Abstract
Bacterial resistance coupled to our current arsenal of antibiotics presents us with a growing threat to public health, thus warranting the exploration of alternative antibacterial strategies. In particular, the targeting of virulence factors has been regarded as a “second generation” antibiotic approach. In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Zn2+ metalloprotease virulence factor, LasB or P. aeruginosa elastase, has been implicated in the development of P. aeruginosa-related keratitis, pneumonia and burn infection. Moreover, the enzyme also plays a critical role in swarming and biofilm formation, both of which are processes that have been linked to antibiotic resistance. To further validate the importance of LasB in P. aeruginosa infection, we describe our efforts toward the discovery of non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors of LasB. Using identified compounds, we have confirmed the role that LasB plays in P. aeruginosa swarming and demonstrate the potential for LasB-targeted small molecules in studying antimicrobial resistant P. aeruginosa phenotypes.
The emergence of antibiotic resistance to nearly all antimicrobial agents on the market today is a great threat to public health, requiring the development of alternative antibacterial strategies. Of these tactics, the targeting of virulence factors has been regarded as a “second generation” antibiotic approach.1–3 Pathogenic bacteria produce virulence factors such as adhesion molecules, secretion systems and other toxic factors including proteases to enhance their ability to cause disease and damage the host's tissues.2, 3 Importantly, because virulence factors do not alter viability, agents targeting such factors should impose weaker selective pressure for the development of resistance.2, 3 Moreover, as many virulence factors are unique to a specific organism, virulence-targeting drugs are unlikely to impact the host's commensal flora.2, 3 The efficacy of exploring such targets remains to be seen; however, inhibitors targeting toxin function and delivery, the regulation of virulence expression and adhesion have been reported with promising in vivo anti-infective properties.2, 3
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a nosocomial, opportunistic Gram-negative bacteria that is the predominant cause of pneumonia in ventilated patients and lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis.4 In addition to respiratory tract infections, the pathogen also causes blood, ear, skin, eye and urinary and gastrointestinal tract infections among others and is responsible for 10–15% of hospital-acquired infections worldwide.4, 5 To promote these clinical manifestations, P. aeruginosa produces a number of surface and secreted virulence factors that facilitate bacterial attachment, colonization and invasion, and tissue damage and cytokine production, respectively.4, 5 Cell-associated virulence factors include flagella, pili, lectins, alginate and lipopolysaccharide while extracellular virulence factors include proteases, hemolysins, cytotoxin, pyocyanin, siderophores and exotoxin A.5 This arsenal of virulence factors ensures that P. aeruginosa infections are both invasive and toxigenic.5 Thus, because of growing antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa including the identification of many multidrug resistant strains,4 new approaches for tackling such infections are warranted.
One P. aeruginosa virulence factor that has been shown to be highly toxic to the host6 is a Zn2+ metalloprotease, LasB or P. aeruginosa elastase,7 which is secreted by the bacteria in a quorum sensing-dependent fashion.8 In particular, LasB has been demonstrated to cause tissue damage and persistent inflammation, degrade plasma proteins and promote invasion and colonization among other pathologies.6 To do so, the enzyme degrades a wide variety of substrates including elastin, fibrin, immunoglobulins, complement factors and cytokines.6 Importantly, infection with a P. aeruginosa strain producing a mutant, inactive elastase was found to be less virulent than the parent strain in a chronic lung infection model in rats.9 Additionally, with respect to the bacteria itself, LasB has been linked to biofilm formation10 and swarming,11 further aiding in its elusion from the host's immune system. Accordingly, LasB has been shown to play a role in the development of P. aeruginosa-related keratitis, pneumonia and burn infection.6
Our laboratories have invested much effort in exploring the modulation of metalloproteases for human health, such as identifying small molecule inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxins,12–18 anthrax lethal factor19–22 and matrix metalloproteinases.21, 22 To do so, we have designed and developed non-peptidic small molecules containing a variety of metal-chelating warheads as active site inhibitors. Because only peptide-based LasB inhibitors have been previously reported23–26 coupled with the potential therapeutic significance of this P. aeruginosa virulence factor, we were interested in expanding the scope of our metalloprotease-targeting design strategies toward the goal of identifying potent small molecule LasB antagonists. Herein, we describe our efforts to discover the first non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors of LasB and validate the role of this virulence factor in swarming, a multicellular bacterial behavior recently linked to antimicrobial resistant phenotypes.27
To initiate our screening efforts, we examined a 323-member small molecule hydroxamic acid library, which was constructed using solid-phase organic synthesis and originally used to identify inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxin A protease.14 All compounds were analyzed for LasB inhibition using a previously reported fluorescence assay based on a LasB-cleavable FRET peptide substrate (see Supporting Information for assay details).23 Library members were initially examined at 50 μM, and from our screening efforts, 8 hits showing 100% inhibition at this concentration were identified following triplicate experiments (see Supporting Information). Of these hit compounds, only two demonstrated dose-dependent LasB antagonism, hydroxamic acids 1 and 2 (Figure 1), with measured IC50 values of 13.6 μM and 16.4 μM, respectively. Despite the in vitro activity of these compounds, unfortunately, no antagonism in bacterial P. aeruginosa elastase assays was observed. One possible explanation for the lack of bacterial cell activity is enzymatic discharging of the hydroxamate moiety, as this chelating motif is known to be unstable.28
Figure 1.
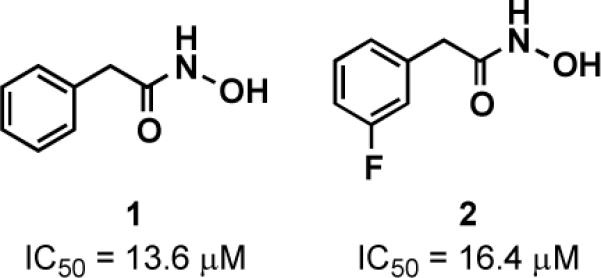
Hydroxamic acid LasB inhibitor hits with IC50 values.
Due to potential instability and off-target effects of the hydroxamate group,28 we were eager to explore additional Zn2+ chelating motifs that may be more stable under biological conditions. Recently, a library of metal chelating fragments (CFL-1.1) was designed by the Cohen laboratory.21, 22 The library consists of 96 fragment chelators, each containing 2–4 donor atoms for metal binding. Some representative library members include picolinic acids, hydroxyquinolones, pyrimidines and hydroxypyrones in addition to other well-known chelating units such as sulfonamides and hydroxamic acids. Members of this fragment library were screened at 1 mM for inhibition of LasB and 11 fragment hits were identified (see Supporting Information). Of these compounds, four showed dose-dependent inhibition of LasB with IC50 values ranging from 80–400 μM (compounds 3–6, Figure 2). Interestingly, all hits contained an O,S atom donor set and have previously been identified from this library as inhibitors of other Zn2+ metalloproteases.19–22
Figure 2.
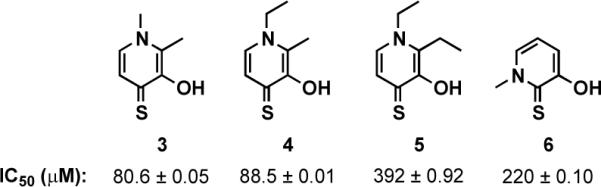
Hit compounds from CFL-1.1 with IC50 values for LasB inhibition.
In order to identify 3,4-HOPTO (3-hydroxy-1-alkyl-2-methylpyridine-4(1H)-thione; 3–5) derivatives with improved in vitro potency against LasB, a sub-library of compounds based on fragments 3 and 4 (see Supporting Information for structures) was screened.21 3,4-HOPTO analogues 8 were constructed via a 1-step condensation of a primary amine with thiomaltol 7 (Scheme 1),21 and initially tested for inhibition at 100 μM. From this sub-library, two compounds were discovered with ~30-fold improvement in potency: analogues 8a and 8b exhibited measured IC50 values of 3.34 μM and 2.73 μM, respectively (Table 1; see Supporting Information for the activity of other sub-library members). Structure-activity relationship studies were then conducted on 8b by varying the substituents of the biphenyl ring; however, no compounds with enhanced LasB inhibition were identified (Table 1). Based on initial docking studies, we hypothesize that the diminished activity of compounds 8c–8g may be due to the restrictive geometry of 3,4-HOPTO–Zn2+ binding which forces the biphenyl side chain into solvent space as the active site of LasB is quite open similar to that of thermolysin (data not shown).23
Scheme 1.
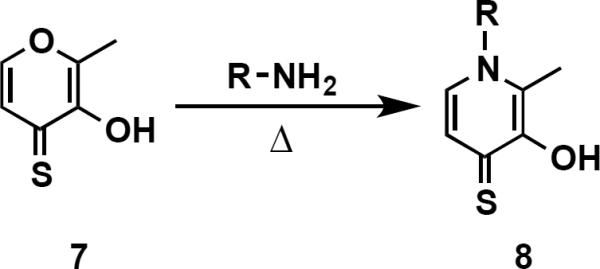
Synthesis of 3,4-HOPTO Analogues
Table 1.
Structures and IC50 Values for 3,4-HOPTO Analogue Hits
| Compound | R | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 8a |
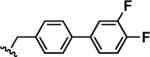
|
3.34 ± 0.03 |
| 8b |
|
2.73 ± 0.03 |
| 8c |
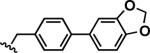
|
3.58 ± 0.05 |
| 8d |
|
4.65 ± 0.17 |
| 8e |
|
6.72 ± 0.01 |
| 8f |
|
8.58 ± 0.01 |
| 8g |
|
5.27 ± 0.01 |
With the in vitro activity of 3,4-HOPTO analogues 8a and 8b confirmed, we were then anxious to examine their activity in a bacterial phenotypic assay, particularly since hydroxamates 1 and 2 displayed no secreted LasB inhibition. In P. aeruginosa, LasB has been demonstrated to be required for both swarming and biofilm formation, and lasB mutants were shown to exhibit strong swarming defects and a ~50% decrease in biofilm formation.11 Swarming and biofilm formation are both social phenomena that require differentiated cells and are regulated by cell-to-cell communication, in particular, quorum sensing.27 Of significance, both bacterial cell states have been found to be highly resistant to antibiotics, and it has recently been hypothesized that antimicrobial resistance is a general feature of bacterial multicellularity.27 As the study of swarming motility is believed to be a useful model to investigate antibiotic resistance in biofilms,27 particularly due to reproducibility issues that often go unreported in biofilm assays, we chose to investigate swarming inhibition in the presence of compounds 8a and 8b.
To examine the effect of compounds 8a and 8b on swarming, P. aeruginosa strain PA14 was grown on swarm agar plates containing 25 μM of 8a or 8b (~95% viability at this concentration; see Supporting Information) for 16 h at 30 °C (see Supporting Information for more detail). As Figure 3 shows, both 8a and 8b almost completely abolished swarming at this concentration in comparison to a DMSO-treated control sample that exhibited a dendritic swarming phenotype typical of P. aeruginosa. We highlight this result as 8a and 8b are the first targeted compounds to show swarming antagonism. Previously, only general virulence factor expression29, 30 and bacterial adhesion inhibitors31 have been examined in swarming assays. Similar to biofilm formation, swarming is also of significance pathologically, as the environment required for swarming motility is similar to that covering epithelial surfaces and the hyperabundant mucous found the in lungs of cystic fibrosis patients.11 Thus, we are hopeful that these compounds will be useful in further understanding the role that LasB plays not only in swarming but also the development of antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa swarm cells and invasion and colonization of tissues by P. aeruginosa.6 Moreover, upon improvement in potency, we are also interested in exploring the applicability of our non-peptidic small molecule LasB inhibitors in animal models of P. aeruginosa infection to study the impact of this metalloprotease in promoting bacterial virulence. Importantly, 3,4-HOPTO derivatives have been previously demonstrated to be nearly non-toxic at concentrations up to 100 μM in mammalian cells.32, 33 We envision that a combination of small molecule LasB inhibitors with traditional antibiotics may represent a new therapy for targeting multidrug resistant P. aeruginosa.
Figure 3.
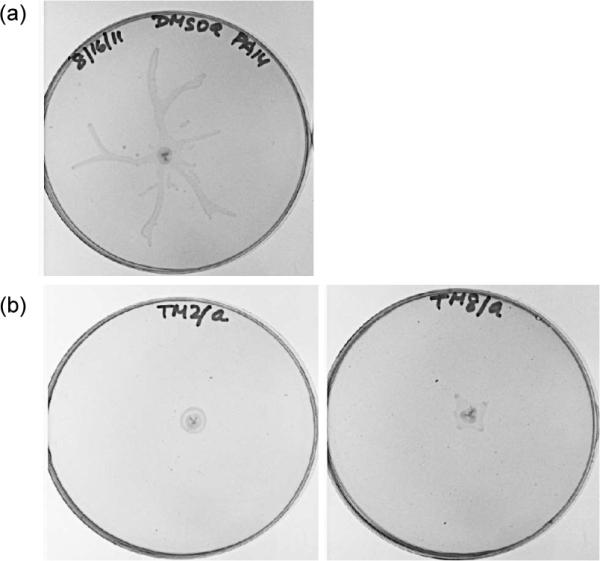
Swarming of P. aeruginosa strain PA14 in the presence of 25 M (a) DMSO (control), (b) 8a (left) or 8b (right).
Lastly, we wish to bring to light that although hydroxamic acids 1 and 2 were only ~5-fold less potent than 3,4-HOPTO analogues 8a and 8b in the in vitro LasB assay, these compounds showed no swarming inhibition (data not shown). As indicated, it is quite possible that instability and off-target effects may be at play as highlighted by others;28 however, it remains to be seen if other factors are involved such as bacterial cell metabolism. Initial stability studies in bacterial culture medium indicate the hydrolytic instability of 1 and 2 in comparison to 8a and 8b which showed no detectable S-oxidation or decomposition over a 48 h period (see Supporting Information). Regardless, compounds 1 and 2 will serve as useful scaffolds for future warhead “hopping” experiments, and these studies will be reported in due course.
In conclusion, we have identified small molecule, Zn2+-chelating inhibitors of the P. aeruginosa elastase LasB with anti-swarming activity. Although compounds 8a and 8b are not the most potent LasB inhibitors to date, they are the first non-peptidic small molecule antagonists discovered.26 Moreover, they are the first targeted compounds to exhibit swarming inhibition. Based on our preliminary findings described here, LasB-targeted chemical probes should aid in elucidating the role of LasB in P. aeruginosa-related infections and its ability to resist antibiotics. Additionally, the discovery and study of such small molecule virulence factor inhibitors will provide additional evidence to discern the impact of targeting bacterial virulence factors as a “second generation” antibiotic approach.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Mr. Greg McElhaney for the preparation of compounds 8a and 8e–8g.
Funding Sources This work was funded by the NIH (Grants R01 AI077644 to K.D.J. and R01 GM098435 to S.M.C.).
ABBREVIATIONS
- P. aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- LasB
P. aeruginosa elastase
- FRET
fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- 3,4-HOPTO
3-hydroxy-1-alkyl-2-methylpyridine-4(1H)-thione
Footnotes
Supporting Information. Representative synthetic procedure, characterization of compounds 8a and 8c–8g, LasB fluorescence assay protocol, supplemental screening results, stability and bacterial toxicity of 8a and 8b, and swarming details. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Author Contributions The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Travis J, Potempa J. Bacterial proteinases as targets for the development of second-generation antibiotics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1477:35–50. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(99)00278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Clatworthy AE, Pierson E, Hung DT. Targeting virulence: a new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007;3:541–548. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barczak AK, Hung DT. Productive steps toward an antimicrobial targeting virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009;12:490–496. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.06.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mesaros N, Nordmann P, Plesiat P, Roussel-Delvallez M, Van Eldere J, Glupczynski Y, Van Laethem Y, Lebecque P, Malfroot A, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: resistance and therapeutic options at the turn of the millennium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007;13:560–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Strateva T, Mitov I. Contribution of an arsenal of virulence factors to pathogenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Ann. Microbiol. 2011;61:717–732. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wretlind B, Pavlovskis OR. Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase and its role in pseudomonas infections. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983;5:S998–S1004. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_5.s998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Morihara K, Tsuzuki H, Oka T, Inoue H, Ebata M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase: isolation, crystallization, and preliminary characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1965;240:3295–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pearson JP, Gray KM, Passador L, Tucker KD, Eberhard A, Iglewski BH, Greenberg EP. Structure of the autoinducer required for expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U. S. A. 1994;91:197–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Woods DE, Cryz SJ, Friedman RL, Iglewski BH. Contribution of toxin A and elastase to virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic lung infections in rats. Infect. Immun. 1982;36:1223–1228. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1223-1228.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kamath S, Kapatral V, Chakrabarty AM. Cellular function of elastase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: role in the cleavage of nucleotide diphosphate kinase and in alginate synthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 1998;30:933–941. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Overhage J, Bains M, Brazas MD, Hancock REW. Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a complex adaptation leading to increased production of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance. J. Bacteriol. 2008;190:2671–2679. doi: 10.1128/JB.01659-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boldt GE, Eubanks LM, Janda KD. Identification of a botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitor displaying efficacy in a cellular model. Chem. Commun. 2006:3063–3065. doi: 10.1039/b603099h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boldt GE, Kennedy JP, Hixon MS, McAllister LA, Barbieri JT, Tzipori S, Janda KD. Synthesis, characterization and development of a high-throughput methodology for the discovery of botulinum neurotoxin A inhibitors. J. Comb. Chem. 2006;8:513–521. doi: 10.1021/cc060010h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Boldt GE, Kennedy JP, Janda KD. Identification of a potent botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitor using in situ lead identification chemistry. Org. Lett. 2006;8:1729–1732. doi: 10.1021/ol0603211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Capkova K, Yoneda Y, Dickerson TJ, Janda KD. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of second-generation hydroxamate botulinum neurotoxin A protease inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007;17:6463–6466. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.09.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Capkova K, Salzameda NT, Janda KD. Investigations into small molecule non-peptidic inhibitors of the botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon. 2009;54:575–582. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.03.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Capkova K, Hixon MS, Pellett S, Barbieri JT, Johnson EA, Janda KD. Benzylidene cyclopentenediones: first irreversible inhibitors against botulinum neurotoxin A's zinc endopeptidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010;20:206–208. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.10.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stowe GN, Silhar P, Hixon MS, Silvaggi NR, Allen KN, Moe ST, Jacobson AR, Barbieri JT, Janda KD. Chirality holds the key for potent inhibition of the botulinum neurotoxin serotype A protease. Org. Lett. 2010;12:756–759. doi: 10.1021/ol902820z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lewis JA, Mongan J, McCammon JA, Cohen SM. Evaluation and binding-mode prediction of thiopyrone-based inhibitors of anthrax lethal factor. ChemMedChem. 2006;1:694–697. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200600102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Agrawal A, de Oliveira CAF, Cheng Y, Jacobsen JA, McCammon JA, Cohen SM. Thioamide hydroxypyrothiones supersede amide hydroxypyrothiones in potency against anthrax lethal factor. J. Med. Chem. 2009;52:1063–1074. doi: 10.1021/jm8013212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Agrawal A, Johnson SL, Jacobsen JA, Miller MT, Chen L, Pellecchia M, Cohen SM. Chelator fragment libraries for targeting metalloproteinases. ChemMedChem. 2010;5:195–199. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200900516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jacobsen JA, Fullager JL, Miller MT, Cohen SM. Identifying chelators for metalloprotein inhibitors using a fragment-based approach. J. Med. Chem. 2011;54:590–602. doi: 10.1021/jm101266s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nishino N, Powers JC. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Elastase: development of a new substrate, inhibitors, and an affinity ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 1980;255:3482–3486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kessler E, Israel M, Landshman N, Chechick A, Blumberg S. In vitro inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by metal-chelating peptide derivatives. Infect. Immun. 1982;38:716–723. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.716-723.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cathcart GR, Gilmore BF, Greer B, Harriott P, Walker B. Inhibitor profiling of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor LasB using N-alpha mercaptoamide template-based inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19:6230–6232. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cathcart GR, Quinn D, Greer B, Harriott P, Lynas JF, Gilmore BF, Walker B. Novel inhibitors of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor LasB: a potential therapeutic approach for the attenuation of virulence mechanisms in pseudomonal infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55:2670–2678. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00776-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lai S, Tremblay J, Deziel E. Swarming motility: a multicellular behavior conferring antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Microbiol. 2009;11:126–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Flipo M, Charton J, Hocine A, Dassonneville S, Deprez B, Deprez-Poulain R. Hydroxamates: relationships between structure and plasma stability. J. Med. Chem. 2009;52:6790–6802. doi: 10.1021/jm900648x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee J, Attila C, Cirillo SLG, Cirillo JD, Wood TK. Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009;2:75–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wu H, Lee B, Yang L, Wang H, Givskov M, Molin S, Hoiby N, Song Z. Effects of ginseng on Pseudomonas aeruginosa motility and biofilm formation. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011;62:49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.O'May C, Tufenkji N. The swarming motility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is blocked by cranberry proanthocyanidins and other tannin-containing materials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77:3061–3067. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02677-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Puerta DT, Griffin MO, Lewis JA, Romero-Perez D, Garcia R, Villarreal FJ, Cohen SM. Heterocyclic zinc-binding groups for use in next-generation matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: potency, toxicity, and reactivity. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2006;11:131–138. doi: 10.1007/s00775-005-0053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jacobsen FE, Buczynski MW, Dennis EA, Cohen SM. A macrophage cell model for selective metalloproteinase inhibitor design. ChemBioChem. 2008;9:2087–2095. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


