Abstract
Background:
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the normal delivery of HIV care, altered social support networks, and caused economic insecurity. People with HIV (PWH) are vulnerable to such disruptions, particularly if they have a history of substance use. We describe engagement in care and adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) for PWH during the pandemic.
Methods:
From May 2020 to February 2021, 773 PWH enrolled in 6 existing cohorts completed 1495 surveys about substance use and engagement in HIV care during the COVID-19 pandemic. We described the prevalence and correlates of having missed a visit with an HIV provider in the past month and having missed a dose of ART in the past week.
Results:
Thirteen percent of people missed an HIV visit in the past month. Missing a visit was associated with unstable housing, food insecurity, anxiety, low resiliency, disruptions to mental health care, and substance use including cigarette smoking, hazardous alcohol use, cocaine, and cannabis use. Nineteen percent of people reported missing at least one dose of ART in the week prior to their survey. Missing a dose of ART was associated with being a man, low resiliency, disruptions to mental health care, cigarette smoking, hazardous alcohol use, cocaine, and cannabis use, and experiencing disruptions to substance use treatment.
Conclusions:
Social determinants of health, substance use, and disruptions to mental health and substance use treatment were associated with poorer engagement in HIV care. Close attention to continuity of care during times of social disruption is especially critical for PWH.
Keywords: antidepressant therapy, care cascade, depression, depressive symptoms, viral non-suppression
1. INTRODUCTION
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic disrupted the normal delivery of medical care, altered social support networks, and caused economic insecurity. People with HIV, in particular those whose social determinants of health and mental health symptoms place them at high risk for poor health outcomes, may have been especially impacted by disruptions to care. Documenting patterns of engagement in HIV care, adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART), and viral suppression, is important for understanding the potential long-term, collateral impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. When people with HIV maintain viral suppression they have better health outcomes and their infection is untransmissible to others (Cohen et al., 2011; Fauci et al., 2019; Insight Start Study Group et al., 2015). Retention in care and adherence to antiretroviral therapy are key upstream indicators of successful viral suppression (Gardner et al., 2011; Greenberg et al., 2009).
The goal of this study was to describe engagement in care and adherence to ART for people with HIV living in North America (the United States and Canada) during the COVID-19 pandemic, and risk factors for poor care continuum outcomes during the pandemic. We focused our investigation on demographics (based on well-documented racial and ethnic disparities in HIV care outcomes), social determinants of health, substance use, mental health symptoms and treatment, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many HIV clinics adapted care models quickly to allow patients to engage in care without requiring in-person visits (e.g., offering telehealth and telephone visits) (Brody et al., 2021; Yelverton et al., 2021). Prior research has suggested that visit completion during the pandemic was similar or better than during the pre-pandemic period (El-Nahal et al., 2021). We hypothesized that accomodations to encourage visit completion might reduce barriers to visit completion (Auchus et al., 2021; Spinelli et al., 2020), and result in relatively few disparities in retention in care. Although prior research has reported the prevalence of viral suppression in the pandemic is similar to pre- pandemic (El Moussaoui et al., 2021; Giacomelli et al., 2021; Izzo et al., 2021), these studies restricted their analysis too patients who had a measured viral load. We did not measure viral load (which would have required an in-person study visit and presented unnecessary risk to participants) and instead focus on ART adherence. We hypothesized that ART adherence would be inversely associated with substance use, mental health symptoms, and other measures of social vulnerability.
2. METHODS
2.1. Study Sample.
The Collaborating Consortium of Cohorts Producing NIDA Opportunities (C3PNO) was established in 2017 by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) to enhance data sharing opportunities and facilitate collaborative research efforts among NIDA-supported cohorts that study HIV/AIDS in the context of substance use. Details of the participating cohorts and other methodology have been previously described (Gorbach et al., 2021) but briefly, the Consortium is comprised of nine NIDA cohorts located in major cities throughout North America (Baltimore, Miami, Chicago, and Los Angeles, United States, and Vancouver, Canada) with a combined sample size of approximately 12,000 active participants. The consortium links a wide range of behavioral, clinical, and biological data from diverse individuals at high-risk for HIV or living with HIV participating in the cohorts. Starting in May 2020, the Consortium launched a COVID-19 survey in order to examine changes in substance use, substance use disorder treatment, and HIV prevention and care in the midst of and following the COVID-19 pandemic.
From May 11, 2020 to February 15, 2021, participating cohorts administered the survey to a minimum of 200 participants who were eligible if they: (1) were enrolled in one of the eight participating C3PNO cohorts; (2) participated in a recent study visit (generally within in the preceding 12 months prior to the emergence of COVID-19); (3) were English and/or Spanish speaking; and (4) were willing and able to complete the survey remotely. Most participants had a recent history of substance use as determined by self-report. The survey was either self-administered online or interviewer-administered by telephone. It took approximately 20 minutes to complete and participants were remunerated for their time. The study was approved by the institutional review of boards of the cohorts and each participant provided informed consent for their study participation.
For this study, we restricted analyses to people with HIV enrolled in C3PNO who completed at least one COVID-19 survey. Participants completed up to 2 surveys during the study period. Very briefly, the included cohorts included: the AIDS Linked to the Intravenous Experience (ALIVE) Study (people who ever injected drugs living in the Baltimore area); the Healthy Young Men’s (HYM) Study (Black, Latino, and multiracial young men who have sex with men in Los Angeles); the Johns Hopkins HIV Clinical Cohort (JHHCC, people with HIV engaged in continuity care at a subspecialty clinic in Baltimore); the Miami Adult Studies on HIV (MASH, people with HIV, HCV, and HIV/HCV co-infection who use cocaine); mSTUDY (young non-white men who have sex with men in Los Angeles); and the Mutlilevel Influences on HIV and Substance Use in young men who have sex with men Cohort (RADAR, young men who have sex with men in Chicago).
2.2. Outcomes.
We considered care continuum outcomes for retention in care, adherence to ART, and receipt of laboratory monitoring of viral load. To measure retention, we used metrics of both kept visits and missed visits (Mugavero et al., 2012). As an indicator of being retained according to kept visits, we report the proportion of participants who had a visit with a doctor, nurse, or other medical provider in the last 6 months. As an indicator of being unretained according to missed visits (Mugavero et al., 2009a; Mugavero et al., 2009b), we looked at participants who reported missing a visit with their HIV care provider in the last month (among those with a visit scheduled in the last month). We report, for completeness, a description of the reasons respondents gave for missing appointments with their HIV care provider.
We also report the proportion of respondents on ART, adherent to ART, and whose viral load was recently measured. Because respondents were not seen in person, viral load values were not available and we could not measure viral suppression. ART use was defined as reporting being on any daily medications for HIV. Non-adherence to ART was defined as reporting missing any HIV medications in the past 7 days; this would include periods in which people missed all HIV medications in the past 7 days. To contextualize these results, we report the reasons respondents gave for missing ART doses. Recent viral load monitoring was defined as reporting having a viral load measurement ≤6 months before their survey.
2.3. Covariates.
We considered demographic, social, mental health, and substance use factors and the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic as correlates of engagement in HIV care. Demographics included age, sex at birth (male sex at birth is inclusive of any transgender women included in the sample; gender was not ascertained on the survey), and race/ethnicity. Social determinants of health that were measured included self-reported housing stability, employment status, and food security. Housing was defined as unstable if respondents reported usually sleeping somewhere other than a house, apartment, dorm, home health facility, or rehabilitation facility. This included things like sleeping at someone else’s house, in a car, on the street, or in a shelter. Employment status was classified as employed if respondents endorsed the statement “I am employed,” unstable employment if respondents indicated having faced a reduction in work hours or furlough or not having formal employment, and unemployed if respondents said they were not working. Food insecurity was defined as reporting not having enough money for food or rationing food. Mental health variables included the GAD-7 as a measure of anxiety, with responses classified according to standard cutoffs as minimal, mild, moderate, or severe anxiety, and the Brief Resiliency Scale with responses classified as low, normal, or high resiliency. Substance use was ascertained for the month prior to the survey and participants reported on presence or absence of tobacco, cocaine, opioids, and cannabis use. We measured hazardous alcohol consumption with a modified USAUDIT-C (Higgins-Biddle and Babor, 2018) that only asked about past month rather than past year alcohol use, and classified use as “hazardous” using standard sex-specific cut-offs,. Participants reported whether or not they had engaged in any substance use treatment including alcohol, 12-step programs, and opioid substitution therapy. We also asked whether people in substance use treatment experienced disruptions in their treatment. Finally, we considered the degree of disruptions to day-to-day life due to the COVID-19 pandemic (reporting the pandemic impacted day-to-day life “much”, “very much”, or “extremely”) and the degree to which the COVID-19 pandemic was impacting respondents mental health. Respondents who reported their level of worry about the pandemic was ≥5 on a scale of 1–10 were classified as having a substantial amount of worry.
2.4. Statistical Analysis.
We described the prevalence of care continuum outcomes using simple proportions. We described univariable and multivariable associations between each of the covariates listed above and 1) having missed a visit with an HIV provider in the past month and 2) having missed a dose of ART in the past week. We estimated crude (adjusted only for cohort) and fully adjusted prevalence ratios using Poisson models with robust variance estimators (an approximation to a log-binomial model when the log-binomial model fails to converge). The robust variance estimator also accounted for possibly correlated outcomes arising from multiple measurements within the same individual.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Study sample.
There were 1495 surveys completed among HIV-positive respondents. We excluded 209 surveys (14% of all surveys) that were missing information on covariates (10 surveys were missing information on housing, employment=6, food insecurity=18, resiliency=1, mental health treatment=4, smoking=2, alcohol=2, cocaine=3, opioids=3, cannabis=10, substance use treatment=12, COVID-19 disruptions=6) or outcomes (most recent kept visit=21, missed HIV care visit=14, missed ART=139, most recent viral load=21). This analysis included 1286 surveys contributed by 773 unique respondents, 66% of whom contributed 2 surveys.
The study sample was mostly male (75%), older (median age was 50), and self-identified as Black, non-Hispanic race/ethnicity (69%). Study participants were socially vulnerable and had a high prevalence of substance use. One in five respondents (21%) reported they were in substance use treatment, but of those in treatment, disruptions were common (73%). One in eleven respondents (9%) were receiving opioid agonist therapy and 26% of those reported a disruption in their treatment. Finally, the COVID-19 pandemic caused “much” to “extreme” disruption to 67% of respondents’ lives and caused substantial worry for 77% of them (Table 1).
Table 1.
Characteristics of 773 persons living with HIV enrolled in a NIDA-funded cohort (and 1286 surveys completed by those persons) who completed 1 or 2 surveys about their experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic, 11 May 2020–15 February 2021
| Observations N=1286 (%) | Persons N=773 (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Agea | 51 (37, 58) | 50 (35, 57) |
| Male sex | 943 (73) | 576 (75) |
| Race/ethnicity | ||
| Black, non-Hispanic | 883 (69) | 530 (69) |
| White, non-Hispanic | 117 (9) | 68 (9) |
| Hispanic | 238 (19) | 142 (18) |
| Other, non-Hispanic | 48 (4) | 33 (4) |
| Unstable housing | 68 (5) | 45 (6) |
| Employment | ||
| Employed | 237 (18) | 134 (17) |
| Unstable employment | 167 (13) | 113 (15) |
| Unemployed | 882 (69) | 526 (68) |
| Food insecure | 354 (28) | 228 (29) |
| Moderate-to-severe anxiety | 228 (18) | 149 (19) |
| Brief Resiliency Scale | ||
| Low resilience | 198 (15) | 125 (16) |
| Normal resilience | 877 (68) | 522 (68) |
| High resilience | 211 (16) | 126 (16) |
| Interruptions to mental health care | 644 (50) | 415 (54) |
| Recent drug use | ||
| Smoking | 548 (43) | 342 (44) |
| Hazardous alcohol use | 138 (11) | 82 (11) |
| Cocaine | 126 (10) | 78 (10) |
| Opioids | 59 (5) | 40 (5) |
| Cannabis | 463 (36) | 291 (38) |
| Current substance use treatment | 241 (19) | 160 (21) |
| Disruptions to substance use treatment | 167 (69) | 116 (73) |
| Current opioid agonist therapy | 99 (8) | 68 (9) |
| Disruptions to opioid agonist therapy | 26 (26) | 18 (26) |
| ≥ “Much” disruptions of COVID-19 pandemic | 848 (66) | 519 (67) |
| Substantial worry due to the pandemic | 1001 (78) | 592 (77) |
Median (Q1, Q3)
The study sample reported a high engagement in medical care: 93% had had a medical visit in the past month (including telehealth visits) and 90% had had a viral load measurement in the past 6 months. Despite the intensity of care, the prevalence of missed HIV visits in the past month was 13%. Across cohorts, prevalence of missed HIV visits ranged from 8% to 26%. Nearly all people in the study sample were on ART (98%). However, 19% of the sample reported missing at least one dose of ART in the week prior to their survey. Across cohorts, prevalence of suboptimal ART adherence ranged from 9% to 37%. Excluding May 2020, the probability of missing a scheduled HIV visit in the past month increased very slightly (0.8% per month, p=0.08) each calendar month, and the probability of missing a dose of ART in the past week was relatively stable (0.1% increase per month, p=0.81) (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
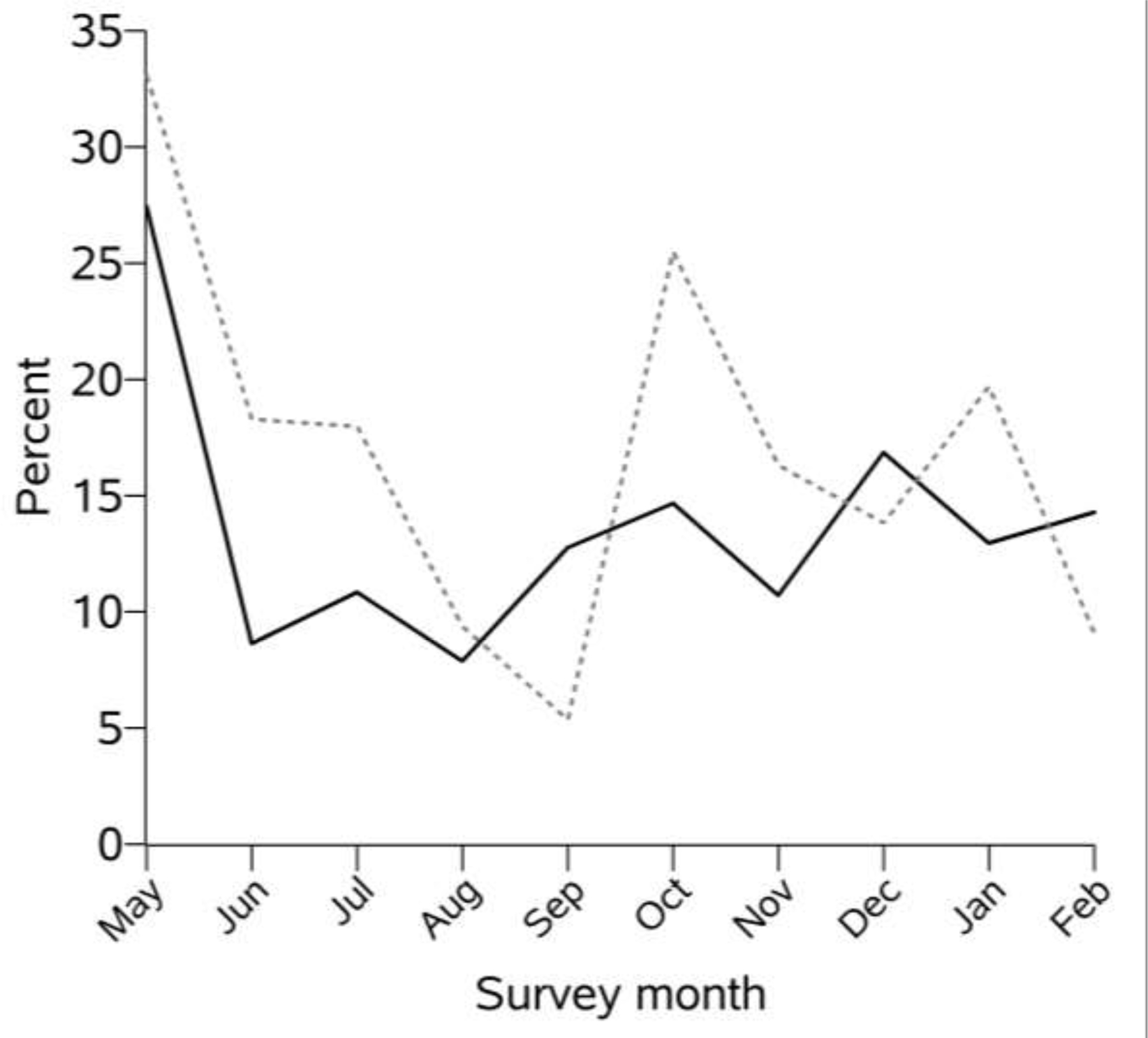
Proportion reporting missing a visit with an HIV provider in the past month (solid black line) and missing any ART in the past week (dashed gray line), by month, among persons with an HIV visit scheduled and persons on ART (respectively) who were enrolled in a NIDA-funded cohort and who completed a survey during the COVID-19 pandemic
3.2. Missed HIV visits.
In crude analyses, adjusted only for cohort and calendar month, the probability of reporting a missed HIV visit in the past month among respondents who had an HIV visit scheduled in the past month was higher among people with unstable housing (prevalence ratio [PR]: 1.45, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.93, 2.25), people who reported food insecurity (PR: 1.47, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.99), people who reported moderate-to-severe anxiety (PR: 1.45, 95% CI: 1.03, 2.04) or low resiliency (PR: 1.59, 95% CI: 1.12, 2.26, relative to normal resiliency), people who reported disruptions in their mental health care as a result of the pandemic (PR: 1.38, 95% CI: 1.00, 1.90), and people who were using substances (smoking PR: 1.73, 95% CI: 1.28, 2.35; hazardous alcohol use PR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.01, 2.24; cocaine PR: 1.78, 95% CI: 1.22, 2.59; and cannabis PR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.18, 2.19). In multivariable models, the only covariate that remained statistically significantly associated with missing an HIV visit in the past month was smoking (PR: 1.50, 95% CI: 1.09, 2.08). The following covariates had associations of similar magnitude with missing a visit although associations were not statistically significant: unstable housing (PR: 1.33, 95% CI: 0.83, 2.10), low resiliency (PR: 1.43, 95% CI: 0.99, 2.07), cocaine use (PR: 1.31, 95% CI: 0.85, 2.03), and cannabis use (PR: 1.32, 95% CI: 0.92, 1.89). Of people who missed an HIV visit in the past month, 26% missed because they forgot, 18% had their visit canceled due to COVID-19, 12% reported that attending was inconvenient for them, and 9% reported being unable to attend a telehealth visit. Three percent reported missing their HIV appointment because they had COVID-19 symptoms.
3.3. ART adherence.
In crude analyses, adjusted only for cohort, the probability of missing at least one dose of ART in the past week among people on ART was higher among men (PR: 1.75, 95% CI: 1.11, 2.75), people reporting low resiliency (PR: 1.69, 95% CI: 1.32, 2.16), people who experienced disruptions in their mental health care (PR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.65), and people who were using substances (smoking PR: 1.36, 95% CI: 1.08, 1.70; hazardous alcohol use PR: 1.61, 95% CI: 1.17, 2.21; cocaine PR: 1.94, 95% CI: 1.46, 2.58; and cannabis PR: 1.54, 95% CI: 1.21, 1.97). Missing ART was not associated with receiving substance use treatment, but was strongly associated with experiencing a disruption to substance use treatment (PR: 2.54, 95% CI: 1.21, 5.34). In multivariable models, only male sex (PR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.04, 2.60), low resiliency (PR: 1.62, 95% CI: 1.27, 2.06), cocaine use (PR: 1.65, 95% CI: 1.22, 2.22), cannabis use (PR: 1.32, 95% CI: 1.00, 1.74), and disruptions to substance use treatment (PR: 2.37, 95% CI: 1.14, 4.94) were strongly and statistically significantly associated with missing at least one dose of ART in the past week. Of people who missed ART in the past week, the majority (77%) forgot. A substantial proportion of respondents (15%) reported they missed taking ART because they could not get a refill of their medications or because they were concerned about going to the pharmacy because of the COVID-19 pandemic (7%).
4. DISCUSSION
In this sample of people with HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic, the majority of whom had a history of drug use or who reported current drug use, one in eight persons had missed a scheduled HIV visit in the past month and one in five persons had missed an ART dose in the last week. This, despite otherwise high engagement in care: the vast majority of people had attended a medical visit in the past month; virtually all people in this sample were prescribed ART; and 90% of people had had a viral load measurement in the past 6 months.
We cannot measure changes in retention and ART adherence in this cohort from pre-pandemic to during the pandemic, nor interpret our results as the “effect” of the pandemic on the HIV care continuum. Prior research comparing indicators in the pre-pandemic and pandemic period show an initial increase in disrupted services and missed visits at the start of the pandemic (Qiao et al., 2021; Quiros-Roldan et al., 2020) but overall similar or higher probability of visit completion during the pandemic (El-Nahal et al., 2021). The probability of having missed a scheduled HIV visit in this study appears to be in line with pre-pandemic estimates (while not measured on the same timeline as pre-pandemic investigations into the care continuum which looked a the prevalence of any missed visits in the 2 years (68%) (Mugavero et al., 2014); if we assume the probability of missing a given visit was 13% as reported here, and patients would on average attend 6–8 visits over a 2-year period based on a visit frequency of 3–4 months, the probability of missing at least one visit in that period would be 68%). Even if we assume that the COVID-19 pandemic did not increase the probability of missing a visit, missed visits are associated with subsequent loss of viral suppression, mortality, and racial/ethnic disparities in HIV outcome and 13% probability of a missed visit in the past month is cause for concern and a possible point of intervention (Batey et al., 2020; Mugavero et al., 2014; Zinski et al., 2015).
Retention in and engagement in care during the COVID-19 pandemic looked very different from pre-pandemic. In response to the need for increased social distancing, HIV clinics implemented telehealth options for visit completion or postponed visits (Budak et al., 2021; Ridgway et al., 2020). While traditionally, “telehealth” has implied video visits accessed over the internet, and therefore has required access to smartphones or computers and the internet, during the pandemic, many HIV clinics offered telephone-only telehealth visits, or made other accomodations, such as providing patients with smartphones, in order to reduce the impact of these barriers (Auchus et al., 2021; Brody et al., 2021; Budak et al., 2021; Dandachi et al., 2020; Yelverton et al., 2021). In many cases (Auchus et al., 2021; Brody et al., 2021; Coppock et al., 2021; El-Nahal et al., 2021; Mayer et al., 2020), but not all (Fadul, 2020; Quiros-Roldan et al., 2020), offering visits via telehealth appears to have been successful at keeping people engaged in care at pre-pandemic levels, at least in the short term. Indeed, offering telehealth options for HIV visits has been associated with fewer disparities in the limited instances in which it has been studied (Auchus et al., 2021; Brody et al., 2021; El-Nahal et al., 2021). We do not know what proportion of HIV care visits attended by patients in this study were telehealth versus in-person visits, nor what proportion of telehealth visits were video versus telephone-only visits. In the Johns Hopkins HIV Clinic (some patients of which contributed to this analysis), during the first 6.5 months of the pandemic, 70% of “telehealth” visits were conducted over the telephone only (El-Nahal et al., 2021). The impact of telehealth on long-term outcomes such as viral suppression and non-AIDS-related comorbidities (e.g., substance abuse treatment, cancer screening, and chronic non-infectious diseases) has yet to be seen.
In unadjusted analyses, we found that missing an HIV visit was associated with social determinants of health, mental health symptoms, and substance use. In prior studies, social determinants of health (Aidala et al., 2007; Aidala et al., 2016; Terzian et al., 2015; Yehia et al., 2015), mental health symptoms (Yehia et al., 2015), and substance use (Hartzler et al., 2018) have been consistently associated with poor engagement in HIV care. Given the impact of socioeconomic conditions on engagement in HIV care, efforts to mitigate the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the economy, such as eviction moratoriums, expanded unemployment assistance, and provision of food through food banks may be particularly important for people with HIV.
Other researchers have reported the prevalence of viral suppression during the pandemic is similar to pre-pandemic (El Moussaoui et al., 2021; Giacomelli et al., 2021; Izzo et al., 2021). However, these reports should be interpreted cautiously as they have been restricted to people who had a viral load measured in each period, and the frequency of viral load testing appears to have gone down during the pandemic (El Moussaoui et al., 2021). Despite the implementation of mail delivery of prescriptions during the pandemic, intended to reduce barriers to ART adherence (Budak et al., 2021), ART adherence in our sample remained below the 90% goal for viral suppression set in the End the HIV Epidemic plan (Fauci et al., 2019). As with the retention outcome, we were unable to measure changes in ART adherence from pre-pandemic levels, however, and therefore cannot attribute this to the COVID pandemic. A previous analysis in this cohort that included a different subset of patients than we included here, reported 33% of patients had missed at least one dose of ART in the past 7 days prepandemic (Gorbach et al., 2020). Therefore, although the level of ART adherence during the pandemic was still too low, it may actually be better than pre-pandemic. One small study of people with HIV in Atlanta actually reported increased ART adherence during, versus in the month before, the COVID-19 pandemic (Kalichman et al., 2020). In line with our findings, a cross-sectional survey of MSM in 20 countries from April to May 2020 found that 18% of respondents were unable to or had difficulty refilling their ART prescriptions (Rao et al., 2021). In Haiti, there was an abrupt 18% decline in the proportion of ART refills that were dispensed on time corresponding to the start of the pandemic (Celestin et al., 2021). The proportion of patients who don’t refill prescriptions on time represent perhaps a lower bound on the proportion of patients who have problems with adherence to ART (since these numbers exclude persons who have sufficient ART in their possession but forget to take doses as prescribed).
Missed ART was associated with mental health symptoms and substance use. Additionally, we found missing ART doses were associated with being a man and with experiencing disruptions to substance use treatment. While some studies have reported similar findings (e.g. no association between housing stability and ART adherence) (Terzian et al., 2015) our findings stand in contrast to most pre-pandemic studies that found housing insecurity (Aidala et al., 2016; Harris et al., 2017; Leaver et al., 2007; Mugavero et al., 2012; Palepu et al., 2011) and female sex (Arnsten et al., 2002; Berg et al., 2004) to be associated with poor ART adherence. It may be that traditional risk factors are operating differently during the pandemic, or that in our sample of people with a high prevalence of substance use, substance use is superseding other risk factors in determining ART adherence. Finding substance use associated with ART non-adherence was consistent with prior studies, in particular the finding that the strongest association was with cocaine use (Arnsten et al., 2002).
Our finding that disruptions to mental health care and substance use treatment were associated with ART non-adherence is consistent with prior studies that have found mental health and substance use treatment, in general, improves ART adherence (Berg et al., 2004). We caution against making a causal claim about the impact of treatment disruptions, however, because experiencing disruptions may be a marker of social vulnerability, internet literacy, or socioeconomic status. However, mental health care and substance use treatment are valuable independent of any potential link with ART adherence. The challenge is determining how to continue to provide mental health care and substance use treatment while maintaining social distancing. We don’t have information on what disruptions people experienced. It may have been that mental health and substance use treatment were stopped completely, or that therapy sessions were switched to telemedicine and patients were unable to access them, or that patients accessed telemedicine therapy sessions but found them less engaging than in-person sessions. Encouragingly, disruptions to opioid treatment programs do not have the same strong relationship with ART adherence. It may be that ‘disruptions’ to services provided at opioid treatment programs was mitigated by the relaxing of federal regulations that allowed for increased take-home methadone doses and reduced barriers to continued opioid agonist therapy (Peavy et al., 2020).
Finally, . as with self-reported measures, patients may have over-reported attendance at HIV care visits and ART adherence. Additionally, we do not have a comprehensive list of all patients who were eligible for this survey but who chose not to participate; it may be that individuals who participated in this study were the least vulnerable to/least impacted by the pandemic and we have overestimated the prevalence of retention and adherence in these cohorts.
5. CONCLUSIONS
Herein, we have described the prevalence of missed HIV visits and ART adherence during the COVID-19 pandemic in a sample of people with HIV who might be at high risk for poor HIV control given their high prevalence of substance use. Close attention to continuity of care during times of social disruption is especially critical for people with HIV and particularly those with current and past substance use.
Supplementary Material
Table 2.
Prevalence of indicators of engagement or disengagement in HIV care among persons with HIV who were enrolled in a NIDA-funded cohort and completed a survey during the COVID-19 pandemic, 11 May 2020–15 February 2021
| Metric | Estimate, N (%) |
|---|---|
| No medical visit within the past montha | 86/1286 (7) |
| Any missed scheduled HIV appointments in the past month | 146/1108 (13) |
| On ART | 1261/1286 (98) |
| Missed any ART in the last week | 235/1261 (19) |
| >6 months since last viral load measurement | 130/1286 (10) |
Includes telehealth and remote visits
Table 3.
Patient characteristics and their associations with the prevalence of self-report of missing a visit with an HIV provider in the prior month, among persons who had a scheduled visit with an HIV provider in the prior month and who were enrolled in a NIDA-funded cohort and completed a survey during the COVID-19 pandemic, 11 May 2020–15 February 2021
| Covariate | Crude Prevalence Ratio | Adjusted Prevalence Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Age, 1-year increment | 0.98 (0.96, 1.00) | 0.99 (0.97, 1.01) |
| Male sex | 1.25 (0.71, 2.20) | 1.18 (0.67, 2.07) |
| Race/ethnicity, ref Black, non-Hispanic | ||
| White, non-Hispanic | 0.95 (0.54, 1.66) | 0.96 (0.56, 1.63) |
| Hispanic | 0.92 (0.63, 1.34) | 0.95 (0.63, 1.45) |
| Other, non-Hispanic | 1.05 (0.56, 1.98) | 0.80 (0.40, 1.61) |
| Unstable housing | 1.45 (0.93, 2.25) | 1.32 (0.83, 2.10) |
| Employment, ref Employed | ||
| Unstable employment | 0.79 (0.52, 1.20) | 0.61 (0.38, 0.99) |
| Unemployed | 1.10 (0.79, 1.54) | 0.79 (0.52, 1.20) |
| Food insecurity | 1.47 (1.09, 1.99) | 1.31 (0.95, 1.82) |
| Moderate-to-severe anxiety | 1.45 (1.03, 2.04) | 1.13 (0.77, 1.64) |
| Resiliency, ref Normal | ||
| Low | 1.59 (1.12, 2.26) | 1.43 (0.99, 2.07) |
| High | 0.78 (0.51, 1.20) | 0.90 (0.57, 1.42) |
| Disruption in mental health care | 1.38 (1.00, 1.90) | 1.23 (0.87, 1.72) |
| Recent drug use | ||
| Smoking | 1.73 (1.28, 2.35) | 1.50 (1.09, 2.08) |
| Hazardous alcohol use | 1.51 (1.01, 2.24) | 1.15 (0.74, 1.78) |
| Cocaine | 1.78 (1.22, 2.59) | 1.31 (0.85, 2.03) |
| Opioids | 1.24 (0.67, 2.30) | 0.88 (0.44, 1.77) |
| Cannabis | 1.61 (1.18, 2.19) | 1.32 (0.92 1.89) |
| Substance use treatment | 0.85 (0.55, 1.31) | 0.85 (0.39, 1.86) |
| Disruptions to substance use treatment | 1.23 (0.54, 2.80) | 1.06 (0.46, 2.40) |
| Current opioid agonist therapy | 1.28 (0.65, 2.52) | 1.11 (0.43, 2.87) |
| Disruptions to opioid agonist therapy | 1.13 (0.34, 3.80) | 1.20 (0.32, 4.46) |
| ≥ “Much” disruptions of COVID-19 pandemic | 1.26 (0.86, 1.83) | 1.18 (0.79, 1.75) |
| Substantial worry due to the pandemic | 1.03 (0.72, 1.47) | 0.88 (0.59, 1.31) |
Table 4.
Patient characteristics and their associations with the prevalence of self-report of missing any antiretroviral medications in the past week, among persons with HIV on ART who were enrolled in a NIDA-funded cohort and completed a survey during the COVID-19 pandemic, 11 May 2020–15 February 2021
| Covariate | Crude Prevalence Ratio | Adjusted Prevalence Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Age, 1-year increment | 0.99 (0.97, 1.01) | 0.99 (0.98, 1.01) |
| Male sex | 1.75 (1.11, 2.75) | 1.64 (1.04, 2.60) |
| Race/ethnicity, ref Black, non-Hispanic | ||
| White, non-Hispanic | 0.96 (0.64, 1.44) | 0.92 (0.61, 1.40) |
| Hispanic | 1.02 (0.75, 1.39) | 1.10 (0.79, 1.54) |
| Other, non-Hispanic | 1.29 (0.82, 2.04) | 1.13 (0.68, 1.87) |
| Unstable housing | 1.24 (0.84, 1.82) | 1.14 (0.75, 1.74) |
| Employment, ref Employed | ||
| Unstable employment | 1.00 (0.73, 1.36) | 0.85 (0.59, 1.23) |
| Unemployed | 0.93 (0.72, 1.22) | 0.86 (0.62, 1.19) |
| Food insecurity | 1.16 (0.91, 1.47) | 1.07 (0.85, 1.34) |
| Moderate-to-severe anxiety | 1.25 (0.96, 1.62) | 0.96 (0.73, 1.27) |
| Resiliency, ref Normal | ||
| Low | 1.69 (1.32, 2.16) | 1.62 (1.27, 2.06) |
| High | 0.87 (0.63, 1.20) | 1.02 (0.72, 1.43) |
| Disruption in mental health care | 1.29 (1.01, 1.65) | 1.20 (0.93, 1.54) |
| Recent drug use | ||
| Smoking | 1.36 (1.08, 1.70) | 1.14 (0.89, 1.46) |
| Hazardous alcohol use | 1.61 (1.17, 2.21) | 1.27 (0.91, 1.77) |
| Cocaine | 1.94 (1.46, 2.58) | 1.65 (1.22, 2.22) |
| Opioids | 1.30 (0.84, 2.03) | 1.08 (0.72, 1.61) |
| Cannabis | 1.54 (1.21, 1.97) | 1.32 (1.00, 1.74) |
| Substance use treatment | 0.98 (0.72, 1.35) | 0.60 (0.29, 1.25) |
| Disruptions to substance use treatment | 2.54 (1.21, 5.34) | 2.37 (1.14, 4.94) |
| Current opioid agonist therapy | 0.86 (0.45, 1.61) | 0.67 (0.32, 1.37) |
| Disruptions to opioid agonist therapy | 1.01 (0.34, 2.99) | 0.85 (0.34, 2.17) |
| ≥ “Much” disruptions of COVID-19 pandemic | 1.08 (0.84, 1.40) | 1.01 (0.78, 1.31) |
| Substantial worry due to the pandemic | 1.05 (0.79, 1.38) | 0.95 (0.71, 1.26) |
HIGHLIGHTS.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, missing an HIV visit or a dose of ART was common
Social determinants of health were associated with missing an HIV visit
Substance use was associated with missing an HIV visit or ART dose
Disrupted mental health treatment was tied to a missed HIV visit or ART dose
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (U24 DA044554; K01 AA028193; K01 AI125087; K24 AA027483; K08 MH113094; U01 DA036935; U01 AI069918; T32 HP10025; U01 DA0251525; U01 DA036297; K24 AI118591).
Role of Funding Source:
The funding source had no role in the design and conduct of the study, the analysis and interpretation of data, or in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- ART
Antiretroviral therapy
- C3PNO
Collaborating Consortium of Cohorts Producing NIDA Opportunities
- COVID
Coronavirus disease
- HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
- NIDA
National Institute on Drug Abuse
- USAUDIT-C
United States Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test – Consumption questions
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Declaration of Competing Interests: No conflict declared.
Conflict of Interest: No conflict declared.
REFERENCES
- Aidala AA, Lee G, Abramson DM, Messeri P, Siegler A, 2007. Housing need, housing assistance, and connection to HIV medical care. AIDS and Behavior 11(2), 101–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aidala AA, Wilson MG, Shubert V, Gogolishvili D, Globerman J, Rueda S, Bozack AK, Caban M, Rourke SB, 2016. Housing status, medical care, and health outcomes among people living with HIV/AIDS: a systematic review. American journal of public health 106(1), e1–e23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnsten JH, Demas PA, Grant RW, Gourevitch MN, Farzadegan H, Howard AA, Schoenbaum EE, 2002. Impact of active drug use on antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users. Journal of general internal medicine 17(5), 377–381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auchus IC, Jaradeh K, Tang A, Marzan J, Boslett B, 2021. Transitioning to Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Patient Perspectives and Attendance at an HIV Clinic in San Francisco. AIDS Patient Care STDS 35(7), 249–254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batey DS, Kay ES, Westfall AO, Zinski A, Drainoni ML, Gardner LI, Giordano T, Keruly J, Rodriguez A, Wilson TE, Mugavero MJ, 2020. Are missed- and kept-visit measures capturing different aspects of retention in HIV primary care? AIDS Care 32(1), 98–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg KM, Demas PA, Howard AA, Schoenbaum EE, Gourevitch MN, Arnsten JH, 2004. Gender differences in factors associated with adherence to antiretroviral therapy. Journal of general internal medicine 19(11), 1111–1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaskaran K, Rentsch CT, MacKenna B, Schultze A, Mehrkar A, Bates CJ, Eggo RM, Morton CE, Bacon SC, Inglesby P, 2021. HIV infection and COVID-19 death: a population-based cohort analysis of UK primary care data and linked national death registrations within the OpenSAFELY platform. The Lancet HIV 8(1), e24–e32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulle A, Davies M-A, Hussey H, Ismail M, Morden E, Vundle Z, Zweigenthal V, Mahomed H, Paleker M, Pienaar D, 2020. Risk factors for COVID-19 death in a population cohort study from the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Braunstein SL, Lazar R, Wahnich A, Daskalakis DC, Blackstock OJ, 2020. COVID-19 infection among people with HIV in New York City: A population-level analysis of linked surveillance data. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brody JK, Rajabiun S, Strupp Allen HJ, Baggett T, 2021. Enhanced Telehealth Case Management Plus Emergency Financial Assistance for Homeless-Experienced People Living With HIV During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am J Public Health 111(5), 835–838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budak JZ, Scott JD, Dhanireddy S, Wood BR, 2021. The Impact of COVID-19 on HIV Care Provided via Telemedicine-Past, Present, and Future. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 18(2), 98–104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celestin K, Allorant A, Virgin M, Marinho E, Francois K, Honoré JG, White C, Valles JS, Perrin G, De Kerorguen N, Flowers J, Balan JG, Koama JBT, Barnhart S, Puttkammer N, 2021. Short-Term Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on HIV Care Utilization, Service Delivery, and Continuity of HIV Antiretroviral Treatment (ART) in Haiti. AIDS Behav 25(5), 1366–1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M, Gamble T, Hosseinipour MC, Kumarasamy N, Hakim JG, Kumwenda J, Grinsztejn B, Pilotto JH, Godbole SV, Mehendale S, Chariyalertsak S, Santos BR, Mayer KH, Hoffman IF, Eshleman SH, Piwowar-Manning E, Wang L, Makhema J, Mills LA, de Bruyn G, Sanne I, Eron J, Gallant J, Havlir D, Swindells S, Ribaudo H, Elharrar V, Burns D, Taha TE, Nielsen-Saines K, Celentano D, Essex M, Fleming TR, Team HS, 2011. Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med 365(6), 493–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T, Woodward B, Alom S, Harky A, 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outcomes in HIV/AIDS patients: a systematic review. HIV medicine 21(9), 567–577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D, Quimby C, Nunez J, Whitener C, Zurlo J, 2021. People Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Experiences With Telemedicine. Health Promot Pract 22(3), 298–299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costenaro P, Minotti C, Barbieri E, Giaquinto C, Donà D, 2021. SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in people living with HIV: a systematic review. Reviews in medical virology 31(1), 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandachi D, Dang BN, Lucari B, Teti M, Giordano TP, 2020. Exploring the attitude of patients with HIV about using telehealth for HIV care. AIDS Patient Care and STDs 34(4), 166–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger RW, Lerner AM, Fauci AS, 2021. Human Immunodeficiency Virus/AIDS in the Era of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Juxtaposition of 2 Pandemics. The Journal of Infectious Diseases [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- El Moussaoui M, Lambert N, Maes N, Fombellida K, Vaira D, Moutschen M, Darcis G, 2021. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic situation on HIV care in Liège, Belgium. HIV Res Clin Pract 22(3), 63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Nahal WG, Shen NM, Keruly JC, Jones JL, Fojo AT, Lau B, Manabe YC, Moore RD, Gebo KA, Lesko CR, Chander G, 2021. Telemedicine and visit completion among people with HIV during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to pre-pandemic. AIDS [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fadul N, 2020. 112. A Quality Management Project of a Midwestern Academic HIV Clinic Operation During COVID-19: Implementation Strategy and Preliminary Outcomes, Open Forum Infectious Diseases Oxford University Press, p. S184. [Google Scholar]
- Fauci AS, Redfield RR, Sigounas G, Weahkee MD, Giroir BP, 2019. Ending the HIV Epidemic: A Plan for the United States. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association 321(9), 844–845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner EM, McLees MP, Steiner JF, Del Rio C, Burman WJ, 2011. The spectrum of engagement in HIV care and its relevance to test-and-treat strategies for prevention of HIV infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases 52(6), 793–800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geretti AM, Stockdale AJ, Kelly SH, Cevik M, Collins S, Waters L, Villa G, Docherty A, Harrison EM, Turtle L, 2020. Outcomes of COVID-19 related hospitalization among people with HIV in the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol (UK): a prospective observational study. Clinical Infectious Diseases [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Giacomelli A, Bonazzetti C, Conti F, Pezzati L, Oreni L, Micheli V, Mancon A, Vimercati S, Albrecht M, Passerini M, Cossu MV, Capetti AF, Meraviglia P, Antinori S, Rizzardini G, Galli M, Ridolfo AL, 2021. Brief Report: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Virological Suppression in People Living With HIV Attending a Large Italian HIV Clinic. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 88(3), 299–304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach PM, Javanbakht M, Kim S, Ragsdale A, Mandler R, Siminski S, 2020. The HIV care continuum among drug users in the US: Findings from the C3PNO consortium, International Workshop on HIV and Hepatitis Observational Databases. Cancelled due to COVID-19 pandemic
- Gorbach PM, Siminski S, Ragsdale A, Investigators CP, 2021. Cohort profile: the collaborating consortium of cohorts producing NIDA opportunities (C3PNO). International Journal of Epidemiology 50(1), 31–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg AE, Hader SL, Masur H, Young AT, Skillicorn J, Dieffenbach CW, 2009. Fighting HIV/AIDS in Washington, D.C. Health affairs 28(6), 1677–1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris RA, Xue X, Selwyn PA, 2017. Housing stability and medication adherence among HIV-positive individuals in antiretroviral therapy: a meta-analysis of observational studies in the United States. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 74(3), 309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzler B, Dombrowski JC, Williams JR, Crane HM, Eron JJ, Geng EH, Mathews C, Mayer KH, Moore RD, Mugavero MJ, 2018. Influence of substance use disorders on 2-year HIV care retention in the United States. AIDS and Behavior 22(3), 742–751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins-Biddle JC, Babor TF, 2018. A review of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), AUDIT-C, and USAUDIT for screening in the United States: Past issues and future directions. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 44(6), 578–586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insight Start Study Group, Lundgren JD, Babiker AG, Gordin F, Emery S, Grund B, Sharma S, Avihingsanon A, Cooper DA, Fatkenheuer G, Llibre JM, Molina JM, Munderi P, Schechter M, Wood R, Klingman KL, Collins S, Lane HC, Phillips AN, Neaton JD, 2015. Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy in Early Asymptomatic HIV Infection. N Engl J Med 373(9), 795–807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo I, Carriero C, Gardini G, Fumarola B, Chiari E, Castelli F, Quiros-Roldan E, 2021. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on HIV viremia: a single-center cohort study in northern Italy. AIDS Res Ther 18(1), 31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalichman SC, Eaton LA, Berman M, Kalichman MO, Katner H, Sam SS, Caliendo AM, 2020. Intersecting pandemics: Impact of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) protective behaviors on people living with HIV, Atlanta, Georgia. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Leaver CA, Bargh G, Dunn JR, Hwang SW, 2007. The effects of housing status on health-related outcomes in people living with HIV: a systematic review of the literature. AIDS and Behavior 11(2), 85–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko CR, Bengtson AM, 2021. HIV and COVID-19: Intersecting Epidemics With Many Unknowns. American journal of epidemiology 190(1), 10–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer KH, Levine K, Grasso C, Multani A, Gonzalez A, Biello K, 2020. 541. Rapid Migration to Telemedicine in a Boston Community Health Center is Associated with Maintenance of Effective Engagement in HIV Care, Open Forum Infectious Diseases Oxford University Press US, pp. S337–S338. [Google Scholar]
- Mugavero MJ, Lin HY, Allison JJ, Giordano TP, Willig JH, Raper JL, Wray NP, Cole SR, Schumacher JE, Davies S, Saag MS, 2009a. Racial disparities in HIV virologic failure: do missed visits matter? J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 50(1), 100–108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugavero MJ, Lin HY, Willig JH, Westfall AO, Ulett KB, Routman JS, Abroms S, Raper JL, Saag MS, Allison JJ, 2009b. Missed visits and mortality among patients establishing initial outpatient HIV treatment. Clin Infect Dis 48(2), 248–256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugavero MJ, Westfall AO, Cole SR, Geng EH, Crane HM, Kitahata MM, Mathews WC, Napravnik S, Eron JJ, Moore RD, Keruly JC, Mayer KH, Giordano TP, Raper JL, 2014. Beyond core indicators of retention in HIV care: missed clinic visits are independently associated with all-cause mortality. Clin Infect Dis 59(10), 1471–1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugavero MJ, Westfall AO, Zinski A, Davila J, Drainoni ML, Gardner LI, Keruly JC, Malitz F, Marks G, Metsch L, Wilson TE, Giordano TP, Retention in Care Study, G., 2012. Measuring retention in HIV care: the elusive gold standard. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 61(5), 574–580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palepu A, Milloy M, Kerr T, Zhang R, Wood E, 2011. Homelessness and adherence to antiretroviral therapy among a cohort of HIV-infected injection drug users. Journal of Urban Health 88(3), 545–555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L, Rentsch C, Sigel K, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Brown S, Goetz M, 2020. COVID-19 in the largest US HIV cohort. AIDS 2020, 23rd. [Google Scholar]
- Peavy KM, Darnton J, Grekin P, Russo M, Green CJB, Merrill JO, Fotinos C, Woolworth S, Soth S, Tsui JI, 2020. Rapid implementation of service delivery changes to mitigate COVID-19 and maintain access to methadone among persons with and at high-risk for HIV in an opioid treatment program. AIDS and Behavior 24(9), 2469–2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiao S, Li Z, Weissman S, Li X, Olatosi B, Davis C, Mansaray AB, 2021. Disparity in HIV Service Interruption in the Outbreak of COVID-19 in South Carolina. AIDS Behav 25(1), 49–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiros-Roldan E, Magro P, Carriero C, Chiesa A, El Hamad I, Tratta E, Fazio R, Formenti B, Castelli F, 2020. Consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on the continuum of care in a cohort of people living with HIV followed in a single center of Northern Italy. AIDS Res Ther 17(1), 59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao A, Rucinski K, Jarrett BA, Ackerman B, Wallach S, Marcus J, Adamson T, Garner A, Santos G-M, Beyrer C, 2021. Perceived interruptions to HIV prevention and treatment services associated with COVID-19 for gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men in 20 countries. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 87(1), 644–651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway JP, Schmitt J, Friedman E, Taylor M, Devlin S, McNulty M, Pitrak D, 2020. HIV Care Continuum and COVID-19 Outcomes Among People Living with HIV During the COVID-19 Pandemic, Chicago, IL. AIDS and Behavior, 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli MA, Hickey MD, Glidden DV, Nguyen JQ, Oskarsson JJ, Havlir D, Gandhi M, 2020. Viral suppression rates in a safety-net HIV clinic in San Francisco destabilized during COVID-19. Aids 34(15), 2328–2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzian AS, Irvine MK, Hollod LM, Lim S, Rojas J, Shepard CW, 2015. Effect of HIV housing services on engagement in care and treatment, New York City, 2011. AIDS and Behavior 19(11), 2087–2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yehia BR, Stewart L, Momplaisir F, Mody A, Holtzman CW, Jacobs LM, Hines J, Mounzer K, Glanz K, Metlay JP, 2015. Barriers and facilitators to patient retention in HIV care. BMC infectious diseases 15(1), 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelverton V, Qiao S, Weissman S, Olatosi B, Li X, 2021. Telehealth for HIV Care Services in South Carolina: Utilization, Barriers, and Promotion Strategies During the COVID-19 Pandemic. AIDS Behav, 1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zinski A, Westfall AO, Gardner LI, Giordano TP, Wilson TE, Drainoni ML, Keruly JC, Rodriguez AE, Malitz F, Batey DS, Mugavero MJ, 2015. The Contribution of Missed Clinic Visits to Disparities in HIV Viral Load Outcomes. Am J Public Health 105(10), 2068–2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


