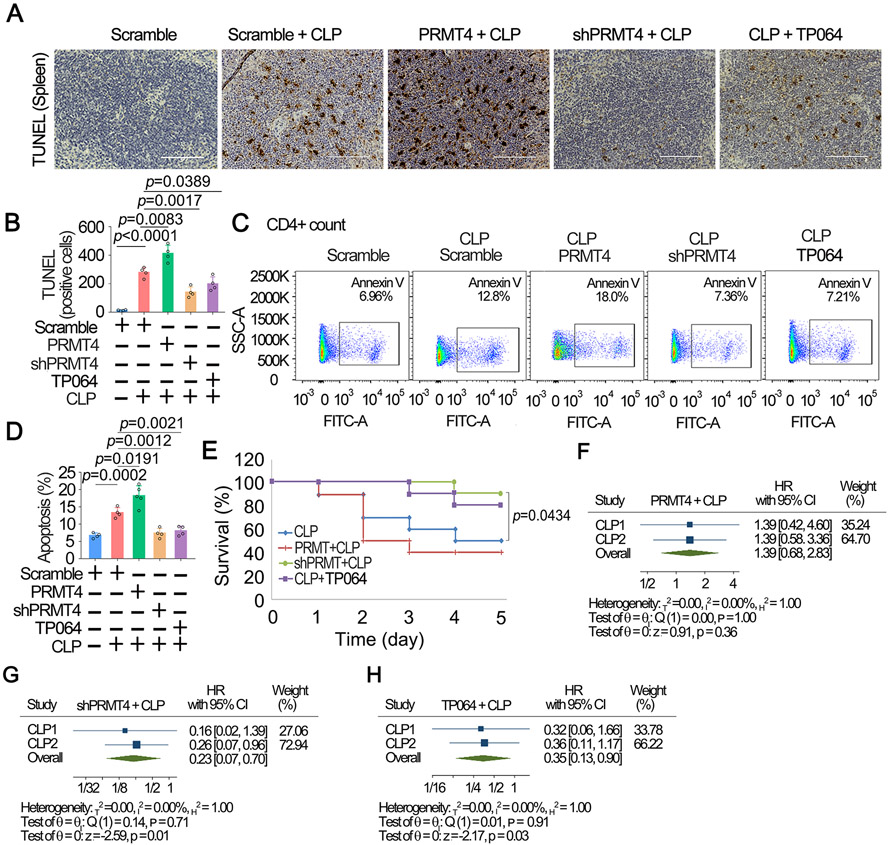
Fig. 7. Inhibition of PRMT4 suppresses splenic lymphocyte death in a polymicrobial sepsis model.
A. CLP was performed in PRMT4 knocked down or overexpressed mice (n=8). TP064 (0.2 μg/mouse) was administrated i.v. in one group for 48 h. Spleen tissues were stained with TUNEL. B. TUNEL positive cells in spleen tissues. C, D. Isolated splenic CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (C). CD4 was used as a T cell marker. The data from C were plotted in D. E. Survival studies were conducted in the CLP model, and mice were observed for 5 days (n = 16). F-H. Meta-analysis was conducted among two independent sets of murine data using CLP only as reference group: PRMT4 + CLP (F), shPRMT4 + CLP (G), and TP064 + CLP (H). Two independent experiments were conducted [n = 26, (10, 16)]. Scale bar=100 μm.