CHAPTER SUMMARY
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health threat that has stimulated the scientific community to search for non-traditional therapeutic targets. Because virulence, but not the growth, of many Gram-negative bacterial pathogens depends on the multi-component type three secretion system injectisome (T3SSi), the T3SSi has been an attractive target for identifying small molecules, peptides, and monoclonal antibodies that inhibit its function to render the pathogen avirulent. While many small molecule lead compounds have been identified in whole cell-based high throughput screens (HTSs), only a few protein targets of these compounds are known, an important step to developing more potent and specific inhibitors. Evaluation of the efficacy of compounds in animal studies is ongoing. Some efforts involving the development of antibodies and vaccines that target the T3SSi are further along and include an antibody that is currently in phase II clinical trials. Continued research into these anti-virulence therapies, used alone or in combination with traditional antibiotics, requires combined efforts from both pharmaceutical companies and academic labs.
INTRODUCTION
Antibiotic resistance is a great and growing threat to public health motivating scientists to find innovative strategies to cure infections (1–3). An alternative approach to classical antibiotics is to target virulence factors (4) – bacterial factors required for infection or damage but not for growth outside the host (2, 5, 6). An anti-virulence factor should render the bacteria non-pathogenic by neutralizing a critical virulence element thereby allowing clearance of the pathogen by the host immune system (5–8).
The type 3 secretion system/injectisome (T3SSi) is expressed in a broad spectrum of Gram-negative bacteria and is usually crucial for virulence (4, 9). This needle and syringe-like apparatus functions as a conduit for the delivery of effector proteins from the bacterial cytoplasm into host cells (Fig 1A). These T3SSi systems share homology with 8 essential core components of flagellar T3SS and contain an additional 20–30 proteins involved in expression, secretion and translocation of effector proteins (9–11). Therapeutic strategies against the T3SSi have been pursued that include interfering with transcriptional regulation, chaperone-effector interaction, assembly of various structures (outer ring, needle, tip complex), or effector translocation or function (4, 5, 12–18).
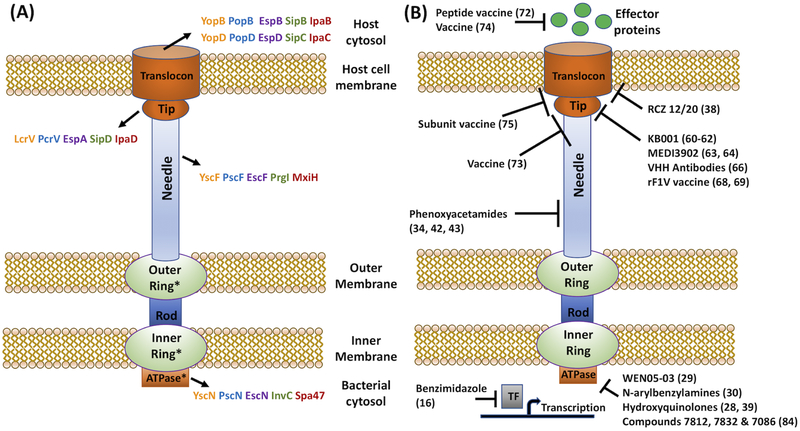
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of T3SSi. * indicate regions with conserved components between T3SSi and flagella. Yersinia = orange; Pseudomonas = blue; EPEC/EHEC = purple; Salmonella = green; Shigella = red. (B) Potential targets of compounds based on inhibition of T3SSi function, biochemical or binding studies, genetic resistance, or animal studies.
Targeting the T3SSi as an effective means of curtailing infection has been rationalized in several ways. Since the injectisome is absent in many resident microbiota, one proposed advantage is that more of the microbiome would be preserved during treatment. Furthermore, the likelihood of developing resistance in resident microbiota that can be transferred by horizontal gene transfer to pathogenic bacteria is minimal. However, due to the homology between some components of the T3SSi and flagella, some inhibitors also affect flagella (13, 19, 20), an observation that may mitigate this advantage. Another potential benefit is that since these anti-virulence agents should minimally affect bacterial growth, they may exert low selective pressure in the environment and therefore drug resistance may develop infrequently. To our knowledge this has not been experimentally tested in an animal model of infection. On the other hand, disadvantages to be considered include that anti-T3SSi agents may not impede bacterial growth in infected immunocompromised individuals and that some infections require bactericidal agents. Nonetheless, discovering and studying reagents that inhibit the T3SSi remains attractive both for the potential therapeutic benefits and their use as important tools to elucidate the structure-functional relationships of this complex machinery.
This review focuses on advances in T3SSi-targeted therapies in the past 4 years (Tables 1–2) including small molecules, antibodies, and vaccines, whose molecular targets are known (Fig. 1B). Excellent in-depth reviews covering progress of the field until 2014–2015 and structure of molecules include (2, 21, 22). Some previously well-studied compounds are also summarized in Table 1.
Table 1:
Possible Targets and Function of Small Molecule Inhibitors of the T3SS
| Compound | Organism | Target | Inhibits bacterial growth? | Toxic to cells? | In vivo studies? | Phenotype/Readout | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAH (C1, C2) SABC4 |
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | No | NT | No | Inhibits T3SS transcription and Yop secretion; C2 and C4 inhibit flagellar motility | (13) | |
| SAH (C1–C23) C1-INP0007 |
Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion and translocation | (14) | |
| SAH C1-INP0007 SAH C11-INP0403 |
Salmonella enterica | No | No | Yes | Inhibits secretion and blocks invasion; First study to validate SAH in vivo using bovine intestinal ligated loops | (27) | |
| SAH C11-INP0403 (ME0053) |
S. enterica | Suggested indirect effect-iron chelation | No | No | No | Inhibits T3SS transcription and secretion; Upregulation of iron acquisition | (25) |
| SAH INP0341 SAH INP0400 |
Chlamydia trachomatis | Suggested indirect effect-iron chelation | No | No | Yes | Inhibits T3SS transcription; Upregulation of iron acquisition; Protects mice against vaginal infection when administered topically | (35, 80, 81) |
| SAH INP0341 | C. trachomatis | No | No | No | Mutations isolated in HemG suggesting indirect effect on T3SS | (37) | |
| SAH INP0400 SAHINP0402 (C15) | Shigella flexneri | Suggested to inhibit T3SS basal needle assembly | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion and blocks invasion; Fewer and shorter needle assembly | (17) |
| SAHME0052(C8, INP0010) SAHMEOO53(C11, INP0403) SAHME0054(C10, INP0401) SAH ME0055(C17; INPOO31) |
EHEC | Suggested to inhibit T3SS regulators | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion | (15) |
| SAH ME0052(C8, INPOO10) SAH ME0055(C17, INPOO31) |
Y. pseudotuberculosis Escherichia coli | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion; Pull down assays identified WrbA, FoIX and Tpx bind to SAH suggesting indirect effect on T3SS | (36) | |
| SAH INP0404 SAH INP0405 |
S. enterica | No | No | NA | Mutations isolated in FlhAgene suggest targeting of T3SS basal body | (19) | |
| SAH INP0341 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | No | No | No | Inhibits T3SS transcription and ExoS secretion | (39) | |
| SAH RCZ12 and RCZ20 |
EHEC | EspD ‒ needle pore protein | No | No | No | Inhibits EspD secretion; Fewer/shorter needle assembly | (38) |
| SAB Compound 4 | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion | (40) | |
| SAH INP0007 | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | No | No | Affects YscD puncta formation | (40) | |
| SAH INP0010 | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | Yes | No | Affects YscD puncta formation | (40) | |
| Salicylideneanilide C3 | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | NT | No | Inhibits secretion and transcription | (13) | |
| Salicylideneanilide | EPEC | No | No | No | Inhibits T3SS transcription and EspB secretion | (26) | |
| Benzimidazole | Y. pseudotuberculosis | LcrF ‒ T3SS master regulator | No | No | Yes | Reduces cytotoxicity in infected cells; Protective in a murine model | (16) |
| C15, C19, C22, C24 and C38 |
Y. pseudotuberculosis P. aeruginosa |
No | No | No | Inhibits effector translocation | (18) | |
| C20 |
Y. pseudotuberculosis P. aeruginosa |
Suggested to interfere with adherence | No | No | No | Inhibits effector translocation | (18) |
| Compound D |
Y. pseudotuberculosis Yersinia pestis P. aeruginosa |
Suggested to target YopD ‒ translocon | NT | Yes | No | Inhibits effector secretion | (82) |
| Thiazolidinones |
S. enterica P. aeruginosa Yersinia Entercolitica Psuedomonas syringae |
Inhibits T2SS suggesting common target with T3SS such as secretin | No | No | Yes tobacco plants | Inhibits transcription and secretion; Reduces needle complex formation; Reduces hypersensitivity response in plant leaves | (83) |
| Phenoxyacetamides | P. aeruginosa | Suggested to target PscF ‒ needle protein | No | No | No | Isolation of PscF mutants resistant to phenoxyacetamide inhibitors | (34, 42, 43) |
| Phenoxyacetamides | P. aeruginosa | NT | NT | Yes | Reduces abscess size in mouse model of P. aeruginosa abscess formation | (44) | |
| Piericidins | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | No | No | Inhibits T3SS-dependent NF-kB activation | (45) | |
| Piericidin A1 | Y. pseudotuberculosis | Suggested to target YscF-needle protein | NT | NT | No | Reduces number of needles present | (46) |
| Library of compounds | Salmonella spp. | SipD ‒ tip protein SipB ‒ translocon protein | NT | NT | No | Surface plasmon resonance screen to find compounds that bind to SipD and SipB | (48) |
| Library of compounds | Shigella spp. | IpaD ‒ tip protein | NT | NT | No | Surface plasmon resonance screen to find compounds that bind to IpaD | (49) |
| Malic diamide | Y. pseudotuberculosis | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion of YopB and YopD | (40) | |
| Flavonoids | S. enterica | Covalent labeling ofSPI-1 substrates | No | NT | No | Inhibits bacterial invasion of host cells | (47) |
| Compounds 7812, 7832, 7086 | Y. pestis | T3SS ATPase YscN | No; 7086 -Yes | No | No | Inhibits secretion | (84) |
| WEN05–03 | EPEC | T3SS ATPase EscN | No | No | No | Inhibits ATP hydrolysis; Reduces toxicity to infected HeLa cells | (29) |
| N-arylbenzylamines | C. trachomatis | Suggested to target T3SS ATPase SctN | No | No | No | Reduces secretion and chlamydial inclusions in host cells | (30) |
| Hydroxyquinolines INP1750INP1767 INP1855 |
C. trachomatis Y. pseudotuberculosis |
No | No | No | Inhibits cytotoxicity | (41) | |
| Hydroxyquinoline INP1855 |
P. aeruginosa | Suggested to target T3SS ATPase | No | No | Yes | Reduces cytotoxicity on host cells; Reduces bacterial burden and lung pathology in infected mice; Reduces activity of homologous T3SS ATPase YscN | (28) |
| Hydroxyquinoline INP1750 |
P. aeruginosa Y. pseudotuberculosis |
Suggested to target T3SS ATPase | No | No | No | Inhibits secretion and flagellar motility; Reduces activity of Yersinia T3SS ATPase YscN | (39) |
| Licoflavonol | S. enterica | No | NT | No | Reduces expression of chaperone sicA and invF-transcriptional regulator for SPI-1 effector proteins | (50) | |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | EPEC/EHEC S. enterica Y. pseudotuberculosis |
No | NT | No | Reduces adherence of EHEC/EPEC; Reduces Salmonella invasion into host cells; Reduces Yersinia induced cell death | (52) | |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | S. enterica | No | NT | No | Reduces Salmonella invasion into host cells | (51) | |
|
Psidium guajava leaf extract |
EPEC/EHEC S. enterica Y. pseudotuberculosis |
No | NT | No | Reduces adherence of EHEC/EPEC; Reduces Salmonella invasion into host cells; Reduces Yersinia induced cell death | (53) | |
| Sanguinarine chloride | S. enterica | No | Yes at higher conc. | No | Inhibits bacterial invasion of host cells | (54) | |
| Thymol | S. enterica | Slightly at higher conc. | Slightly at higher conc. | Yes | Inhibits bacterial invasion of host cells; Protects mice against infection | (85) | |
| Obovatol | S. enterica | No | NT | No | Reduces hemolysis of sheep red blood cells | (55) | |
| 7-hydroxycoumarin ‒ Umbelliferone |
Ralstonia solanacearum |
Yes(86) | NT | Yes tobacco plants | Reduces expression of T3SS effector genes; Reduces disease progression on tobacco plants | (87) | |
| SAHs | R. solanacearum | Minimal | NT | Yes tomato plants | Inhibits translocation; reduces bacterial growth on tomato plants | (56) | |
| SAHs | Erwinia amylovora | No | NT | Yes apple plants | Reduces expression of T3SS genes; reduces disease symptoms on apple plants | (57) | |
| Phenols | Xanthomonas oryzae | No | NT | Yes rice plants | Reduces expression of hrpG and hrpX-regulators of hrp genes which regulate T3SS effector expression; Reduces disease symptoms on rice plants | (58) | |
| Thiazolidin-2-cyanamide derivatives | X. oryzae | No | NT | Yes rice plants | Reduces expression of hrpG and hrpX-regulators of hrp genes which regulate T3SS effector expression; Reduces disease symptoms on rice plants | (59) |
NT = Not Tested; EHEC = Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli; EPEC = Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; T3SS = Type III secretion system
Table 2:
Antibodies, vaccines, and peptomers against T3SS components
| Class | Organism | Target | Phenotype/Readout | Therapeutic Potential | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody ‒ KB001 |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
PcrV ‒ tip | Protects host cells against T3SS mediated toxicity and protects mice against acute pulmonary infection (reviewed in (88)) | Did not meet efficacy endpoints in phase II clinical trials | (60–62) |
| Bispecific Antibody ‒ MEDI3902 |
P. aeruginosa | PcrV ‒ tip Psl ‒ exopolysaccharide | In vitro cytotoxicity protection and in vivo protection of acute pneumonia model in mice | Currently in phase II clinical trials | (63, 64) |
| Single-VH Domain Antibodies |
Shigella flexneri | IpaD ‒ tip | Reduces hemolysis of sheep red blood cells | (66) | |
| rF1V Vaccine | Yersinia pestis | LcrV ‒ tip F1 protein |
Enhances survival of cynomolgus macaques infected with lethal aerosol challenge of Y. pestis | Orphan Drug designation by FDA | (69) |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-sera | STEC | STECO103 T3SS proteins | Blocks adherence of STEC to host cells; Immunized mice not protected against fecal shedding | (71) | |
| Peptide vaccine | Salmonella enterica | Ssel ‒ effector | Protects mice against acute infection | (72) | |
| Vaccine | S. enterica | Prgl ‒ needle SipD - tip |
Protects mice against infection | (73) | |
| Vaccine | S. enterica | SseB ‒ effector Flagellin |
Protects mice against infection | (74) | |
| Subunit vaccine | S. enterica | S1: Fusion of SipD and SipB-tip and translocon S2: Fusion of SseB and SseC-tip and translocon |
Protects mice against lethal challenge | (75) | |
| Polypeptide |
S. enterica S. flexneri |
SipB ‒ translocon IpaB ‒ translocon |
Inhibits bacterial invasion into host cells | Polypeptide too large for therapeutic potential | (76) |
| Peptides | EPEC | EspA-tip | Inhibits EspA polymerization thereby preventing A/E lesions | (77) | |
| Peptides | EHEC Citrobacter rodentium |
EspA-tip | Protects mice against colon damage after C. rodentium challenge | (78) | |
| Peptomers ‒ phepropeptin D derivatives |
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis P. aeruginosa |
Inhibits secretion of T3SS proteins; Inhibits Yersinia YopM effector translocation and reduces cell rounding | (79) |
STEC = Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli; EPEC = Enteropathogenic Escherichia col
SMALL MOLECULES
Many studies use HTSs to identify small molecule inhibitors of T3SSi via phenotypic readouts of T3SSi functions including inhibition of T3SSi expression in bacteria (13, 15, 23–25), secretion of effectors into the extracellular supernatant (14, 17, 25–27), or translocation of effector proteins into host cells (14, 18). A benefit of such approaches is that identified molecules are effective in the context of the bacterium. However, complications include that the inhibitors may target more than one protein, may target a host protein, or may alter T3SSi function by generally affecting bacterial cell physiology rather than a specific component of the machinery. Consequently, identification of the specific targets of many small molecule inhibitors has lagged and structure activity relationship (SAR) studies are complicated if the molecule targets several proteins.
Recently, several exciting advances have been made in both target identification and in identifying lead compounds with sufficiently low IC50 for in vivo studies. More classical pharmacological approaches that identify compounds that bind to a protein or inhibit its biochemical activity have been fruitfully employed (16, 28–30). Increasingly, the structures of T3SS components are being exploited to elucidate the design of potential inhibitors to these proteins (31–34).
Salicylidene Acylhydrazides
Salicylidene acylhydrazides (SAHs) are the first identified and most widely studied class of synthetic small molecules that target the T3SSi across many bacterial species (13, 14). Several studies suggest that some of these molecules have multiple targets or act indirectly on the T3SSi by impacting bacterial physiology (19, 25, 35–37). Of the derivatives generated, many show promising results. Modifications to improve stability and selectivity of SAH ME0055 resulted in two new synthesized compounds, RCZ12 and RCZ20, that inhibit secretion of EHEC T3SS translocon protein, EspD, as effectively as ME0055 (Fig. 1B). Unlike the parent compound, RCZ12 and RCZ20 have no effect on bacterial growth suggesting they are more specific (38). Affinity-chromatography experiments revealed the coiled-coil domain 1 of EspD as the inhibitors’ key domain-binding site (38). These compounds show dual functionality by also downregulating transcription of the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) that encodes the T3SS (38). Recent mechanistic analysis of another SAH, INP0341, shows that it prevents T3SS expression in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates without affecting growth (39).
A very recent study employed a multiple-assay approach to elucidate the mechanism of action of a group of previously identified T3SS inhibitors (40). Compound SAH INP0007 disrupts YscD puncta formation suggesting interference with needle assembly and significantly decreases flagellar motility. Whether inhibition occurs by directly binding to a common core component between the T3SSi and flagella, or by interfering with other processes that render bacteria less able to build both systems, is still unknown (40). Compound 4 (C4), a haloid-containing sulfonamidobenzamide (SAB), which was originally identified along with SAHs as inhibitors of the T3SS (13), is now postulated to have an indirect effect on T3SS transcription by inhibiting the secretion process (40).
Compounds Targeting the T3SS ATPase
Using the known structure of the EPEC EscN ATPase, a computational HTS identified compounds predicted to block the protein’s active site (29). One lead compound (WEN05–03) competitively inhibits hydrolysis of ATP by EscN and reduces toxicity to infected HeLa cells (29). Another study using molecular docking and virtual screening identified a series of N-arylbenzylamines predicted to target the SctN T3SS ATPase of C. trachomatis (30). Two of these compounds block translocation of the T3SS effector, IncA, into cultured cells and reduce chlamydial survival in these cells (30). Hydroxyquinoline (HQ) derivatives were first described as inhibitors of T3SSi gene expression in Y. pseudotuberculosis and C. trachomatis (41). HQ INP1855 inhibits YscN ATPase activity in vitro as well as impairs flagellar motility providing evidence that it might target conserved ATPases found in T3SS and flagella (28). In addition, HQ INP1855 reduces P. aeruginosa T3SS-mediated cytotoxicity in cultured cells, blocks secretion of ExoS effector protein, as well as enhances survival and reduces bacterial burden and lung pathology of mice infected intranasally with P. aeruginosa (28). HQ INP1750 acts similarly to HQ INP1855 and inhibits both ExoS secretion as well as flagellar motility (39). However, a direct interaction between these HQ derivatives and T3SS ATPases remains to be shown.
Compounds Targeting Needles or Needle Assembly
Phenoxyacetamide (PXA) was first discovered as an inhibitor of the T3SSi in P. aeruginosa and SAR analysis demonstrated strict stereoselectivity suggesting an interaction with a specific target or site (42). Isolation of several mutants in PscF resistant to PXA inhibitors provides genetic evidence that PXAs target the needle protein (34, 43). Modeling of PXA inhibitors supports the idea that these molecules intercalate within the needle and interact simultaneously with several assembled PscF subunits; however, biochemical and structural studies are needed to demonstrate a direct interaction. Importantly, injection of PXA (MBX2359) into abscesses formed by P. aeruginosa significantly reduces abscess size providing evidence that these inhibitors are efficacious in infection models in mammals (44).
Piericidins, a class of compounds derived from Actinomycetales, inhibits translocation of YopM into cultured cells (45). A follow-up study showed that Yersinia treated with Piericidin A1 has fewer needles, suggesting that it inhibits a step prior to or during needle assembly (46). The related Psc T3SS of P. aeruginosa and the Ysa T3SS of Y. enterocolitica are not inhibited, indicating its specificity but potentially limiting its usefulness without additional SAR analysis (46).
Compounds Targeting Translocon and/or Effector Secretion and Activity
Using click chemistry, the flavonoids baicalein and quercetin were found to covalently modify S. Typhimurium translocases and effectors, resulting in changes to stability or activity (47). The N-terminal chaperone-binding domain is proposed to be the modified site (47). These flavonoids inhibit invasion of S. Typhimurium into cultured cells but have no effect on effector secretion or needle assembly (47). Screening libraries for compounds that bind to Salmonella SipD (48) or Shigella IpaD tip proteins (49) identified a new class of small molecules based on the indole scaffold as potential inhibitors of the T3SSi. Malic diamide (42), a compound structurally related to PXA, significantly inhibits the secretion of YopB and YopD proteins required for translocation, without disrupting needle YscF puncta formation indicating that it targets the translocon (40).
In the past few years, several natural compounds have been identified, typically in screens for secretion (50–53), translocation into target cells (54) or by inhibiting the effects on T3SSi-mediated functions on targeted host cells (55). Potentially promising compounds are listed in Table 1, but to our knowledge, the specificity against T3SSi or protein targets have not been investigated in depth.
Anti-T3SS Compounds Tested Against Plant Pathogens
Plants are also susceptible to infection by bacteria harboring T3SSs, and there have been several recent exciting findings. Natural and synthetic compounds were screened for the ability to reduce expression of the R. solanacearum T3SS pilus gene hrpY (56). The most potent inhibitors were SAHs, which inhibit secretion of T3SS effector AvrA and limit bacterial growth on tomato plants (56). SAHs also reduce the expression of T3SS genes of Erwinia amylovora and reduce disease symptoms on inoculated crab apple pistils (57). Phenolic compounds repress the expression of T3SS transcriptional regulators hrpG and hrpX of Xanthomonas oryzae and reduce disease symptoms on rice leaves (58). Thiazolidine-2-cyanamide compounds also reduce relative expression of X. oryzae hrpG and hrpX and disease symptoms on rice (59).
ANTIBODIES, VACCINES, AND PEPTIDES
Recent advances in targeting T3SSi using antibodies, vaccines, and polypeptides are summarized below and in Table 2.
Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody, KB001, that binds to the P. aeruginosa T3SS tip protein, PcrV, initially showed promise in the treatment of patients with airway-associated P. aeruginosa infection or colonization, but failed in phase II clinical trials for not meeting efficacy endpoints (60–62). By contrast, a bispecific antibody, MEDI3902, against P. aeruginosa PcrV and the Psl exopolysaccharide, is effective against a wide range of clinical isolates and is currently in phase II clinical trials for prevention of ventilator nosocomial pneumonia (63, 64).
Single-domain antibodies that consist of the N-terminal variable region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain (VHH) but not the light chain can be isolated from camelid species (65). A panel of VHH single-domain antibodies was raised against the Shigella flexneri IpaD tip protein (66). Four such antibodies that bound IpaD significantly inhibit hemolysis of sheep red blood cells, a measure of T3SS translocon functionality (66). Structural binding analysis revealed that these inhibitory VHHs mostly bound to the distal domain of IpaD, suggesting the importance of this region in T3SS function (66).
Vaccines
Work towards a plague vaccine has led to testing a recombinant vaccine consisting of the Yersinia pestis F1 protein and the T3SS tip protein LcrV, reviewed in (67). The FDA has granted Orphan Drug status for the development of this rF1V vaccine, as a prophylactic for high risk individuals (68, 69). Efforts to lessen Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) disease burden in cattle to reduce transmission to humans are ongoing. Cohorts of cattle immunized against serotype O157 have reduced shedding of O157 but not of other STEC serotypes due to serotype specificity (70). To develop vaccines against a different prevalent serotype, anti-sera to five T3SS proteins, EspA, EspB, EspF, NleA and Tir, of STEC serotype 0103 were studied. These anti-sera block STEC adherence to HEp-2 cells (71). In efficacy studies, mice developed strong serum IgG titers against four of these five proteins, but still shed 0103 after oral administration indicating that the bacteria could still be transmitted (71).
Recent attempts to develop T3SS-targeted vaccines against Salmonella enterica show some success in mouse studies. A peptide vaccine that elicits a CD4 T cell response against T3SS effector protein SseI, protects mice against acute infection, a tantalizing result given that only a single peptide elicits protection (72). Mice were immunized by different routes with Salmonella T3SS proteins SipD and PrgI in combination or alone; oral immunization with SipD provides the highest level of protection against lethal challenge (73). Increased protection is observed when flagellin is added to a vaccine against Salmonella T3SS protein SseB (74). A subunit vaccine against Salmonella consisting of two components, S1 (a genetic fusion of SPI-1 translocon proteins SipB and SipD) and S2 (a genetic fusion of SPI-2 proteins SseB and SseC) elicits strong IgG titers to all four proteins in mice (75). These mice are significantly protected against challenge with S. typhimurium and S. enteritidis and experience reduced cecal inflammation (75). These results warrant studies on long-term protection.
Peptides
Anti-T3SS peptides (Table 2) have been identified against Salmonella (76), EPEC (77), and EHEC (78) and more recently, in Yersinia (79). Derivatives of the natural compound phepropeptin D that contained various peptoid substitutions on the cyclic peptide backbone, significantly inhibits NF-kB signaling, secretion of the effector protein YopE, and translocation of YopM into HeLa cells by Yersinia (79). The peptomers do not affect Yersinia growth or flagellar motility indicating their potential specificity to the T3SSi. Several derivatives also inhibit secretion of the P. aeruginosa effector protein ExoU suggesting that they might target a conserved component of these two injectisome systems (79).
CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVE
Discovery of and research into inhibitors of the T3SSi is a highly active area with many candidates from different classes that are effective in blocking the function of T3SS. Although antibodies and vaccines are further along in the pipeline, many small molecule inhibitors show promise. Some molecules have a narrower spectrum of activity, while others have broader spectrums including those that target components conserved between the T3SSi and flagella. Both have benefits and disadvantages. For instance, an effective, but narrow spectrum molecule against the T3SSi of the multi-drug resistant P. aeruginosa could save many lives each year. By contrast, a narrow spectrum molecule effective towards Y. pestis would not save many lives annually unless a major outbreak occurred. Yet importantly, study of such a molecule could help elucidate structure-function relations of the T3SSi and be used as a platform to develop molecules highly effective against homologous components in other T3SSi. Resistance mutants, biochemical assays, structural modeling, and rational designs are helping to identify targets and generate more potent inhibitors. Validating their efficacy in animal systems is ongoing. Both basic science and clinical translational research from academic and pharmaceutical groups is crucial to the advancement of these molecules to combat the rising threat of antibiotic resistance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Anne McCabe for useful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. ACF was supported in part by NIH T32 AI007077; LS was supported in part by NIH AI007422; JM was supported by NIH R01 AI113166, NIH STTR R41 AI22433 and NIH U19 AI131126. JM has an ongoing NIH funded collaboration with Paratek Inc (STTR R41 AI22433).
REFERENCES
- 1.Bassetti M, Merelli M, Temperoni C, Astilean A. 2013. New antibiotics for bad bugs: where are we? Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 12:22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McShan AC, De Guzman RN. 2015. The bacterial type III secretion system as a target for developing new antibiotics. Chem Biol Drug Des 85:30–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Czaplewski L, Bax R, Clokie M, Dawson M, Fairhead H, Fischetti VA, Foster S, Gilmore BF, Hancock RE, Harper D, Henderson IR, Hilpert K, Jones BV, Kadioglu A, Knowles D, Olafsdottir S, Payne D, Projan S, Shaunak S, Silverman J, Thomas CM, Trust TJ, Warn P, Rex JH. 2016. Alternatives to antibiotics-a pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect Dis 16:239–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Keyser P, Elofsson M, Rosell S, Wolf-Watz H. 2008. Virulence blockers as alternatives to antibiotics: type III secretion inhibitors against Gram-negative bacteria. J Intern Med 264:17–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baron C 2010. Antivirulence drugs to target bacterial secretion systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:100–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Allen RC, Popat R, Diggle SP, Brown SP. 2014. Targeting virulence: can we make evolution-proof drugs? Nat Rev Microbiol 12:300–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clatworthy AE, Pierson E, Hung DT. 2007. Targeting virulence: a new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat Chem Biol 3:541–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Maura D, Ballok AE, Rahme LG. 2016. Considerations and caveats in anti-virulence drug development. Curr Opin Microbiol 33:41–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cornelis GR. 2006. The type III secretion injectisome. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:811–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Galan JE, Wolf-Watz H. 2006. Protein delivery into eukaryotic cells by type III secretion machines. Nature 444:567–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Galan JE, Lara-Tejero M, Marlovits TC, Wagner S. 2014. Bacterial type III secretion systems: specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:415–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Titball RW, Howells AM, Oyston PC, Williamson ED. 1997. Expression of the Yersinia pestis capsular antigen (F1 antigen) on the surface of an aroA mutant of Salmonella typhimurium induces high levels of protection against plague. Infect Immun 65:1926–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kauppi AM, Nordfelth R, Uvell H, Wolf-Watz H, Elofsson M. 2003. Targeting bacterial virulence: inhibitors of type III secretion in Yersinia. Chem Biol 10:241–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nordfelth R, Kauppi AM, Norberg HA, Wolf-Watz H, Elofsson M. 2005. Small-molecule inhibitors specifically targeting type III secretion. Infect Immun 73:3104–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tree JJ, Wang D, McInally C, Mahajan A, Layton A, Houghton I, Elofsson M, Stevens MP, Gally DL, Roe AJ. 2009. Characterization of the effects of salicylidene acylhydrazide compounds on type III secretion in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun 77:4209–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garrity-Ryan LK, Kim OK, Balada-Llasat JM, Bartlett VJ, Verma AK, Fisher ML, Castillo C, Songsungthong W, Tanaka SK, Levy SB, Mecsas J, Alekshun MN. 2010. Small molecule inhibitors of LcrF, a Yersinia pseudotuberculosis transcription factor, attenuate virulence and limit infection in a murine pneumonia model. Infect Immun 78:4683–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Veenendaal AK, Sundin C, Blocker AJ. 2009. Small-molecule type III secretion system inhibitors block assembly of the Shigella type III secreton. J Bacteriol 191:563–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Harmon DE, Davis AJ, Castillo C, Mecsas J. 2010. Identification and characterization of small-molecule inhibitors of Yop translocation in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:3241–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Martinez-Argudo I, Veenendaal AK, Liu X, Roehrich AD, Ronessen MC, Franzoni G, van Rietschoten KN, Morimoto YV, Saijo-Hamano Y, Avison MB, Studholme DJ, Namba K, Minamino T, Blocker AJ. 2013. Isolation of Salmonella mutants resistant to the inhibitory effect of Salicylidene acylhydrazides on flagella-mediated motility. PLoS One 8:e52179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Negrea A, Bjur E, Ygberg SE, Elofsson M, Wolf-Watz H, Rhen M. 2007. Salicylidene acylhydrazides that affect type III protein secretion in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:2867–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Duncan MC, Linington RG, Auerbuch V. 2012. Chemical inhibitors of the type three secretion system: disarming bacterial pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5433–41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Charro N, Mota LJ. 2015. Approaches targeting the type III secretion system to treat or prevent bacterial infections. Expert Opin Drug Discov 10:373–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wolf K, Betts HJ, Chellas-Gery B, Hower S, Linton CN, Fields KA. 2006. Treatment of Chlamydia trachomatis with a small molecule inhibitor of the Yersinia type III secretion system disrupts progression of the chlamydial developmental cycle. Mol Microbiol 61:1543–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Muschiol S, Bailey L, Gylfe A, Sundin C, Hultenby K, Bergstrom S, Elofsson M, Wolf-Watz H, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B. 2006. A small-molecule inhibitor of type III secretion inhibits different stages of the infectious cycle of Chlamydia trachomatis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14566–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Layton AN, Hudson DL, Thompson A, Hinton JC, Stevens JM, Galyov EE, Stevens MP. 2010. Salicylidene acylhydrazide-mediated inhibition of type III secretion system-1 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is associated with iron restriction and can be reversed by free iron. FEMS Microbiol Lett 302:114–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gauthier A, Robertson ML, Lowden M, Ibarra JA, Puente JL, Finlay BB. 2005. Transcriptional inhibitor of virulence factors in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:4101–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hudson DL, Layton AN, Field TR, Bowen AJ, Wolf-Watz H, Elofsson M, Stevens MP, Galyov EE. 2007. Inhibition of type III secretion in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by small-molecule inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:2631–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Anantharajah A, Faure E, Buyck JM, Sundin C, Lindmark T, Mecsas J, Yahr TL, Tulkens PM, Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Guery B, Van Bambeke F. 2016. Inhibition of the Injectisome and Flagellar Type III Secretion Systems by INP1855 Impairs Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenicity and Inflammasome Activation. J Infect Dis 214:1105–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bzdzion L, Krezel H, Wrzeszcz K, Grzegorek I, Nowinska K, Chodaczek G, Swietnicki W. 2017. Design of small molecule inhibitors of type III secretion system ATPase EscN from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Acta Biochim Pol 64:49–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grishin AV, Luyksaar SI, Kapotina LN, Kirsanov DD, Zayakin ES, Karyagina AS, Zigangirova NA. 2018. Identification of chlamydial T3SS inhibitors through virtual screening against T3SS ATPase. Chem Biol Drug Des 91:717–727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Galan JE, Collmer A. 1999. Type III secretion machines: bacterial devices for protein delivery into host cells. Science 284:1322–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dean P 2011. Functional domains and motifs of bacterial type III effector proteins and their roles in infection. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:1100–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Abrusci P, McDowell MA, Lea SM, Johnson S. 2014. Building a secreting nanomachine: a structural overview of the T3SS. Curr Opin Struct Biol 25:111–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bowlin NO, Williams JD, Knoten CA, Torhan MC, Tashjian TF, Li B, Aiello D, Mecsas J, Hauser AR, Peet NP, Bowlin TL, Moir DT. 2014. Mutations in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa needle protein gene pscF confer resistance to phenoxyacetamide inhibitors of the type III secretion system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:2211–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Slepenkin A, Enquist PA, Hagglund U, de la Maza LM, Elofsson M, Peterson EM. 2007. Reversal of the antichlamydial activity of putative type III secretion inhibitors by iron. Infect Immun 75:3478–89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang D, Zetterstrom CE, Gabrielsen M, Beckham KS, Tree JJ, Macdonald SE, Byron O, Mitchell TJ, Gally DL, Herzyk P, Mahajan A, Uvell H, Burchmore R, Smith BO, Elofsson M, Roe AJ. 2011. Identification of bacterial target proteins for the salicylidene acylhydrazide class of virulence-blocking compounds. J Biol Chem 286:29922–31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Engstrom P, Nguyen BD, Normark J, Nilsson I, Bastidas RJ, Gylfe A, Elofsson M, Fields KA, Valdivia RH, Wolf-Watz H, Bergstrom S. 2013. Mutations in hemG mediate resistance to salicylidene acylhydrazides, demonstrating a novel link between protoporphyrinogen oxidase (HemG) and Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity. J Bacteriol 195:4221–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zambelloni R, Connolly JPR, Huerta Uribe A, Burgess K, Marquez R, Roe AJ. 2017. Novel compounds targeting the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli type three secretion system reveal insights into mechanisms of secretion inhibition. Mol Microbiol 105:606–619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Azantharajah A, Buyck JM, Sundin C, Tulkens PM, Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Van Bambeke F. 2017. Salicylidene Acylhydrazides and Hydroxyquinolines Act as Inhibitors of Type Three Secretion Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Distinct Mechanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Morgan JM, Lam HN, Delgado J, Luu J, Mohammadi S, Isberg RR, Wang H, Auerbuch V. 2018. An Experimental Pipeline for Initial Characterization of Bacterial Type III Secretion System Inhibitor Mode of Action Using Enteropathogenic Yersinia. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Enquist PA, Gylfe A, Hagglund U, Lindstrom P, Norberg-Scherman H, Sundin C, Elofsson M. 2012. Derivatives of 8-hydroxyquinoline--antibacterial agents that target intra- and extracellular Gram-negative pathogens. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:3550–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aiello D, Williams JD, Majgier-Baranowska H, Patel I, Peet NP, Huang J, Lory S, Bowlin TL, Moir DT. 2010. Discovery and characterization of inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:1988–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Williams JD, Torhan MC, Neelagiri VR, Brown C, Bowlin NO, Di M, McCarthy CT, Aiello D, Peet NP, Bowlin TL, Moir DT. 2015. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel phenoxyacetamide inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system (T3SS). Bioorg Med Chem 23:1027–43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Berube BJ, Murphy KR, Torhan MC, Bowlin NO, Williams JD, Bowlin TL, Moir DT, Hauser AR. 2017. Impact of Type III Secretion Effectors and of Phenoxyacetamide Inhibitors of Type III Secretion on Abscess Formation in a Mouse Model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Duncan MC, Wong WR, Dupzyk AJ, Bray WM, Linington RG, Auerbuch V. 2014. An NF-kappaB-based high-throughput screen identifies piericidins as inhibitors of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis type III secretion system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:1118–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Morgan JM, Duncan MC, Johnson KS, Diepold A, Lam H, Dupzyk AJ, Martin LR, Wong WR, Armitage JP, Linington RG, Auerbuch V. 2017. Piericidin A1 Blocks Yersinia Ysc Type III Secretion System Needle Assembly. mSphere 2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tsou LK, Lara-Tejero M, RoseFigura J, Zhang ZJ, Wang YC, Yount JS, Lefebre M, Dossa PD, Kato J, Guan F, Lam W, Cheng YC, Galan JE, Hang HC. 2016. Antibacterial Flavonoids from Medicinal Plants Covalently Inactivate Type III Protein Secretion Substrates. J Am Chem Soc 138:2209–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.McShan AC, Anbanandam A, Patnaik S, De Guzman RN. 2016. Characterization of the Binding of Hydroxyindole, Indoleacetic acid, and Morpholinoaniline to the Salmonella Type III Secretion System Proteins SipD and SipB. ChemMedChem 11:963–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dey S, Anbanandam A, Mumford BE, De Guzman RN. 2017. Characterization of Small-Molecule Scaffolds That Bind to the Shigella Type III Secretion System Protein IpaD. ChemMedChem 12:1534–1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Guo Z, Li X, Li J, Yang X, Zhou Y, Lu C, Shen Y. 2016. Licoflavonol is an inhibitor of the type three secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477:998–1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tsou LK, Yount JS, Hang HC. 2017. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits bacterial virulence and invasion of host cells. Bioorg Med Chem 25:2883–2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nakasone N, Higa N, Toma C, Ogura Y, Suzuki T, Yamashiro T. 2017. Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the type III secretion system of Gram-negative enteropathogenic bacteria under model conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nakasone N, Ogura Y, Higa N, Toma C, Koizumi Y, Takaesu G, Suzuki T, Yamashiro T. 2018. Effects of Psidium guajava leaf extract on secretion systems of Gram-negative enteropathogenic bacteria. Microbiol Immunol doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang T, Deng X, Chu X. 2018. Natural compound sanguinarine chloride targets the type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Biochem Biophys Rep 14:149–154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Choi WS, Lee TH, Son SJ, Kim TG, Kwon BM, Son HU, Kim SU, Lee SH. 2017. Inhibitory effect of obovatol from Magnolia obovata on the Salmonella type III secretion system. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 70:1065–1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Puigvert M, Sole M, Lopez-Garcia B, Coll NS, Beattie KD, Davis RA, Elofsson M, Valls M. 2018. Type III secretion inhibitors for management of bacterial plant diseases. Mol Plant Pathol doi: 10.1111/mpp.12736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yang F, Korban SS, Pusey PL, Elofsson M, Sundin GW, Zhao Y. 2014. Small-molecule inhibitors suppress the expression of both type III secretion and amylovoran biosynthesis genes in Erwinia amylovora. Mol Plant Pathol 15:44–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fan S, Tian F, Li J, Hutchins W, Chen H, Yang F, Yuan X, Cui Z, Yang CH, He C. 2017. Identification of phenolic compounds that suppress the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae on rice via the type III secretion system. Mol Plant Pathol 18:555–568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Xiang X, Tao H, Jiang S, Zhang LH, Cui ZN. 2018. Synthesis and bioactivity of thiazolidin-2-cyanamide derivatives against type III secretion system of Xanthomonas oryzae on rice. Pestic Biochem Physiol 149:89–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Francois B, Luyt CE, Dugard A, Wolff M, Diehl JL, Jaber S, Forel JM, Garot D, Kipnis E, Mebazaa A, Misset B, Andremont A, Ploy MC, Jacobs A, Yarranton G, Pearce T, Fagon JY, Chastre J. 2012. Safety and pharmacokinetics of an anti-PcrV PEGylated monoclonal antibody fragment in mechanically ventilated patients colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Crit Care Med 40:2320–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Milla CE, Chmiel JF, Accurso FJ, VanDevanter DR, Konstan MW, Yarranton G, Geller DE, Group KBS. 2014. Anti-PcrV antibody in cystic fibrosis: a novel approach targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway infection. Pediatr Pulmonol 49:650–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Jain R, Beckett VV, Konstan MW, Accurso FJ, Burns JL, Mayer-Hamblett N, Milla C, VanDevanter DR, Chmiel JF, Group KAS. 2018. KB001-A, a novel anti-inflammatory, found to be safe and well-tolerated in cystic fibrosis patients infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Cyst Fibros 17:484–491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.DiGiandomenico A, Keller AE, Gao C, Rainey GJ, Warrener P, Camara MM, Bonnell J, Fleming R, Bezabeh B, Dimasi N, Sellman BR, Hilliard J, Guenther CM, Datta V, Zhao W, Gao C, Yu XQ, Suzich JA, Stover CK. 2014. A multifunctional bispecific antibody protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Transl Med 6:262ra155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tabor DE, Oganesyan V, Keller AE, Yu L, McLaughlin RE, Song E, Warrener P, Rosenthal K, Esser M, Qi Y, Ruzin A, Stover CK, DiGiandomenico A. 2018. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV and Psl, the molecular targets of bispecific antibody MEDI3902, are conserved among diverse global clinical isolates. J Infect Dis doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Harmsen MM, De Haard HJ. 2007. Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:13–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Barta ML, Shearer JP, Arizmendi O, Tremblay JM, Mehzabeen N, Zheng Q, Battaile KP, Lovell S, Tzipori S, Picking WD, Shoemaker CB, Picking WL. 2017. Single-domain antibodies pinpoint potential targets within Shigella invasion plasmid antigen D of the needle tip complex for inhibition of type III secretion. J Biol Chem 292:16677–16687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Verma SK, Tuteja U. 2016. Plague Vaccine Development: Current Research and Future Trends. Front Immunol 7:602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Price JL, Manetz TS, Shearer JD, House RV. 2013. Preclinical safety assessment of a recombinant plague vaccine (rF1V). Int J Toxicol 32:327–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fellows P, Price J, Martin S, Metcalfe K, Krile R, Barnewall R, Hart MK, Lockman H. 2015. Characterization of a Cynomolgus Macaque Model of Pneumonic Plague for Evaluation of Vaccine Efficacy. Clin Vaccine Immunol 22:1070–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Smith DR. 2014. Vaccination of Cattle against Escherichia coli O157:H7. Microbiol Spectr 2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Desin TS, Townsend HG, Potter AA. 2015. Antibodies Directed against Shiga-Toxin Producing Escherichia coli Serotype O103 Type III Secreted Proteins Block Adherence of Heterologous STEC Serotypes to HEp-2 Cells. PLoS One 10:e0139803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kurtz JR, Petersen HE, Frederick DR, Morici LA, McLachlan JB. 2014. Vaccination with a single CD4 T cell peptide epitope from a Salmonella type III-secreted effector protein provides protection against lethal infection. Infect Immun 82:2424–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jneid B, Moreau K, Plaisance M, Rouaix A, Dano J, Simon S. 2016. Role of T3SS-1 SipD Protein in Protecting Mice against Non-typhoidal Salmonella Typhimurium. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10:e0005207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lee SJ, Benoun J, Sheridan BS, Fogassy Z, Pham O, Pham QM, Puddington L, McSorley SJ. 2017. Dual Immunization with SseB/Flagellin Provides Enhanced Protection against Salmonella Infection Mediated by Circulating Memory Cells. J Immunol 199:1353–1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Martinez-Becerra FJ, Kumar P, Vishwakarma V, Kim JH, Arizmendi O, Middaugh CR, Picking WD, Picking WL. 2018. Characterization and Protective Efficacy of Type III Secretion Proteins as a Broadly Protective Subunit Vaccine against Salmonella enterica Serotypes. Infect Immun 86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Hayward RD, Hume PJ, McGhie EJ, Koronakis V. 2002. A Salmonella SipB-derived polypeptide blocks the ‘trigger’ mechanism of bacterial entry into eukaryotic cells. Mol Microbiol 45:1715–27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Larzabal M, Mercado EC, Vilte DA, Salazar-Gonzalez H, Cataldi A, Navarro-Garcia F. 2010. Designed coiled-coil peptides inhibit the type three secretion system of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. PLoS One 5:e9046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Larzabal M, Zotta E, Ibarra C, Rabinovitz BC, Vilte DA, Mercado EC, Cataldi A. 2013. Effect of coiled-coil peptides on the function of the type III secretion system-dependent activity of enterohemorragic Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Citrobacter rodentium. Int J Med Microbiol 303:9–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lam H, Schwochert J, Lao Y, Lau T, Lloyd C, Luu J, Kooner O, Morgan J, Lokey S, Auerbuch V. 2017. Synthetic Cyclic Peptomers as Type III Secretion System Inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Slepenkin A, Chu H, Elofsson M, Keyser P, Peterson EM. 2011. Protection of mice from a Chlamydia trachomatis vaginal infection using a Salicylidene acylhydrazide, a potential microbicide. J Infect Dis 204:1313–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Pedersen C, Slepenkin A, Andersson SB, Fagerberg JH, Bergstrom CA, Peterson EM. 2014. Formulation of the microbicide INP0341 for in vivo protection against a vaginal challenge by Chlamydia trachomatis. PLoS One 9:e110918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Jessen DL, Bradley DS, Nilles ML. 2014. A type III secretion system inhibitor targets YopD while revealing differential regulation of secretion in calcium-blind mutants of Yersinia pestis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:839–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Felise HB, Nguyen HV, Pfuetzner RA, Barry KC, Jackson SR, Blanc MP, Bronstein PA, Kline T, Miller SI. 2008. An inhibitor of gram-negative bacterial virulence protein secretion. Cell Host Microbe 4:325–36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Swietnicki W, Carmany D, Retford M, Guelta M, Dorsey R, Bozue J, Lee MS, Olson MA. 2011. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of Yersinia pestis Type III secretion system YscN ATPase. PLoS One 6:e19716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Zhang Y, Liu Y, Qiu J, Luo ZQ, Deng X. 2018. The Herbal Compound Thymol Protects Mice From Lethal Infection by Salmonella Typhimurium. Front Microbiol 9:1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Yang L, Ding W, Xu Y, Wu D, Li S, Chen J, Guo B. 2016. New Insights into the Antibacterial Activity of Hydroxycoumarins against Ralstonia solanacearum. Molecules 21:468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yang L, Li S, Qin X, Jiang G, Chen J, Li B, Yao X, Liang P, Zhang Y, Ding W. 2017. Exposure to Umbelliferone Reduces Ralstonia solanacearum Biofilm Formation, Transcription of Type III Secretion System Regulators and Effectors and Virulence on Tobacco. Front Microbiol 8:1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sawa T, Ito E, Nguyen VH, Haight M. 2014. Anti-PcrV antibody strategies against virulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Hum Vaccin Immunother 10:2843–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]