Abstract
We have whole exome sequenced 176 individuals from the isolated population of the island of Vis in Croatia in order to describe exonic variation architecture. We found 290 577 single nucleotide variants (SNVs), 65% of which are singletons, low-frequency, or rare variants. A total of 25 430 (9%) SNVs are novel, previously not catalogued in NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project, UK10K-Generation Scotland, 1000 Genomes Project, ExAC, or NCBI Reference Assembly dbSNP. The majority of these variants (76%) are singletons. Comparable to data obtained from UK10K-GS that were sequenced and analysed using the same protocols, we detected an enrichment of potentially damaging variants (non-synonymous and loss-of-function) in the low frequency and common variant categories. On average 115 (range 93-140) genotypes with loss-of-function variants, 23 (15-34) of which were homozygous, were identified per person. The landscape of loss-of-function variants across an exome revealed that variants mainly accumulated in genes on xenobiotic-related pathways, of which majority coded for enzymes. The frequency of loss-of-function variants was additionally increased in Vis ROH regions where variants mainly affected signalling pathways. This work confirms the isolate status of Vis population by means of whole exome sequence and reveals the pattern of loss-of-function mutations which resembles the trails of adaptive evolution that were found in other species. By cataloguing the exomic variants and describing the allelic structure of the Vis population, this study will serve as a valuable resource for future genetic studies of human diseases, population genetics, and evolution in this population.
Keywords: single nucleotide variants, exome sequencing, loss of function, isolates, xenobiotics
INTRODUCTION
Recent advances in genotyping and sequencing technologies have opened a route to a new dimension of population studies, enabling the development of clear insight into the past of any population and corroboration of existing evidence from the domains of palaeontology, archaeology and historical evidence with unprecedented validation and precision. This type of analysis is interesting not only on the global scale,1 but also on a local scale, particularly in the case of special and isolated populations. Such populations may retain their genetic isolation and uniqueness due to a number of possible factors, including geographical, ethnic, or linguistic barriers, and have been estimated to encompass over 11.5 million individuals in Europe alone.2
The Croatian Adriatic islands are geographically and habitat-unique localities and are characterised by distinctive population histories, which include varying founding times and consequent population age, severe plague bottlenecks, and massive waves of emigration due to deteriorating economical conditions.3 The genetic structure was also affected by historic events, such as near annihilation of the island populations in the conflicts with the ancient Roman Empire, a shift caused by the massive Slavs arrival in approximately 700 AD and clashes with the Ottoman Empire.3-6 Genetic studies revealed a reduction of haplotype diversity in Vis compared to an outbread population from Scotland and presented a founder effect in Vis mtDNA sequences7. Besides drift and increased homogeneity, isolated populations also tend to harbour unique rare variants,8 making them very useful tools in genetic association studies.9 These properties have contributed to the development of the 10 001 Dalmatians resource (http://www.mefst.hr/default.aspx?id=826), the largest research-oriented biobank in Croatia, now commonly used in genetic studies worldwide.10
The aim of this study is to perform an exhaustive exploratory analysis of the exomic structure of the modern-day population of the island of Vis. By cataloguing exomic variants, investigating their frequencies and functional effects, and examining autozygosity, we describe the allelic architecture of this isolated population, providing the basis for a valuable resource for future genetic studies focusing on disease susceptibility, population genetics, and evolution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participant recruitment and sample collection
We conducted exome-wide sequencing of 193 individuals from the isolated population of the island of Vis, Croatia. The sample for this study was based on the initial cohort of 1 026 participants which were initially recruited in the CROATIA-Vis study (the 10 001 Dalmatians project) between 2003 and 2004.11 The participants were recruited on the basis of vital registries, postal invitations, and other means of invitations. In total, 193 participants (38% men) were selected for the purpose of this study on the basis of three criteria. The first criterion was that a participant originated from the island of Vis, which was verified by the Parish records that were reconstructed for the period of 1850 onwards, and later corroborated by the genealogical records provided by the subjects. Secondly, we used the participants whose DNA was successfully extracted and who were not identified as genetic outliers in the initial CROATIA-Vis study by principal components analysis of genome-wide, Illumina HumanHap 300 genotypes. Lastly, we used ANCHAP, a method for detecting IBD in isolated populations, to select a sample of participants which maximised the whole sample haplotypes representation7. Mean genomic kinship of the sample was 0.002, as estimated by the KING algorithm.
All subjects were asked to provide written consent, after being informed on the study goals and main approaches, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the ethics committees of the University of Zagreb (No, 018057) and the University of Split School of Medicine (No, 2181-198-A3-04110-11-0008), Croatia, and the Multi-Centre Research Ethics Committee for Scotland (No, 01/0/71).
Exome capture and sequencing
Sequencing was performed at Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge, UK. The exomes were captured from blood genomic DNA, using SureSelect Human All Exon SeqCap pulldown technology and were sequenced with 75bp paired-end reads on Illumina HiSeq platform according to manufacturer’s protocol. The capture kit used for exome enrichment was Agilent’s SureSelect Human All Exon 50 Mb (Agilent, CA), targets 51.8 Mb of human genome by design and encompasses unified set of coding exons annotated on August, 2010 by GENCODE or CCDS databases (including 10 bp of flanking sequence for each consensus CDS). The probe design also includes small non-coding RNA regions annotated by miRBase (v.13) and Rfam databases, and overall, reports a 100% breadth of coverage.
Compared to the CCDS database, the total of 653 828 probes tile to 97% of targeted bases. If regions captured upstream and downstream of targets are considered, the kit targets 90.5Mb of genome, providing additionally a broad coverage of non-coding DNA in exon-flanking regions (promoters and UTRs).
Variant calling and annotation
Details of the workflow used for SNV calling on the exome data are given in Supplementary material. Called SNVs were annotated with dbSNP137 rsIDs and 1000 Genomes super population allele frequencies that were extracted from the final 1000 Genomes Phase 1 integrated (v3) callset. Functional annotations were called with the Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor v2.8 against Ensembl 70, which provided coding consequence predictions and SIFT, PolyPhen and Condel annotations as well as GERP conservation scores (http://www.ensembl.org/info/docs/tools/vep/index.html).
The same calling and annotation protocol was also applied to the Generation Scotland UK10K_OBESITY_GS whole exome data, that was used for comparison with Vis dataset (UK10K-GS - release 2012-11-27 variant dataset, after the initial QC dataset included n=377 samples from Scotland ascertained on the basis of BMI>40 or pedigrees discordant for BMI). Variants in the UK10K-GS dataset were generated by WES as part of the UK10K project that used the same targeted regions, sequencing protocols, and downstream bioinformatics pipeline as our study.
The generated WES data have been submitted to the European Genome-phenome Archive (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/home) with the accession numbers EGAS00001000336 and EGAD00001001387.
Performance of whole-exome sequencing
Sequencing depth and coverage of targeted regions were calculated using Samtools’ 0.1.19 bamcheck (v2012-09-04).
We collected high-coverage exon-capture data for 193 samples with a median of 99.9 (range, 71.6–170.1) million reads per subject, and median raw depth for the Sure Select target regions of 110×. Median insert size across all samples was 181 (range, from 173 to 203 per sample). On average, 99.6% (99.2–99.7%) of per subject reads were mapped to the human reference genome, with reads in the target regions mapped to 100%. After removal of PCR duplicates, 90.7% (84.8–93.8%) of per subject reads were retained. Among those uniquely mapped, 85.1% (79.2–93.9%) of per subject reads were within the target regions.
The median value of aligned read depth on the target regions per subject was 110× (78-193×) with 51.5 Mb (99.5% of target regions) covered by at least 30×, and 39.9 Mb (77.2%) covered by at least 50×. For sequences falling outside the target but within the calling regions, 29.2 Mb (75.3% of out-target calling region) were covered by at least 30× read and 15.6 Mb (40.2%) were covered by at least 50× reads. The analysis of aggregate on-target Ti/Tv ratio implied that the calling pipeline produced a good quality variant call set (Supplementary material, Ti/Tv ratio).
Standard sample and SNV quality controls (QC) were performed on the Vis and UK10K-GS multi-sample called exome-sequence datasets, and are described in detail in Supplementary material. Close relatives were removed from both samples based on pairwise IBD sharing. Only bi-allelic SNVs were included in the study.
General description of Vis exome-sequence
We examined the distribution of all SNVs according to internal, sample specific allele frequency categories. We also examined the proportion of functional effects in each allele frequency category. For description purposes we used the most deleterious effect of the variant according to severity estimated by Ensembl (http://www.ensembl.org/info/docs/variation/predicted_data.html). For the data representation in the main text we have summarised Ensembl consequence annotations into fewer categories (Supplementary Table 1).
We compared Vis exome data with the UK10K-GS WES dataset, NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project (NHLBI) (http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/), NCBI Reference Assembly dbSNP (dbSNP) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/) as well as 1000Genomes (http://www.1000genomes.org/data#DataAvailable) and Exome Aggregation Consortium datasets (ExAC) (http://exac.broadinstitute.org/) in order to identify novel variants not reported in the reference datasets. We uniquely identified variants using chromosome, base pair position and an allele identity in each dataset before comparison. All variants were on hg 19, build 37.
To calculate dN/dS ratios we determined the number of non-synonymous (missense, stop_lost, stop_gained, or initiator_codon variants) and synonymous (synonymous, and stop_retained variants) substitutions, and adjusted the values for multiple substitutions. Only substitutions within known protein-coding CDS were analysed.
Autozygosity was detected through runs of homozygosity (ROH) on a set of common, independent SNVs. Due to reduced SNV density in such set (~50k), only long ROHs (>5Mb) were analysed. Calls were made in PLINK v1.07 using parameters optimized for detection of ROHs in WES sequences.12 ROH hotspots and coldspots were identified if the SNP-wise ROH frequency was above, or below the 95%th percentile of the level of sharing, respectively.
Loss of function variants
SNVs predicted by the Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor as stop-gained (nonsense) or splice site–disrupting (splice donor or acceptor) SNVs were defined as LoF variants. In total 1775 putative LoF variants were obtained in Vis. Potential LoF variants that were likely due to reference errors or annotation artefacts were filtered. SNVs were marked as false positives if the inferred LoF allele was also the ancestral state (73 SNVs in Vis and 115 in UK10K-GS) indicating that a gain-of-function allele was the recent mutation on a site. We also excluded LoF SNVs (24 in Vis and 17 in UK10K-GS) that were identified as major allelic variant (MAF>0.5) in our samples, and in all super populations from the 1000Genomes project: EUR, ASN, AFR, AMR. At these sites the reference genome differed from majority of analyzed humans indicating a probable reference genome error. In example, at these sites we observed extremely high frequency of homozygous LoF variants (0.26 - 0.89) (Supplementary Table 2). After filtering, there were 1 678 remaining LoF variants in Vis, and 3 149 in the UK10K dataset.
The analysis of overrepresentation of Gene Ontology (GO) annotations and the pathway analysis were performed on a set of genes containing LoF variants using ConsensusPathDB-human database.13 FDR q-value of 0.1 and a p-value of 0.05 were used to identify overrepresented functional groups.
RESULTS
General description of Vis exome-sequence
Overall, the performance of whole-exome sequencing with high percentage of reads uniquely mapped to target regions, with aligned read depth on target region of 110×, and 51.5 Mb (99.5%) of target regions covered by at least 30×; indicated efficient targeted sequencing.
We found 290 577 SNVs of which 65% were singletons, low frequency, or rare (Table 1, more detailed category definitions are provided in Supplementary Table 3). Rare variants (MAF≤0.01) were the most prevalent in both LoF and nonsynonymous variants, with the percentage of rare SNVs among LoF variants significantly outnumbering the corresponding percentage among nonsynoymous SNVs. On contrary, the percentages of both low (0.01<MAF≤0.05), and common (MAF>0.05) frequency variants among nonsynonymous SNVs was significantly higher than among LoF SNVs (Supplementary Figure 2a, 95% CI).
Table 1.
The count of all variants, and completely novel variants in each functional effect group separated by allele frequency categories.
| All variants | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant consequence annotations | All variants | Singletons | Doubletons | MAF≤0.01 | 0.01<MAF≤0.02 | 0.02<MAF≤0.05 | 0.05<MAF≤0.1 | MAF>0.1 |
| loss_of_function | 1775 | 892 | 219 | 100 | 152 | 93 | 79 | 240 |
| non_synonymous | 60011 | 22939 | 6988 | 3626 | 6119 | 4834 | 3944 | 11561 |
| splice_region | 8748 | 2657 | 886 | 468 | 892 | 791 | 689 | 2365 |
| synonymous | 44582 | 12891 | 4292 | 2501 | 4491 | 4111 | 3658 | 12638 |
| UTR | 17165 | 4945 | 1792 | 1073 | 1865 | 1585 | 1438 | 4467 |
| ncRNA | 23033 | 6292 | 2210 | 1256 | 2274 | 2190 | 2145 | 6666 |
| intronic | 131531 | 35463 | 13016 | 7519 | 13797 | 12426 | 11828 | 37482 |
| upstream | 2056 | 506 | 206 | 118 | 204 | 181 | 209 | 632 |
| downstream | 1142 | 265 | 108 | 63 | 105 | 114 | 131 | 356 |
| regulatory | 73 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 11 | 23 |
| intergenic | 461 | 106 | 28 | 18 | 43 | 38 | 50 | 178 |
| Total | 290577 | 86969 | 29753 | 16747 | 29950 | 26368 | 24182 | 76608 |
| Completely novel variants | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant consequence annotations | All variants | Singletons | Doubletons | MAF≤0.01 | 0.01<MAF≤0.02 | 0.02<MAF≤0.05 | 0.05<MAF≤0.1 | MAF>0.1 |
| loss_of_function | 269 | 230 | 27 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| non_synonymous | 4783 | 3978 | 515 | 167 | 116 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| splice_region | 552 | 455 | 60 | 17 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| synonymous | 2141 | 1738 | 250 | 85 | 57 | 5 | 1 | 5 |
| UTR | 1702 | 1312 | 240 | 81 | 59 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| ncRNA | 2273 | 1772 | 305 | 109 | 71 | 8 | 3 | 5 |
| intronic | 13308 | 10328 | 1890 | 604 | 427 | 30 | 11 | 18 |
| upstream | 230 | 175 | 32 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| downstream | 120 | 86 | 19 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| regulatory | 9 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| intergenic | 44 | 38 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 25431 | 20118 | 3344 | 1087 | 769 | 54 | 16 | 43 |
Relative to UK10K-GS, the Vis sample shows a depletion of rare variants and excess of low frequency, and common variants (Supplementary Figure 2b). The comparison of potentially deleterious variants (non-synonymous and LoF) showed the same pattern i.e. a decrease of rare, and an excess of low and common frequency variants in Vis (Supplementary Figure 2b). This difference was not the consequence of different sample sizes. When we randomly re-sampled (n=100) the same number of individuals from each population and compared allele frequencies of variants shared by both populations between Vis and UK10K-GS, again a decrease in proportion of shared rare variants (p 7.1×10−27), and increase in proportion of shared low frequency variants (p 7.0×10−20) were observed in Vis (Supplementary Figure 2 c). Moreover, frequency of shared variants declared as rare or low frequency in Vis was significantly increased compared to same variants in UK10K-GS. Median difference in allele frequency per shared variant was 0.0008 for rare and 0.003 for low frequency variants, which corresponds in both cases to 8% of the total frequency range of particular frequency category (one sample U-test for median of differences against zero, p ≤ 3.2×10−20).
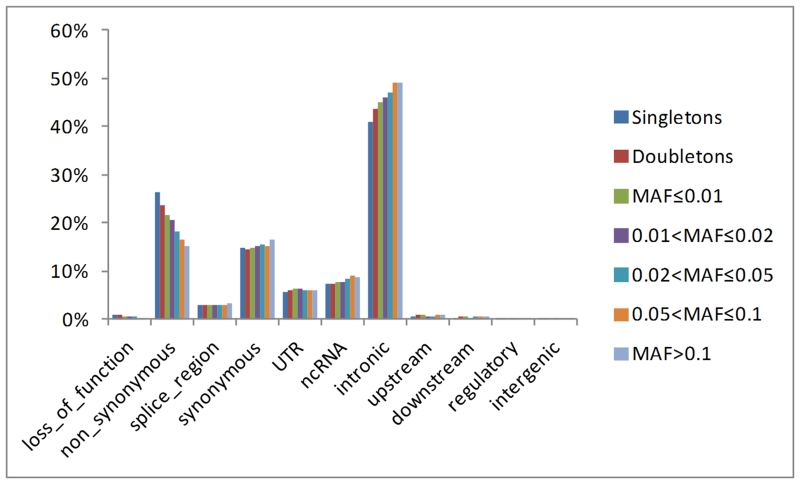
The majority of detected variants in Vis are intronic (45%) (Figure 1; more detailed category definitions are provided in Supplementary Figure 3) pointing out that our baits also captured some of the intronic regions that surround exons. Intron SNVs were positioned predominantly (83.3%) within 200 bp from the nearest exon boundary with a median distance of 89bp (IQR, 53-132). If we exclude intronic regions then, consistently with previous reports, non-synonymous are the most common (21%), followed by synonymous (15%) variants and of these the majority are singletons and rare variants (Table 1). Aggregate site frequency spectra by variant functional consequence are shown in Supplementary Figure 4.
Figure 1.
Proportion of functional effects by allele frequency categories.
The ratio of substitution rates at non-synonymous and synonymous sites for all variants was 1.20; 1.57 for rare and 1.16 for low frequency variants, and 0.86 for common variants. The dN/dS ratios revealed that non-synonymous substitutions were prevalent in rare and low frequency variants, whereas the trend was reversed for common variants. Consistent with purifying selection in large populations these values were somewhat lower in UK10K-GS dataset: dN/dS=1.11 for all variants; and 1.38, 1.09, and 0.85 for rare, low frequency, and common variants respectively. In line with this finding, median inbreeding coefficient FIT for MHC region showed reduced heterozygosity in Vis: −0.021, compared to UK10K-GS: −0.036.
The average genome-based kinship in Vis sample was low (0.002) indicating that, as expected, unrelated individuals were selected in the study. On the other hand, the average individual autozygosity in Vis that was derived from long ROHs (>5Mb) was consistent with 2nd-cousin relationship, FROH >5Mb 0.017, SEM 0.004.14 Moreover, in comparison to UK10K-GS (FROH >5Mb 0.001, SEM 0.0007), a significantly higher proportions of individuals with long ROHs were found in Vis (1% vs 11% in Vis, chi-square, P=4.34×10−7). Median lengths per affected individual in Vis of total, and per segment ROH length were 10 Mb (range, 7–35) and 9 Mb (7-22) respectively, whereas the corresponding values in UK10K were 9 Mb (5-16) for both parameters.
Novel variants
We identified a total of 108 615 (37%) novel variants in the Vis exome-sequence data that were not present in UK10K-GS, 136 617 (47%) novel variants not present in NHLBI, 114 176 (39%) novel variants not present in ExAC, 60 345 (21%) novel variants not present in the 1000Genomes, 34 497 (12%) novel variants not present in dbSNP and a total of 25 430 (9%) novel variants not present in any of the above mentioned datasets (Supplementary Figure 5). The count of novel variants by MAF for comparisons of Vis exome data with UK10K-GS, NHLBI, ExAC, 1000Genomes and dbSNP (Supplementary Table 4) clearly shows that the majority of novel variants belong to the rare allele frequency spectrum (up to MAF 0.02).1 As expected, the greatest number of singletons and doubletons are found in dbSNP (78%), followed by comparison with ExAC (58%), then 1000Genomes (54%), NHLBI (43%), and UK10K-GS (31%). A larger proportion of common allele novel variants (~40% of all common variants) was identified through comparisons with NHLBI or ExAC datasets as these variants are mostly intronic (≥69%) and are simply not present in datasets which are limited to exome sequence only. We can also see that there are very few common novel variants identified through comparison with 1000Genomes (0.01%) and dbSNP (0.001%) which are databases with a very good capture of common variation (Supplementary Table 4). Due to the intronic regions within the exome calling for the Vis sample, the largest effect category group of novel variants in all five comparisons is intronic, followed by either non-synonymous (UK10K-GS, 1000Genomes, dbSNP) or non-coding RNA (NHLBI, ExAC) groups (Supplementary Figure 5). A detailed presentation of the number of both summarised and the full set of functional effects of novel variants by MAF can be found in Supplementary material (Supplementary Tables 5 and 6, Supplementary Figures 6 and 7).
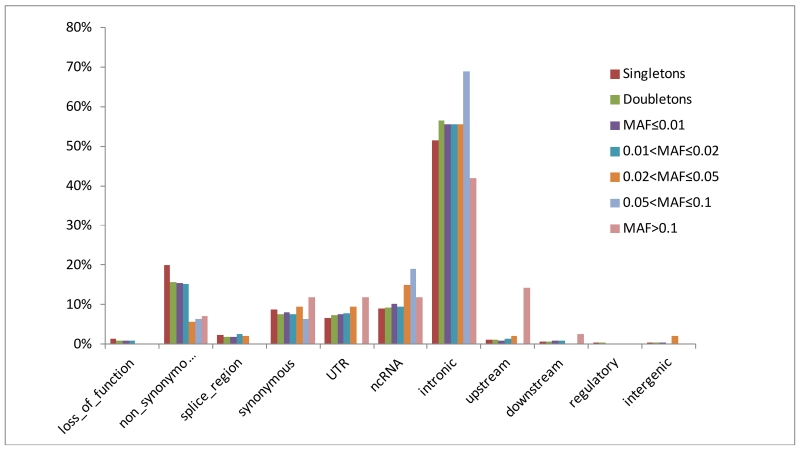
A detailed view of the allele frequency/functional effect distributions of completely novel variants (Table 1, Figure 2) show that 79% of these were singletons and an additional 17% were rare or low frequency, highlighting the ability of WES to identify rare and low frequency variants. On the contrary, only 59 completely novel variants (0.23%) were common suggesting that the discovery of a large number of common novel variation through exome-sequencing is highly unlikely. Of completely novel variants, 52% were intronic, 18% were non-synonymous, whereas percentages of non-coding RNA, synonymous, and UTR variants were comparable (from 7% to 9%) indicating that in comparison to distribution of all variants, number of completely novel synonymous variants is substantially decreased (Figure 1, Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Proportion of functional effects of completely novel variants by MAF.
Loss of function variants
The average number of LoF genotypes per genome in Vis and UK10K-GS samples was 115 (range, 93-140) and 122 (96-149), respectively; whereas the corresponding number of LoF variants in homozygous state: 23 (15 - 34) and 24 (13 - 37); was comparable between the datasets. On average, an individual in Vis had lower counts of LoF genotypes by 6% (mean difference of 6.5 genotypes per genome, 95% CI 5-8, p=3.3×10−16), LoF variants by 5% (7.7, 95% CI 6-9, p=6.6×10−16), and homozygous LoF variants by 5% (1.3, 95% CI 0.6-2.0, p=3.1×10−4) than in UK10K-GS.
In comparison to the dataset of high confidence LoF SNVs (n=880) published by MacArthur et al.15, we identified 172 overlapping LoF SNVs in Vis, and 227 in UK10K-GS dataset. Using only these SNVs the estimated number of potentially harmful LoF genotypes per individual was 28 (17-39) in Vis and 29 (17-39) in UK10K-GS, and the corresponding number of homozygous high confidence LoF variants was 5 (1-12) and 6 (0-14).
As expected, the largest proportion of LoF variants in Vis belonged to the singleton category, whereas the proportions of doubleton, low frequency, and common variants were comparable (Supplementary Figure 2a). Compared to LoF variants in UK10K_GS sample, there was a depletion of LoF singletons (two-proportion z-test, p=0.002), and overall rare LoF variants (p=1×10−6) in Vis, and an excess of low-frequency (p=1×10−5) and common variants (p=0.016) (Supplementary Figure 2b). A similar finding is observed when we compared allele frequency distributions of all variants shared by the two datasets or when we re-sampled the same number of individuals from each population and compared distributions of shared LoF variants.
Of the mapped genes containing LoF variants (n=1451), 1355 and 786 genes were found in at least one GO-term category, or one pathway respectively. Pathways that were significantly overrepresented included 52 identified genes of which the vast majority were related to xenobiotic- (metabolization or activation; 27 genes or 52%), and/or to lipid-metabolism (30 genes or 58%), Table 2. The most significant over-represented GO-terms were: ion-binding, hydrolase, and oxidoreductase activity (GO:0043167, GO:0016787, GO:0016491), with most genes assigned to these three categories being associated with enzyme activity (61%).
Table 2.
Genes with LoF variants - summary of predicted gene product function and location using gene ontology terms and pathway analysis.
| Overrepresented pathways | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| Pathway name | Pathway source | Total set size | No. of identified genes | p-value | q-value | Description |
| CYP2E1 reactions | Reactome | 11 | 6 (54.5%) | 0.00004 | 0.0518 | xenobiotics-related |
| Leukotriene metabolism | EHMN | 104 | 19 (18.3%) | 9.89e-05 | 0.0518 | lipid metabolism |
| Galactose metabolism | KEGG | 30 | 9 (30.0%) | 0.000148 | 0.0518 | other |
| Tryptophan degradation | INOH | 66 | 14 (21.2%) | 0.000158 | 0.0518 | xenobiotics-related* |
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | KEGG | 74 | 15 (20.3%) | 0.000159 | 0.0518 | xenobiotics-related |
| Androgen and estrogen biosynthesis and metabolism | EHMN | 87 | 16 (18.4%) | 0.000318 | 0.0789 | lipid metabolism |
| Fatty acids | Reactome | 15 | 6 (40.0%) | 0.000339 | 0.0789 | lipid metabolism |
| Xenobiotics | Reactome | 21 | 7 (33.3%) | 0.000398 | 0.0803 | xenobiotics-related |
| Chemical carcinogenesis | KEGG | 81 | 15 (18.5%) | 0.000448 | 0.0803 | xenobiotics-related |
| C21-steroid hormone biosynthesis and metabolism | EHMN | 57 | 12 (21.1%) | 0.000493 | 0.0803 | lipid metabolism |
| Overrepresented GO terms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||
| GO term | GO group | Total set size | No. of identified genes | p-value | q-value |
| GO:0043167 ion binding | molecular function | 6117 | 531 (8.7%) | 8.85e-08 | 4.6e-06 |
| GO:0016787 hydrolase activity | 2477 | 235 (9.5%) | 3.66e-06 | 9.51e-05 | |
| GO:0016491 oxidoreductase activity | 728 | 77 (10.6%) | 0.000529 | 0.00917 | |
| GO:0019825 oxygen binding | 47 | 9 (19.1%) | 0.00601 | 0.071 | |
| GO:0030246 carbohydrate binding | 279 | 32 (11.5%) | 0.00683 | 0.071 | |
| GO:0004601 peroxidase activity | 41 | 8 (19.5%) | 0.00836 | 0.0724 | |
|
| |||||
| GO:0005929 cilium | cellular compartment | 465 | 53 (11.4%) | 0.000719 | 0.0302 |
| GO:0044441 ciliary part | 309 | 38 (12.3%) | 0.000987 | 0.0302 | |
| GO:0005578 proteinaceous extracellular matrix | 356 | 42 (11.9%) | 0.00113 | 0.0302 | |
| GO:0034358 plasma lipoprotein particle | 39 | 8 (20.5%) | 0.00612 | 0.0926 | |
| GO:0005615 extracellular space | 1338 | 120 (9.0%) | 0.00686 | 0.0926 | |
| GO:0072562 blood microparticle | 135 | 18 (13.4%) | 0.00821 | 0.0926 | |
| GO:0032994 protein-lipid complex | 41 | 8 (19.5%) | 0.00836 | 0.0926 | |
| GO:0005604 basement membrane | 97 | 14 (14.6%) | 0.00926 | 0.0926 | |
Annotations are ordered by p-values
Tryptophan degradation pathway is classified as xenobiotic-related as tryptophan metabolites are known to activate aryl hydrocarbon receptor, transcription factor known to mediate most of the toxic and carcinogenic effects of a wide variety of environmental contaminants
We analysed in more detail a subclass of LoF variants exhibiting high MAF variability across Vis and the 1000Genomes Project super populations. In total, we identified nine LoF variants belonging to this subclass (Table 3). Unlike the majority of LoF variants that are expected to be rare and to have limited geographic distribution, the allele frequency of these variants ranged from rare to common across different populations.
Table 3.
Putative LoF variants (n=9) with extremely high variability among populations: Vis and 1000Genomes super populations EUR, ASN, AFR, AMR. Population allele frequency of variants range from rare to common major allele.
| Allele frequency in population | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHR | Position [bp] | ID | REF | ALT | Vis | EUR | AMR | AFR | ASN | Functional annotation* Gene/regulatory element ID, functional annotation, number of transcripts; |
| 1 | 27942176 | rs2231879 | T | C | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.51 | - |
Regulatory element ID: ENSR00001518649, regulatory_region_variant, -- Gene ID: FGR, splice_acceptor_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 1; intron_variant, 6 |
| 5 | 111481696 | rs17134155 | C | T | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 0.05 |
Regulatory element ID: ENSR00001287518, regulatory_region_variant, -- Gene ID: EPB41L4A, splice_acceptor_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 1 |
| 6 | 139576544 | rs41289819 | G | A | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.53 | 0.02 | Gene ID: TXLNB, stop_gained:373:125, 1; intron_variant, 1 |
| 7 | 144364918 | rs67644764 | G | T | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.61 | 0.002 | Gene ID: TPK1, stop_gained:71:24, 1; intron_variant,NMD_transcript_variant, 2; intron_variant, 3; intron_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 1; upstream_gene_variant, 2; synonymous_variant,NMD_transcript_variant:129:43:L>L, 1; 5_prime_UTR_variant, 1 |
| 16 | 66861836 | rs7195853 | G | A | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.03 | Gene ID: NAE1 splice_donor_variant,NMD_transcript_variant, 1; intron_variant,NMD_transcript_variant, 3; intron_variant, 8; intron_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 4; |
| 16 | 90110950 | rs1048149 | C | T | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.03 |
Regulatory element ID: ENSR00000512444, regulatory_region_variant, -- Gene ID: ENSG00000222019, stop_gained:68:23, 2; stop_gained,NMD_transcript_variant:68:23, 1; non_coding_exon_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 1 Gene ID: GAS8, 3_prime_UTR_variant,NMD_transcript_variant, 1; 3_prime_UTR_variant, 1; downstream_gene_variant, 5; non_coding_exon_variant,nc_transcript_variant, 1 |
| 17 | 72588806 | rs545652 | C | A | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.52 | 0.04 |
Gene ID: C17orf77, stop_gained:621:207, 2; downstream_gene_variant, 1 Gene ID: CD300LD, upstream_gene_variant, 1 |
| 22 | 42336172 | rs5758511 | G | A | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.51 |
Regulatory element ID: ENSR00000085774, regulatory_region_variant, -- Gene ID: CENPM stop_gained:7:3, 1; intron_variant, 5; downstream_gene_variant, 1 |
| X | 75004529 | rs1343879 | C | A | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.91 | Gene ID: MAGEE2, stop_gained:358:120, 1 |
Called with the Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor v2.8 against Ensembl 70 ;
The genomic reference sequence used is GRCh37/hg19
LoF variants in runs of homozygosity (ROH) regions
The distribution of LoF variants across an exome with respect to ROH hotspots and coldspots regions has shown an increase in frequency of LoF variants in hotspots which was significant at α = 0.1 (OR 1.18, P=0.083). The pathway and GO-term analyses of genes containing the hotspot LoF variants have shown intriguing results. Of the 92 mapped genes carrying a LoF variant in a ROH hotspot region, 59% were assigned to overrepresented GO-terms, all of which were exclusively membrane-related, either by the location, or the membrane-related function or process (Table 4). Moreover, with regard to processes or functions assigned to these terms, as a rule they were included in some sort of cell’s response to either internal or external signal. Similar was found with pathway analysis which showed that of 48 mapped genes 53% belonged to over-represented pathways that were mainly related to cell’s response to environmental signals such as xenobiotics, odorant molecules or allografts. Majority of identified genes in overrepresented families (76%) belonged to cytochrome P450 (CYP) or solute-carrier (SLC) gene superfamilies, olfactory receptors (OR), or to HLA gene family.
Table 4.
Genes with LoF variants in ROH hotspots - summary of predicted gene product function and location using gene ontology terms and pathway analysis.
| Overrepresented pathways | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| Pathway name | Pathway source | Total set size | No. of Identified genes | p-value | q-value | Description |
| Allograft Rejection | Wikipathways | 80 | 5 (6.2%) | 2.21e-05 | 0.00225 | immune response to allograft |
| Cytochrome P450 - arranged by substrate type | Reactome | 61 | 4 (6.6%) | 0.00013 | 0.00662 | xenobiotics-metabolism |
| Phase 1 - Functionalization of compounds | Reactome | 79 | 4 (5.1%) | 0.000353 | 0.00882 | xenobiotics-metabolism |
| Olfactory Signaling Pathway | Reactome | 427 | 8 (1.9%) | 0.000401 | 0.00882 | response to external signal |
| Warfarin Pathway, Pharmacokinetics | PharmGKB | 8 | 2 (25.0%) | 0.000496 | 0.00882 | xenobiotics-metabolism |
| Allograft rejection - Homo sapiens (human) | KEGG | 37 | 3 (8.1%) | 0.000519 | 0.00882 | immune response to allograft |
| Overrepresented GO terms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| GO term | GO group | Total set size | No. of Identified genes | p-value | q-value | Description |
| GO:0098805 whole membrane | Cellular component | 1916 | 20 (1.0%) | 0.000295 | 0.00534 | membrane location |
| GO:0098576 lumenal side of membrane | 30 | 3 (10.3%) | 0.000305 | 0.00534 | membrane location | |
| GO:0098589 membrane region | 1086 | 13 (1.2%) | 0.00119 | 0.0138 | membrane location | |
| GO:0005886 plasma membrane | 4864 | 34 (0.7%) | 0.00315 | 0.0276 | membrane location | |
| GO:0071944 cell periphery | 4967 | 34 (0.7%) | 0.00453 | 0.0317 | membrane location | |
| GO:0048475 coated membrane | 88 | 3 (3.4%) | 0.00756 | 0.0362 | membrane location | |
| GO:0031300 intrinsic component of organelle membrane | 271 | 5 (1.9%) | 0.00781 | 0.0362 | membrane location | |
| GO:0044459 plasma membrane part | 2528 | 20 (0.8%) | 0.00829 | 0.0362 | membrane location | |
|
| ||||||
| GO:0005549 odorant binding | Molecular function | 85 | 4 (4.7%) | 0.000612 | 0.0134 | binding - external signal |
| GO:0003823 antigen binding | 103 | 4 (4.0%) | 0.00117 | 0.0134 | binding - external signal | |
| GO:0004871 signal transducer activity | 1663 | 16 (1.0%) | 0.00296 | 0.0227 | response to internal/external signal | |
| GO:0004872 receptor activity | 1583 | 15 (1.0%) | 0.00469 | 0.0269 | response to internal/external signal | |
|
| ||||||
| GO:0045321 leukocyte activation | Biological process | 701 | 10 (1.4%) | 0.00123 | 0.0704 | response to internal/external signal |
| GO:0052192 movement in environment of other organism involved in symbiotic interaction | 84 | 3 (3.6%) | 0.00665 | 0.099 | response to external signal | |
| GO:0042221 response to chemical | 4132 | 29 (0.7%) | 0.0073 | 0.099 | response to external signal | |
| GO:0002252 immune effector process | 765 | 9 (1.2%) | 0.00762 | 0.099 | response to internal/external signal | |
Annotations are ordered by p-values
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this work was to provide a comprehensive insight into the exomic structure of the isolated population of the Adriatic island of Vis and to compare it with the UK10K-GS exome dataset, and with reference databases (NHLBI, 1000Genomes, dbSNP, and ExAC). Our data support the findings that the population of Vis is a true genetic isolate. In comparison with the UK10K-GS exomes, we see a depletion of rare and an excess of low frequency and common variants, which is suggesting that the population of Vis had undergone a bottleneck in which the majority of rare variants have vanished but those that did stay in the population have risen in frequency. We see there is a burden of potentially deleterious variants in low, and common allele frequency groups in Vis compared to UK10K-GS (Supplementary Figure 2b). This is in line with several recent studies that identified an excess of deleterious variants in the low frequency range.16-20 Similarly, it was already shown that there are more deleterious variants in European than in African populations due to a long bottleneck effect during out of Africa migrations.21 Additionally, although unrelated individuals were included in our study, compared to the UK10K-GS sample Vis sample had higher prevalence of individuals affected with long ROH regions, and had higher FROH >5Mb index. In fact, the value of FROH index in Vis was similar to the value observed for unrelated sample of Orkney inbread population14.
Recent population genetics studies indicate that rapid growth increases the load of rare variants22,23 and likely plays a role in the individual genetic burden.23 Furthermore, it was demonstrated in a simulation study that population growth dramatically increases the number of deleterious sites in the population and increases the deleterious burden carried by each individual by approximately 6%24. Following these findings, one might expect that a population with slower population growth may have a relatively smaller load of rare variants and deleterious sites. Thus, the slightly lower average number of LoF variant genotypes per Vis genome compared to UK10K-GS genome could, at least in part, be due to limited population growth of the old isolate on Vis3, compared to the UK10K-GS population.
Estimates on average abundance of LoF genotypes per genome in Vis (115) or UK10K-GS (122) were somewhat larger than the value of 110 estimated from the pilot phase of the 1000Genomes Project25. The pilot-phase value was based on a highly-curated LoF variant list and assessed around 100 LoF variants per individual with ~20 variants in homozygous sites15, suggesting slight overestimation of individual number of LoF genotypes in our sample, possibly due to a less-strict filtering procedure.
We detected a ~6% difference in the average per-genome number of LoF variant genotypes between Vis and UK10K-GS. This small difference persisted (~6%) after singleton and doubleton variants (those most affected by differences in sample size22 and also the most abundant LoF variants) were removed in order to investigate the effect of sample size differences on estimates of individual genetic burden in Vis (n=176) and UK10K-GS (n=377).
Genes containing LoF variants in Vis were overrepresented in xenobiotic- and lipid-metabolism pathways. Having in mind that the identified lipid pathways are actually involved in the biosynthesis of known endogenious xenobiotics (steroids, eicosanoids, fatty acids), overrepresented genes in Vis were almost entirely xenobiotic-related suggesting that LoF mutations may be accumulating in genes controlling the cell’s reaction to foreign molecules from the environment. The finding is in line with a most recent view that gene losses are not necessarily evolutionary disadvantages but can also contribute to selective advantage in humans.26 In bacteria, in constant nutrient-limited environment, LoF mutations have been shown to enhance fitness by disproportionately affecting enzymatic and regulatory pathways,27 similar to what was found in our study. In addition, overrepresented genes found within ROH hotspot regions in Vis were predominantly involved in some sort of external or internal signalling. The disruption of signaling networks responsible for regulating the response to environmental changes was identified in yeast as the major theme of adaptive evolution in constant environments.28 Whether the same adaptive evolutionary process could also be used to explain the evolution of Vis population given the constant physical (geography and climate) and nutrient-limited environment should be investigated further.
As the majority of LoF variants are rare and expected to have very limited geographic distribution,29,30 we were particularly interested in the subclass of putative LoF variants exhibiting extremely high variability of allele frequency across populations, ranging from rare to major allelic variant. We identified nine LoF variants with marked geographical differences which are, therefore, probable targets of positive selection.31 Most of the variants were associated with proteins involved in immune/defense response to pathogens (FGR-regulator of immune response, CD300LD-immune receptor, NAE1-a protooncogen involved in regulation of apoptosis, CENPM-centromere protein which also encodes a human minor histocompatibility antigen, GAS8-cytoskeletal linker, a putative tumor suppressor also implicated in influenza virus release); or proteins that are potential targets for pathogens to infect cells (ie. glycosylated extracellular membrane proteins such as MAGEE2-a member of tumor specific antigen family, TXLNB gene suspected of role in vesicle traffic)(Table 3). In addition, four (44%) of these nine variants were also assigned in the ENSEMBLE GENE e72 database as “unclassified regulatory features” i.e. regulatory variants that could be involved in gene transcription regulation.
A primary purpose of this study was also to catalogue variants that were not previously found in reference databases (UK10K-GS, NHLBI, 1000Genomes and dbSNP). We found 9% of all variants in Vis to be completely novel. Unsurprisingly, the vast majority of completely novel variants were singletons, rare, or low frequency. The most common functional effect categories were intronic variants, followed by non-synonymous, and synonymous. An interesting observation is that the number of SNVs found in dbSNP (88%) was lower than anticipated for a European sample.32 With most variants already catalogued in dbSNP and/or by 1000Genomes, it is expected for a single European sample that more than 90% of true variants are identified in the dbSNP database.32 When we took into account the rate of completely novel variants, i.e. those not found in any of the four reference datasets; the aggregate rate for known SNVs increased. Although this lower rate could be due to false positive calls, the observed Ti/Tv ratio was comparable to other WES studies (Supplementary material). Alternatively, the somewhat lower dbSNP rate might be a consequence of two main factors: background population and demographic history. Our study samples were taken from an isolated island population where we expect a drift up in the frequency of rare variants unique to our sample which could result in increased proportion of detected novel variants.
Complete identification of all human variants is one of the key goals of modern genetics. This study represents a step forward in this major challenge by providing a population-based catalogue of variants and, importantly, identifying completely novel exomic variants in the population isolate from the Adriatic island of Vis. It also reveals the landscape of loss-of-function mutations that is intriguing in terms of adaptive evolution. By providing a relatively large set of variants not seen elsewhere, this study serves as a valuable resource in understanding human variation, especially in the light of genetic studies of human diseases, population genetics and evolution in this population.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research leading to these results has received funding from the Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013, No. 262055). The study was additionally supported by the Wellcome Trust No. 098051, Medical Research Council UK, Seventh Framework Programme No. 313010, Croatian Science Foundation No. 8875, and the Croatian Ministry of Science, Education and Sports No. 216-1080315-0302. The authors acknowledge the use of UK10K cohort Generation Scotland as well as NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project and its ongoing studies which produced and provided exome variant calls for comparison. We also acknowledge the staff of several institutions in Croatia that supported the field work, including but not limited to the University of Split and Zagreb Medical Schools and the Institute for Anthropological Research in Zagreb.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary information is available at EJHG website
REFERENCES
- 1.Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56–65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rudan I. Health effects of human population isolation and admixture. Croatian medical journal. 2006;47:526–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vitart V, Biloglav Z, Hayward C, et al. 3000 years of solitude: extreme differentiation in the island isolates of Dalmatia, Croatia. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2006;14:478–487. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barac L, Pericic M, Klaric IM, et al. Y chromosomal heritage of Croatian population and its island isolates. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2003;11:535–542. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Biloglav Z, Zgaga L, Smoljanovic M, et al. Historic, demographic, and genetic evidence for increased population frequencies of CCR5Delta32 mutation in Croatian Island isolates after lethal 15th century epidemics. Croatian medical journal. 2009;50:34–42. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2009.50.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rudan I, Campbell H, Rudan P. Genetic epidemiological studies of eastern Adriatic Island isolates, Croatia: objective and strategies. Collegium antropologicum. 1999;23:531–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Glodzik D, Navarro P, Vitart V, et al. Inference of identity by descent in population isolates and optimal sequencing studies. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2013;21:1140–1145. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tachmazidou I, Dedoussis G, Southam L, et al. A rare functional cardioprotective APOC3 variant has risen in frequency in distinct population isolates. Nature communications. 2013;4:2872. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Panoutsopoulou K, Tachmazidou I, Zeggini E. In search of low-frequency and rare variants affecting complex traits. Human molecular genetics. 2013;22:R16–21. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rudan I, Marusic A, Jankovic S, et al. “10001 Dalmatians:” Croatia launches its national biobank. Croatian medical journal. 2009;50:4–6. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2009.50.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Polasek O. Future of biobanks - bigger, longer, and more dimensional. Croatian medical journal. 2013;54:496–500. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2013.54.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Magi A, Tattini L, Palombo F, et al. H3M2: detection of runs of homozygosity from whole-exome sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:2852–2859. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kamburov A, Stelzl U, Lehrach H, Herwig R. The ConsensusPathDB interaction database: 2013 update. Nucleic acids research. 2013;41:D793–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McQuillan R, Leutenegger AL, Abdel-Rahman R, et al. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. American journal of human genetics. 2008;83:359–372. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.MacArthur DG, Balasubramanian S, Frankish A, et al. A systematic survey of loss-of-function variants in human protein-coding genes. Science. 2012;335:823–828. doi: 10.1126/science.1215040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Casals F, Hodgkinson A, Hussin J, et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals a rapid change in the frequency of rare functional variants in a founding population of humans. PLoS genetics. 2013;9:e1003815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Li Y, Vinckenbosch N, Tian G, et al. Resequencing of 200 human exomes identifies an excess of low-frequency non-synonymous coding variants. Nature genetics. 2010;42:969–972. doi: 10.1038/ng.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tennessen JA, Bigham AW, O’Connor TD, et al. Evolution and functional impact of rare coding variation from deep sequencing of human exomes. Science. 2012;337:64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1219240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lim ET, Wurtz P, Havulinna AS, et al. Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the Finnish founder population. PLoS genetics. 2014;10:e1004494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Panoutsopoulou K, Hatzikotoulas K, Xifara DK, et al. Genetic characterization of Greek population isolates reveals strong genetic drift at missense and trait-associated variants. Nature communications. 2014;5:5345. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lohmueller KE, Indap AR, Schmidt S, et al. Proportionally more deleterious genetic variation in European than in African populations. Nature. 2008;451:994–997. doi: 10.1038/nature06611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Coventry A, Bull-Otterson LM, Liu X, et al. Deep resequencing reveals excess rare recent variants consistent with explosive population growth. Nature communications. 2010;1:131. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Keinan A, Clark AG. Recent explosive human population growth has resulted in an excess of rare genetic variants. Science. 2012;336:740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.1217283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gazave E, Chang D, Clark AG, Keinan A. Population growth inflates the per-individual number of deleterious mutations and reduces their mean effect. Genetics. 2013;195:969–978. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.153973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.1000 Genomes Project Consortium A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061–1073. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Alkuraya FS. Human knockout research: new horizons and opportunities. Trends in genetics : TIG. 2015;31:108–115. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hottes AK, Freddolino PL, Khare A, Donnell ZN, Liu JC, Tavazoie S. Bacterial adaptation through loss of function. PLoS genetics. 2013;9:e1003617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kvitek DJ, Sherlock G. Whole genome, whole population sequencing reveals that loss of signaling networks is the major adaptive strategy in a constant environment. PLoS genetics. 2013;9:e1003972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mathieson I, McVean G. Differential confounding of rare and common variants in spatially structured populations. Nature genetics. 2012;44:243–246. doi: 10.1038/ng.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nelson MR, Wegmann D, Ehm MG, et al. An abundance of rare functional variants in 202 drug target genes sequenced in 14,002 people. Science. 2012;337:100–104. doi: 10.1126/science.1217876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, et al. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature. 2007;447:661–678. doi: 10.1038/nature05911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nature genetics. 2011;43:491–498. doi: 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.