Abstract
The MRN (MRE11-RAD50-NBS1) complex is essential for repair of DNA double strand breaks and stalled replication forks. Mutations of the MRN complex subunit MRE11 cause the hereditary cancer-susceptibility disease Ataxia Telangiectasia Like Disorder (ATLD). Here we show that MRE11 directly interacts with PIH1D1, a subunit of HSP90 co-chaperone R2TP complex, which is required for the assembly of large protein complexes, such as RNA polymerase II, small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins and mTORC1. The MRE11-PIH1D1 interaction is dependent on casein kinase 2 (CK2) phosphorylation of two acidic sequences within the MRE11 C-terminus containing serines 558/561 and 688/689. Conversely, the PIH1D1 phospho-binding domain PIH-N is required for association with MRE11 phosphorylated by CK2. Consistent with these findings, depletion of PIH1D1 resulted in MRE11 destabilization and affected DNA damage repair processes dependent on MRE11. Additionally, mutations of serines 688/689, which abolish PIH1D1 binding, also resulted in decreased MRE11 stability. Since depletion of R2TP frequently leads to instability of its substrates and since truncation mutation of MRE11 lacking serines 688/689 leads to decreased levels of the MRN complex both in ATLD patients and an ATLD mouse model, our results suggest that the MRN complex is a novel R2TP complex substrate and that their interaction is regulated by CK2 phosphorylation.
Keywords: MRN complex, R2TP complex, CK2, stability, MRE11, PIH1D1
Introduction
Genome instability is one of the hallmarks of cancer cells and is frequently associated with mutations in genes involved in the DNA damage response (DDR). NBS1 and MRE11 genes code for proteins essential for recognition and repair of damaged DNA and their mutation predisposes to hereditary cancer-prone Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) and Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder (ATLD), respectively (1, 2). Moreover, mutations of both genes have been found in patients with breast and colon cancer (3–6). MRE11, NBS1 and RAD50 form the MRN complex that allows recognition of DNA double strand breaks, activates two major DDR kinases ATM and ATR, stabilizes ends of broken DNA, and facilitates DNA repair by homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) (7–10).
ATLD patients develop cerebellar ataxia and their cells exhibit chromosomal instability, radio-sensitivity and DNA damage-dependent checkpoint defects (11). Mutations in the N-terminal part of MRE11, containing nuclease domain important for initiation of HR, cause mainly structural and functional defects of the protein (10). Several of these mutations prevent interactions between MRE11, NBS1 and RAD50 and are associated with decreased levels of MRN complex (12). The MRE11 C-terminal part contains two potential DNA binding domains and a glycine-arginine-rich motif, involved in regulation of MRE11 nuclease activity and DNA binding (Figure 1a) (13, 14). Moreover, phosphorylation of serines 676 and 678 by ATM and RSK and interaction of the last 13 aa of MRE11 C-terminus with CDK2 affect processing of damaged DNA ends (15–17). In contrast to the ATLD single point mutations, MRE11 truncated at R633 (known as ATLD1) binds NBS1 and RAD50. Interestingly, the level of MRN complex in ATLD1 patient cells is also decreased. Whilst Mre11ATLD1/ATLD1 mice completely recapitulate the checkpoint phenotypes seen in ATLD patients including decreased level of MRN complex, it is currently unclear why the MRN complex becomes unstable in the ATLD1 human and Mre11ATLD1/ATLD1 mice cells (18).
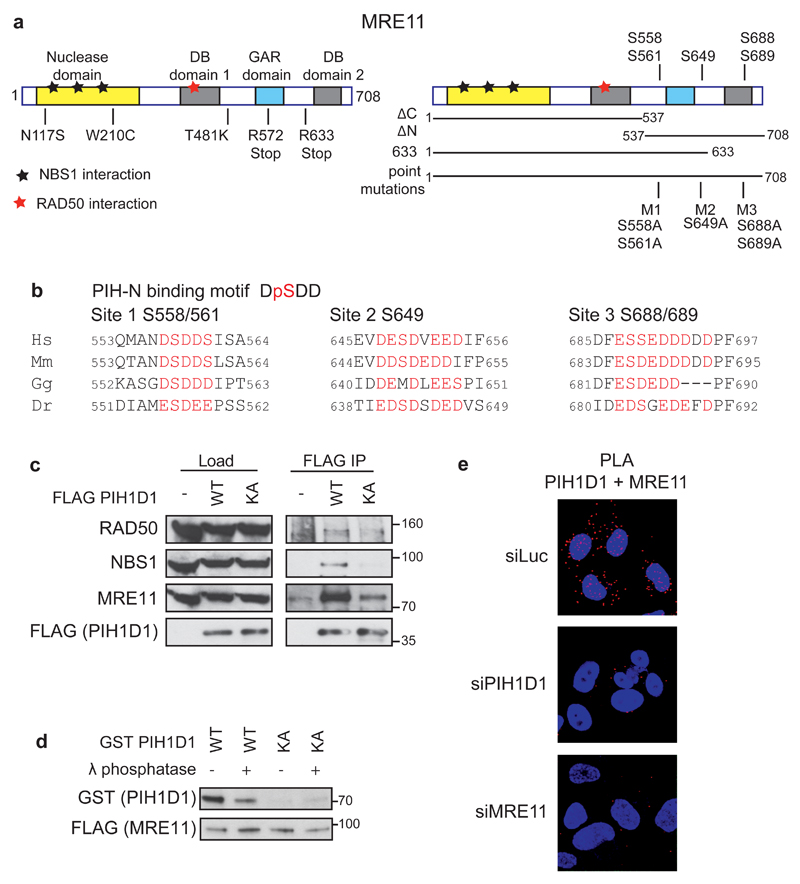
Figure 1. PIH1D1 interacts with MRN complex.
(a) Schematic representation of human MRE11 comprising of a nuclease domain, two DNA binding domains (DB1 and DB2) and Glycine-Arginine Rich domain (GAR). Positions of ATLD mutations (left panel) and putative PIH-N phospho-binding sites (right panel) are indicated. Bars below the right panel represent the MRE11 constructs used in this study. (b) Conservation of the PIH-N consensus motif in the C-terminus of MRE11. Acidic amino acids and serines that form potential PIH-N binding sites are displayed in red. (c) FLAG PIH1D1 WT interacts with MRN complex components. HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG PIH1D1 WT or phospho-binding mutant PIH1D1 KA were lysed in IP buffer (50 mM Tris-HCL pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1 % Triton X-100, 1 mM EDTA, 2.5 mM EGTA, 10 % v/v glycerol supplemented with cOmplete EDTA free protease inhibitor, PhosSTOP phosphatase inhibitor (Roche) and EtBr (50 μg/ml)) and sonicated 3x 10s. Cleared cell extracts were incubated with anti-FLAG M2 Affinity gel (Sigma-Aldrich) for 2 hours. Beads were washed 4x with IP buffer, boiled in 2x LSB buffer (100 mM Tris pH 6,8, 200 mM DTT, 4% SDS, 0,2% bromophenol blue, 20% v/v glycerol) and bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting using antibodies against RAD50 (Abcam, ab119708), MRE11 (Cell Signaling, #4895), NBS1 (Cell Signaling, #3002). (d) MRE11-PIH1D1 interaction depends on MRE11 phosphorylation and on the PIH-N domain of PIH1D1. FLAG MRE11 was purified from HEK293T using anti-FLAG M2 Affinity gel. Beads were washed with IP buffer supplemented with 1 M NaCl, treated or not with λ phosphatase for 30 min at 30°C and MRE11 was eluted with 3X FLAG peptide (30 µg, Sigma-Aldrich). GST PIH1D1 WT and phospho-binding mutant GST PIH1D1 KA were purified from BL21 E. coli and pull down with purified MRE11 was performed as described previously (20). (e) MRE11 and PIH1D1 interact in vivo. U2OS cells grown on coverslips were transfected with 40nM siRNA targeting luciferase (CGUACGCGGAAUACUUCGA, Sigma), PIH1D1 (1:1 mixture of GAAUGGAAAUGUAGUCUUA and GAGAAGAGGCUGCUGGCUU in the untranslated region of PIH1D1 as described (20)) or MRE11 (GAGCAUAACUCCAUAAGUA in the untranslated region of MRE11 mRNA) with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX reagent according to the manufacturers. Cells were permeabilized with 0.2 % Triton X-100 for 5 min at room temperature and Proximity ligation assay (PLA) was performed using MRE11 (Cell Signaling, #4895), PIH1D1 (Abcam, ab57512) antibodies and Duolink reagent according to the manufacturers protocol (Sigma-Aldrich). Red signal is PLA staining, DAPI is in blue. Representative image is shown.
The C-terminus of MRE11 encompasses several conserved acidic motifs that are predicted consensus phosphorylation sites of casein kinase 2 (CK2) and resemble binding sites for the PIH1D1 subunit of the HSP90 co-chaperone complex R2TP (Figure 1b) (19, 20). The R2TP complex is involved in assembly of large protein complexes such as small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins, RNA polymerase II and complexes comprising phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-related kinases (PIKKs), including major DDR kinases ATM, ATR and DNA-PK (21–24). It contains two subunits specific for the complex - PIH1D1, which possesses a PIH-N domain involved in recognition of R2TP complex substrates and RPAP3, which interacts with HSP90 by its tetratricopeptide domains. In addition the complex comprises two ATPases RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 that are associated with many other cellular complexes (19, 20, 24–27). Depletion of the R2TP complex frequently leads to instability of its substrates, including PI3Ks and RNA polymerase II (21, 22, 24, 28).
Here we show that PIH1D1 binds directly two CK2-phosphorylated sites within the MRE11 C-terminus. We further demonstrate that depletion of PIH1D1 resulted in MRE11 destabilization and that mutations of PIH1D1 binding sites in MRE11 C-terminus decrease MRE11 stability. In addition depletion of PIH1D1 impaired DDR processes regulated by MRN complex. Taken together, we provide an insight into the molecular basis of MRN complex instability in ATLD1 patients and reveal a new mode of regulation of MRN complex activity by CK2 and the HSP90 co-chaperone R2TP complex.
Results and discussion
PIH1D1 interacts directly with MRE11 in a phospho-dependent manner
We and others have previously shown that PIH1D1 binds acidic sequence DpSDD phosphorylated by CK2 (19, 20). It has been suggested that PIH-N domain may bind to this conserved motif present in MRE11 C-terminus (serine 558) (19). The MRE11 C-terminus also contains another two highly acidic regions conserved in mammals, which may be potentially recognized by PIH-N domain (Figure 1b). To determine if R2TP complex is involved in MRN complex assembly we first investigated whether PIH1D1 can interact with MRE11 and if the interaction requires PIH1D1 phospho-binding ability. Overexpressed FLAG-tagged wild-type PIH1D1 (FLAG PIH1D1 WT) co-immunoprecipitated with components of MRN complex, while PIH1D1 K64A mutation that abolishes phosphobinding (FLAG PIH1D1 KA) failed to do so (20) (Figure 1c). Furthermore, FLAG MRE11 WT purified from whole cell extract pulled down recombinant wild type GST-tagged PIH1D1 (GST PIH1D1 WT) and this interaction was abolished either by dephosphorylation of MRE11 by λ phosphatase or by the PIH1D1 K64A mutation (Figure 1d). We further confirmed the interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1 both in the cytoplasm and nucleus in vivo by a proximity ligation assay (Figure 1e). Based on these data we conclude that PIH1D1 binds MRE11 directly in vitro and in vivo and that the interaction depends on phosphorylation of MRE11 and an intact PIH1D1 phospho-binding domain PIH-N. Since PIH1D1 has only been shown to be exclusively active as a part of the R2TP complex, our data suggest that MRE11 and possibly the whole MRN complex may be a substrate of this HSP90 co-chaperone.
PIH1D1 interacts with phosphorylated MRE11 serine 558/561 and S688/689
Truncated MRE11 in ATLD1 preserves serine 558 but at the same time it is missing the two other acidic sites. To test whether the ATLD1 mutant is able to bind PIH1D1, we performed pull-down assay with recombinant GST PIH1D1 WT and FLAG MRE11 WT or MRE11 ATLD1 truncation (FLAG MRE11 633) purified from whole cell extracts. Importantly, the FLAG MRE11 633 interaction with PIH1D1 is greatly reduced (Figure 2a), suggesting that the DpSDD motif may not be the main or the only site responsible for the interaction. To identify which of the acidic motifs further down within the C-terminus participates in the interaction, we performed peptide pull-downs with biotinylated peptides coupled to streptavidin beads from cell extract. The peptides comprised phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated MRE11 sequences, potentially able to bind PIH1D1 (Table S2a). We observed that the DpSDD motif-containing peptide could bind PIH1D1, but only if both serines 558 and 561 within this peptide were phosphorylated. The second site, containing a motif similar to DSDD (serine 649), did not bind PIH1D1 while the third acidic sequence could bind PIH1D1, but only if both serines 688 and 689 were phosphorylated (Figure 2b). We confirmed these results by an Isothermal titration calorimetric (ITC) assay (Figure 2c, Table S2b), in which only the double phospho-peptides interacted with PIH1D1 N terminal PIH-N domain fragment (aa51-180). Although the observed affinities are in both cases ~3-5 fold weaker (26 μM for serine 558/561 and 41 μM for serine 688/689) than interaction between PIH-N and its substrate TEL2 (9.8 μM, Table S2b), the presence of two sites able to bind PIH1D1 may increase stability of the interaction. Alternatively, other subunits of the R2TP complex may bind to other MRE11 interacting partners (such as NBS1 or RAD50), which would result in overall stronger binding.
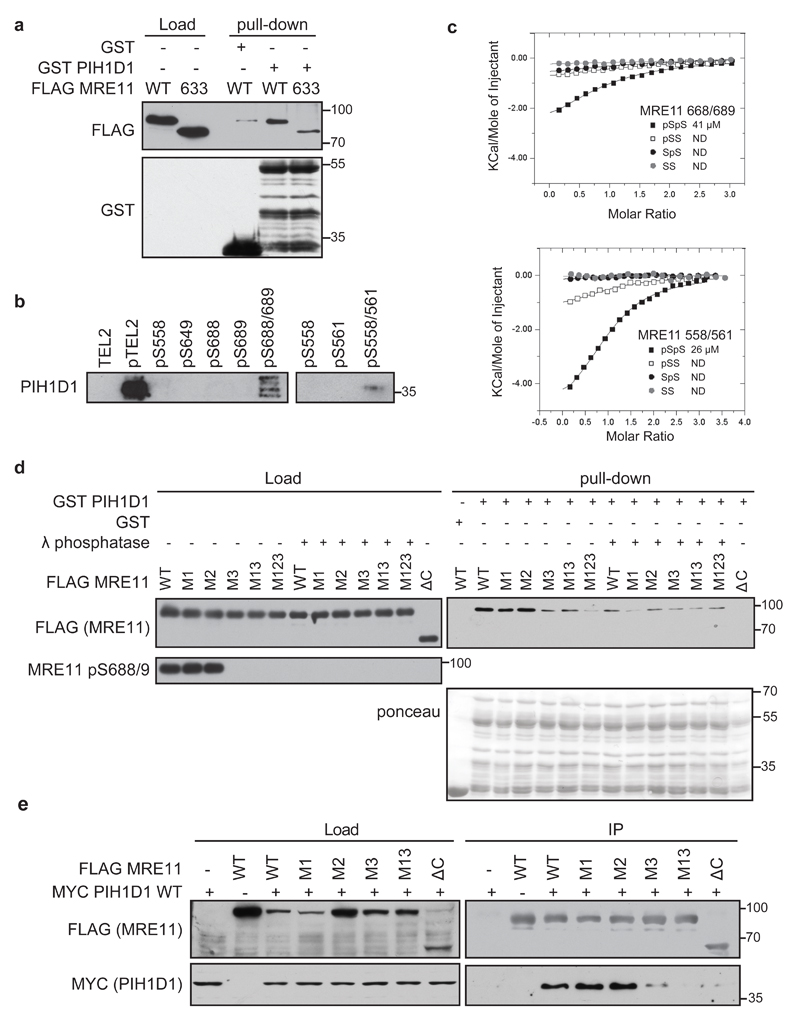
Figure 2. Phosphorylated serine 558/561 and 688/689 of MRE11 interact directly with PIH1D1.
(a) MRE11 ATLD1 truncation reduces binding of PIH1D1. GST or GST PIH1D1 WT were bound to Glutathione sepharose Beads (Genscript) for 2 hr at 4oC, washed with TBS-Tween (150 mM NaCl, 3 mM Kcl, 25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.2, 10% glycerol) and incubated with 90µl of eluted FLAG MRE11 WT or FLAG MRE11 truncated at residue 633 for 1hr at 4oC. The beads were 4x washed with TBS-Tween and boiled in 2xLSB buffer. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Recombinant full length GST PIH1D1 is at mark 55kDa, other bands are degradation products. (b) Biotinylated peptides containing a double phosphorylation of serine 558/561 or 688/681 pull down PIH1D1. Biotinylated peptides were synthesized by the Francis Crick Institute Peptide Chemistry facility and peptide pull-down from HeLa nuclear extract (4 mg/ml, Ipratech) was performed as described previously (20). Bound PIH1D1 was analyzed by immunoblotting. Phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated TEL2 peptides were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. (c) Isothermal titration calorimetric (ITC) analysis of MRE11 binding (see tab S2 for sequences) to PIH1D1 1-180. Purification of PIH1D1 1-180 PIH-N domain fragment and ITC was performed as described previously (REF) (d) Phosphorylation of serine 688/689 is required for interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1. GST or GST PIH1D1 WT were incubated with purified FLAG MRE11 WT or mutants M1, M2, M3, M13, M123 and interaction was assessed by immunoblotting against FLAG. Where indicated, purified MRE11 was treated with λ phosphatase prior the pull down assay. Staining with MRE11 pS688/9 antibody was used as control of efficient dephosphorylation. Recombinant full length GST PIH1D1 is at mark 55kDa, other bands are degradation products. (e) Interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1 in cells depends on serine 688/689. HCT116 cells were co-transfected with plasmids coding MYC PIH1D1 and FLAG MRE11 WT, M1, M2, M3, M13 or MRE11 ∆C mutants. Cell extracts were incubated with anti-FLAG M2 Affinity gel and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed with MYC (GeneTex, GTX115046) and FLAG antibodies.
To determine which of the two sites is the major binding site, we performed pull-down assays with GST PIH1D1 and FLAG MRE11 WT, the N-terminal part of MRE11 lacking all potential PIH1D1 binding sites (FLAG MRE11 ΔC, aa1-537) or MRE11 with serine 558/561 (M1), serine 649 (M2), serine 688/689 (M3) or their combinations mutated to alanine (FLAG MRE11 M1, M2, M3, M13, M123). While mutation M2 had no appreciable effect on PIH1D1 binding and M1 slightly reduced interaction with PIH1D1, mutation M3, its combination with M1 (M13) and mutation of all three sites (M123) greatly reduced the interaction with PIH1D1. The interaction of FLAG MRE11 WT, M2 and M1 with PIH1D1 was abolished by λ phosphatase treatment of the purified MRE11 prior the pull-down (Figure 2d). We have confirmed these results by co-immunoprecipitating FLAG MRE11 WT, M1, M2, M3, M13 and ΔC with MYC PIH1D1 (Figure 2e). Our data suggest that the interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1 depends on phosphorylated serine 688/689 and to some extent also on phosphorylated serine 558/561 of MRE11. Given that the binding site comprising serine 688/689 differs from the DpSDD PIH1D1 binding motif, we have identified a new target sequence of PIH-N domain.
MRE11 serines 558/561 and 688/689 are phosphorylated by CK2
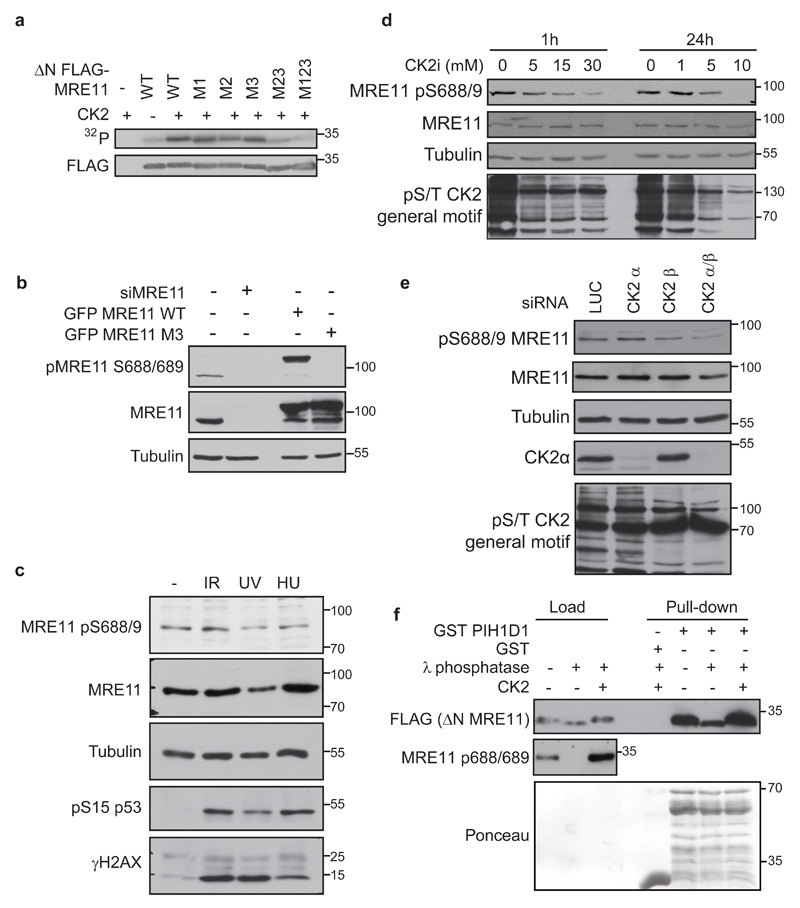
We have previously shown that the PIH1D1 binding motif DpSDD is phosphorylated by CK2 (19, 20). Since serines 561, 688 and 689 are also predicted consensus sequences of CK2, we tested whether these sites are indeed phosphorylated by CK2. In vitro kinase assays revealed that MRE11 C-terminus can be phosphorylated by recombinant CK2 and that this phosphorylation is abolished by mutation of all five serines (558, 561, 649, 688 and 689) to alanine (Figure 3a). Subsequently we raised an antibody against a synthetic peptide phosphorylated on serine S688/689 and validated its specificity on endogenous and overexpressed MRE11 by western blot and immunofluorescence. On western blot the antibody recognizes a band of the correct molecular weight of endogenous MRE11 and, crucially, the signal disappears after treatment with MRE11 siRNA (siMRE11) (Figure 3b). Consistent with the predominantly nuclear localization of MRE11, the antibody stains cell nuclei in non-transfected cells and both nuclei and cytoplasm in cells overexpressing MYC MRE11 WT (Figure S3). In contrast, the antibody does not recognize overexpressed MYC and GFP MRE11 M3 on western blot and immunofluorescence (Figure 3b, S3). The overall level of phosphorylated serine 688/689 did not change after various DNA damage treatments, consistent with the constitutive activity of CK2 (Figure 3c). To confirm that serines 688 and 689 are phosphorylated by CK2 in vivo, we treated U2OS cells with a CK2 inhibitor or siRNA targeting CK2 subunits α and β. Western blot analysis of cell lysates revealed that inhibition of CK2 or downregulation of both CK2 subunits reduces phosphorylation of serine 688/689 to an extent comparable to other CK2 substrates (Figure 3d and 3e). To further confirm that CK2 phosphorylation of serine 558/561 and serine 688/689 can promote the interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1, we performed pull-down assays with recombinant GST PIH1D1 and MRE11 C-terminal part (FLAG MRE11 ΔN, aa537-708) purified from whole cell extract (Figure 3f), treated or untreated with λ phosphatase. Dephosphorylation of the MRE11 C-terminus abolished the interaction, while rephosphorylation of the ΔN construct by recombinant CK2 rescued the interaction. Based on these results we conclude that the PIH1D1/MRE11 interaction is dependent on CK2 phosphorylation. MRE11 is phosphorylated on serine 688/689 in the cytoplasm and nucleus, which is in accordance with our PLA results showing MRE11 and PIH1D1 interaction in both cellular compartments.
Figure 3. Serines 558/561 and 688/689 are phosphorylated by CK2.
(a) CK2 phosphorylates MRE11 in vitro. FLAG MRE11FLAG MRE11 ∆N WT or M1, M2, M3, M23, M123 proteins were immunoprecipitated from HEK293T cells using anti-FLAG M2 Affinity gel. Beads were washed with 1M NaCl to eliminate contamination with protein kinases and incubated with 10 U of CK2 holoenzyme complex (α2/β; Biaffin GmbH) in 30 µl of kinase buffer (20 mM TRIS-HCl pH 8.0; 50 mM KCl; 10 mM MgCl2) supplemented with 33 µM ATP and γ32P ATP (5 µCi) and incubated for 30 min at 37oC. Reaction was stopped by addition of 4X Laemmli buffer (200 mM Tris pH 6,8, 400 mM DTT, 8% SDS, 0,4% bromophenol blue, 40% v/v glycerol) and phosphorylation of MRE11 was detected by autoradiography. Amount of the FLAG-MRE11 was determined by immunoblotting. (b) MRE11 pS688/689 antibody specifically recognizes phosphorylated MRE11. We raised a rabbit polyclonal antibody against synthetic VSKGVDFEpSpSEDDDDD peptide where pSpS represent phosphorylated serines corresponding to pS688/9 of human MRE11 and performed a two-step affinity purification using non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated peptide (Davids Biotechnologie GmbH). U2OS cells were transfected with siRNA against MRE11 (siMRE11) or with plasmids coding for GFP MRE11 WT or GFP MRE11 S688/9A. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Antibody against tubulin (GeneTex, GTX112141) was used as loading control. (c) Phosphorylation of MRE11 on serine 688/689 does not change in the presence of genotoxic stress. DNA damage was induced in U2OS cells by exposure to ionizing radiation (10 Gy 1 hour, generated by X-ray instrument T-200, Wolf-Medizintechnik), UVC (10 J/m2 1hour) or hydroxy urea (2mM 16 hours) and whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (d) CK2 inhibition decreases phosphorylation of MRE11 S688/689. U2OS cells were treated with DMSO or CK2 inhibitor (5-30 μM, CX-4945, MedChemExpress) for 1 or 24 h and whole cell lysates were probed with indicated antibodies. Antibody recognizing a general phospho-CK2 substrate (Cell Signaling, #8738) was used as control of CK2i efficiency. (e) CK2 knock down decreases phosphorylation of MRE11 S688/689. U2OS cells were treated with siLUC and siRNA targeting CK2 subunit α, β or both for 4 days. Whole cell lysates were probed with indicated antibodies. Antibody recognizing CK2 α was from GeneTex (GTX107897) (f) CK2 promotes the interaction between PIH1D1 and MRE11. Purified FLAG MRE11 ∆N was de-phosphorylated with λ phosphatase and re-phosphorylated by recombinant CK2 as indicated and incubated with GST or GST PIH1D1. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Recombinant full length GST PIH1D1 is at mark 55kDa, other bands are degradation products.
The R2TP complex is important for DDR and for MRE11 stability
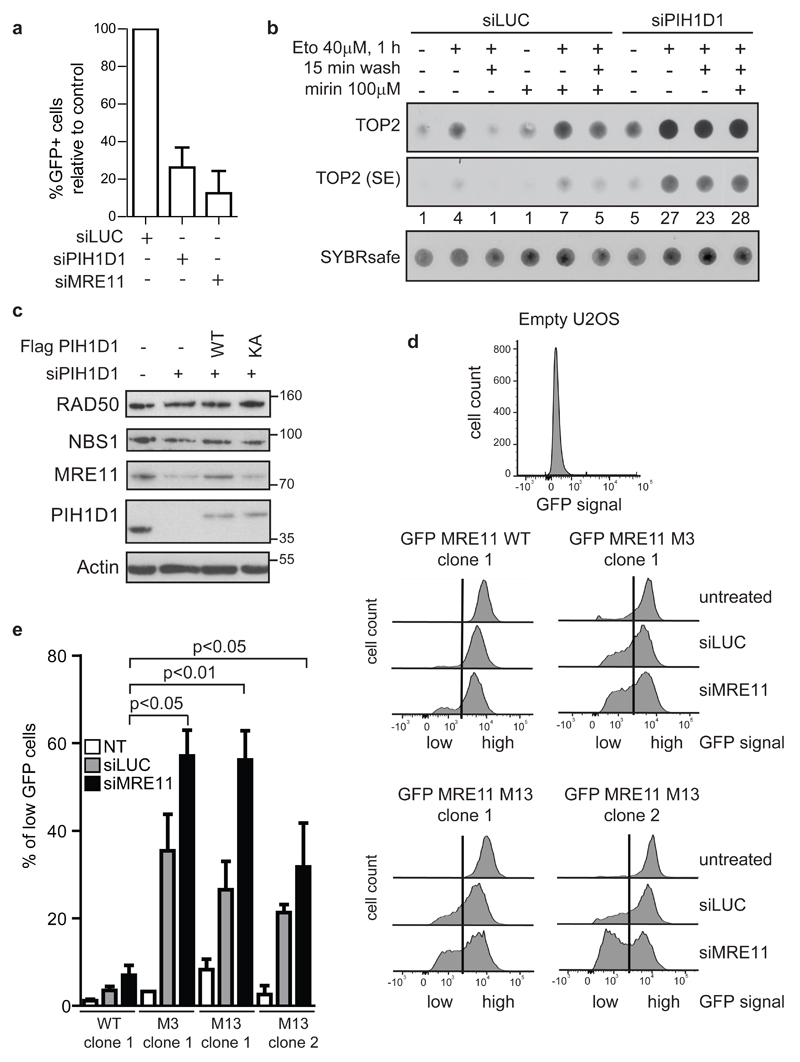
We and others have shown that R2TP complex regulates assembly and stability of ATM and ATR complexes (22, 29, 30). Accordingly, we have previously shown that depletion of PIH1D1 leads to decreased phosphorylation and protein levels of p53 after gamma irradiation (20). To see if PIH1D1 affects processes that are directly regulated by MRN complex, we assessed efficiency of HR in U2OS/DR-GFP cells treated with control siRNA (siLUC), PIH1D1 (siPIH1D1) and MRE11 (siMRE11) siRNA (31, 32). Similarly to siMRE11 treatment, depletion of PIH1D1 strongly decreased HR (Figure 4a), indicating that PIH1D1 is involved in regulation of protein complexes required for HR, such as MRN complex. To investigate whether downregulation of PIH1D1 affects other processes directly regulated by MRE11, we assayed the removal of topoisomerase 2 (TOP-2) adducts from DNA in the presence and absence of MRE11 inhibitor mirin, siPIH1D1 and siLUC by a slot blot experiment (Figure 4b) (33–35). Treatment of cells with etoposide resulted in increased levels of TOP2 covalently bound to DNA, which was efficiently removed 15 min after the etoposide was washed off the cells. Incubation of cells with mirin led to further increased levels of TOP2 covalently bound to DNA in the presence of etoposide and TOP2 remained bound to DNA after removal of etoposide. Depletion of PIH1D1 showed increased basal loading of TOP2 on DNA probably reflecting accumulation of endogenous DNA damage during siPIH1D1 treatment (Figure 4b). Importantly, similarly to the treatment with mirin, PIH1D1 depletion strongly reduced removal of TOP2 adducts induced by etoposide. These results suggest that PIH1D1 indeed affects function of the MRN complex although we cannot exclude that some of the observed phenotypes are also due to PIH1D1 function in assembly of other complexes.
Figure 4. The interaction of MRE11 with PIH1D1 is important for MRE11 stability.
(a) Depletion of PIH1D1 negatively affects HR. U2OS-DR-GFP cells (32) were transfected every 2 days with 40 nM siRNA targeting either luciferase, PIH1D1, MRE11 or combinations. For expression of ISceI, cells were transfected with pCBASce and efficiency of homologous repair was determined after 48 h as percentage of GFP-positive cells by flow cytometry (n=4). Bars show the normalized mean with SD. (b) Depletion of PIH1D1 impairs removal of TOP2-adducts from DNA. Formation of TOP2-DNA adducts was determined by modified RADAR assay as described (37). U2OS cells were transfected every 2 days for 8 days with 40 nM of siLUC or a mixture of two siRNAs targeting PIH1D1, treated with 40 μM Etoposide for 1 h in the presence or absence of 100 μM Mirin, washed for 15 min where indicated and lysed in 400 μl RLT buffer (Qiagen). DNA was precipitated by 100 μl of sodium acetate (3 M, pH 5.2) and 1 ml ethanol and centrifugation at 20 000 g. Pellet was resuspended in 8 mM NaOH and DNA concentration was determined by Hoechst 33258 in TNE buffer (2M NaCl, 1mM EDTA, 50mM Tris pH7.5) using Envision 2104 multi label reader (Perkin Elmer). DNA (200 ng) was incubated with SYBR safe in (50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl) and slot blotted onto Nitrocellulose and detected by Quantum imaging system (Vilbert lourmat). Membrane was incubated with topo IIα antibody (Santa Cruz, sc-365918), signal was quantified with ImageJ and normalized to the amount of DNA. (c) Depletion of PIH1D1 results in destabilization of MRE11. RPE cells reconstituted with empty plasmid, FLAG PIH1D1 WT or PIH1D1 KA (as described previously (20)), were treated with siRNA targeting luciferase or the 3' UTR region of PIH1D1 for 10 days. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (d) Mutation of serine 558/561 together with 688/69 leads to destabilization of MRE11. Individual clones of U2OS cells stably transfected with GFP MRE11 WT, M3 and M13 were transfected with siRNA targeting luciferase (siLUC), 3'UTR of MRE11 (siMRE11) or left untreated. siRNA was retransfected every 2 days and cells were grown for 12 days. Cells were collected and incubated with Hoechst 33258. GFP signal was analysed in Hoechst negative cells by flow cytometry using BD LSR II. Shown are representative plots. The vertical line in the plots indicates the gating; cells with GFP intensity left from the vertical line are considered to have low amounts of GFP MRE11, cells right from the vertical line are considered to have high GFP MRE11. (e) The percentage of cells from (d) that have low GFP MRE11 was quantified using Graphpad prism software (n=3). Bars show mean plus SD, statistical significance was determined with the student’s t-test. Variance between the samples was equal (F-test).
Next we investigated whether the R2TP complex affects stability of MRN complex subunits. In our previous work reconstitution of murine embryonic fibroblasts with a mutant R2TP complex co-chaperone Tel2, unable to bind PIH1D1, exhibited decreased levels of PIKKs only after 11 days after endogenous Tel2 knock-out. Hence, to determine the importance of the R2TP complex for MRE11 stability, we treated RPE cells reconstituted with empty vector, FLAG PIH1D1 WT or FLAG PIH1D1 KA with siRNA targeting 3' untranslated region of PIH1D1 mRNA (siPIH1D1) for 10 days. The treatment resulted in major decrease of MRE11 levels and slight reduction of NBS1 level in cells reconstituted with empty vector and FLAG PIH1D1 KA, while reconstitution of cells with FLAG PIH1D1 WT restored MRE11 and NBS1 levels to levels of RPE cells transfected with empty vector treated with siLUC (Figure 4c). To confirm that PIH1D1 has an impact on stability of MRE11 in other cell types, we have treated U2OS cells with siLUC or siPIH1D1 for 7 days and HCT116 cells for 10 days. The treatment with siPIH1D1 led to decreased levels of MRE11 and slight decrease of RAD50 and NBS1 in contrast to treatment with siLUC (Figure S4a). As downregulation of MRE11 by siRNA leads to prominent instability of NBS1 and RAD50 (Figure S4b), we hypothesize that prolonged treatment of the cells with siPIH1D1 would ultimately lead to much more pronounced instability of RAD50 and NBS1. However, since prolonged siPIH1D1 treatment is lethal, we were unable to prove this hypothesis. We have noticed that the effect of siPIH1D1 on MRE11 stability requires highly efficient knock-down of PIH1D1 and we suppose that even a small level of PIH1D1 in the cells is sufficient to promote assembly of MRN complex or maintaining of MRE11 stability. Therefore, a faster major effect on stability of all MRN complex components would require PIH1D1 levels reaching zero. However we have not been able to knock-out PIH1D1 by CRISPR because PIH1D1 is an essential gene in human cells and its knock-out leads to cellular death (36).
Next we investigated whether mutation of MRE11 interaction sites with PIH1D1 also leads to destabilization of MRE11. We established U2OS cell lines stably expressing GFP MRE11 WT, M1, M3 and M13, and selected two clones for MRE11 WT and M13 and one clone for MRE11 M1 and M3 with comparable expression levels of exogenous MRE11 (Figure S4c). To verify that the constructs are functional in cells in vivo, we tested their ability to be recruited to the site of the DNA damage and to repair damaged DNA. Experiments with laser irradiation-induced damage showed that all proteins are indeed recruited to sites of DNA damage (Figure S4d). In addition, GFP MRE11 WT, M3 and M13 are able to rescue formation of RPA foci in S phase cells after camptothecin treatment in cells where endogenous MRE11 has been downregulated by siRNA (Figure S4e). Interestingly, we observed a significant decrease of RPA foci in cells reconstituted with GFP MRE11 M1. Our results confirm that we have generated a relevant model system to study the effect of the selected mutations on the physiological functions and stability of MRE11. Furthermore, these results show that serine mutations do not affect MRE11 binding to the site of the damage and suggest that phosphorylation of serine 558/561 and 688/689 may regulate MRE11 in distinct manner since their mutation has a different outcome on the processing of broken DNA ends.
As MRE11 forms dimer and the presence of endogenous MRE11 could affect stability of the GFP constructs, we treated the U2OS cells reconstituted with the GFP MRE11 constructs with siLUC or siMRE11 for 12 or 17 days prior assessment of MRE11 stability. FACS analysis revealed that cells untreated with siRNA maintain stable levels of all GFP constructs. After treatment with control siLUC levels of GFP signal decreased in cells reconstituted with GFP MRE11 M13 and GFP MRE11 M3 in contrast to GFP MRE11 WT and M1. Treatment with siMRE11 led to a further decrease of the expression of GFP MRE11 M13 and M3 (Figure 4d, 4e, S4g). Since frequent transfection with siLUC lead to increased intensity of γH2AX staining in cells (Figure S4f) and since R2TP complex may be important under stress conditions, we reasoned that decrease of GFP signal of M13 and M3 constructs after siLUC may be a result of stress caused by frequent transfection per se or due to constant DNA damage stress caused by the transfection and that depletion of endogenous MRE11 may enhance this effect in MRE11 M3 and M13 reconstituted cells. Based on these results we conclude that CK2-dependent interaction between MRE11 with PIH1D1 is important for MRE11 stability and that MRE11 serine S688/689 is the main site involved in this interaction.
Overall, we believe that we discovered a new mode of regulation of MRE11 stability by CK2 and the HSP90 co-chaperone R2TP complex through its phospho-specific interaction with the R2TP subunit PIH1D1. Since the R2TP complex is involved in assembly and/or quality control of large protein complexes, the interaction between MRE11 and PIH1D1 may be important for assembly of complexes comprising MRE11 such as MRN, which is in accordance with the fact that ATLD1 human and mouse cells have overall decreased levels of all MRN complex components. The presence of serine 558/561 in the ATLD1 mutation may allow weaker interaction with PIH1D1 that would be sufficient to keep MRN complex level high enough for patient and mice survival.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Acknowledgments
All cell lines were from the Cell Services of The Friancis Crick Institute and were regularly tested for mycoplasma infection. This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (14-34264S), Institutional grant of IMG (RVO 68378050), the Wellcome Trust (200462/Z/16/Z). PM was partially supported by the Grant Agency of the Charles University (309015). SJS, TF and SJB are supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (FC001156), the UK Medical Research Council (FC001156) and the Wellcome Trust (FC001156).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Stewart GS, Maser RS, Stankovic T, Bressan DA, Kaplan MI, Jaspers NG, et al. The DNA double-strand break repair gene hMRE11 is mutated in individuals with an ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder. Cell. 1999 Dec 10;99(6):577–87. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Varon R, Vissinga C, Platzer M, Cerosaletti KM, Chrzanowska KH, Saar K, et al. Nibrin, a novel DNA double-strand break repair protein, is mutated in Nijmegen breakage syndrome. Cell. 1998 May 1;93(3):467–76. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartkova J, Tommiska J, Oplustilova L, Aaltonen K, Tamminen A, Heikkinen T, et al. Aberrations of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 DNA damage sensor complex in human breast cancer: MRE11 as a candidate familial cancer-predisposing gene. Molecular oncology. 2008 Dec;2(4):296–316. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2008.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Heikkinen K, Rapakko K, Karppinen SM, Erkko H, Knuutila S, Lundan T, et al. RAD50 and NBS1 are breast cancer susceptibility genes associated with genomic instability. Carcinogenesis. 2006 Aug;27(8):1593–9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kleibl Z, Kristensen VN. Women at high risk of breast cancer: Molecular characteristics, clinical presentation and management. Breast. 2016 Aug;28:136–44. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chubb D, Broderick P, Dobbins SE, Frampton M, Kinnersley B, Penegar S, et al. Rare disruptive mutations and their contribution to the heritable risk of colorectal cancer. Nature communications. 2016;7:11883. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lamarche BJ, Orazio NI, Weitzman MD. The MRN complex in double-strand break repair and telomere maintenance. FEBS letters. 2010 Sep 10;584(17):3682–95. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Williams GJ, Lees-Miller SP, Tainer JA. Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 conformations and the control of sensing, signaling, and effector responses at DNA double-strand breaks. DNA repair. 2010 Dec 10;9(12):1299–306. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cannavo E, Cejka P. Sae2 promotes dsDNA endonuclease activity within Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 to resect DNA breaks. Nature. 2014 Oct 2;514(7520):122–5. doi: 10.1038/nature13771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Paull TT, Gellert M. The 3' to 5' exonuclease activity of Mre 11 facilitates repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Molecular cell. 1998 Jun;1(7):969–79. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Taylor AM, Groom A, Byrd PJ. Ataxia-telangiectasia-like disorder (ATLD)-its clinical presentation and molecular basis. DNA repair. 2004 Aug-Sep;3(8–9):1219–25. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Regal JA, Festerling TA, Buis JM, Ferguson DO. Disease-associated MRE11 mutants impact ATM/ATR DNA damage signaling by distinct mechanisms. Human molecular genetics. 2013 Dec 20;22(25):5146–59. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dery U, Coulombe Y, Rodrigue A, Stasiak A, Richard S, Masson JY. A glycine-arginine domain in control of the human MRE11 DNA repair protein. Molecular and cellular biology. 2008 May;28(9):3058–69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02025-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yu Z, Vogel G, Coulombe Y, Dubeau D, Spehalski E, Hebert J, et al. The MRE11 GAR motif regulates DNA double-strand break processing and ATR activation. Cell research. 2012 Feb;22(2):305–20. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen C, Zhang L, Huang NJ, Huang B, Kornbluth S. Suppression of DNA-damage checkpoint signaling by Rsk-mediated phosphorylation of Mre11. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013 Dec 17;110(51):20605–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306328110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kijas AW, Lim YC, Bolderson E, Cerosaletti K, Gatei M, Jakob B, et al. ATM-dependent phosphorylation of MRE11 controls extent of resection during homology directed repair by signalling through Exonuclease 1. Nucleic acids research. 2015 Sep 30;43(17):8352–67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Buis J, Stoneham T, Spehalski E, Ferguson DO. Mre11 regulates CtIP-dependent double-strand break repair by interaction with CDK2. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2012 Feb;19(2):246–52. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Theunissen JW, Kaplan MI, Hunt PA, Williams BR, Ferguson DO, Alt FW, et al. Checkpoint failure and chromosomal instability without lymphomagenesis in Mre11(ATLD1/ATLD1) mice. Molecular cell. 2003 Dec;12(6):1511–23. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00455-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pal M, Morgan M, Phelps SE, Roe SM, Parry-Morris S, Downs JA, et al. Structural basis for phosphorylation-dependent recruitment of Tel2 to Hsp90 by Pih1. Structure. 2014 Jun 10;22(6):805–18. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Horejsi Z, Stach L, Flower TG, Joshi D, Flynn H, Skehel JM, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent PIH1D1 interactions define substrate specificity of the R2TP cochaperone complex. Cell reports. 2014 Apr 10;7(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boulon S, Pradet-Balade B, Verheggen C, Molle D, Boireau S, Georgieva M, et al. HSP90 and its R2TP/Prefoldin-like cochaperone are involved in the cytoplasmic assembly of RNA polymerase II. Molecular cell. 2010 Sep 24;39(6):912–24. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Horejsi Z, Takai H, Adelman CA, Collis SJ, Flynn H, Maslen S, et al. CK2 phospho-dependent binding of R2TP complex to TEL2 is essential for mTOR and SMG1 stability. Molecular cell. 2010 Sep 24;39(6):839–50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Machado-Pinilla R, Liger D, Leulliot N, Meier UT. Mechanism of the AAA+ ATPases pontin and reptin in the biogenesis of H/ACA RNPs. Rna. 2012 Oct;18(10):1833–45. doi: 10.1261/rna.034942.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhao R, Kakihara Y, Gribun A, Huen J, Yang G, Khanna M, et al. Molecular chaperone Hsp90 stabilizes Pih1/Nop17 to maintain R2TP complex activity that regulates snoRNA accumulation. The Journal of cell biology. 2008 Feb 11;180(3):563–78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rosenbaum J, Baek SH, Dutta A, Houry WA, Huber O, Hupp TR, et al. The emergence of the conserved AAA+ ATPases Pontin and Reptin on the signaling landscape. Science signaling. 2013 Mar 12;6(266):mr1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhao R, Davey M, Hsu YC, Kaplanek P, Tong A, Parsons AB, et al. Navigating the chaperone network: an integrative map of physical and genetic interactions mediated by the hsp90 chaperone. Cell. 2005 Mar 11;120(5):715–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Benbahouche Nel H, Iliopoulos I, Torok I, Marhold J, Henri J, Kajava AV, et al. Drosophila Spag is the homolog of RNA polymerase II-associated protein 3 (RPAP3) and recruits the heat shock proteins 70 and 90 (Hsp70 and Hsp90) during the assembly of cellular machineries. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):6236–47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.499608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kim SG, Buel GR, Blenis J. Nutrient regulation of the mTOR complex 1 signaling pathway. Molecules and cells. 2013 Jun;35(6):463–73. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-0138-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rendtlew Danielsen JM, Larsen DH, Schou KB, Freire R, Falck J, Bartek J, et al. HCLK2 is required for activity of the DNA damage response kinase ATR. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2009 Feb 13;284(7):4140–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808174200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rao F, Cha J, Xu J, Xu R, Vandiver MS, Tyagi R, et al. Inositol pyrophosphates mediate the DNA-PK/ATM-p53 cell death pathway by regulating CK2 phosphorylation of Tti1/Tel2. Molecular cell. 2014 Apr 10;54(1):119–32. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bennardo N, Gunn A, Cheng A, Hasty P, Stark JM. Limiting the persistence of a chromosome break diminishes its mutagenic potential. PLoS genetics. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gunn A, Stark JM. I-SceI-based assays to examine distinct repair outcomes of mammalian chromosomal double strand breaks. Methods in molecular biology. 2012;920:379–91. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-998-3_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Deshpande RA, Lee JH, Arora S, Paull TT. Nbs1 Converts the Human Mre11/Rad50 Nuclease Complex into an Endo/Exonuclease Machine Specific for Protein-DNA Adducts. Molecular cell. 2016 Nov 03;64(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hoa NN, Shimizu T, Zhou ZW, Wang ZQ, Deshpande RA, Paull TT, et al. Mre11 Is Essential for the Removal of Lethal Topoisomerase 2 Covalent Cleavage Complexes. Molecular cell. 2016 Dec 01;64(5):1010. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.11.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Aparicio T, Baer R, Gottesman M, Gautier J. MRN, CtIP, and BRCA1 mediate repair of topoisomerase II-DNA adducts. The Journal of cell biology. 2016 Feb 15;212(4):399–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201504005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luo H, Lin Y, Gao F, Zhang CT, Zhang R. DEG 10, an update of the database of essential genes that includes both protein-coding genes and noncoding genomic elements. Nucleic acids research. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D574–80. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kiianitsa K, Maizels N. A rapid and sensitive assay for DNA-protein covalent complexes in living cells. Nucleic acids research. 2013 May;41(9):e104. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.