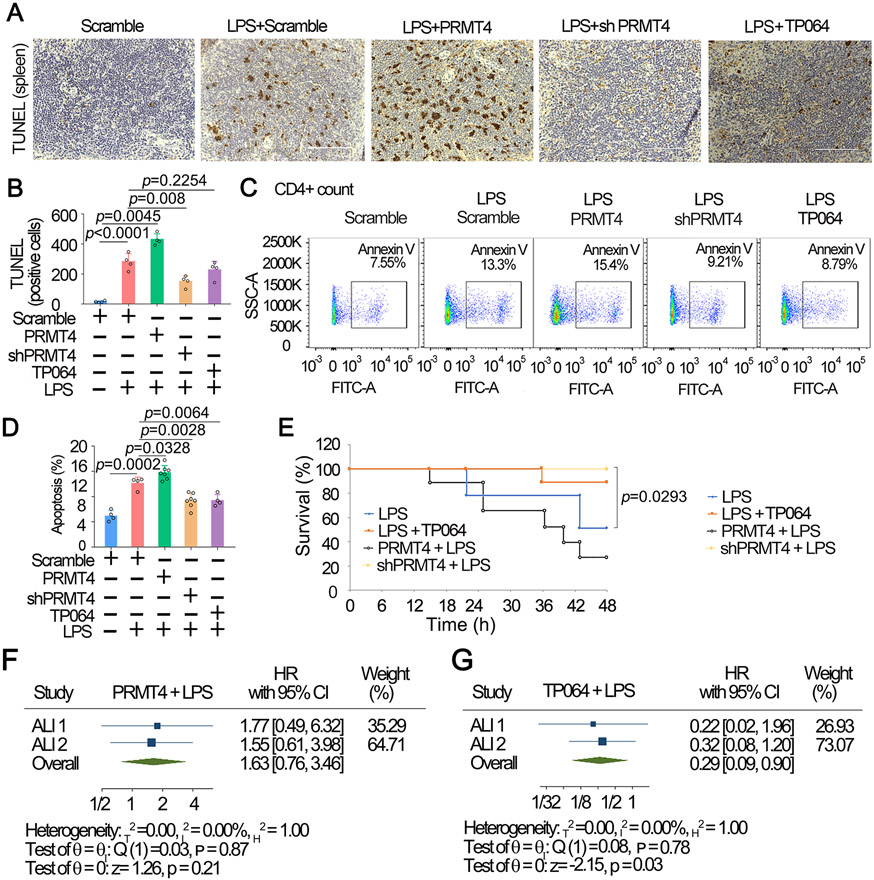
Fig. 6. Inhibition of PRMT4 suppresses splenic lymphocyte death in an LPS challenged mouse model.
A. PRMT4 was knocked down or overexpressed by i.t. administrated lentiviral constructs for 14 d. LPS or PRMT4 inhibitor were given (i.t.) as indicated for 24 h (n=8). Spleen tissues were stained with TUNEL. B. TUNEL positive cells in spleen tissues were quantitated. C, D. CD4 positive lymphocytes were isolated from splenic tissues in above PRMT4 knockdown or overexpression experiments (A) and analyzed with flow cytometry. CD4 was used as a T cell marker. % of apoptosis were quantitated in D (n=3). E. Survival studies were conducted in the LPS lung injury model, mice were observed for 48 h (n = 10). F,G. Two stage meta-analysis was conducted using two independent sets of murine data using LPS only group as reference: PRMT4 +LPS (F) and TP064 + LPS (G). The data of shPRMT4 group was not shown due to the hazard ratio (HR) was not computable. Two independent experiments were conducted [n = 26, (10, 16)]. Scale bar=100 μm.