Abstract
Cancer invasion is a hallmark of metastasis. The mesenchymal mode of cancer cell invasion is mediated by elongated membrane protrusions driven by the assembly of branched F-actin networks. How deregulation of actin regulators promotes cancer cell invasion is still enigmatic. We report that increased expression and membrane localization of the actin regulator Lamellipodin correlates with reduced metastasis-free survival and poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. In agreement we find that Lamellipodin depletion reduced lung metastasis in an orthotopic mouse breast cancer model. Invasive 3D cancer cell migration as well as invadopodia formation, and matrix degradation were impaired upon Lamellipodin depletion. Mechanistically, we show that Lamellipodin promotes invasive 3D cancer cell migration via both actin-elongating Ena/VASP proteins and the Scar/WAVE complex, which stimulates actin branching. In contrast, Lamellipodin interaction with Scar/WAVE but not Ena/VASP is required for random 2D cell migration. We identify a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism that regulates selective recruitment of these effectors to Lamellipodin: Abl-mediated Lamellipodin phosphorylation promotes its association with both Scar/WAVE and Ena/VASP, while Src-dependent phosphorylation enhances binding to Scar/WAVE but not Ena/VASP. Through these selective, regulated interactions Lamellipodin mediates directional sensing of EGF gradients and invasive 3D migration of breast cancer cells. Our findings imply that increased Lamellipodin levels enhance Ena/VASP and Scar/WAVE activities at the plasma membrane to promote 3D invasion and metastasis.
Keywords: Lamellipodin, breast cancer metastasis, 3D migration, Ena/VASP proteins, Scar/WAVE complex
Introduction
Breast cancer metastasis is one of the leading causes of cancer-associated mortality in women worldwide1. Metastasis is a multistep process2. After breaching the basement membrane metastasizing cancer cells migrate through the dense extracellular matrix (ECM) of the tumor stroma in order to intravasate2,3. Carcinoma cells that migrate in a mesenchymal mode form elongated membrane protrusions driven by the assembly of branched F-actin networks. Actin polymerization-driven migration and invasion is coordinated by the proto-oncogenes c-Src and c-Abl kinases and cytoskeletal regulatory proteins including Rac GTPase, the Scar/WAVE-complex, and Ena/VASP proteins4–7.
Ena/VASP proteins (Mena, EVL and VASP) enhance processive filament elongation8–14. Mena is up-regulated in breast cancer and promotes invasion15,16. We identified Lamellipodin (Lpd) as a binding partner of Ena/VASP proteins5,17,18. Lpd localizes to lamellipodia, thin membrane protrusions at the leading edge of migrating cells17. The Lpd–Ena/VASP interaction is positively regulated by Abl kinase-mediated Lpd phosphorylation, which drives Ena/VASP recruitment to lamellipodia by Lpd19.
Lpd is required for lamellipodium formation17 and binds directly to the Scar/WAVE-complex20. Scar/WAVE activates the Arp2/3 complex to nucleate branched actin networks during lamellipodia formation4–7. Surprisingly, Lpd-driven random cell migration in 2D requires Lpd binding to Scar/WAVE, but not to Ena/VASP20.
The mechanisms by which actin regulators coordinate the interplay between actin-elongation and actin-branching factors to promote cancer cell invasion remain incompletely understood. Here we report that Lamellipodin mediates invasive 3D migration of cancer cells via selective, regulated interactions with Ena/VASP and Scar/WAVE. Our findings point to key roles for increased Lpd levels in breast cancer invasion and metastasis.
Results
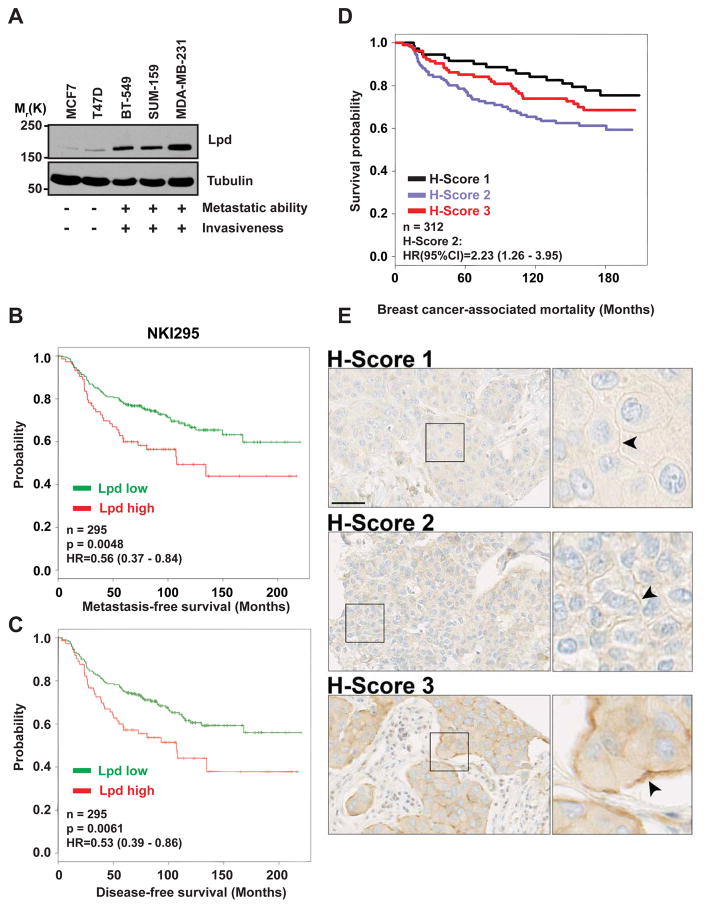
We observed higher Lpd levels in invasive and metastatic basal cell lines compared to non-invasive, luminal tumor cell lines (Figure 1A). Therefore, we analyzed publicly available datasets21 to examine whether Lpd mRNA levels correlated with occurrence of distant metastases in breast cancer patients. Lpd was over-expressed in several types of breast tumors compared to matched healthy tissue (Supplemental Figure 1A). High levels of Lpd mRNA correlated with reduced metastasis-free, and disease-free survival of breast cancer patients in three separate cohorts22–24 (Figure 1B,C; Supplemental Figure 1B,C). In addition, we explored whether Lpd protein expression levels correlate with clinical outcome for breast cancer patients by staining a tumor microarray (TMA)25 generated from 312 patients with invasive breast cancer with anti-Lpd antibodies. Moderately, but not highly, increased abundance of Lpd in the cytoplasm (Histoscore 2; Hazard ratio (HR) (95% CI): 1.765 (1.026–3.036); Supplemental Figure 1D and 2A,B) and at the plasma membrane (Histoscore 2: HR, (95% CI): 2.231 (1.26–3.949); Figure 1D,E; compared to respective histoscores 1) were significantly associated with increased risk of breast cancer-associated mortality. Furthermore, we observed an inverse correlation between Lpd intensity at the plasma membrane and Her2 expression (Supplemental Figure 1E). Consistent with Lpd’s predominant role at the plasma membrane in promoting cell motility and migration17,19,20, we observed a significant association between highly, but not moderately, increased Lpd staining intensity at the plasma membrane and reduced disease-free (Histoscore 3: HR (95% CI): 1.652 (1.24–2.428)) and metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients (Histoscore 3: HR (95% CI): 1.515 (1.054–2.178); Figure 1E compared to respective histoscores 1).
Figure 1. Increased Lpd expression correlates with poor prognosis for breast cancer patients.
(A) Western blot analysis of Lpd expression in human breast cancer cell lines with varying metastatic potential. Loading control: Tubulin. (B) Kaplan-Meier analysis of metastasis-free survival in the NKI295 data set. Patients were stratified by expression of Lpd. The p value was calculated by a log rank test. (C) Kaplan-Meier analysis of disease-free survival in the NKI295 data set. Patients were stratified by expression of Lpd. The p value was calculated by a log rank test. (D) Kaplan Meier plots of breast cancer associated mortality of histoscore 1–3 for Lpd intensity at the plasma membrane. Histoscore 2: Hazard Ratio (HR) (95% CI): 2.23 (1.26–3.95). (E) Representative examples of Lpd immunohistochemistry staining for histoscore 1–3 for Lpd staining intensity at the plasma membrane. Scale bar, 5 μm. See also Figure S1 and S2.
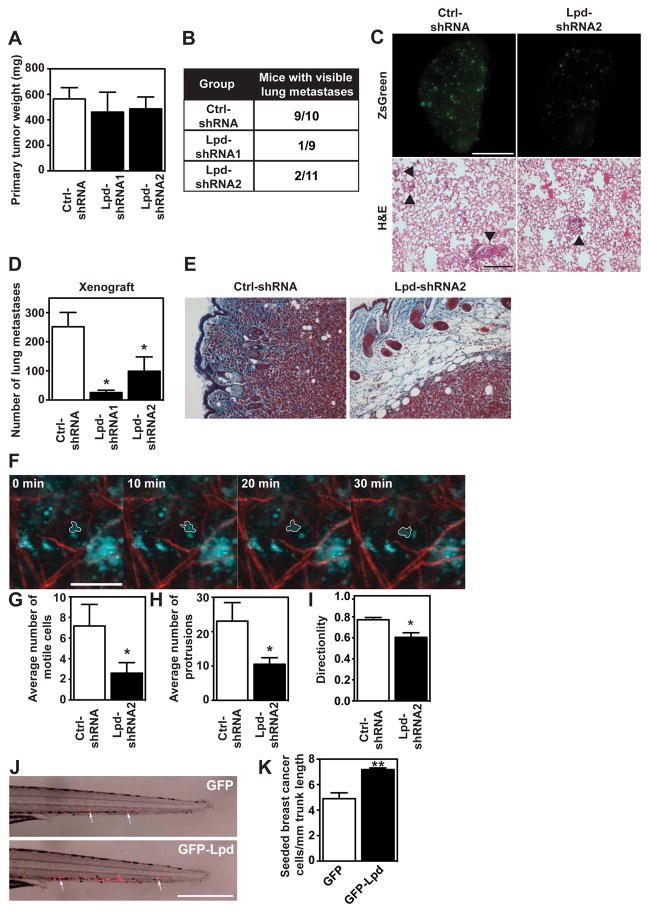
To investigate the requirement for Lpd in metastasis, we tested the effect of reducing Lpd expression in MDA-MB-231-LM2 cells (further referred to as LM2), a highly metastatic derivative of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells26, on their ability to metastasize from an orthotopic mammary tumor to the lungs. We generated stable LM2 cell lines with two independent Lpd-targeting shRNAs or a non-targeting control shRNA, all three retroviruses also conferring the cis-linked marker ZsGreen (Supplemental Figure 2C). Lpd knockdown and control cells were injected orthotopically into the mammary fat pad of immunodeficient mice. Primary tumors formed six weeks after injection from Lpd-deficient cells were similar in size to those arising from control LM2 cells, suggesting that loss of Lpd did not affect primary tumor growth (Figure 2A). Importantly, only 3 out of 20 mice bearing Lpd-depleted tumors developed macroscopic lung metastases, compared to 9 out of 10 control tumor-bearing mice (Figure 2B). In addition, animals with tumors generated from Lpd-depleted cells that metastasized displayed significantly reduced numbers of pulmonary ZsGreen-positive metastases compared to the metastatic burden of animals with control tumors (Figure 2C,D).
Figure 2. Lpd is required for lung metastasis from orthotopic mammary tumors.
(A–E) NOD/SCID/IL2Rγ-null nice were injected orthotopically with LM2 cells stably expressing Ctrl-shRNA or Lpd-shRNA1 or Lpd-shRNA2. Tumors were allowed to grow for 6 ± 0.5 weeks. (A) Primary tumor weights at sacrifice of individual mice are shown. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Number of animals per group is indicated in Figure 2B. (B) The number of mice that presented with visible metastases in the lung is indicated. (mice with lung metastases/ total number of mice analyzed) (C) Representative images of whole left pulmonary lobe from LM2 (control or knockdown)-tumor-bearing mice with ZsGreen-positive metastatic foci (top panel). Scale bar, 5 mm. Representative lung sections stained with H&E, arrowhead indicates presence of metastatic foci (bottom panel). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Numbers of ZsGreen-positive metastatic foci in the left pulmonary lobe were counted. Quantification of data shown in (C, top panel). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.05. Number of animals per group is indicated in Figure 2B. (E) Representative images of paraffin tissue sections stained with Masson’s trichrome of primary tumors to show local invasion. Scale Bar, 20 μm. (F–I) Tumor cell motility in vivo monitored by multi-photon confocal imaging. (F) Image shows a Ctrl-shRNA Zsgreen-tumor. Cyan= Zsgreen-positive cells, red = collagen fibers. One motile Ctrl-shRNA-expressing tumor cell is outlined. Scale bar 40 μm. (G) The average numbers of motile cells per field were determined. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; *P ≤ 0.05, n=5 mice per group. (H) The average numbers of cells extending protrusions per field were determined. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m; unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05; n=5 mice per group. (I) Directionality of the motile cells (net path/total path) was determined. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m; unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05; n=5 mice per group.
(J,K) Red fluorescently labeled MDA-MB-231 cells overexpressing GFP-Lpd or GFP as control were implanted into the perivitelline cavity of zebrafish embryos and dissemination to the trunk region quantified two days after injection. (J) Image of representative zebrafish trunks, two days after injection. Arrows point to seeded tumor cells. Scale bar, 500 μm. (K) Quantified data from (J) represented as mean number of seeded tumor cells per mm of trunk length. mean ± s.e.m, data from 53 fish embryos for GFP and 49 fish embryos for GFP-Lpd from 3 independent experiments; t-test; ** P ≤ 0.01. See also Figure S2.
We then explored whether Lpd promotes cancer cell invasion during metastasis. In fixed samples, tumors generated from control-shRNA LM2 cells, prominently invaded the surrounding stroma. However, tumors from Lpd knockdown cells were markedly less invasive (Figure 2E). We investigated Lpd function in cancer invasion in more detail by intravital imaging. Compared to control-shRNA LM2 tumors, Lpd knockdown tumors had fewer motile cells, which migrated less directionally and extended protrusions less frequently (Figure 2F,G,H,I; Supplemental Video 1, 2), indicating that Lpd is required for invasive cancer cell phenotypes in vivo.
To examine Lpd-driven breast cancer intravasation and dissemination, we implanted fluorescently labeled MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells into the perivitelline cavities of zebrafish embryos. In this assay, the injected cancer cells intravasate, and then infiltrate the trunk of the fish27,28. Overexpression of GFP-Lpd in MDA-MB-231 cells enhanced the frequency of seeding of these breast cancer cells compared to GFP expressing control cells (Figure 2J,K). We then performed tail vein injections of the Lpd knockdown and control LM2 cell lines into immunocompromised mice and quantified lung metastases after 28 days to test whether Lpd influenced the later stages of the metastatic cascade. Lpd depletion did not reduce the number of metastatic foci in the lungs of the mice compared to controls (Supplemental Figure 2D,E). Taken together, our results reveal that Lpd promotes local tumor invasion, intravasation, and metastasis in vivo, but is not required for extravasation.
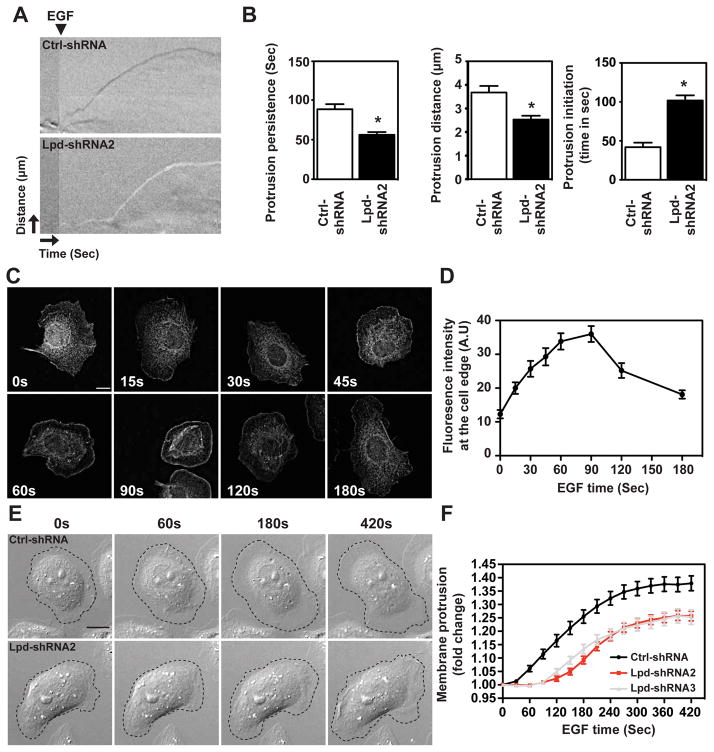
Breast cancer cell migration towards blood vessels is guided by cues from the tumor microenvironment, such as EGF29. We reasoned that the effect of Lpd depletion on EGF-induced 3D invasion might arise from defects in lamellipodial dynamics. Depletion of Lpd in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells decreased lamellipodia size (Supplemental Figure 3A), similar to B16-F1 mouse melanoma cells, in which Lpd-depletion also reduces protrusion speed under steady state conditions17. EGF-stimulated MDA-MB-231 Lpd knockdown cells displayed reduced protrusion persistence and distance, without affecting protrusion speed (Supplemental Figure 3B). We chose MTLn3 cells, a mammary adenocarcinoma cancer cell line, in which protrusion responses to EGF have been extensively characterized, to examine EGF-elicited protrusion in more detail since lamellipodial size is least affected by Lpd knockdown in this cell line (Supplemental Figure 3A). In agreement with our findings in MDA-MB-231 cells, in EGF-stimulated MTLn3 cells reduced Lpd levels significantly decreased protrusion persistence and distance (Figure 3A,B), but did not affect protrusion speed (Supplemental Figure 3D) compared to controls. Lpd was diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm of serum-starved cells, but was rapidly recruited to the cell edge following bath application of EGF (Figure 3C,D). Lamellipodial initiation was detected 30 seconds after EGF stimulation in Ctrl-shRNA-expressing cells, but was delayed significantly when Lpd levels were reduced (Figure 3B,E,F; Supplemental Figure 3E; Supplemental Videos 3, 4). Taken together, our data suggest that in breast cancer cells, Lpd depletion reduces EGF-elicited lamellipodial protrusion formation and persistence, but not speed.
Figure 3. Lpd is required for EGF-induced membrane-protrusion.
(A) Representative kymographs of Ctrl-shRNA and Lpd-shRNA2 MTLn3 cells. A line drawn perpendicular to the cell surface is shown for each frame of a time-lapse movie to depict temporal dynamics of cell edge. X-axis: time (arrow length: 20 seconds); Y-axis: distance (arrow length: 3.1 μm). (B) Quantification of protrusion parameters from kymographic analysis of Ctrl-shRNA and Lpd-shRNA2 MTLn3 cells. Data represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05. (C) Micrographs showing immunofluorescence for endogenous Lpd in MTLn3 cells stimulated with 5 nM EGF (post-stimulation time is indicated). Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Quantification of data shown in (C): mean fluorescence intensity of Lpd within a 0.66μm zone at the lamellipodial edge is plotted as a function of time; >30 cells analyzed from at least three independent experiments. Error bars indicate s.em. (E) Representative micrographs from time-lapse movies of Ctrl-shRNA (control non-targeting shRNA) and Lpd-shRNA2 expressing MTLn3 cells stimulated with 5nM EGF. Dashed line shows cell edge. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Quantification of membrane protrusions on Ctrl-shRNA and Lpd-shRNA treated cells. Cell area was determined after EGF stimulation and normalized to the pre-treatment cell area; >30 cells analyzed from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate s.e.m. See also Figure S3.
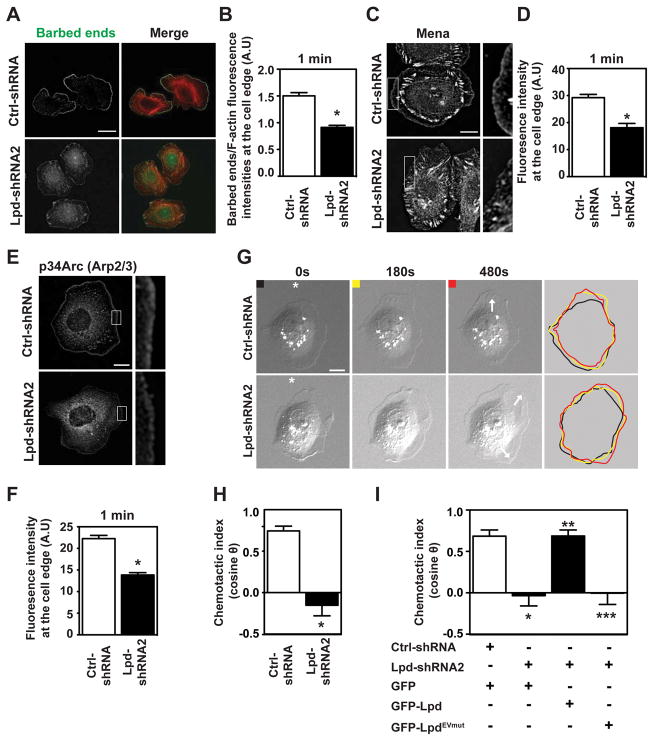
Membrane extension during lamellipodial protrusion is driven by actin polymerization4–6. To determine how Lpd depletion influences actin polymerization, we used a G-actin incorporation assay30 to measure the abundance and distribution of polymerization-competent, free (uncapped) F-actin barbed-ends in lamellipodia of living cells. Silencing Lpd significantly reduced free barbed-end formation 1 minute after EGF stimulation, relative to Ctrl-shRNA-expressing cells (Figure 4A,B). Collectively, these data indicate that Lpd promotes lamellipodial protrusion by increasing actin polymerization downstream of EGFR activation.
Figure 4. Lpd is required for chemosensing.
(A) Barbed-end incorporation after 5 nM EGF stimulation in Ctrl-shRNA- and Lpd-shRNA2-MTLn3 cells. Fixed cells expressing rhodamine-labeled actin were co-stained with phalloidin. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Relative number of barbed-ends incorporation at the lamellipodium edge at 1 min after 5 nM EGF stimulation; over 60 cells analyzed. (n=3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05. (C) Mena immunofluorescence in Ctrl-shRNA and Lpd-shRNA2 MTLn3 cells. Cells were stimulated for 1 min with 5 nM EGF. Insets show enlarged image of Mena staining. Scale bar, 10μm. (D) Quantification of data shown in (C); mean fluorescence intensity of Mena at the lamellipodium edge (within 0.66μm of leading edge); over 45 cells analyzed. (n=3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05. (E) p34Arc immunofluorescence in Ctrl-shRNA- and Lpd-shRNA2-MTLn3 cells, 1 min after 5 nM EGF stimulation. Insets show enlarged image of p34Arc staining. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Quantification of data shown in (E); mean fluorescence intensity of p34Arc at the lamellipodium edge (within 0.66 μm of the leading edge); over 45 cells analyzed. (n=3). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05. (G) Representative micrographs from time-lapse movies of Ctrl-shRNA- and Lpd-shRNA2-MTLn3 cells stimulated with an EGF-filled micropipette (position indicated by asterisk). White arrows on the 480s frames indicate the directions of protrusion overtime. Scale bar, 10 μm. Colored lines indicate cell contour. (H) Quantification of chemotactic index of Ctrl-shRNA- and Lpd-shRNA2-MTLn3 cells. Over 25 cells analyzed from at least three independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Unpaired t-test; * P ≤ 0.05. (I) Quantification of chemotactic index of Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 cells transfected with GFP-vector (n = 13 cells); and Lpd-shRNA2 MTLn3 cells transfected with either GFP-vector (n = 22 cells), GFP-Lpd (n = 17 cells) or GFP-LpdEVmut (n = 17 cells). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Bonferroni’s test; * P ≤ 0.05 vs Ctrl-shRNA+GFP; ** P ≤ 0.05 vs Lpd-shRNA2+GFP; *** P ≤ 0.05 vs Lpd-shRNA2+GFP-Lpd. The difference between Lpd-shRNA2+GFP and Lpd-shRNA2+GFP-LpdEVmut was not significant. See also Figure S4 and S5.
EGF-dependent membrane protrusion in MTLn3 cells requires Ena/VASP proteins and Arp2/3-mediated dendritic nucleation16,31 and Lpd binds both Ena/VASP proteins and the Arp2/3 activating Scar/WAVE-complex17,19,20. Consistent with this, membrane recruitment of Mena (Figure 4C,D) and Arp2/3 complex to the protruding edge (Figure 4E,F) were significantly reduced in Lpd-depleted cells after EGF stimulation.
We hypothesized that the requirement for Lpd in EGF-induced protrusion reflects Lpd-mediated initiation of chemotactic responses. The initial step of chemotaxis is directional sensing32,33. We used a micropipette to generate a spatially restricted EGF gradient. Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 cells formed new protrusions towards the pipette, demonstrating their ability to sense the EGF gradient. However, those of Lpd-reduced cells were random relative to the micropipette (Figure 4G,H; Supplemental Figure 4A,B; Supplemental Video 5, 6). Chemotactic indices confirmed the lack of directional bias in Lpd-deficient MTLn3 protrusions (Figure 4H), highlighting an essential role for Lpd in the initial steps of chemotaxis towards EGF.
Lpd is concentrated at the edges of lamellipodia that protrude in response to uniform EGF stimulation. Correlative differential interference contrast microscopy and immunofluorescence imaging in live cells revealed enrichment of Lpd at the edges of cells oriented towards the micropipettes containing EGF (Supplemental Figure 4C), confirming that Lpd was enriched in membranes exposed to the highest concentration of the EGF gradient and supporting a function for Lpd in linking gradient-sensing to directed membrane protrusion.
We hypothesized that EGF chemosensing might involve Lpd-mediated recruitment of Ena/VASP proteins. We tested whether Lpd-depleted cells, expressing either GFP-Lpd or an Lpd mutant in which all Ena/VASP binding sites had been rendered non-functional by mutation (GFP-LpdEVmut), could respond to EGF gradients in the micropipette assay and discovered that, while GFP-Lpd effectively rescued the chemosensing defects in Lpd-depleted cells, GFP-LpdEVmut conferred no significant phenotypic rescue (Figure 4I and Supplemental Figure 5C). In line with this finding, a function-perturbing approach34 revealed that Ena/VASP proteins were required for chemosensing (Supplemental Figure 5A,B). Thus, extension of lamellipodia towards EGF during chemosensing by breast carcinoma cells requires the Lpd-dependent recruitment of Ena/VASP proteins, despite the dispensability of Ena/VASP for Lpd-driven random 2D cell migration.
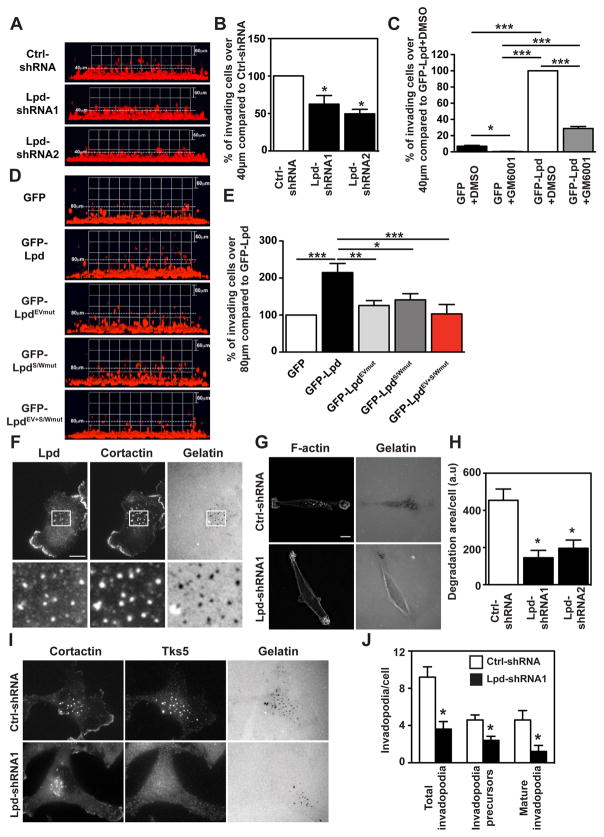
We next analyzed the requirements for Lpd during EGF-dependent 3D invasion. In 3D inverted chemotaxis assays towards EGF with MDA-MB-231 or SUM-159 invasive breast cancer lines35,36 knockdown of Lpd significantly decreased invasion through matrigel (Figure 5A,B; Supplemental Figure 6A) and collagen (Supplemental Figure 6B,C,D) compared to control-shRNA expressing cells. Conversely, Lpd overexpression significantly increased invasion towards EGF (Figure 5D,E).
Figure 5. Lpd is required for 3D-invasion of cancer cells.
(A–B) Inverted invasion assays were performed using MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing mCherry-H2B (labeling the nucleus) transfected with Ctrl-shRNA, Lpd-shRNA1, or Lpd-shRNA2. Additionally cells were co-transfected with empty Blasticidin vector as well and transfected cells were selected. The nuclei of the cells were visualized using confocal microscopy. (A) The image stacks were processed by Volocity software to make a 3D reconstruction. (B) Quantification of the number of nuclei of invading cells above 40μm from the data shown in (A). n=4 (with approximately 4000 cells per experiment). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.05. (C) Inverted invasion assays with GFP or GFP-Lpd expressing MDA-MB-231 cells treated with the MMP inhibitor 10μM GM6001 or just the solvent DMSO as control. Quantification of the number of nuclei of invading cells above 40μm from the data shown in Supplementary Figure 6E. n=3. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Tukey’s; * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001. (D) Inverted invasion assays were performed using MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stably expressing mCherry-H2B (labeling the nucleus) transfected with GFP-Lpd, GFP-LpdEVmut, GFP-LpdS/Wmut, GFP-LpdEV+S/Wmut, or GFP empty vector as control. The nuclei of the cells were visualized using confocal microscopy. The image stacks were processed by Volocity software to make a 3D reconstruction. (E) Quantification of the number of nuclei of invading cells above 40μm from the data shown in (D). n=3 (with approximately 4000 cells per experiment). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001. (F) MDA-MB-231 plated on Alexa 488 gelatin/fibronectin matrix, fixed, and stained for Lpd, and the invadopodia marker cortactin. White boxes: enlarged images shown in insets. Scale bar: 10 μm. (G) Steady-state assay for invadopodial matrix degradation. MDA-MB-231 cells were plated for 8 hours on Alexa 488-gelatin/fibronectin matrices, fixed and stained with phalloidin. Scale bar, 10 μm. (H) Quantification of data shown in (G): invadopodial degradation area/cells in the steady-state matrix degradation assay, normalized to number of cells/field. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. (n=3). Mann-Whitney test; *, P < 0.05. (I) MDA-MB-231 stably expressing Ctrl-shRNA or Lpd-shRNA cells were plated on 405-gelatin and immunostained with cortactin and Tks5 antibodies to identify invadopodia. Scale bar, 10 μm. (J) Quantification of data shown in (I); Number of total invadopodia, invadopodia precursors and mature invadopodia per cell were determined; Ctrl-shRNA cells (n=52) or Lpd-shRNA cells (n=57). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Mann-Whitney test; *, P < 0.05.
See also Figure S6.
Since invasion is known to be partially dependent on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) digestion of ECM, we tested whether Lpd increases invasion via MMP-dependent or migration-dependent mechanisms. MMP inhibitor treatment of GFP expressing control cells reduced invasion, as expected. Similarly, MMP inhibitor treatment reduced invasion of Lpd overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells. However, Lpd overexpressing cells treated with MMP inhibitors invaded significantly further compared to GFP control cells treated with the inhibitor suggesting that Lpd functions to increase invasion by increasing migration and potentially MMP-dependent ECM degradation (Figure 5C and Supplementary Figure 6E).
The aforementioned findings prompted us to investigate Lpd’s role in MMP dependent degradation. Carcinoma cells can utilize protrusive invadopodia, sites of MMP exocytosis, to invade through the basement membrane and ECM-rich interstitial stroma37–39. We observed that Lpd co-localized with the invadopodial marker cortactin at invadopodia, at sites of matrix degradation (Figure 5F). Previously, we reported that Mena promotes invadopodium stabilization and matrix degradation16, and here we observed that Lpd depletion appeared to reduce the amount of Mena within invadopodia considerably, potentially reflecting a role for Lpd in Mena recruitment to invadopodia (Supplemental Figure 6H). Silencing of Lpd in MDA-MB-231 cells decreased the number of precursors, mature invadopodia, and the total number of invadopodia in comparison to control cells (Figure 5I,J). Furthermore, Lpd-depleted MDA-MB-231 cells exhibited a significant decrease in their ability to degrade matrix relative to control cells (Figure 5G,H). Taken together, these results suggest that Lpd is required for invadopodial precursor formation or for both precursor formation and subsequent stabilization/maturation, and for invadopodia-mediated matrix degradation.
To test the relative contribution of Lpd interactions with Ena/VASP proteins or with the Scar/WAVE-complex during MDA-MB-231 3D invasion, we overexpressed a panel of Lpd mutants in which all Ena/VASP (GFP-LpdEVmut), all Scar/WAVE-binding sites (GFP-LpdS/Wmut), or all Ena/VASP and all Scar/WAVE-binding sites (GFP-LpdEV+S/Wmut) had been mutated. All of these mutants localized to the leading edge of MDA-MB-231 cells (Supplemental Figure 6F,G). At steady state when embedded in 3D matrigel, MDA-MB-231 cells overexpressing GFP-Lpd displayed significantly more protrusions, which protruded faster compared to GFP control cells. However, expression of Lpd-Ena/VASP-, Lpd-Scar/WAVE- and double-binding mutants all failed to increase protrusion numbers and speed (Figure 7H and Supplemental Figure 7G). Similarly, these mutants did not support invasion through matrigel towards EGF, suggesting that Lpd promotes 3D chemotactic invasion via both Ena/VASP and Scar/WAVE (Figure 5D,E). These findings, combined with our previous observation that Lpd interaction with Scar/WAVE but not Ena/VASP is required for random 2D migration, prompted us to hypothesize that interactions between Lpd and these actin regulators may be differentially regulated.
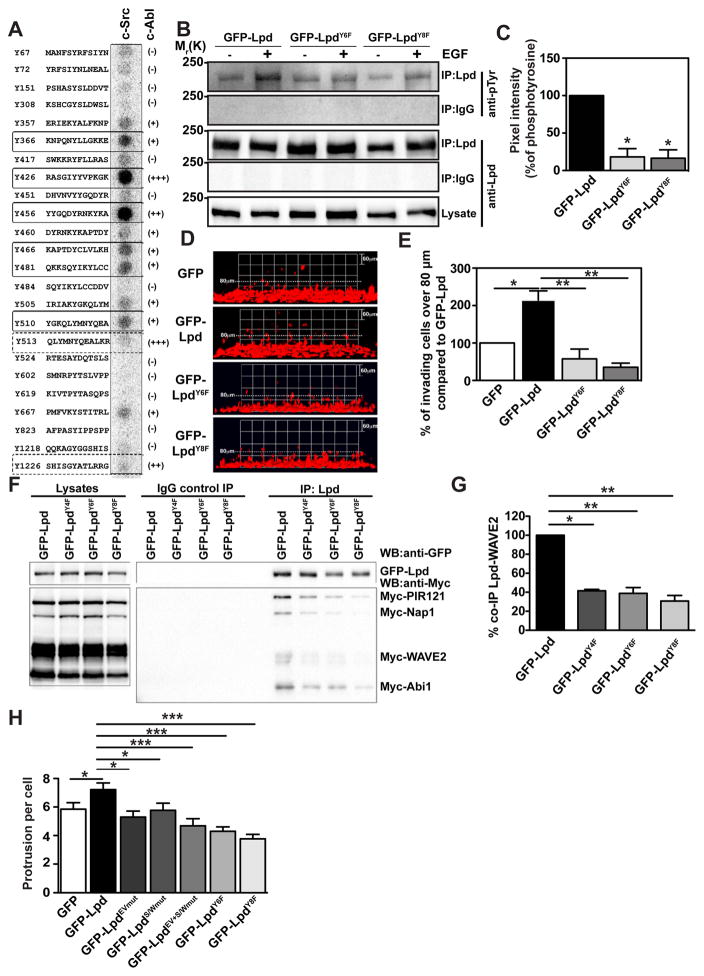
Figure 7. Phosphorylation of Lpd by c-Src and c-Abl is required for cancer cell invasion.
(A) Peptides harbouring all the tyrosine residues in Lpd were directly synthesized onto a membrane. An in vitro kinase assay was performed: the membranes were incubated with purified c-Src kinase and γ-3P-ATP. Phosphorylation was detected using a phosphorimager and visualised as high intensity spots. Increasing levels of cAbl phosphorylation of respective peptides as identified by19 are indicated by (+), (++), (+++), and (-) for not phosphorylated. Straight rectangles represent the common phosphorylation sites for both c-Src and c-Abl, and dotted rectangles represents cAbl specific phosphorylation sites19. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-LpdY6F, GFP-LpdY8F, or GFP-Lpd as control. HeLa cells were serum starved overnight and stimulated with 100ng/ml EGF for 5 minutes. Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using Lpd-specific antibodies or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-Lpd and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. (C) Quantified band intensities of chemiluminescence blots (B) of GFP-Lpd, GFP-Lpd phospho-mutants, and pTyr imaged with a CCD camera. pTyr normalised against the immunoprecipitated Lpd. Baseline phosphorylation in the absence of EGF was subtracted from the corresponding EGF+ samples. n=6, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.0001. (D–E) Inverted invasion assays were performed using MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stably expressing mCherry-H2B (labeling the nucleus) transfected with GFP-Lpd, GFP-LpdY6F, GFP-LpdY8F, or GFP empty vector as control. The nuclei of the cells were visualized using confocal microscopy. (D) The image stacks were processed by Volocity software to make a 3D reconstruction. (E) Quantification of the number of nuclei of invading cells above 80μm. n=6 (with approximately 4000 cells per experiment). Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.001, ** P ≤ 0.0001. Error bars represent s.e.m. (F) HEK293FT cells were transfected with GFP-Lpd, GFP-LpdY4F, GFP-LpdY6F, GFP-LpdY8F and Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex. Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using GFP-specific antibody or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-GFP, anti-Myc and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. (G) Quantified band intensities of chemiluminescence blots (F) of GFP-Lpd and Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex imaged with a CCD camera. Scar/WAVE2 was normalized against the immunoprecipitated Lpd. n=4, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001. (H) Quantification of the number of protrusion of MDA-MB-231 transfected with GFP-Lpd, GFP-LpdEVmut, GFP-LpdS/Wmut, GFP-LpdEV+S/Wmut, GFP-LpdY6F, GFP-LpdY8F or GFP empty vector as control plated in 3D matrigel. n= 35–46 cells for each mutant; from 5 experiments. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.05, *** P< 0.001).
See also Figure S7 and S8.
Previously we found that Lpd is phosphorylated by Abl kinases upon growth factor stimulation, and this positively regulates its interaction with Ena/VASP proteins and their recruitment to the leading edge of cells19. Since Src kinases are also activated upon growth factor stimulation and increased Src activity promotes cancer cell invasion40, we explored whether Lpd interactions with downstream partners are regulated by Src phosphorylation.
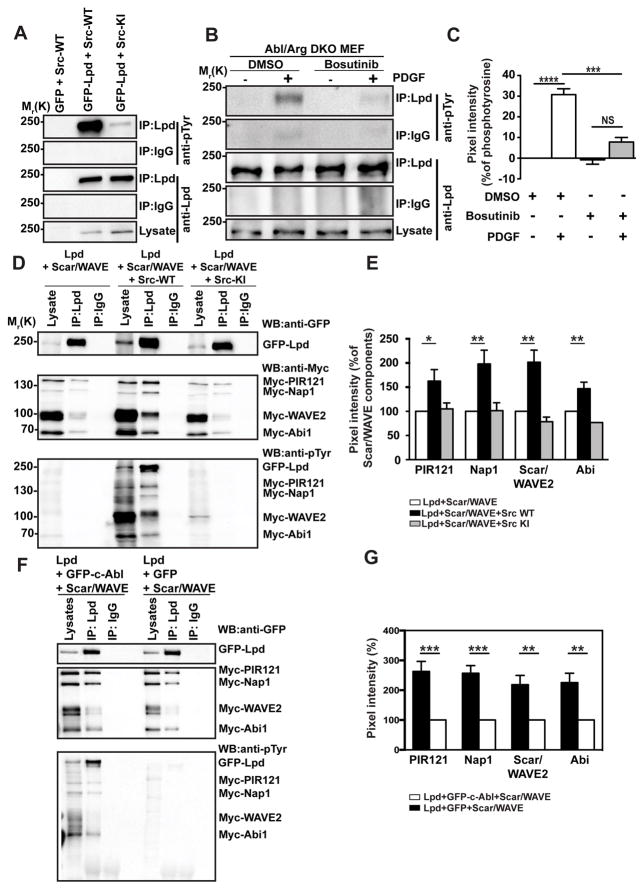
We expressed GFP-Lpd with wild-type c-Src or a kinase-inactive mutant of c-Src and, after immunoprecipitation of Lpd, observed that it was tyrosine phosphorylated in cells expressing wild-type but not kinase-inactive c-Src (Figure 6A). Both Src and Abl kinases are activated downstream of growth factor receptors, and Src phosphorylation of Abl kinases contributes to their activation40–42. To distinguish between Src and Abl phosphorylation of Lpd and to investigate whether endogenous Lpd is phosphorylated by Src tyrosine kinases, we made use of Abl/Arg double knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts43. After PDGF-BB stimulation, Lpd was robustly tyrosine phosphorylated in the absence of both Abl kinases, Abl and Arg. This was blocked by the Src inhibitor Bosutinib (Figure 6B,C), indicating Src kinase activity leads to Lpd phosphorylation upon growth factor receptor activation.
Figure 6. c-Src phosphorylates Lpd and the Lpd-Scar/WAVE interaction is positively regulated by c-Abl and c-Src.
(A) HEK293FT cells were transfected with either GFP as control or GFP-Lpd and cotransfected with Src-WT (wild type) or Src-KI (kinase inactive). Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using Lpd-specific antibodies or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-Lpd and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. n=3. (B) Abl and Arg double knockout MEFs (Abl/Arg DKO) were serum starved overnight and treated with 10μM Bosutinib (c-Src kinase inhibitor) for 2 hours before stimulating with 20ng/ml PDGF-BB for 2 minutes. Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using Lpd-specific antibodies or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-Lpd and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. (C) Quantified band intensities of chemiluminescence blots from (B) of Lpd and pTyr imaged with a CCD camera. pTyr was normalized against the immunoprecipitated Lpd. The pTyr signal from Rabbit IgG control lanes was subtracted from the pTyr signal from the immunoprecipitated Lpd lanes. n=3, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; *** P ≤ 0.001, **** P ≤ 0.0001, NS – not significant. (D) HEK293FT cells were transfected with GFP-Lpd, Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex and either Src-WT (wild type) or Src-KI (kinase inactive). Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using Lpd-specific antibody or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-GFP, anti-Myc and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. (E) Quantified band intensities of chemiluminescence blots (D) of GFP-Lpd and Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex imaged with a CCD camera. Individual Scar/WAVE components were normalized against the immunoprecipitated Lpd. n=4, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01. (F) HEK293FT cells were transfected with GFP-Lpd, Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex and either GFP-c-Abl or GFP. Immunoprecipitation was performed from cell lysates using Lpd-specific antibody or rabbit IgG as control followed by Western blotting with anti-GFP, anti-Myc and anti-phosphotyrosine (pTyr) antibodies. (G) Quantified band intensities of chemiluminescence blots (F) of GFP-Lpd and Myc tagged components of the Scar/WAVE complex imaged with a CCD camera. Individual Scar/WAVE components were normalized against the immunoprecipitated Lpd. n=4, data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. One-way ANOVA; Dunnett’s; ** P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001.
We first investigated whether Src phosphorylation controls Lpd-Ena/VASP interaction, since this is positively regulated by Abl phosphorylation19. Surprisingly, c-Src-induced Lpd phosphorylation did not affect Lpd-Ena/VASP binding (Supplemental Figure 7A,B). In contrast, co-immunoprecipitation between GFP-Lpd and Myc-tagged Scar/WAVE-complex revealed that significantly more Scar/WAVE-complex co-precipitated with Lpd when either c-Src or c-Abl was co-expressed. (Figure 6D–G). We also tested whether the interaction between endogenous Lpd and Scar/WAVE is positively regulated by c-Src by using ectopically expressed GST-tagged Abi (which reduces endogenous Abi and thereby replaces it44) to efficiently pull down the Scar/WAVE complex and associated proteins. GST-Abi pulldowns from cells co-expressing GFP-Src contained higher levels of endogenous Scar/WAVE2 co-precipitating with endogenous Lpd compared to GFP controls (Supplementary Figure 7C,D). Conversely, GST-Abi pulldowns from cells co-expressing GFP-Src treated with the c-Src inhibitor (KB SRC 4) contained lower levels of endogenous Scar/WAVE2 co-precipitating with endogenous Lpd compared to GST-Abi pulldowns from DMSO treated control cells (Supplementary Figure 7E,F). Together, these findings indicate that the Lpd-Ena/VASP interaction is regulated by c-Abl phosphorylation, whereas the Lpd-Scar/WAVE interaction is positively regulated by both c-Abl and c-Src-dependent phosphorylation.
To better understand this differential regulation, we identified potential direct c-Src phosphorylation sites in Lpd, using purified c-Src kinase to phosphorylate an immobilized peptide array covering all putative tyrosine phosphorylation sites in Lpd. This analysis revealed that Lpd harbors two robustly and four weakly phosphorylated c-Src tyrosine phosphorylation sites (Figure 7A). We have previously mapped eight c-Abl tyrosine phosphorylation sites in Lpd19, which partly overlap with these newly identified c-Src sites (Figure 7A). To verify that the Lpd phosphorylation sites identified in vitro were phosphorylated in cells, we mutated the tyrosines in the six c-Src (GFP-LpdY6F) and the eight c-Abl phosphorylation sites (GFP-LpdY8F) to phenylalanine, rendering them non-phosphorylatable. Overexpression of GFP-Lpd induced low levels of Lpd tyrosine phosphorylation, which was markedly enhanced by stimulation with 100 ng/ml EGF for 5 minutes. In contrast, neither GFP-LpdY6F nor GFP-LpdY8F tyrosine phosphorylation was enhanced when cells expressing these constructs were stimulated with EGF (Figure 7B,C). We found that the GFP-LpdY6F and GFP-LpdY8F mutants interacted significantly less with the Scar/WAVE complex (Figure 7F,G; Supplemental Figure 8D). Nevertheless, GFP-LpdY6F and -LpdY8F mutants localized to the leading edge of MDA-MB-231 cells similar to wild-type Lpd (Supplemental Figure 6F,G). Taken together, our data indicates that full-length Lpd can be phosphorylated at these sites in cells upon EGFR activation, likely as a consequence of activated Abl- and Src-kinases.
To verify that both Src and Abl kinases are required for breast cancer invasion towards EGF, we tested the invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 cells with and without incubation with the Src and Abl inhibitors Dasatinib or STI571. As expected, we found that breast cancer cell invasiveness is impaired when Src or Abl kinases were inhibited (Supplemental Figure 8A,B).
To investigate the functional significance of Lpd tyrosine phosphorylation for breast cancer invasion, we compared the effects of overexpressing the non-phosphorylatable mutants, GFP-LpdY6F or GFP-LpdY8F with control GFP-Lpd. We observed that, in contrast to GFP-Lpd, neither of the mutants increased protrusion numbers or speed in cells embedded in matrigel at steady state, or the invasiveness of breast cancer cells through matrigel towards EGF (Figure 7D,E,H and Supplemental Figure 8C) suggesting that phosphorylation by both Abl and Src kinases is required for Lpd-mediated breast cancer invasion.
Discussion
Here we reveal that Lpd is required for metastasis in an orthotopic breast cancer mouse model, and that increased Lpd levels correlate with reduced metastasis free survival in breast cancer patients. Lpd promotes metastasis in vivo by supporting tumor invasion and intravasation. Lpd function in metastasis may be mediated via both Ena/VASP and the Scar/WAVE-complex since we observed that Lpd mediates breast cancer invasion via both actin effectors. Both Ena/VASP and Scar/WAVE are implicated in breast cancer metastasis by multiple lines of evidence15,16,45,46. Our results suggest that the pro-metastatic function of Lpd may, in part, involve coordinating the activities of these two distinct types of actin regulators to optimize chemotactic invasion and matrix degradation by invading tumor cells.
Here we provide evidence that Lpd is a substrate of Src kinases and that phosphorylation of Lpd by Src positively regulates the Lpd-Scar/WAVE-complex interaction, but not the Lpd-Ena/VASP interaction, whereas c-Abl mediated phosphorylation of Lpd positively regulates both Lpd-Ena/VASP and Lpd-Scar/WAVE interaction. This differential regulation of Lpd-Ena/VASP or Lpd-Scar/WAVE recruitment may allow Lpd to fine-tune actin cytoskeletal dynamics via Ena/VASP-mediated actin filament elongation and Scar/WAVE-Arp2/3-mediated nucleation/branching, consistent with the context-dependent differential requirements for these interactions we observed. Lpd driven random 2D cell migration requires Scar/WAVE, but not Ena/VASP20, Lpd-dependent chemosensing in 2D requires Ena/VASP, and interactions with both SCAR/WAVE and Ena/VASP are required for 3D chemotaxis and migration. These findings lead to the interesting possibility that Lpd balances actin nucleation/branching and filament elongation activities to optimize protrusion morphology and dynamics during cellular responses to growth factors and ECM composition and organization.
Surprisingly, we observed that only moderately, but not highly increased levels of Lpd correlate with increased risk of breast cancer-associated mortality suggesting that not all of Lpd functions (cell invasion, cell proliferation and EGFR endocytosis)47,48 induced by high but not medium levels of Lpd may be beneficial for tumors cells. However, in agreement with its role in metastasis, we found that highly increased Lpd abundance at the plasma membrane of cancer cells in breast tumors correlates with reduced disease- and metastasis-free interval. The increased membrane accumulation of Lpd protein observed in our TMA analysis may reflect the known role of Lpd in regulating membrane protrusion in migrating cells17,20. Furthermore, consistent with the TMA analysis, we found that increased Lpd mRNA levels correlate with reduced metastasis-free survival of breast cancer patients.
Based on our findings, we propose that Lpd functions as an essential component of a pro-metastatic signaling pathway composed of Src and Abl kinases, Lpd, Ena/VASP, and Scar/WAVE that promotes metastatic progression.
Methods
Plasmids and shRNAs
GFP-VASP, pMSCV-mRFP1-FP4/AP4-mito34, Myc-Pir121, -Nap1, -Abi1d, -WAVE2 in pRK5-Myc-DEST20. Lpd17 in pENTR (Invitrogen), mutated using Quikchange® (Agilent), transferred into pCAG-DEST-EGFP (Gateway®) (pCAG-EGFP; C.Cepko, Addgene,11150). pCB6-Src-WT-EGFP, pCB6-Src-KI(kinase-inactive)-EGFP49, (M.Way).
GFP-LpdS/Wmut 20:AAS82582.1) Site1:(aa968-978)GKKP(P>A) (P>A) T(P>A)Q(R>A)N; Site2:(aa1119-1129) APP(P>A)TR(P>A)K(R>A)ND; SITE3:(aa1230-1244) RRGP(P>A)A(P>A)(P>A)(K>A)(R>A)DQNT.
GFP-LpdEVmut 20:(AAS82582.1) FP4-1:aa869 F>A; FP4-2:aa916 F>A; FP4-3:aa927 F>A; FP4-4:aa1064 F>A; FP4-5:aa1073 F>A; FP4-6:aa1082 L>A; FP4-7:aa1202 L>A.
GFP-LpdY4F 19: (AAS82582.1) Y>F:aa 426, 456, 513, 1226; GFP-LpdY6F: (AAS82582.1) Y>F:aa366, 426, 456, 466, 481, 510; GFP-LpdY8F: (AAS82582.1) Y>F:aa366, 426, 456, 466, 481, 510, 513, 1226;
pLJM1-H2BK-mCherry: histone H2BK amplified from A431 cell by RT-PCR cloned into pLJM1-mCherry (D.Sabatini; Addgene plasmid #19319).
shRNAs were cloned into pLL3.7-Puro, miR30-MLS EGFP/mCherry50, or MSCV-ZsG-2A-Puro-miR30 retroviral vector51. Cells were FACS sorted or puromycin (Invitrogen) selected and knockdown tested by Western blot. shRNA (5′–3′) used:
humanLpd-shRNA1:TTTCCCCAAAAGATAATTCTG
humanLpd-shRNA2:TTCCCATACTTTGCAATGCGG
ratLpd-shRNA2:TAGAGCTCACAGTACTTTGGG
ratLpd-shRNA3:AAGAGGTCCAATCATAAGCTG
Control-shRNA (targeting luciferase):TTAATTAAAGACTTCAAGCGG
Human Lpd-shRNA-1:GCGTCAAATCACAGAAACG
Human Lpd-shRNA-2:GCTCTGAATCAGGGAGAGA
Control-shRNA (Lpd-scrambled):GCCGATAACCGAGAATACC
Cell culture and transfection
HEK293, BT549, MCF7, T47D cells from ATCC and maintained according to ATCC’s protocol. SUM-159 and MTLn3 cells cultured as described52,53. HEK cells expressing GST-Abi2 and GFP-Src were treated for one hour with 100μM KB SRC 4 (Tocris) before lysis. Abl1/Abl2 double knockout MEF’s (gift of T.Koleske, Yale), MDA-MB-231 cells (gift of A.Ridley) and MDA-MB-231 LM2 cells26 (gift from J.Massague, MSKCC) were cultured in high-glucose DMEM, penicillin, streptomycin, 10% FBS. MTLn3 and MDA-MB-231 transfection: Lipofectamine2000 (Invitrogen). Abl1/2DKO MEFs were serum starved (18h) and treated with 10 μM Bosutinib (Cambridge Biosciences) (2 hours) in DMSO or DMSO (control), then stimulated with 20ng/ml PDGF-BB (2 minutes).
Antibodies
Lpd pab 391717, Mena mab A351F7D954, Wave2 (Cell Signaling Technology), p34Arc (Millipore, 07-227), Tubulin (DM1A), Hsc70 mab (Santa Cruz), GFP mab (Roche), Myc mab (Sigma, 9E10), pTyr mab (Millipore, 4G10), Vimentin (550513, Biosciences). Alexa-conjugated secondary antibodies, phalloidin (Invitrogen, Biotium) diluted 1:50-1000.
Immunoprecipitation, GST-pulldowns and Western Blotting
Was performed as described20.
Peptide array assay
Was done using Src kinase (NEB) as described19.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy
Cells were plated on glass coverslips, fixed and stained as described19. Imaged: Deltavision microscope (Applied Precision, Olympus IX71, 60X/1.4NA, Softworx software) (SGI, Mountain View, CA). Olympus IX-81 microscope (Metamorph, Photometrics CascadeII 512B camera, 40xUPlanFL, 60xPlanApoNA1.45, or 100x UPlanApoS NA1.4 objectives) was used. Leading edge localization (Supplemental Figure 6G) was quantified by two blinded observers from 3 independent datasets (n=32–38 cells for each mutant).
Inverted Invasion Assay
5×105 MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing mCherry-H2B were seeded onto underside of 8μm pore-size transwell inserts (Greiner Bio-One Ltd) containing matrigel ((BD Biosciences, UK) polymerised 30 min (37°C)). Inserts were inverted after cells adhered (4 hours), placed in serum-free medium, and normal growth medium containing EGF (25 ng/ml) placed on top. Inhibitors used: 10μM GM6001; STI571 10μM; Dasatinib 10nM. 72 hours later, cells that did not cross the transwell filter were removed, invading cells visualised by confocal microscopy; 2.5μm sections. The number of nuclei of invading cells above 40 μm or 80 μm was automatically quantified using Volocity software.
Membrane Protrusion Assays
Membrane protrusion assay for EGF treated cells was performed as described16. Kymographic analysis was performed to analyze the protrusion parameters including: protrusion persistence, distance, velocity and protrusion initiation after EGF stimulation.
For membrane protrusion assay in 3D matrigel, MDA-MB-231 cells were stained with CellTracker Green dye (ThermoFisher, UK) embedded in matrigel (BD Biosciences, UK) in μ-slide chambers (81506 Ibidi, Germany). 4 hours after plating, 5 minute movies, one frame every 15 sec; 40x; Olympus IX-81 were generated and protrusive activity around the entire circumference between frames automatically quantified from thresholded movies using ImageJ plugin ADAPT55.
Micropipette assay
Barbed-End Assay
G-actin was extracted from rabbit muscle acetone powder and standard techniques used to gel-filter over a Superdex-200 gel filtration column. The G-actin was polymerized to F-actin in F actin buffer (1 mM ATP, 5 mM MgCl2, 50mM KCl, 50mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0), labeled with Rhodamine-X succinimidyl ester (Invitrogen; following manufacturer’s instructions), depolymerized in G-actin buffer (0.2 mM ATP, 0.5 mM DTT, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 2 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0) to G-actin, and passed through PD-10 columns (GE Healthcare) to eliminate free rhodamine. The barbed-end assay in MTLn3 cells was performed as described16. Images taken with deconvolution microscope; the ratio of the barbed-end intensity to phalloidin intensity along the edge (the zone between 0 and 0.66μm inside the cell) quantified as described above.
Invadopodium degradation and immunofluorescence
MDA-MB-231 cells used in this study were cultured on FN/gelatin matrix (for 8 hours) or thin gelatin matrix (for 4 hours), and treated as described57.
Zebrafish tumor cell dissemination assay
The zebrafish tumor cell dissemination assay was done as described28.
Mouse models
Tumor growth and spontaneous metastasis formation assayed by injecting tumor cells orthotopically into inguinal mammary fat pads (6–8 week-old female NOD/SCID/IL2Rγ-null mice) (Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME). Mice anesthetized with isoflurane, injected with 1.5×105 cells in Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution (Gibco); sacrificed 6±0.5 weeks post-injection; tumors dissected, weighed, flash frozen, stored (−80°C) or fixed: 3.8% formaldehyde, imaged with a fluorescence microscope, and embedded in paraffin and sectioned. Lungs were collected, fixed: 3.8% formaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, sectioned and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). ZsGreen-positive foci were counted in left pulmonary lobe using ImageJ.
Intravital imaging
Female NOD/SCID/IL2Rγ-null mice (6–8 week-old) injected in the mammary fat pad with Ctrl-shRNA or LpdhsRNA2-expressing LM2 cells. Experiments was performed as described previously58. 5 mice per group. Collagen I fibers imaged by second harmonic generated polarized light. Cell motility observed by time-lapse imaging: 30 min in 2-min cycles. Three-dimensional time-lapse videos analysed: Image J. Tumour cell motility quantified manually. A cell was scored as motile if the translocation of the cell body was visible over the course of a 30 min video within a visual field that is defined in three dimensions as 50 μm by 512×512 pixels. Protrusion was defined as tumors cells showing a dynamic lamellipodia-like morphology. A protrusion was defined to be at least 5 μm long, but less than half the length of the cell. Directionality was calculated as described58.
Statistics
Statistical analysis performed by ANOVA with appropriate posthoc tests (see figure legends), or Student’s t-test using Prism 5 (GraphPAD Software). P values <0.05 considered significant.
Clinical data sets analysis
Oncomine (www.oncomine.org) for Lpd mRNA expression from microarray data21. Statistical survival analysis (Kaplan-Meier plots): ROCK (http://www.rock.icr.ac.uk). Expression value of Lpd: upper quartile (25% against rest) for the NKI29524 and Loi22 data sets, or upper tertile (33% against rest) for the Miller23 data set. The log rank p-value was used for statistical significance.
Tissue microarrays
TMAs: 0.6 mm2 cores of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded invasive breast tumor samples (312 consecutive patients) with clinicopathological data (King’s Health Partners Cancer Biobank, London, UK). Automated immunohistochemistry (IHC) (VENTANA Discovery UTLRA) of 3 μm TMA sections, deparaffinized (EZ prep; Ventana Medical) (30 minutes, 72°C), antigen retrieval: automated slide stainer (ULTRA CC2 solution, Ventana Medical) (68 minutes, 91°C). Affinity purified polyclonal rabbit Lpd antibody in PBS (1:250) (32 minutes, room temperature). Slides counterstained with hematoxylin II and bluing reagent (Ventana Medical) (4 minutes each), dehydrated: 1x 70% IMS, 1 minute, 2x 100% IMS, 1.5 minutes, 3x xylene, 1 minute, mounted (Eukitt®) and imaged (Leica microscope, 40x).
Intensity of Lpd in cytoplasm and membrane assessed on TMAs using weighted histoscore (H-Score) method: Intensity in majority of cells assessed as negative and weak (1), or moderate and strong (2), then multiplied by the percentage of cells within this category. The weighted histoscore: 0–200; divided into thirtiles. Cytoplasma: histoscore 1 (0–88.75); histoscore 2 (88.75–170); histoscore 3 (170–200). Membrane: histoscore 1 (0–25); histoscore 2 (25–95); histoscore 3 (95–200). TMA’s were assessed by two independent observers (U.P. and C.G.). Intensity scores that varied by more than a factor of one or a proportion by more than 20% were jointly reassessed and consensus reached. For all other cases, the mean score was used. Disease specific survival curves generated using Kaplan-Meier method. The log-rank test was used to compare statistically significant differences between subgroups. Univariate and multivariate analyses Cox proportional hazards regression models used to evaluate overall and breast cancer-specific death by histoscore of Lpd intensity in cytoplasm and at membrane. All analyses: Statistical Analysis Systems (SAS); 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Study approval
TMA: NHS Research Ethics Committee, King’s Health Partners Cancer Biobank, London, UK. Mice: All animal experiments and husbandry were approved by MIT’s Department of Comparative Medicine and Committee on Animal Care. Zebrafish: Northern Stockholm Experimental Animal Ethical Committee.
Supplementary Material
Video S1: Intravital imaging of ZsGreen-Ctrl-shRNA tumor.
Representative 30 minute time lapse movie from multiphoton imaging of a ZsGreen-Ctrl-shRNA tumor. Cyan= Zsgreen-positive cells, red= collagen fibers. Images were taken every 2 min for 30 min. Video is played at 5 frames per second.
Video S2: Intravital imaging of ZsGreen-Lpd-shRNA2 tumor.
Representative 30 minute time lapse movie from multiphoton imaging of a ZsGreen-Lpd-shRNA2 tumor. Cyan= Zsgreen-positive cells, red= collagen fibers. Images were taken every 2 min for 30 min. Video is played at 5 frames per second.
Video S3: Membrane protrusion in Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 stimulated with EGF.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Ctrl-shRNA infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF 5nM. EGF was added after 1min. Images were taken every 3 sec for 10 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S4: Membrane protrusion in Lpd-shRNA MTLn3 stimulated with EGF.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Lpd-shRNA2 infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF 5nM. EGF was added after 1min. Images were taken every 3 sec for 10 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S5: A directed membrane protrusion towards the EGF-filled micropipette in Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 cell.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Ctrl-shRNA infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with an EGF-filled micropipette. Images were taken every 3 sec for 8 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S6: Absence of directed membrane protrusion towards the EGF-filled micropipette in Lpd-shRNA cell.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Lpd-shRNA2 infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF-filled micropipette. Images were taken every 3 sec for 8 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Gertler and Krause labs for helpful discussions and technical assistance; R.Weinberg for his helpful discussions; J.Lamar, S.Hansen, D.Mullins, M.Way, C.Cepko, D.Sabatini, T.Koleske and M.Hemann for reagents; the Koch Institute Swanson Biotechnology Center - specifically M.Griffin (Flow Cytometry Core Facility), E.Vasile (Microscopy Core Facility) and K.Cormier (Hope Babette Tang Histology Facility) for technical support. D. Barry and M. Way (LRI, CRICK, UK) for adapting the Image J plugin ADAPT for us to V1.33.
Patient samples and data were provided by King’s Health Partners Cancer Biobank, London, UK, which is supported by the Experimental Cancer Medicine Centre at King’s College London and the Department of Health via the National Institute for Health Research comprehensive Biomedical Research Centre award. G.C. received a postdoctoral fellowship from the Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research; U.P. received a King’s College Overseas Research PhD Studentship (KORS). This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute (U54-CA112967 and U54-CA163109), funds from the Ludwig Center for Metastasis Research at MIT (F.B.G., G.C., A.N., R.O.H.), the Koch Institute Support Grant P30-CA14051 from the National Cancer Institute, the Biotechnology and Biological Science Research Council, UK (BB/F011431/1; BB/J000590/1; BB/N000226/1) and the Wellcome Trust (082907/Z/07/Z) (M.K.).
Footnotes
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
“Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/oncogene)”
References
- 1.Eccles SA, Aboagye EO, Ali S, Anderson AS, Armes J, Berditchevski F, et al. Critical research gaps and translational priorities for the successful prevention and treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15:R92. doi: 10.1186/bcr3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Friedl P, Alexander S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell. 2011;147:992–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Roussos ET, Condeelis JS, Patsialou A. Chemotaxis in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:573–587. doi: 10.1038/nrc3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ridley AJ. Life at the leading edge. Cell. 2011;145:1012–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Krause M, Gautreau A. Steering cell migration: lamellipodium dynamics and the regulation of directional persistence. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2014;15:577–590. doi: 10.1038/nrm3861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Insall RH, Machesky LM. Actin dynamics at the leading edge: from simple machinery to complex networks. Dev Cell. 2009;17:310–322. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bisi S, Disanza A, Malinverno C, Frittoli E, Palamidessi A, Scita G. Membrane and actin dynamics interplay at lamellipodia leading edge. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013;25:565–573. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Breitsprecher D, Kiesewetter AK, Linkner J, Vinzenz M, Stradal TE, Small JV, et al. Molecular mechanism of Ena/VASP-mediated actin-filament elongation. Embo J. 2011;30:456–467. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, et al. Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell. 2002;109:509–521. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00731-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barzik M, Kotova TI, Higgs HN, Hazelwood L, Hanein D, Gertler FB, et al. Ena/VASP proteins enhance actin polymerization in the presence of barbed end capping proteins. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:28653–28662. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503957200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chereau D, Dominguez R. Understanding the role of the G-actin-binding domain of Ena/VASP in actin assembly. J Struct Biol. 2006;155:195–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pasic L, Kotova T, Schafer DA. Ena/VASP proteins capture actin filament barbed ends. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:9814–9819. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710475200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Breitsprecher D, Kiesewetter AK, Linkner J, Urbanke C, Resch GP, Small JV, et al. Clustering of VASP actively drives processive, WH2 domain-mediated actin filament elongation. Embo J. 2008;27:2943–2954. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hansen SD, Mullins RD. VASP is a processive actin polymerase that requires monomeric actin for barbed end association. J Cell Biol. 2010;191:571–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201003014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Roussos ET, Wang Y, Wyckoff JB, Sellers RS, Wang W, Li J, et al. Mena deficiency delays tumor progression and decreases metastasis in polyoma middle-T transgenic mouse mammary tumors. Breast Cancer Res. 2010;12:R101. doi: 10.1186/bcr2784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Philippar U, Roussos ET, Oser M, Yamaguchi H, Kim HD, Giampieri S, et al. A Mena invasion isoform potentiates EGF-induced carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Dev Cell. 2008;15:813–828. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Krause M, Leslie JD, Stewart M, Lafuente EM, Valderrama F, Jagannathan R, et al. Lamellipodin, an Ena/VASP ligand, is implicated in the regulation of lamellipodial dynamics. Dev Cell. 2004;7:571–583. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Krause M, Dent EW, Bear JE, Loureiro JJ, Gertler FB. ENA/VASP PROTEINS: Regulators of the Actin Cytoskeleton and Cell Migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:541–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.050103.103356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Michael M, Vehlow A, Navarro C, Krause M. c-Abl, Lamellipodin, and Ena/VASP proteins cooperate in dorsal ruffling of fibroblasts and axonal morphogenesis. Curr Biol. 2010;20:783–791. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Law AL, Vehlow A, Kotini M, Dodgson L, Soong D, Theveneau E, et al. Lamellipodin and the Scar/WAVE complex cooperate to promote cell migration in vivo. J Cell Biol. 2013;203:673–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201304051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N, Varambally R, Ghosh D, et al. ONCOMINE: a cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia. 2004;6:1–6. doi: 10.1016/s1476-5586(04)80047-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Loi S, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Wirapati P, Lallemand F, Tutt AM, et al. Predicting prognosis using molecular profiling in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer treated with tamoxifen. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:239. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB, Vergara L, Ploner A, et al. An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:13550–13555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506230102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, et al. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1999–2009. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Youssef G, Gillett C, Agbaje O, Crompton T, Montano X. Phosphorylation of NTRK1 at Y674/Y675 induced by TP53-dependent repression of PTPN6 expression: a potential novel prognostic marker for breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2014;27:361–374. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, et al. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature. 2005;436:518–524. doi: 10.1038/nature03799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Arjonen A, Kaukonen R, Mattila E, Rouhi P, Hognas G, Sihto H, et al. Mutant p53-associated myosin-X upregulation promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:1069–1082. doi: 10.1172/JCI67280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee SL, Rouhi P, Dahl Jensen L, Zhang D, Ji H, Hauptmann G, et al. Hypoxia-induced pathological angiogenesis mediates tumor cell dissemination, invasion, and metastasis in a zebrafish tumor model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:19485–19490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909228106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Goswami S, Sahai E, Wyckoff JB, Cammer M, Cox D, Pixley FJ, et al. Macrophages promote the invasion of breast carcinoma cells via a colony-stimulating factor-1/epidermal growth factor paracrine loop. Cancer Res. 2005;65:5278–5283. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Symons MH, Mitchison TJ. Control of actin polymerization in live and permeabilized fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:503–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bailly M, Macaluso F, Cammer M, Chan A, Segall JE, Condeelis JS. Relationship between Arp2/3 complex and the barbed ends of actin filaments at the leading edge of carcinoma cells after epidermal growth factor stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1999;145:331–345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iglesias PA, Devreotes PN. Navigating through models of chemotaxis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:35–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2007.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Janetopoulos C, Firtel RA. Directional sensing during chemotaxis. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:2075–2085. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bear JE, Loureiro JJ, Libova I, Fassler R, Wehland J, Gertler FB. Negative regulation of fibroblast motility by Ena/VASP proteins. Cell. 2000;101:717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80884-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hennigan RF, Hawker KL, Ozanne BW. Fos-transformation activates genes associated with invasion. Oncogene. 1994;9:3591–3600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sanz-Moreno V, Gadea G, Ahn J, Paterson H, Marra P, Pinner S, et al. Rac activation and inactivation control plasticity of tumor cell movement. Cell. 2008;135:510–523. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. 2012;196:395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Beaty BT, Condeelis J. Digging a little deeper: The stages of invadopodium formation and maturation. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2014.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Poincloux R, Lizarraga F, Chavrier P. Matrix invasion by tumour cells: a focus on MT1-MMP trafficking to invadopodia. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3015–3024. doi: 10.1242/jcs.034561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kim LC, Song L, Haura EB. Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:587–595. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Greuber EK, Smith-Pearson P, Wang J, Pendergast AM. Role of ABL family kinases in cancer: from leukaemia to solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:559–571. doi: 10.1038/nrc3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bradley WD, Koleske AJ. Regulation of cell migration and morphogenesis by Abl-family kinases: emerging mechanisms and physiological contexts. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3441–3454. doi: 10.1242/jcs.039859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Koleske AJ, Gifford AM, Scott ML, Nee M, Bronson RT, Miczek KA, et al. Essential roles for the Abl and Arg tyrosine kinases in neurulation. Neuron. 1998;21:1259–1272. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80646-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Derivery E, Lombard B, Loew D, Gautreau A. The Wave complex is intrinsically inactive. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66:777–790. doi: 10.1002/cm.20342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Roussos ET, Balsamo M, Alford SK, Wyckoff JB, Gligorijevic B, Wang Y, et al. Mena invasive (MenaINV) promotes multicellular streaming motility and transendothelial migration in a mouse model of breast cancer. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:2120–2131. doi: 10.1242/jcs.086231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Di Modugno F, Mottolese M, Di Benedetto A, Conidi A, Novelli F, Perracchio L, et al. The cytoskeleton regulatory protein hMena (ENAH) is overexpressed in human benign breast lesions with high risk of transformation and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive/hormonal receptor-negative tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:1470–1478. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vehlow A, Soong D, Vizcay-Barrena G, Bodo C, Law AL, Perera U, et al. Endophilin, Lamellipodin, and Mena cooperate to regulate F-actin-dependent EGF-receptor endocytosis. Embo J. 2013;32:2722–2734. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lyulcheva E, Taylor E, Michael M, Vehlow A, Tan S, Fletcher A, et al. Drosophila pico and its mammalian ortholog lamellipodin activate serum response factor and promote cell proliferation. Dev Cell. 2008;15:680–690. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Newsome TP, Weisswange I, Frischknecht F, Way M. Abl collaborates with Src family kinases to stimulate actin-based motility of vaccinia virus. Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:233–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dickins RA, Hemann MT, Zilfou JT, Simpson DR, Ibarra I, Hannon GJ, et al. Probing tumor phenotypes using stable and regulated synthetic microRNA precursors. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1289–1295. doi: 10.1038/ng1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lamar JM, Stern P, Liu H, Schindler JW, Jiang ZG, Hynes RO. The Hippo pathway target, YAP, promotes metastasis through its TEAD-interaction domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E2441–2450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212021109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ignatoski KM, Ethier SP. Constitutive activation of pp125fak in newly isolated human breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999;54:173–182. doi: 10.1023/a:1006135331912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mouneimne G, Soon L, DesMarais V, Sidani M, Song X, Yip SC, et al. Phospholipase C and cofilin are required for carcinoma cell directionality in response to EGF stimulation. J Cell Biol. 2004;166:697–708. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200405156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lebrand C, Dent EW, Strasser GA, Lanier LM, Krause M, Svitkina TM, et al. Critical role of Ena/VASP proteins for filopodia formation in neurons and in function downstream of netrin-1. Neuron. 2004;42:37–49. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Barry DJ, Durkin CH, Abella JV, Way M. Open source software for quantification of cell migration, protrusions, and fluorescence intensities. J Cell Biol. 2015 doi: 10.1083/jcb.201501081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mouneimne G, DesMarais V, Sidani M, Scemes E, Wang W, Song X, et al. Spatial and temporal control of cofilin activity is required for directional sensing during chemotaxis. Curr Biol. 2006;16:2193–2205. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sharma VP, Eddy R, Entenberg D, Kai M, Gertler FB, Condeelis J. Tks5 and SHIP2 regulate invadopodium maturation, but not initiation, in breast carcinoma cells. Curr Biol. 2013;23:2079–2089. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.08.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gligorijevic B, Wyckoff J, Yamaguchi H, Wang Y, Roussos ET, Condeelis J. N-WASP-mediated invadopodium formation is involved in intravasation and lung metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:724–734. doi: 10.1242/jcs.092726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Video S1: Intravital imaging of ZsGreen-Ctrl-shRNA tumor.
Representative 30 minute time lapse movie from multiphoton imaging of a ZsGreen-Ctrl-shRNA tumor. Cyan= Zsgreen-positive cells, red= collagen fibers. Images were taken every 2 min for 30 min. Video is played at 5 frames per second.
Video S2: Intravital imaging of ZsGreen-Lpd-shRNA2 tumor.
Representative 30 minute time lapse movie from multiphoton imaging of a ZsGreen-Lpd-shRNA2 tumor. Cyan= Zsgreen-positive cells, red= collagen fibers. Images were taken every 2 min for 30 min. Video is played at 5 frames per second.
Video S3: Membrane protrusion in Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 stimulated with EGF.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Ctrl-shRNA infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF 5nM. EGF was added after 1min. Images were taken every 3 sec for 10 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S4: Membrane protrusion in Lpd-shRNA MTLn3 stimulated with EGF.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Lpd-shRNA2 infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF 5nM. EGF was added after 1min. Images were taken every 3 sec for 10 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S5: A directed membrane protrusion towards the EGF-filled micropipette in Ctrl-shRNA MTLn3 cell.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Ctrl-shRNA infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with an EGF-filled micropipette. Images were taken every 3 sec for 8 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.
Video S6: Absence of directed membrane protrusion towards the EGF-filled micropipette in Lpd-shRNA cell.
This DIC movie shows time-lapse video microscopy of Lpd-shRNA2 infected MTLn3 cells. MTLn3 cells were starved for 3 hours and then stimulated with EGF-filled micropipette. Images were taken every 3 sec for 8 min. Video is played at 40 frames per second.