Abstract
Objective:
Test Web-based Implementation for the Science of Enhancing Resilience (WISER) intervention efficacy in reducing Healthcare Worker (HCW) burnout.
Design:
RCT using two cohorts of HCWs of four NICUs each, to improve HCW well-being (primary outcome: burnout). Cohort 1 received WISER while Cohort 2 acted as a waitlist control.
Results:
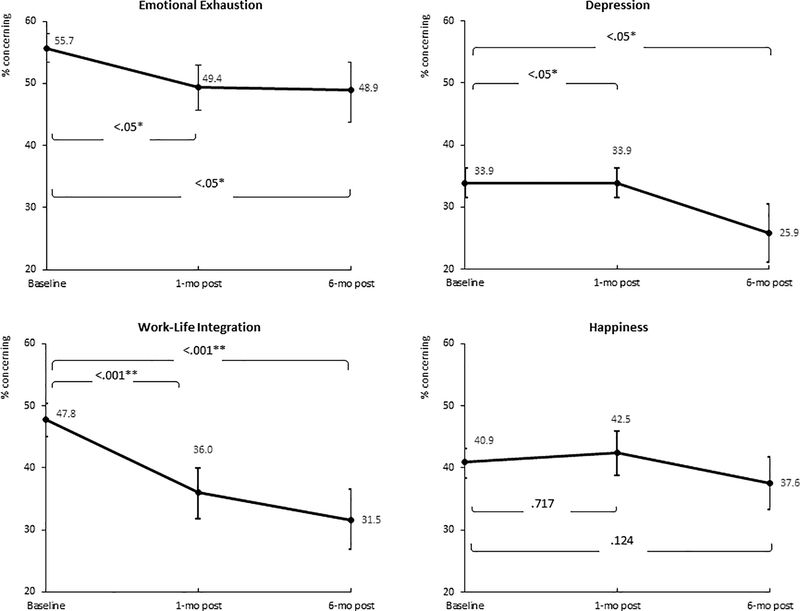
Cohorts were similar, mostly female (83%) and nurses (62%). In Cohorts 1 and 2 respectively, 182 and 299 initiated WISER, 100 and 176 completed 1-month follow-up, and 78 and 146 completed 6-month follow-up. Relative to control, WISER decreased burnout (−5.27 (95%CI: −10.44, −0.10), p=0.046). Combined adjusted cohort results at 1-month showed that the percentage of HCWs reporting concerning outcomes was significantly decreased for burnout (−6.3% (95%CI: −11.6%, −1.0%); p=0.008), and secondary outcomes depression (−5.2% (95%CI: −10.8, −0.4); p=0.022) and work-life integration (−11.8% (95%CI: −17.9, −6.1); p<0.001). Improvements endured at 6 months.
Conclusion:
WISER appears to durably improve HCW well-being.
Clinical Trials Number:
NCT02603133; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02603133
INTRODUCTION
Burnout is characterized as a state of depletion, detachment, and cynicism resulting from prolonged high levels of stress.1 Health care workers (HCWs) in general, especially critical care workers, are at risk for burnout,2,3 fueled by changes in technology and guidelines, endeavors for high-quality care, and emotional challenges of dealing with critically ill patients and their families.4–6 Emotional exhaustion alone, one of three domains of burnout, affects 25–50% of neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) HCWs,1,5 with up to half of nurses and physicians across specialties meeting criteria for severe burnout.7–9 Burnout among HCWs has been linked to adverse patient events, including increased rates of infections,10,11 and self-reported errors.10,12 Furthermore, burnout may lead clinicians to drop out of the work force, increasing costly turnover,13,14 and further exacerbate staffing shortages.15
Feasible interventions to alleviate burnout are few, and none have been tested and reported in the NICU setting.9 Since 2011, we have developed and refined an interactive, low-burden program (Web-based Implementation for the Science of Enhancing Resilience (WISER)) to target enduring reductions in burnout. This stepwise program uses updated versions of evidence-based interventions drawn from positive psychology that have been effective in improving well-being and reducing depression symptoms, delivered via mobile platform.16–19 WISER components are sequenced purposefully to maximize participant engagement and learning. Components gradually encourage participants to first notice and savior positive emotions and then to act to elicit them. Reminders promote mastery through practice.
Use of and access to well-being interventions must be easy and engaging in order to be utilized by busy HCWs. Our objective was to test the efficacy of WISER in improving NICU HCW burnout (primary outcome), depression, work-life integration, and happiness (secondary outcomes):
Hypothesis 1: Efficacy of WISER: the intervention will improve HCW burnout (primary outcome is emotional exhaustion), depression, work-life integration, and happiness (secondary outcomes) in cohort 1 compared with waitlist control in cohort 2 by the 1-month post intervention primary endpoint.
Hypothesis 2: WISER will be effective at 1-month post intervention.
Hypothesis 3: Effect of WISER will endure at 6-months post intervention.
Hypothesis 4: The condensed cohort 2 intervention will be not be less effective than the full intervention for cohort 1.
METHODS
Design
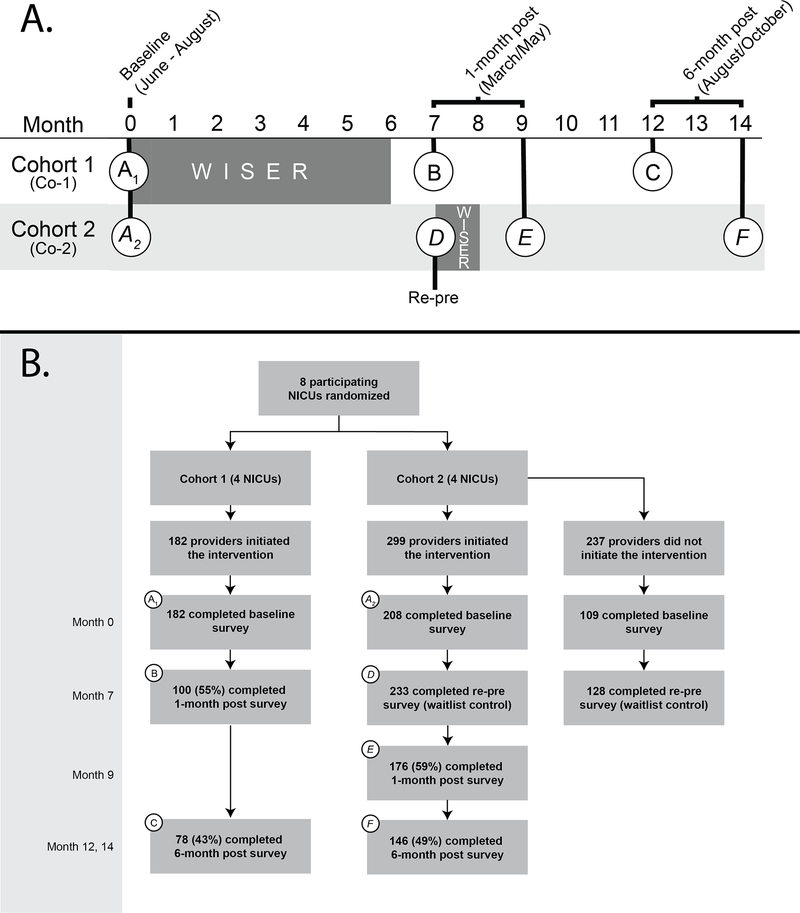
We conducted a pragmatic, cluster randomized controlled trial (RCT) in eight academic level 4 NICUs randomized to two cohorts of four NICUs each. Each cohort included a mix of NICUs that were either within a free-standing children’s hospital or part of an adult hospital. We selected a clustered design to mitigate the risk of contamination. Cohort 1 received the intervention immediately, while cohort 2 acted as a waitlist control. Enrollment began in June 2016. Cohort 1 received the intervention from August 2016 to January 2017, then cohort 2 received the intervention from March to April 2017. Participants were informed of their start date and follow-up dates shortly after enrollment. We assessed cohorts at four time points (Figure 1a). Each cohort received the intervention; therefore, blinding was not feasible. In addition, given the pragmatic nature of this trial, whereby the second cohort received an abbreviated version of the intervention, blinding was also not feasible as part of the evaluation.
Figure 1.
a) Schematic of WISER study design. Active WISER period shaded gray. Seven assessment points presented in circles; two baseline assessments (A1 and A2) two 1-month followups (B and E), two 6-month followups (C and F), and one Re-pre (D) that was second baseline assessment for Cohort 2 for comparison with 1 month post of Cohort 1. 1b) CONSORT Diagram
Efficacy of WISER intervention: cohort 1 change at 1-month (B-A1) vs. cohort 2 control (D-A2); Within-cohort change from baseline to 1-month: B-A for cohort 1; E-D for cohort 2; Within-cohort change from baseleine to 6-months: C-A for cohort 1; F-D for cohort 2; Non-inferiority of cohort 2 change versus cohort 1 at 1-month: (B-A) vs. (E-D); Non-inferiority of cohort 2 change versus cohort 1 at 6-month: (C-A) vs. (F-D)
Participants
Participants were HCWs indicating the NICU as their primary location of work. To be eligible, participants had to be employed for at least four weeks prior to the trial and dedicate at least 0.4 full time equivalent to the NICU. HCWs who did not meet eligibility criteria could choose to participate, but their data were not included in the analyses. NICUs were regionally diverse, located in Massachusetts, North Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, New Mexico, and California.
Intervention
WISER is comprised of six guided well-being modules based on adult learning principles, combining educational material with practice-based learning.20 Individual modules have been favorably evaluated as brief, feasible and practical16–19. Each module was sent at 7pm local time, introduced with an 8–10 minute evidence-based educational video, with simple and engaging reflective activities lasting from 2 to 7 minutes. Modules were delivered electronically with a thematic introduction and continued in the following order: (1) gratitude, (2) three good things, (3) awe, (4) random acts of kindness, (5) identifying and using signature strengths, and (6) relationship resilience (for details see eAppendix, Section A). Cohort 1 participants were invited to view modules by mobile-or email, each introduced monthly and lasting 10 days. Cohort 2 received the intervention in condensed form over the course of 28 consecutive days. Evaluation was performed via electronic survey administration.
Measures
Primary Outcome
The primary outcome of burnout was evaluated using a widely used16,18,21–23 5-item derivative of the emotional exhaustion scale of the Maslach Burnout Inventory,24 shown to have excellent psychometric properties16–18,21,25, external validity22,23,25, and is responsive to interventions.16–18 According to a psychometric meta-analysis, of the three sub-scales of burnout (emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and personal accomplishment), emotional exhaustion consistently produces the largest and most consistent Cronbach alpha estimates.26
To reduce participant respondent burden, we used a 5-item derivative of the original 9-item scale. This 5-item version is reliable (Cronbach α=.92),16–18,21,22,25 predicts prevalence of disruptive behaviors as well as symptoms of depression27 and is associated with HCW work-life balance.27 HCW emotional exhaustion assessments with this 5-item version are also associated with improvement readiness (the capacity of HCWs to initiate and sustain quality improvement initiatives)25 and the use of Patient Safety Leadership WalkRounds.21 Importantly, HCW assessments using this scale are consistently responsive to interventions.16–18,21 For this study we will use the terms burnout to describe the general phenomenon and emotional exhaustion in conjunction with its measurement.
For ease of interpretability, we defined a “percent concerning” measure to highlight the proportion of respondents in each cohort reporting undesirable results. We used the established threshold of 50 or higher,16,21,22,25,27 which reflects “not disagreeing,” on average, to emotional exhaustion items (see eAppendix Section B for detail).
Secondary Outcomes
Depressive symptoms were assessed via the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale-10-item version (CES-D10), a psychometrically sound tool for screening respondents for clinical depression.28 Depression and emotional exhaustion share some features (e.g., exhaustion and impaired concentration),27,29 and emotional exhaustion is a risk factor for depression, but emotional exhaustion is generally viewed as an occupational phenomenon, and depression is a psychological condition. Work-life integration was evaluated using the work-life climate scale, which has been used with HCWs and exhibits good psychometrics.22,23 Subjective Happiness was evaluated with the subjective happiness scale (SHS), a validated, psychometrically sound, and internationally used scale of global happiness.30,31 For further measurement details, see eAppendix, Section B.
The survey also captured respondent characteristics including gender, race/ethnicity, shift type, job position, and years in specialty. Job positions included attending physician, fellow (trainee) physician, neonatal nurse practitioner, registered nurse, respiratory care practitioner, and other.
Randomization
NICUs were randomly assigned to immediate intervention or waitlist control through a random number generator using even and odd numbers for assignment.
Statistical Analyses
For comparability we rescaled outcome measures to 100-point scales. To test our hypotheses (Figure 1a), we used a generalized linear mixed effects modeling framework that included fixed effects for time and cohort, and random effects for worksite and participant.32 To facilitate interpretation of results, we combined the two cohorts and used percent concerning thresholds. This technique is commonly used in safety culture and well-being research when looking across a set of metrics (some positively and some negatively valenced) such that a “low percent concerning,” or a reduction in percent concerning was easier to interpret.1,16–18,21,25 For context, we display the combined group study results for emotional exhaustion within a cross-sectional sample of 16,797 respondents (of 23,853 invited, response rate 70.4%), from 818 work units in 31 hospitals in Michigan. We also performed a sensitivity analysis, in which we adjusted for gender, race/ethnicity, shift type, job position, and years in specialty.
All hypothesis tests were conducted in SAS PROC GLIMMIX and included a Kenward-Roger degree of freedom correction.33 A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed in SAS version 9.4. EAppendix, Sections C–D provides additional details.
RESULTS
Enrollment and participation in the trial are shown in Figure 1b (CONSORT Diagram). In cohort 1, 182 respondents initiated the intervention by clicking a WISER text or email message. Of these, 100 (55%) and 78 (43%) were still participating at 1- and 6-month follow-up, respectively. Based on qualitative comments from participants that the 6-month intervention period was too lengthy, we shortened the intervention for cohort 2, condensing it into 28 text messages over 28 consecutive days. In cohort 2, initiation of the first module improved, with 299 respondents initiating WISER, of which 233 acted as waitlist control, 176 (59%) completed 1-month and 146 (49%) completed 6-month assessment post-intervention. Table 1 displays the characteristics of the study population by cohort and time point. Cohorts 1 and 2 had similar demographics at baseline. No adverse events were reported.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population
| Cohort 1 |
Cohort 2 |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1-mo post | 6-mo post | Baseline | Waitlist* | 1-mo post | 6-mo post | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| N | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Total | 182 | 100.0 | 100 | 100.0 | 78 | 100.0 | 208 | 100.0 | 233 | 100.0 | 176 | 100.0 | 146 | 100.0 |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||
| Male | 20 | 11.0 | 13 | 13.0 | 6 | 7.7 | 8 | 3.8 | 6 | 2.6 | 6 | 3.4 | † | |
| Female | 162 | 89.0 | 87 | 87.0 | 72 | 92.3 | 200 | 96.2 | 172 | 73.8 | 149 | 84.7 | 129 | 88.4 |
| Race/ethnicity ** | ||||||||||||||
| White | 126 | 69.2 | 74 | 74.0 | 57 | 73.1 | 182 | 87.5 | 199 | 85.4 | 154 | 87.5 | 132 | 90.4 |
| Hispanic | 14 | 7.7 | 6 | 6.0 | † | 7 | 3.4 | 11 | 4.7 | 7 | 4.0 | † | ||
| African American | 6 | 3.3 | † | † | 9 | 4.3 | 11 | 4.7 | 7 | 4.0 | † | |||
| Asian | 34 | 18.7 | 14 | 14.0 | 14 | 17.9 | 9 | 4.3 | 8 | 3.4 | 6 | 3.4 | † | |
| Typical Shift | ||||||||||||||
| Days | 111 | 61.0 | 57 | 57.0 | 47 | 60.3 | 114 | 54.8 | 95 | 40.8 | 91 | 51.7 | 75 | 51.4 |
| Evenings/Nights | 31 | 17.0 | 16 | 16.0 | 13 | 16.7 | 54 | 26.0 | 49 | 21.0 | 33 | 18.8 | 33 | 22.6 |
| Variable | 40 | 22.0 | 27 | 27.0 | 18 | 23.1 | 40 | 19.2 | 34 | 14.6 | 31 | 17.6 | 25 | 17.1 |
| Healthcare Worker Role | ||||||||||||||
| Physician 1 | 48 | 26.4 | 31 | 31.0 | 22 | 28.2 | 31 | 14.9 | 33 | 14.2 | 28 | 15.9 | 20 | 13.7 |
| Nurse 2 | 97 | 53.3 | 49 | 49.0 | 42 | 53.8 | 140 | 67.3 | 162 | 69.5 | 113 | 64.2 | 102 | 69.9 |
| APP 3 | 9 | 4.9 | † | † | 12 | 5.8 | 12 | 5.2 | 9 | 5.1 | 6 | 4.1 | ||
| Others 4 | 28 | 15.4 | 16 | 16.0 | 12 | 15.4 | 25 | 12.0 | 25 | 10.7 | 26 | 14.8 | 17 | 11.6 |
| Work Experience in Current Position | ||||||||||||||
| < 1 year | 25 | 13.7 | 14 | 14.0 | 8 | 10.3 | 28 | 13.5 | 12 | 5.2 | 19 | 10.8 | 11 | 7.5 |
| 1–10 years | 91 | 50.0 | 46 | 46.0 | 35 | 44.9 | 114 | 54.8 | 106 | 45.5 | 83 | 47.2 | 80 | 54.8 |
| ≥ 11 years | 66 | 36.3 | 40 | 40.0 | 35 | 44.9 | 66 | 31.7 | 60 | 25.8 | 53 | 30.1 | 42 | 28.8 |
| Outcome (% concerning) 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Emotional Exhaustion | 60.2 | 46.5 | 50.0 | 59.0 | 55.2 | 47.2 | 49.7 | |||||||
| Depression | 39.4 | 35.5 | 20.6 | 34.9 | 34.2 | 23.4 | 25.4 | |||||||
| Work-Life Integration | 40.7 | 40.0 | 35.9 | 37.0 | 41.6 | 42.1 | 40.4 | |||||||
| Happiness | 55.3 | 40.0 | 33.3 | 52.2 | 47.6 | 32.4 | 28.1 | |||||||
Physician includes Attending, Staff, Fellow, and resident Physician.
Nurse includes Registered Nurse, Nurse Manager, and Charge Nurse.
Advance Practice Provider (APP) includes Physician Assistant and Nurse Practitioner.
Other roles include Therapist (e.g., Respiratory, Physical, Occupational, and Speech Therapist), Administrative Support (e.g., Clerk, Secretary, and Receptionist), Clinical Support (e.g., CMA, Nurses Aid), Pharmacist, Clinical Social Worker, Manager, Dietician/Nutritionist, Student, and others.
Percent concerning rates were calculated using previously published thresholds.
Updated baseline for waitlist control.
Across cohorts 5 individuals reported other race/ethnicity.
Categories with ≤ 5 individuals are not reported in order to protect subject privacy. Data may not add up to 100% due to missing data.
Implementation of WISER demonstrated both efficacy and enduring effectiveness for burnout (emotional exhaustion) supporting the 4 hypotheses (Table 2).
Table 2.
Effect of WISER intervention (100-point scale) estimated from generalized linear mixed effects model
| H1: Efficacy of WISER 1 |
Effect of WISER within cohort |
H4: Full and condensed intervention similarly effective 4 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | H2: 1-mo 2 |
H3: 6-mo 3 |
|||||||
| Estimate (95%CI) | P-value | Estimate (95%CI) | P-value | Estimate (95%CI) | P-value | Time | Estimate (95%CI) | P-value | |
|
| |||||||||
| Emotional Exhaustion | |||||||||
| −5.27 (−10.44 −0.10) | 0.046 | C1 | −5.64 (−9.59 −1.68) | 0.005 | −4.85 (−9.25 −0.45) | 0.031 | 1-mo | −1.37 (−6.78 4.04) | 0.619 |
| C2 | −4.27 (−7.96 −0.57) | 0.024 | −1.92 (−5.91 2.07) | 0.346 | 6-mo | −2.94 (−8.88 3.00) | 0.332 | ||
| −5.21 (−7.92 −2.51) | <.001 | C1+C2 | −3.23 (−6.22 −0.25) | 0.034 | 1.98 (−1.20 5.15) | 0.221 | NA | NA | NA |
| Depression | |||||||||
| −1.20 (−5.30 2.89) | 0.564 | C1 | −2.14 (−5.28 1.01) | 0.183 | −6.06 (−9.52 −2.60) | <.001 | 1-mo | 2.72 (−1.55 7.00) | 0.212 |
| C2 | −4.86 (−7.76 −1.96) | 0.001 | −2.50 (−5.64 0.64) | 0.118 | 6-mo | −3.56 (−8.23 1.11) | 0.135 | ||
| −3.72 (−5.75 −1.68) | <.001 | C1+C2 | −3.90 (−6.14 −1.67) | <.001 | −0.19 (−2.55 2.17) | 0.875 | NA | NA | NA |
| Work-Life Integration | |||||||||
| 2.99 (−0.19 6.17) | 0.065 | C1 | 5.18 (2.75 7.60) | <.001 | 7.33 (4.64 10.01) | <.001 | 1-mo | 1.09 (−2.24 4.43) | 0.520 |
| C2 | 4.08 (1.80 6.37) | <.001 | 2.92 (0.47 5.37) | 0.019 | 6-mo | 4.40 (0.77 8.04) | 0.018 | ||
| 4.57 (2.97 6.17) | <.001 | C1+C2 | 5.07 (3.32 6.82) | <.001 | 0.50 (−1.36 2.37) | 0.596 | NA | NA | NA |
| Happiness | |||||||||
| 1.37 (−1.60 4.34) | 0.366 | C1 | 0.60 (−1.68 2.87) | 0.607 | −0.03 (−2.55 2.48) | 0.979 | 1-mo | 1.14 (−1.98 4.25) | 0.474 |
| C2 | −0.54 (−2.67 1.59) | 0.619 | 0.81 (−1.48 3.09) | 0.489 | 6-mo | −0.84 (−4.24 2.56) | 0.628 | ||
| −0.20 (−1.74 1.34) | 0.794 | C1+C2 | 0.11 (−1.58 1.80) | 0.896 | 0.32 (−1.49 2.13) | 0.731 | NA | NA | NA |
Hypothesis 1: Efficacy of WISER: the intervention will improve NICU healthcare worker burnout (emotional exhaustion; primary outcome), depression, happiness, and work-life integration (secondary outcomes) in cohort 1 compared with waitlist control in cohort 2. (C1: 1-month post - baseline) - (C2: waitlist - baseline).
Hypothesis 2: WISER will be effective at 1 month. C1: 1-month post - baseline; C2: 1-month post - waitlist.
Hypothesis 3: Effect of WISER will endure at 6 months. C1: 6-month post - baseline; C2: 6-month post - waitlist.
Hypothesis 4: The effect of the condensed cohort 2 intervention will be not be less effective than the full intervention in cohort 1. At 1-mo: (C1: 1-month post - baseline) - (C2: 1-month post - waitlist); At 6-mo: (C1: 6-month post - baseline) - (C2: 6-month post - waitlist).
The intervention will improve NICU HCW burnout (primary outcome), depression, work-life integration, and happiness (secondary outcomes) in cohort 1 compared with waitlist control in cohort 2 (Hypothesis 1):
This represents the randomized controlled trial component of this study. On a 100-point scale, compared with cohort 2 (waitlist control), the WISER intervention in cohort 1 improved emotional exhaustion (−5.3, 95% CI −10.4 to −0.1, p=0.046) and resulted in improved work-life integration (+3.0, 95% CI −0.2 to 6.2, p=0.065) that was not statistically significant. Depression and happiness were not significantly affected.
The following hypotheses look at the cohorts individually in a non-randomized fashion: WISER will be effective at 1 month (Hypothesis 2):
On a 100-point scale, at 1 month in cohort 1, WISER was associated with reduced emotional exhaustion (−5.6, 95% CI −9.6 to −1.7, p=0.005) and improved work-life integration (+5.2, 95% CI 2.8 to 7.6, p<0.001). At 1 month in cohort 2, WISER was associated with reduced emotional exhaustion (−4.3, 95% CI −8.0 to −0.6, p=0.024), depression (−4.9, 95% CI −7.8 to −2.0, p=0.001), and improved work-life integration (+4.1, 95% CI 1.8 to 6.4, p<0.001). Happiness did not change significantly in either cohort.
The effect of WISER will endure at 6 months (Hypothesis 3):
Outcomes at 6 months showed a similar pattern to 1-month results. In cohort 1, emotional exhaustion (−4.8, 95% CI −9.2 to −0.4, p=0.031), depression (−6.1, 95% CI −9.5 to −2.6, p0<0.001), and work-life integration (+7.3, 95% CI 4.6 to 10.0, p<0.001) all improved. In cohort 2, WISER was associated with improved work-life integration (+2.9, 95% CI 0.5 to 5.4, p=0.019). Happiness did not change significantly in either cohort.
The condensed cohort 2 intervention will not be less effective than the intervention for cohort 1 (Hypothesis 4):
No significant differences in improvement were noted between full and condensed cohorts in any of the outcomes.
Combined cohort analyses
In combined cohorts at 1-month and 6-months on the 100-point scale, WISER was associated with improved emotional exhaustion, depression, and improved work-life integration. Happiness did not change significantly (Table 2). Percent concerning analyses for the combined cohorts similarly showed significant improvement for all metrics except happiness at 1-month and 6-month post intervention (Table 1, Figure 2). Similar results were seen for each cohort on the 100-point scales (eAppendix Figure A).
Figure 2.
Effect of WISER on the percent concerning scale
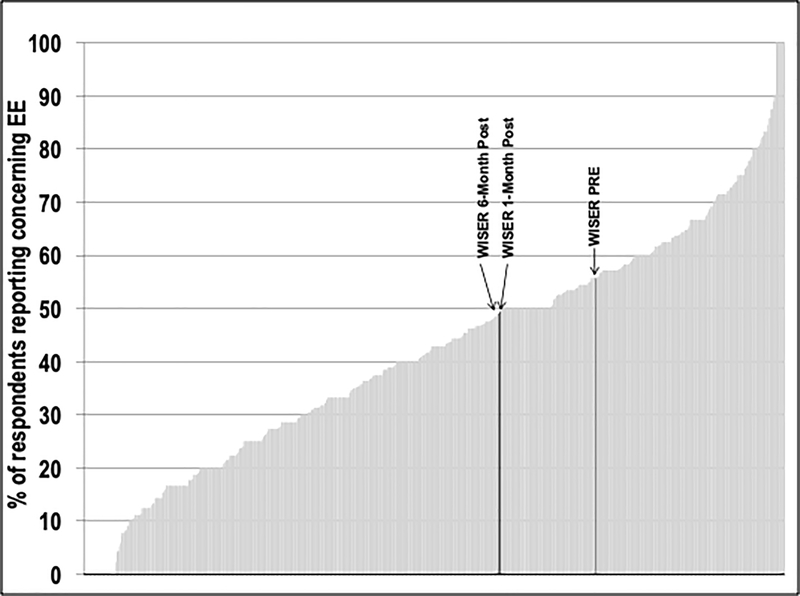
Figure 3 shows the effect of WISER contextualized to a sample of work units in 31 Michigan hospitals. Emotional exhaustion across work units measured varied from 0% to 100% concerning. WISER improved the relative position of our sample of NICUs from 55.7% concerning to 49.4% (1-month post) and 48.9% (6-month post) concerning, equivalent to an improvement from the 73rd percentile to the 59th percentile (lower is better).
Figure 3.
Percent Concerning Emotional Exhaustion in WISER and Acroos 818 Work Units in 31 Hospitals in Michigan
In sensitivity analyses, demographic factors (i.e., gender, race/ethnicity, shift type, job position, years in specialty differences) did not differ significantly for initiators compared to non-initiators in all cases, except that nurses in cohort 2 were more likely to initiate WISER compared to other HCWs (eAppendix Table eTA). Additional adjustment for gender, race/ethnicity, shift type, job position, and years in specialty did not change the results (eAppendix Tables eTB/eTC).
DISCUSSION
In this pragmatic trial, the WISER intervention demonstrated efficacy in reducing burnout (emotional exhaustion) among participating NICU HCWs, compared to a waitlist control at the 1-month primary endpoint. This result was supported by findings in the observational portions of the trial examining the individual cohorts. Six months after completion of the intervention, participants continued to exhibit lower emotional exhaustion. In addition, participation in WISER was associated with improvements in work-life integration and depression both at 1-month and 6-months. Our findings suggest that personal well-being interventions based on positive psychology research may help stem and reverse the rising tide in HCW burnout. This may be especially salient during the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, which is overwhelming the well-being landscape of HCWs, and will require innovative interventions that can be delivered at scale and on demand to HCWs that are suffering.34 Effect sizes for improvement suggest that our results are clinically meaningful, comparing favorably with lengthier and more resource-dependent interventions intended to improve well-being and mental health.16,35 Statistical power was strongest in the combined cohort analyses, wherein well-being improvements were significant and durable for emotional exhaustion, depression and work-life integration.
In this pragmatic trial, we condensed the WISER program in the second cohort based on feedback from participants in cohort 1. The result of this change in intervention delivery is that only the comparison of cohort 1 with the waitlist control, i.e. improved emotional exhaustion, provides causal inference, whereas other comparisons should be viewed as observational. The shortened intervention facilitated completion of the intervention by more participants. However, although statistical testing revealed that both interventions the one month to the six-month intervention were equally effective, within-cohort analysis showed some attenuation of the effects six months after WISER in cohort 2. Although the means for emotional exhaustion, depression and work-life integration improved, only work-life integration met criteria for statistical significance. Potential reasons for the attenuation could relate to the shorter duration of the intervention (28 days vs. 6 months), selective attrition by those less burned out, insufficient power, or external confounding. Additional study is needed to determine the optimal design of WISER, including dose, number and sequencing of modules. Ideally, larger sample sizes would also allow for subgroup analyses by subtypes of respondents, years of experience, etc.
Despite the well-documented descriptions of burnout in healthcare, few interventions have been tested in randomized trials. The WISER intervention packages tools that promote noticing and savoring positive emotions and are feasible and scalable, in contrast to other available interventions, such as those focusing on meditation.36 People who suffer from burnout experience decreased ability to notice and savor positive emotions in their lives.29 Rigorous psychological research has consistently shown that experiencing positive emotion is central to building consequential personal resources like well-being,36 as well as helping to find meaning after adversity,37 and accelerating recovery after emotional upheavals.38 Experiencing positive emotions has both psychological and physiological benefit, undoing cardiovascular sequelae of emotional upheavals.39
During the waitlist period, work-life integration improved in the control group. Pilot testing showed similar trends towards improvement in work-life integration when people completed the scale multiple times. It is possible that increasing personal awareness of, e.g., how often one gets less than five hours of sleep, skips meals, and gets home late is itself a subtle intervention.
WISER did not significantly change reported happiness among participants. This finding contrasts a prior cohort study16 and highlights the need for further research to identify a robust set of well-being metrics for HCWs.
This study should be viewed in light of its design. Well-being interventions, in particular, have much higher attrition and non-initiation than other kinds of RCTs (e.g., drug trials40). We similarly experienced this complication which introduced selection bias. We attempted to maximize the pool of potential participants by visiting each NICU to introduce and discuss the study in seminars and on dayshift and nightshift walk rounds. Although almost half of all potentially eligible HCWs expressed interest in WISER, the number who initiated the intervention was considerably smaller; in this study 481 HCWs (out of 1087, 44.3%) initiated WISER. This challenge of low initiation rates among busy HCWs was exemplified in a recent RCT of professional coaching35 for physicians that showed similar efficacy to our study, although only 88 of 764 eligible physicians chose to participate. The present study compares favorably to this and other interventions, including dieting, smoking cessation, and other web-based well-being interventions,41,42 which tend to have high rates of non-initiation (~80%) even when financial incentives are provided.43 Burnout itself may contribute to a lack of initiation energy and may explain the lack of effectiveness found for workplace well-being programs.44 Despite these limitations, our sensitivity analyses demonstrate that the initiators were not measurably different from those who initially expressed interest in the interventions but did not initiate.
Both study cohorts experienced significant attrition, which may also introduce selection bias. Such attrition is well-described among other behavioral and well-being interventions, which commonly report high discontinuation (33–50%),45 and significant loss to follow-up (40–48%).40,43,45–48 It is unknown if participants who were lost to follow-up experienced similar improvements to those who completed the study, suggesting that our results should be interpreted with caution and need to be reproduced in other samples.
Although our study sites were geographically diverse, the participants were mostly white females, reflecting the workforce in many large academic center NICUs. It is uncertain whether our findings are generalizable to other NICUs with more diverse workforces. Given the systemic racism experienced by colleagues and patients in the NICU, future larger samples would ideally allow researchers to tailor WISER modules to specific groups based on their needs, vulnerabilities, and preferences.
CONCLUSION
Our study found that WISER showed promise in reducing the emotional exhaustion component of burnout and was associated with significant improvements in other aspects of well-being. Although initiating the intervention among busy HCWs was challenging, participation in a no-cost, low intensity positive psychology intervention improved burnout, depression, and work-life integration for up to six months beyond the intervention. WISER offers healthcare institutions a free, fun, and feasible tool to stem the crisis in HCW burnout and maintain workforce well-being.
Supplementary Material
Transparency:
The lead author (the manuscript’s guarantor) affirms that this manuscript is an honest, accurate, transparent account of the study being reported; that no important aspects of the study have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the study as originally planned (and, if relevant, registered) have been explained.
Acknowledgments:
We would like to thank the HCWs at the participating institutions: it is their time, thoughtfulness, meaningful contributions, and steadfast dedication to patient-centered care that taught us so much about how to adapt and improve this intervention. We would also like to thank the site nurse leads that helped with the intervention: Florence Chow, Marlee Crankshaw, Lisa Criscoe, Melissa DeColo, Nicole Francis, Kim Jacobs, Belinda Mathis, Nancy Morris, Krista Moses, Rebecca Schiff, Amy Toronto, and Karen Waldo.
Funding source: This work was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development [R01 HD084679-01, Co-PI: Sexton and Profit and K24 HD053771-01, PI: Thomas], and the Jackson Vaughan Critical Care Research Fund.
Footnotes
Financial disclosure: The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Data Sharing Statement: The authors will share survey data from the study upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Ethics approval: The study was approved by Duke University and Stanford University.
Exclusive License: The Corresponding Author has the right to grant on behalf of all authors and does grant on behalf of all authors, a worldwide license to the Publishers and its licensees in perpetuity, in all forms, formats and media (whether known now or created in the future), to i) publish, reproduce, distribute, display and store the Contribution, ii) translate the Contribution into other languages, create adaptations, reprints, include within collections and create summaries, extracts and/or, abstracts of the Contribution, iii) create any other derivative work(s) based on the Contribution, iv) to exploit all subsidiary rights in the Contribution, v) the inclusion of electronic links from the Contribution to third party material where-ever it may be located; and, vi) license any third party to do any or all of the above.
REFERENCES
- 1.Profit J, Sharek PJ, Amspoker AB, et al. Burnout in the NICU setting and its relation to safety culture. BMJ Qual Saf 2014;23:806–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lindblom KM, Linton SJ, Fedeli C, Bryngelsson IL. Burnout in the working population: relations to psychosocial work factors. Int J Behav Med 2006;13:51–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maslach C, Schaufeli WB, Leiter MP. Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol 2001;52:397–422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Braithwaite M Nurse burnout and stress in the NICU. Advances in neonatal care : official journal of the National Association of Neonatal Nurses 2008;8:343–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rochefort CM, Clarke SP. Nurses’ work environments, care rationing, job outcomes, and quality of care on neonatal units. J Adv Nurs 2010;66:2213–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van Mol MM, Kompanje EJ, Benoit DD, Bakker J, Nijkamp MD. The prevalence of compassion fatigue and burnout among healthcare professionals in intensive care units: A systematic review. PloS one 2015;10:e0136955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bellieni CV, Righetti P, Ciampa R, Iacoponi F, Coviello C, Buonocore G. Assessing burnout among neonatologists. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012;25:2130–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shanafelt TD, West CP, Sloan JA, et al. Career fit and burnout among academic faculty. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:990–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.West CP, Dyrbye LN, Erwin PJ, Shanafelt TD. Interventions to prevent and reduce physician burnout: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shanafelt TD, Bradley KA, Wipf JE, Back AL. Burnout and self-reported patient care in an internal medicine residency program. Ann Intern Med 2002;136:358–67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cimiotti JP, Aiken LH, Sloane DM, Wu ES. Nurse staffing, burnout, and health care-associated infection. Am J Infect Control 2012;40:486–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tawfik DS, Profit J, Morgenthaler TI, et al. Physician burnout, well-being, and work unit safety grades in relationship to reported medical errors. Mayo Clin Proc 2018;93:1571–80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fibuch E, Ahmed A. Physician turnover: a costly problem. Physician Leadersh J 2015;2:22–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schloss EP, Flanagan DM, Culler CL, Wright AL. Some hidden costs of faculty turnover in clinical departments in one academic medical center. Acad Med 2009;84:32–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shanafelt TD, Mungo M, Schmitgen J, et al. Longitudinal study evaluating the association between physician burnout and changes in professional work effort. Mayo Clin Proc 2016;91:422–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sexton JB, Adair KC. Forty-five good things: a prospective pilot study of the Three Good Things well-being intervention in the USA for healthcare worker emotional exhaustion, depression, work-life balance and happiness. BMJ Open 2019;9:e022695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Adair KC R-HL, Masoud S, Mosca PJ, Sexton, BJ. Gratitude at Work: A prospective cohort study of a web-based, single-exposure well-being intervention for healthcare workers. J Med Internet Res 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Adair KC KL, Sexton JB. Three Good Tools: Positively reflecting backwards and forward is associated with robust improvements in well-being across three distinct interventions. J Posit Psychol 2020;15:5, 613–622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Seligman ME, Steen TA, Park N, Peterson C. Positive psychology progress: empirical validation of interventions. Am Psychol 2005;60:410–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jarvis P Adult Education and Lifelong Learning: Theory and Practice. 4th ed. New York, NY: Routledge; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sexton JB, Adair KC, Leonard MW, et al. Providing feedback following Leadership WalkRounds is associated with better patient safety culture, higher employee engagement and lower burnout. BMJ Qual Saf 2018;27:261–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schwartz SP, Adair KC, Bae J, et al. Work-life balance behaviours cluster in work settings and relate to burnout and safety culture: a cross-sectional survey analysis. BMJ Qual Saf 2019;28:142–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sexton JB, Schwartz SP, Chadwick WA, et al. The associations between work-life balance behaviours, teamwork climate and safety climate: cross-sectional survey introducing the work-life climate scale, psychometric properties, benchmarking data and future directions. BMJ Qual Saf 2017;26:632–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maslach C, Jackson SE. Maslach Burnout Inventory. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press, Inc.; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adair KC, Quow K, Frankel A, et al. The Improvement Readiness scale of the SCORE survey: a metric to assess capacity for quality improvement in healthcare. BMC Health Serv Res 2018;18:975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wheeler DL, Vassar M, Worley JA, Barnes LLB. A reliability generalization Meta-Analysis of Coefficient Alpha for the Maslach Burnout Inventory. Educ Psychol Meas 2011;71:231–44. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rehder KJ, Adair KC, Hadley A, et al. Associations between a new disruptive behaviors scale and teamwork, patient safety, work-life balance, burnout, and depression. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Andresen EM, Malmgren JA, Carter WB, Patrick DL. Screening for depression in well older adults: evaluation of a short form of the CES-D (Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale). Am J Prev Med 1994;10:77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bianchi R, Laurent E. Emotional information processing in depression and burnout: an eye-tracking study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2015;265:27–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lyubomirsky S, Ross L. Changes in attractiveness of elected, rejected, and precluded alternatives: a comparison of happy and unhappy individuals. J Pers Soc Psychol 1999;76:988–1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Howell RT, Rodzon KS, Kurai M, Sanchez AH. A validation of well-being and happiness surveys for administration via the Internet. Behav Res Methods 2010;42:775–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Turner EL, Prague M, Gallis JA, Li F, Murray DM. Review of recent methodological developments in Group-Randomized Trials: Part 2-Analysis. Am J Public Health 2017;107:1078–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kenward MG, Roger JH. Small sample inference for fixed effects from restricted maximum likelihood. Biometrics 1997;53:983–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Haidari E, Main EK, Cui X, et al. Maternal and neonatal health care worker well-being and patient safety climate amid the COVID-19 pandemic. J Perinatol 2021:1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dyrbye LN, Shanafelt TD, Gill PR, Satele DV, West CP. Effect of a professional coaching intervention on the well-being and distress of physicians: A pilot Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fredrickson BL, Cohn MA, Coffey KA, Pek J, Finkel SM. Open hearts build lives: positive emotions, induced through loving-kindness meditation, build consequential personal resources. J Pers Soc Psychol 2008;95:1045–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fredrickson BL, Kurtz LE. Cultivating positive emotions to enhance human flourishing. S Appl Psyc 2011:35–47. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fredrickson BL, Mancuso RA, Branigan C, Tugade MM. The undoing effect of positive emotions. Motiv Emotion 2000;24:237–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fredrickson BL, Levenson RW. Positive emotions speed recovery from the cardiovascular sequelae of negative emotions. Cogn Emot 1998;12:191–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eysenbach G The law of attrition. J Med Internet Res 2005;7:e11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mongrain M, Anselmo-Matthews T. Do positive psychology exercises work? A replication of Seligman et al. (). J Clin Psychol 2012;68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Halpern SD, Harhay MO, Saulsgiver K, Brophy C, Troxel AB, Volpp KG. A pragmatic trial of E-Cigarettes, incentives, and drugs for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med 2018;378:2302–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Geraghty AW, Torres LD, Leykin Y, Perez-Stable EJ, Munoz RF. Understanding attrition from international Internet health interventions: a step towards global eHealth. Health Promot Int 2013;28:442–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Song Z, Baicker K. Effect of a Workplace wellness program on employee health and economic outcomes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2019;321:1491–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wing RR, Phelan S. Long-term weight loss maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82:222s–5s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Colombo O, Ferretti VV, Ferraris C, et al. Is drop-out from obesity treatment a predictable and preventable event? Nutr J 2014;13:13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Miller BML, Brennan L. Measuring and reporting attrition from obesity treatment programs: A call to action! Obes Res Clin Pract 2015;9:187–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dalle Grave R, Calugi S, Compare A, et al. Weight loss expectations and attrition in treatment-seeking obese women. Obes Facts 2015;8:311–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.