). These results establish that the acquisition of gilt expression contributes to shaping the legs in association with the evolution of the jump behaviour, and that even a small reduction in leg length reduces the ability of water striders to deliver a powerful jump when the predator strikes.
Figure 4. Decreased performance of gilt RNAi water striders in predation test.
(A) Tukey box plots showing leg lengths variations within normal and gilt RNAi individuals at the fifth nymphal instar used in this test. Wild types (n=17) are untreated, M-gilt (Maternal gilt RNAi; n=21) are fifth nymphal instar individual obtained by injecting mothers with gilt ds-RNA, and M-N-gilt (Maternal plus Nymphal gilt RNAi; n=17) received an additional injection at first nymphal instar. (B) Lower performance in simulated predation tests directly correlates with midleg length reduction across gilt RNAi individuals.
Altogether, our findings show that the predation escape strategy employed by water striders relies primarily on a jump reflex, enabled by the long slender legs. We also show that the acquisition of this morphological character involves novel genetic interactions between the Hox protein Ubx and gilt; a previously unknown target, encoding a reducing enzyme. When compared to species that retain ancestral character states where midlegs are shorter than hindlegs, the gain of gilt expression contributes to increase the length of midlegs that is characteristic to species specialized in rowing in open waters. Therefore, the evolution of this novel interaction between Ubx and gilt contributes to shaping the legs in association with the efficient anti-predator strategy that water striders employ to survive aquatic predators22. The jump, though representing a quick reaction to the strike, can only give advantage to the prey if coupled with a primary mechanism of predator detection23. Despite the stealth approach of the fish, water striders are exquisite sensors of vibration owing to a multitude of sensory bristles located in the contact surface between the legs and the water surface24. Therefore, the ability of water striders to detect predators, together with the adapted morphology of their legs may have been key to their success in open water surfaces worldwide. This rich ecological and evolutionary context, together with the amenability to experimental manipulation, make water striders a suitable system to study how genetic interactions evolve in association with adaptive phenotypic evolution.
Methods
Animal collection and rearing
Limnoporus dissortis, Microvelia americana, and Metrobates hesperius were collected from ‘Rivière de l’Acadie,’ at the vicinity of Montréal, Québec, Canada. Aquarius paludum and Hydrometra stagnorum were collected in a pond near Lyon, France. Mesovelia mulsanti were collected in a pond near Cayenne, French Guiana. Halfbeak fishes (Dermogenys sp.) were purchased from a fish store in Lyon, France. Both water striders and fish were kept in aquaria at 25 °C with a 14-hour light/10-hour dark cycle, and both were fed on live crickets. Pieces of floating Styrofoam were regularly supplied to female water striders to lay eggs.
Measurement of fish strike duration
10 high-speed movies were captured using a Miro M310 high-speed camera (Vision Research), at 2000 frames per second, while halfbeak attacked water striders. In each movie, we manually identified the start frame where the animal first triggered the attack and the end frame where the fish’s jaw reach the initial position of the body of the water strider. The strike duration represented by the time elapsed between the start and the end frames was calculated using PCC software (Vision research). Details about software and method of calculation can be found in this tutorial by Vision Research: http://www.visionresearch.com/Service--Support/Tutorials/
Measurement of water strider jump duration
This experiment was conducted in adult water striders to compare with the duration of flight below. To measure jump duration in a controlled manner, we simulated the attack using a dead backswimmer (Notonecta) attached at the end of a wire and manoeuvred by a manipulator. This strategy reproducibly induced water striders to jump. We then filmed ten individuals at 2000 frames per second. In each movie, we identified the start of the jump as the time elapsed between the frame where we see the first movement of the leg pushing downwards, and the frame where all legs lose contact with the water surface. Measurements of the time elapsed between start and end of the jump were performed using PCC software (Vision Research).
Measurement of flight duration
To measure flight duration, we stimulated flight by increasing the density of water striders in the aquaria and by exposing them to an extra source of light. These conditions originate from our own observations while breeding water striders in the lab. We then took ten high-speed movies (2000 frames per second) of ten individuals during flight. In each movie, we identified the start of the flight as the time elapsed between the frame where we first see wings moving and the frame where all legs lose contact with the water surface. Measurements of the time elapsed between start and end of the flight were performed using PCC software (Vision Research).
Limnoporus dissortis reference transcriptome
A mixture of adult males and females, nymphal instars and various embryonic stages of Limnoporus dissortis were used to isolate total RNA using Trizol (Invitrogen). Transcriptome was sequenced using 454 Roche technology and assembled using Newbler program version 2.6 (Roche). A total of 26,237 isotigs defining 16,368 isogroups were assembled. Assembled isotigs were annotated by sequence similarity against the NCBI ‘non-redundant’ protein database using BLAST2GO. In addition to inferred annotations, for each annotated isogroup we predicted PFAM motifs using HMMER3 tools from Sanger institute. Limnoporus dissortis transcriptome can be retrieved in NCBI using the following accession number: PRJNA289202
Quantification of gene expression using comparative transcriptomics
RNA from dissected Limnoporus dissortis legs was used by ProfilExperts (Lyon-France) to conduct deep sequencing using TruSeq RNA kit and Illumina HiSeq2000 technology. A total of ~50 million reads was generated per sample. These reads were trimmed and filtered to remove low-quality bases and aligned against the draft Limnoporus transcriptome and transcript levels were quantified by determining the number of Reads Per Kilobase per Million mapped reads (RPKM) in each sample25. The raw reads of Limnoporus dissortis leg transcriptomes can be retrieved here: PRJNA289202
gilt cloning
Total RNA from L. dissortis, A. paludum, M. hesperius, M. americana, H. stagnorum, and M. mulsanti was extracted from different embryonic stages and nymphal instars. First strand cDNA synthesis was then performed for each species, using total RNA as a template, according to instructions outlined in the Invitrogen cDNA synthesis kit. Specific primers for gilt in Limnoporus dissortis were designed based on sequences obtained from the whole transcriptome of Limnoporus dissortis. Primers for each species used in PCR reaction to amplify a fragment of gilt, can be found in supplementary table 2. Gilt sequence for each species can be retrieved in Genbank. gilt sequences from these various species can be retrieved in GenBank using the following accession numbers: KR704883, KR704884, KR704885, KR704886, KR704887, and KR704888.
Embryo dissection
Embryos were collected, treated with 25% bleach, and then washed with PTW 0.05% (1X PBS; 0.05% Tween-20). For image acquisition, late embryos were dissected out of the eggshell, fixed in 4% formaldehyde, and their images captured using a Zeiss Discovery V12 scope. For staining, embryos of various stages were manually dissected, cleaned from yolk, and fixed following the method below.
In situ hybridization
Dissected embryos were fixed in 200μl 4% Paraformaldehyde (PFA) + 20μl Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO), and 600μl heptane for twenty minutes at room temperature with shaking. Embryos were then washed several times in cold methanol and rehydrated in decreasing concentrations of methanol in PTW 0.05%. These embryos were washed three times in PTW 0.05%, three times in PBT 0.3% (1X PBS; 0.3% Triton X100), and twice with PBT 1% (1X PBS; 1% Triton X100). Following these washes, embryos were transferred to 1:1 PBT 1% / hybridization solution (50% formamide; 5% dextran sulfate; 100μg/ml yeast tRNA; 1X salts). The composition for 100ml 10X salt is as follows: 17.5g sodium chloride, 1.21g tris-base, 0.71g monosodium phosphate, 0.71g sodium phosphate dibasic, 0.2g Ficoll 400, 0.2g Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), 10ml of 0.5M EDTA, 0.2g BSA (pH 6.8). Embryos were pre-hybridized for one hour at 60°C, followed by addition of a Dig-labelled RNA probe overnight at 60°C. Embryos were then transferred gradually from hybridization solution to PBT 0.3% through consecutive washes with 3:1, 1:1, 1:3 pre-warmed hybridization solution: PBT 0.3% gradient. A blocking step was performed with PAT (1X PBS; 1% Triton X100; 1% BSA) at room temperature followed by incubation with anti-DIG antibody coupled with alkaline phosphatase for two hours at room temperature, or at 4°C overnight. Embryos were washed several times in PBT 0.3% then in PTW 0.05% before color reaction is conducted with NBT/BCIP in Alkaline Phosphatase buffer (0.1M Tris pH 9.5; 0.05M MgCl2; 0.1M NaCl; 0.1% Tween-20).
Parental RNAi
Gene knockdown of Ubx and gilt using parental RNAi was conducted following the protocol described in references 11-13. Control RNAi was conducted by injecting ds-yfp (double stranded RNA from the yfp gene sequence). Template for in vitro transcription to produce ds-RNA for each gene was prepared using the T7-tagged primers in supplementary table 3.
Efficiency of gilt RNAi
We verify that gilt RNAi specifically depletes gilt, we stained embryos with a mix containing gilt probe and a ten-fold diluted egfr probe. egfr is expressed in the legs in five stripes prefiguring the joints between leg segments12. This probe mix allows gilt staining to become strong and easily visible before egfr staining. If our RNAi experiment successfully depletes gilt, we expect to see egfr staining but not gilt. In control treatments, this probe mix stains the embryos such that gilt staining appears stronger than egfr staining, thus allowing us to assess gilt expression relative to the strength of egfr staining (Supplementary figure 3a). Staining embryos from gilt RNAi treatments with the same mix fails to detect gilt mRNA in midlegs tarsi even when we allow egfr staining to become strong (Supplementary figure 3b). This demonstrates that our RNAi experiment efficiently depletes gilt transcripts.
Specificity of gilt RNAi
To ensure that our RNAi does not suffer from off target effects, we designed double stranded RNA from two non-overlapping fragments of gilt (Supplementary figure 3c). Injection of double stranded RNA from these three fragments induced the same leg length phenotypes (Supplementary figure 3d-f). Furthermore, we repeated the same experiment on a second species, Aquarius paludum, and obtained the same results (Supplementary figure 3g-j). Therefore, gilt RNAi depletes specifically gilt transcript. To make sure that the leg shortening phenotype of gilt RNAi is not just a reflexion of natural variation in leg length, we measured the legs of individual that reach the first nymphal instar at successive days (Supplementary figure 3k). We found that the first individual that are laid by injected females (days 1 and 2) have either normal leg length or very subtle shortening. The shortening phenotype becomes stronger the following days (Supplementary figure 3k). This indicates that the effect we see on leg length is due to gilt knockdown.
Efficiency of double gilt+Ubx RNAi
We confirmed the efficiency of the double gilt+Ubx knockdown by staining embryos with the mix containing gilt probe and ten-fold diluted egfr probe (Supplementary figure 5). Control embryos show a clear gilt expression in the midlegs (Supplementary figure 5a), Ubx RNAi embryos show gilt expression in both mid- and hind legs (Supplementary figure 5b), whereas single gilt RNAi (Supplementary figure 5c) and double gilt/Ubx RNAi (Supplementary figure 5d) show no gilt expression in either leg despite the clear egfr staining. This demonstrates that the double gilt+Ubx RNAi knockdown was successful.
Leg measurements
A sample of first instar nymphs was used for each RNAi group and control: untreated control n=10; yfp-injected negative control n=7; gilt RNAi n=12; Ubx RNAi n= 13; and Ubx+gilt RNAi n=21. Nymphs were dissected and mounted on slides in Hoyer’s medium. Three sets of measurements were recorded: head width and the length of the tarsus, tibia, and femur individually. Measurements for each leg segment of each pair of legs were recorded on a Zeiss microscope using the Zen software.
Predation test experiment
We conducted predation performance in a controlled setup that induces the water striders to jump near a grid such that the height of the jump can be accurately measured. We triggered the jump by approaching a dead backswimmer under the water striders. Individuals from the different categories (WT, Maternal-gilt RNAi and Maternal-Nymphal-gilt RNAi) were allowed to develop until fifth nymphal instar. We used fifth instars because they are large enough for recording and also because they easily induced to jump. We took a total of seven movies for each individual and extracted jump height. We then sacrificed the individuals and measured their leg length and body length. Finally, we plotted the highest jump from each individual by its leg length corrected to body length.
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses and plots were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 6.00). For differences in leg length between controls and the various RNAi experiments (gilt, Ubx, Ubx+gilt), we performed a one-way ANOVA test to determine statistical significance. We normalized leg length by head width to correct for differences in body size. We did not use body length because body length at the first nymphal instar changes considerably with changes in food intake (well fed individuals tend to swell up). Statistical significance for the various legs and segment of the legs are summarized in supplementary table 4.
For the predation performance experiment, we performed a one-way ANOVA test to determine statistical significance in leg length and jump height between untreated (wt) and various RNAi experiments (Maternal-gilt and Maternal-Nymphal-gilt). We normalized leg length by body length to correct for differences in body size. We used body size because it is a reliable reference at the fifth nymphal instar. Statistical significance for differences in leg length and jump height are summarized in supplementary table 5.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Payre, M. Averof, F. Bonneton, and F. Leulier for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank F. Moreira for help with species identification and PSMN-ENS de Lyon for providing access to servers and calculation power. This work was supported by an ATIP-Avenir from CNRS and an ERC-CoG # 616346 to AK and a PhD fellowship from Université Lyon1 to PR.
Footnotes
Accession codes: The transcriptome data generated in this study have been deposited in NCBI database under the accession code PRJNA289202. gilt sequences generated in this study have been deposited in GenBank nucleotide database under accession codes KR704883 to KR704888.
Conflict of financial interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Carroll SB. Evo-devo and an expanding evolutionary synthesis: a genetic theory of morphological evolution. Cell. 2008;134:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.030. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Davidson EH. The regulatory genome : gene regulatory networks in development and evolution. Academic; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Abouheif E, et al. Eco-Evo-Devo: The Time Has Come. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;781:107–125. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7347-9_6. doi:Doi 10.1007/978-94-007-7347-9__6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barrett RD, Hoekstra HE. Molecular spandrels: tests of adaptation at the genetic level. Nature reviews. Genetics. 2011;12:767–780. doi: 10.1038/nrg3015. doi:10.1038/nrg3015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Emilia Santos M, Berger CS, Refki PN, Khila A. Integrating evo-devo with ecology for a better understanding of phenotypic evolution. Briefings in functional genomics. 2015 doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv003. doi:10.1093/bfgp/elv003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Andersen NM. The semiaquatic bugs (Hemiptera: Gerromorpha). 1982. Vol. ‐ Entomonograph Vol. 3 Scandinavian Science Press LTD. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Damgaard J. Phylogeny of the semiaquatic bugs (Hemiptera-Heteroptera, Gerromorpha) Insect Systematics & Evolution. 2008;39:30. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1163/187631208788784264. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li M, Tian Y, Zhao Y, Bu W. Higher level phylogeny and the first divergence time estimation of Heteroptera (Insecta: Hemiptera) based on multiple genes. Plos One. 2012;7:e32152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032152. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Andersen NM. A comparative study of locomotion on the water surface in semiaquatic bugs (Insecta, Hemiptera, Gerromorpha) Vidensk. Meddr dansk naturh. Foren. 1976:337–396. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hu DL, Chan B, Bush JW. The hydrodynamics of water strider locomotion. Nature. 2003;424:663–666. doi: 10.1038/nature01793. doi:10.1038/nature01793 nature01793 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khila A, Abouheif E, Rowe L. Comparative functional analyses of ultrabithorax reveal multiple steps and paths to diversification of legs in the adaptive radiation of semi-aquatic insects. Evolution; international journal of organic evolution. 2014;68:2159–2170. doi: 10.1111/evo.12444. doi:10.1111/evo.12444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Refki PN, Armisen D, Crumiere AJJ, Viala S, Khila A. Emergence of tissue sensitivity to Hox protein levels underlies the evolution of an adaptive morphological trait. Dev Biol. 2014;392:441–453. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.05.021. doi:Doi 10.1016/J.Ydbio.2014.05.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khila A, Abouheif E, Rowe L. Evolution of a novel appendage ground plan in water striders is driven by changes in the Hox gene Ultrabithorax. PLoS genetics. 2009;5:e1000583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000583. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khila A, Abouheif E, Rowe L. Function, developmental genetics, and fitness consequences of a sexually antagonistic trait. Science. 2012;336:585–589. doi: 10.1126/science.1217258. doi:10.1126/science.1217258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cooper SD. The Effects of Trout on Water Striders in Stream Pools. Oecologia. 1984;63:376–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00390668. doi:Doi 10.1007/Bf00390668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Han CS, Jablonski PG. Male water striders attract predators to intimidate females into copulation. Nature communications. 2010;1:52. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1051. doi:10.1038/ncomms1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rowe L. The Costs of Mating and Mate Choice in Water Striders. Anim Behav. 1994;48:1049–1056. doi:Doi 10.1006/Anbe.1994.1338. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Reckel F, Melzer RR. Regional variations in the outer retina of atherinomorpha (Beloniformes, Atheriniformes, Cyprindontiformes : Toleostei): Photoreceptors, cone patterns, and cone densities. J Morphol. 2003;257:270–288. doi: 10.1002/jmor.10122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fairbairn DJ, King E. Why do Californian striders fly? J Evol Biol. 2008 doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01619.x. doi:JEB1619 [pii] 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2008.01619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.West LC, Cresswell P. Expanding roles for GILT in immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25:103–108. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.11.006. doi:Doi 10.1016/J.Coi.2012.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kongton K, McCall K, Phongdara A. Identification of gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase (GILT) homologues in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Developmental and comparative immunology. 2014;44:389–396. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.01.007. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2014.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Suter RB, Gruenwald J. Predator avoidance on the water surface? Kinematics and efficacy of vertical jumping by Dolomedes (Araneae, Pisauridae) J Arachnol. 2000;28:201–210. doi:Doi 10.1636/0161-8202(2000)028[0201:Paotws]2.0.Co;2. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Edmunds M. Defence in animals : a survey of anti-predator defences. Longman; 1974. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Perez Goodwyn P, Katsumata-Wada A, Okada K. Morphology and neurophysiology of tarsal vibration receptors in the water strider Aquarius paludum (Heteroptera: Gerridae) Journal of insect physiology. 2009;55:855–861. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.06.001. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nature methods. 2008;5:621–628. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1226. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.