Abstract
Tollip is a key negative regulator of innate immunity by preventing excessive pro-inflammatory responses. Tollip genetic variation has been associated with airflow limitation in asthma subjects and Tollip expression. Whether Tollip regulates lung inflammation in a type 2 cytokine milieu (e.g., IL-13) is unclear. Our goal was to determine the in vivo role of Tollip in IL-13-mediated lung eosinophilic inflammation and the underlying mechanisms. Tollip-knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were inoculated intranasally with recombinant mouse IL-13 protein to examine lung inflammation. To determine how Tollip regulates inflammation, alveolar macrophages and bone marrow-derived macrophages from Tollip KO and WT mice were cultured with or without IL-13 and/or IL-33. IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice significantly increased lung eosinophilic inflammation and eotaxin-2 levels compared with the WT mice. IL-13-treated Tollip KO (vs. WT) macrophages, in the absence and particularly in the presence of IL-33, increased expression of the IL-33 receptor ST2L and eotaxin-2 (CCL24), which was in part dependent on enhanced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6). Our results suggest that Tollip down-regulates IL-13-mediated pulmonary eosinophilia in part through inhibiting the activity of the ST2L/IL-33/IRAK1 axis and STAT6.
Keywords: Tollip, eosinophil, eotaxin-2/CCL24, IL-13, IL-33, ST2L
Introduction
Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways, has increased in prevalence and severity in industrialized nations over the past 50 years [1]. To date, two major endotypes of asthma have been described, type 2-high (T2-high) and type 2-low (T2-low). Patients with T2-high asthma have increased eosinophils in sputum and airway tissue [2]. Eosinophils exert toxic effects on host tissue and exaggerate inflammation through the release of a variety of inflammatory mediators [3]. Asthmatics with higher number of eosinophils in blood and/or sputum seem to have more severe disease and more frequent exacerbations than those with lower eosinophil counts [4,5].
Major regulators of asthma such as interleukin-33 (IL-33) stimulate the innate or adaptive immune system to secrete type 2 (T2) cytokines such as IL-13. Because of the extensive use of mouse IL-13 treatment models in asthma research [2,6–8], IL-13 has been considered as one of the key regulators in eosinophil recruitment and survival, and other pathological features of asthma such as airway fibrosis. One of the major mechanisms by which IL-13 induces airway eosinophilia is through the production of eotaxins. Although several types of lung cells produce eotaxins, alveolar macrophages, particularly in the presence of T2 cytokine stimulation, are critical in eotaxin production. Alveolar macrophages are involved in asthma pathogenesis in both humans and mice [9–11]. IL-13 as well as IL-33 have been shown to increase the expression of eotaxin-2 (CCL24) and other chemokines including CCL17, CCL18 and CCL22 [9]. However, the mechanisms regulating eotaxin-2 expression in macrophages exposed to T2 cytokines remain unclear.
Toll-interacting protein (Tollip) is a critical regulator of Toll-like receptor (TLR) and IL-1/IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling by interacting with interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) and subsequently suppressing IRAK1 activity [12]. Many types of cells including macrophages and epithelial cells express Tollip [13–15]. Although Tollip is classically considered as a negative regulator in bacterial infection to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage, its role in non-infectious processes has not been well understood. Several Tollip single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been implicated in sepsis [16], tuberculosis [13], idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [17] and atopic dermatitis [18]. Recently, we have reported that asthma subjects carrying the Tollip rs5743899 AG/GG genotypes demonstrate greater airflow limitation as indicated by a lower FEV1/FVC ratio than those carrying the AA genotype [14]. Moreover, human airway epithelial cells with the AG/GG genotype express less Tollip protein, and produce more eotaxin-3 (CCL26) when stimulated with IL-13 [14]. However, the in vivo role of Tollip in regulating IL-13-mediated lung inflammation, especially eosinophilic inflammation, is not clear.
In the present study, we hypothesized that Tollip deficiency in an in vivo T2 cytokine (e.g., IL-13) milieu enhances eotaxin production and excessive pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation. To test this hypothesis, we used a Tollip-deficient mouse model of IL-13 treatment to determine the role of Tollip in eotaxin production and pulmonary eosinophilia. Additionally, we examined the mechanisms by which Tollip down-regulates eotaxin production by using cell culture models of alveolar macrophages and bone marrow-derived macrophages from Tollip-deficient mice.
Methods
Murine Model of IL-13-Induced Lung Inflammation
Tollip knockout (KO) and IRAK1 KO mice on the C57BL/6 background were obtained from Dr. Liwu Li at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, and bred at National Jewish Health (NJH) Biological Research Center (BRC). ST2 KO mice on the BALB/c background were obtained from Dr. Rafeul Alam at NJH. Wild-type (WT) mice on the C57BL/6 and BALB/c background were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory and housed with the gene knockout mice at NJH BRC under pathogen-free housing conditions. All of the experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at NJH. To establish an acute model of IL-13-induced airway disease, mice were intranasally instilled with 3 doses of IL-13 using modified methods as previously published [19,20]. Mice (13–17 weeks old, both females and males) were adminstered intranasally with recombinant mouse IL-13 (rmIL-13) (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN) at 500 ng/mouse prepared in 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) or 0.1% BSA (control) once daily for 3 consecutive days. Mice were sacrificed after 24 and 48 hours of the last IL-13 treatment. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed with 1 ml saline. BAL cells were used for leukocyte count, and BAL fluid was saved for ELISA.
Mouse Lung Histopathologic Analysis
The apical lobe of the mouse right lung was fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin, and cut at 5 μm thickness for histopathologic analysis. Lung sections were stained with haemotoxylin and eosin (H&E), and evaluated in a blinded fashion under a light microscope using a histopathologic inflammatory scoring system as we described [21]. A final score per mouse on a scale of 0 to 26 (least to most severe) was obtained based on an assessment of the quantity and quality of peribronchiolar and peribronchial inflammatory infiltrates, luminal exudates, perivascular infiltrates, and parenchymal pneumonia.
Murine Macrophage Culture
Murine primary alveolar macrophages (AMs) were obtained by lavaging the lungs. AMs were isolated by adherence and cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin/streptomycin. At 6–8 hours after adherence in 96-well culture plates, AMs were stimulated with rmIL-13 (10 ng/ml) ± rmIL-33 (10 ng/ml, PEPRO TECH. Rocky Hill, NJ). Cell culture supernatants were collected for eotaxin-2 protein measurement. Cells were saved in RLT lysis buffer (QIAGEN Inc., Germantown, MD) at −80°C for subsequent total RNA extraction and RT-PCR.
Because of the limited numbers of AMs available for the mechanistic studies, bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were used to study how Tollip regulates eotaxin-2 production in the presence or absence of IL-13 and/or IL-33. Bone marrow cells from Tollip KO (C57BL/6 background), ST2 KO (BALB/c background), IRAK1 KO (C57BL/6 background) and WT (C57BL/6 and BALB/c) mice were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, penicillin/streptomycin and recombinant mouse macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rmM-CSF, 25 ng/ml) (R&D Systems Inc.) for 7 days to differentiate them into BMDMs. On day 7, BMDMs were harvested by trypsinization, and then seeded at 2×105 cells/well onto 24-well cell culture plates. On day 8, cells were stimulated by rmIL-13 ± rmIL-33, and in some conditions cells were pre-incubated with an anti-mouse ST2L/IL-33R antibody (R&D Systems Inc.) or the rat IgG2B isotype control (R&D Systems Inc.) for 2 hours. At the indicated time points, culture medium and cells were collected for protein and mRNA determination.
ELISA
A murine eotaxin-2 ELISA kit (R&D Systems Inc.) was used to quantify eotaxin-2 in murine BAL fluid and macrophage culture medium. Murine IL-33 ELISA (R&D Systems Inc.) was used to measure IL-33 in BAL fluid. The detection range for eotaxin-2 and IL-33 was from 15.6 to 1,000 pg/ml.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR was conducted using Taqman Gene Expression Assay (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) to determine relative mRNA levels of ST2L and IL-33. Target gene expression was normalized by the housekeeping gene 18S rRNA. The comparative threshold cycle method (ΔΔCt) was applied to determine the relative levels of target genes.
Western Blot Analysis
Equal amounts of protein from samples with different treatments were separated on 10% or 15% SDS-PAGE, transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes, and probed with a goat anti-Tollip antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX), a rabbit anti-IRAK1 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Danvers, MA), a rabbit anti-pIRAK1 antibody (Phospho-Thr209, Aviva Systems Biology, San Diego, CA), a goat anti-ST2L antibody (R&D Systems Inc.), a rabbit anti-STAT6 or anti-pSTAT6 (Phospho-Tyr641, Cell Signaling Technology Inc.) antibody or a mouse anti-GAPDH antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.). Blots were then incubated with appropriate HRP-linked secondary antibodies and developed with ECL Western blotting substrate. Densitometry was performed using the NIH Image-J software. Activation of IRAK1 or STAT6 was measured by analyzing their phosphorylation levels as indicated by the ratio phosphorylated vs. non-phosphorylated IRAK1 or STAT6.
Statistical Analysis
If the data were normally distributed, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test was used for multiple comparisons. The Student’s t-test was used when two groups were compared. For non-parametric data, the Kruskal-Wallis test for multiple comparisons or the Mann-Whitney test for two group comparisons was applied. Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed to determine the relationship of lung eosinophils and eotaxin-2 levels. A p value < 0.05 was considered significant. In the figures, *, **, and *** indicated p<0.05, p<0.01 and p<0.001, respectively.
Results
Tollip Inhibits Eosinophil Recruitment into The Lung of IL-13-Treated Mice
After 24 hours of the last IL-13 treatment, the total leukocyte counts in BAL fluid (BALF) were increased in both WT and Tollip KO mice, and were higher in Tollip KO mice than WT mice although a significant difference was not achieved (p=0.06) (Fig. 1A). Importantly, following IL-13 treatment, the percentage and number of eosinophils in BALF were significantly higher in Tollip KO mice than WT mice (Fig. 1B and 1C). Additionally, lymphocytes were also increased in Tollip KO mice as compared to the WT mice (Fig. 1D). IL-13 increased the number of neutrophils in both WT and Tollip KO mice, but there was no significant difference between the two groups (Fig. 1E). The number of macrophages in BALF did not change after IL-13 exposure (Fig. 1F). Examination of lung histopathology of IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice revealed more severe infiltrate of inflammatory cells including eosinophils around large airways and in the alveolar space (Fig. 2A to 2D). Histopathology score, an indication of overall inflammation levels, was significantly higher in IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice than the WT mice (Fig. 2 E).
Fig. 1.
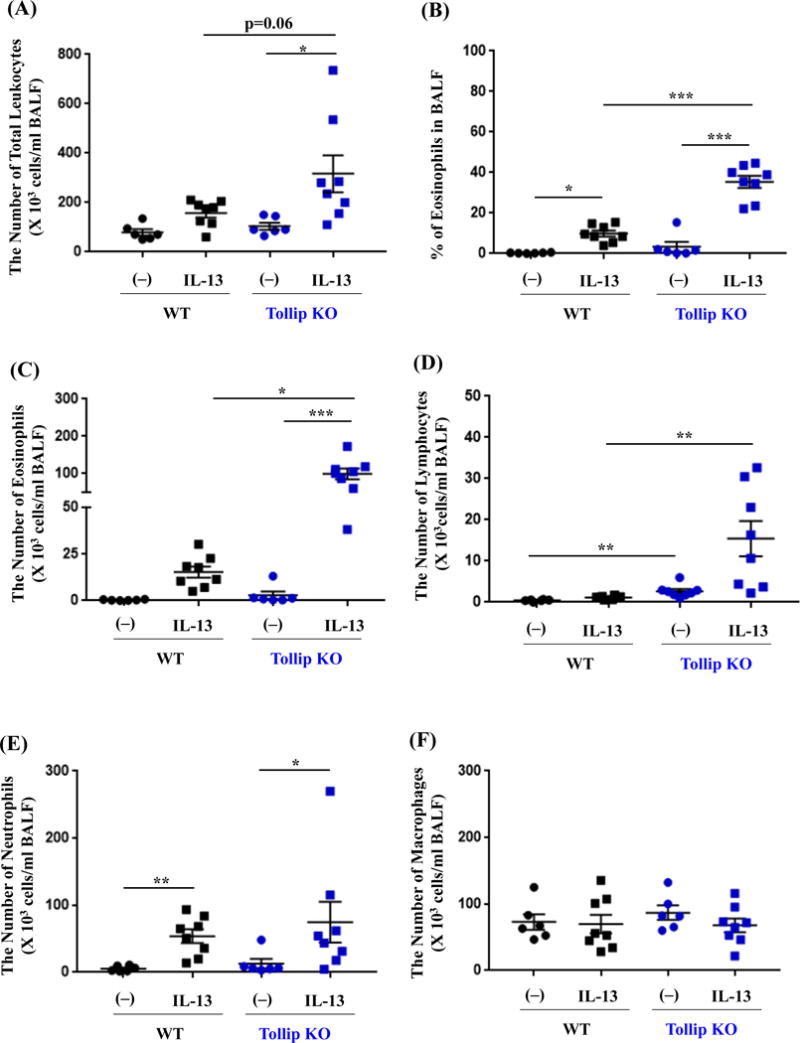
Tollip knockout (Tollip KO) mice treated with IL-13 show exaggerated eosinophil recruitment into the airways. Tollip KO and wild-type (WT) mice were treated with recombinant mouse IL-13 and sacrificed at 24 hours after the last IL-13 treatment. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected for counting the number of total leukocytes (A), eosinophils (B and C), lymphocytes (D), neutrophils (E) and macrophages (F). N=6–8 mice/group. Data are expressed as means±SEM.
Fig. 2.
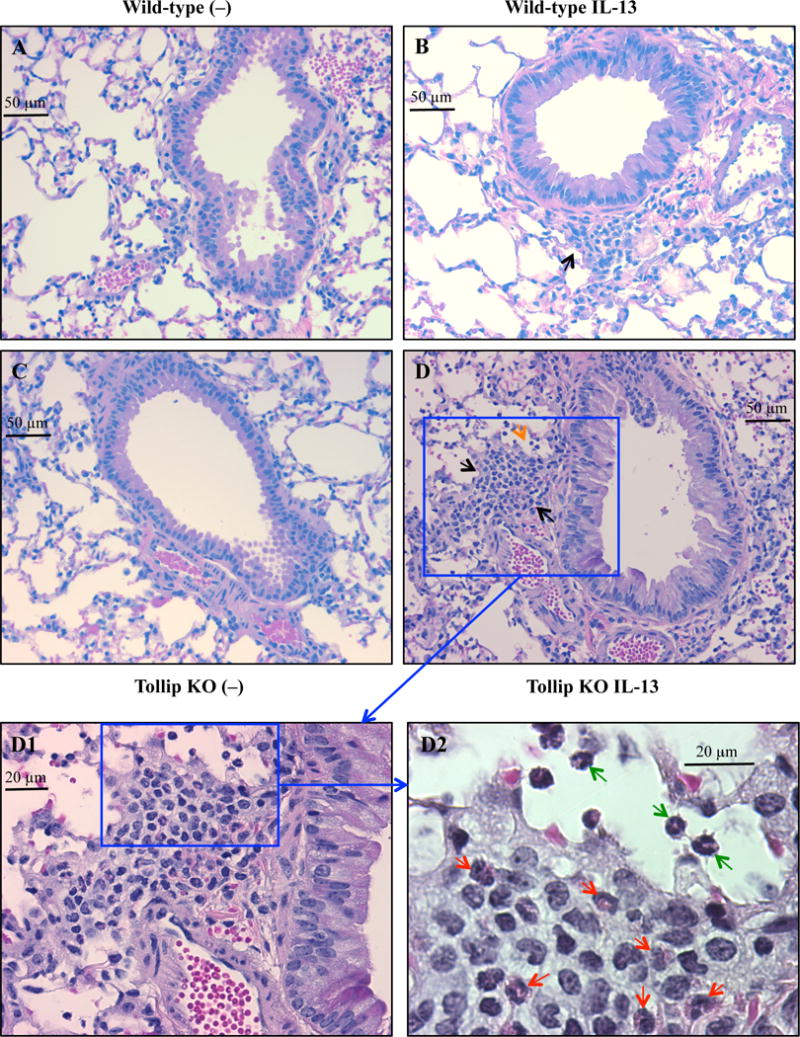
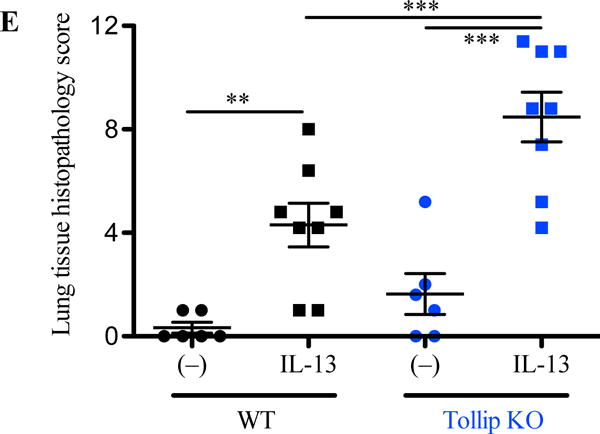
Tollip knockout (Tollip KO) mice treated with IL-13 show increased lung tissue inflammation. Tollip KO and wild-type mice were treated with recombinant mouse IL-13 and sacrificed at 24 hours after the last IL-13 treatment. Histopathologic images of H&E stained lung tissues are from wild-type (A and B) and Tollip KO (C and D) mice. Black and orange arrows indicate leukocyte infiltrate around an airway and in the alveolar space, respectively. To further identify inflammatory cell types in panel D (original magnification, 200×), higher magnification images of a framed inflammation area in panel D are shown in panel D1 (400×) and panel D2 (1000×). In panel D2, the red arrows indicate eosinophils around the airway, while the green arrows indicate eosinophils in the alveolar space. E – Histopathology score. N=6–8 mice/group. Data are expressed as means±SEM.
We also collected BALF at 48 hours after the last IL-13 treatment. Tollip KO mice showed higher eosinophil and lymphocyte counts in BALF than WT mice, but the differences did not reach the statistically significant level (eosinophils: WT, 40,311±9,905 cells/ml; KO, 110,574±26,881 cells/ml, p=0.07. lymphocytes: WT, 4,215±1,119 cells/ml; KO, 16,712±5,172 cells/ml, p=0.13).
Tollip Reduces Lung Secretion of Eotaxin-2 into BALF
As the focus of our study was to investigate how Tollip regulates eosinophilic inflammation, our mechanistic studies were centered on the pathways related to eotaxin expression, particularly at the earlier time point (e.g., 24 hours) to mimic acute inflammation related to asthma exacerbations. In line with the BAL eosinophil data, IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice showed higher levels of eotaxin-2 protein in BALF than the WT mice at 24 hours (Fig. 3A), and at 48 hours (WT, 638±256 pg/ml; KO, 1,654±397 pg/ml, p=0.06). Notably, eotaxin-2 protein levels were positively correlated with BAL eosinophil counts in both Tollip KO and WT mice (Fig. 3B).
Fig. 3.
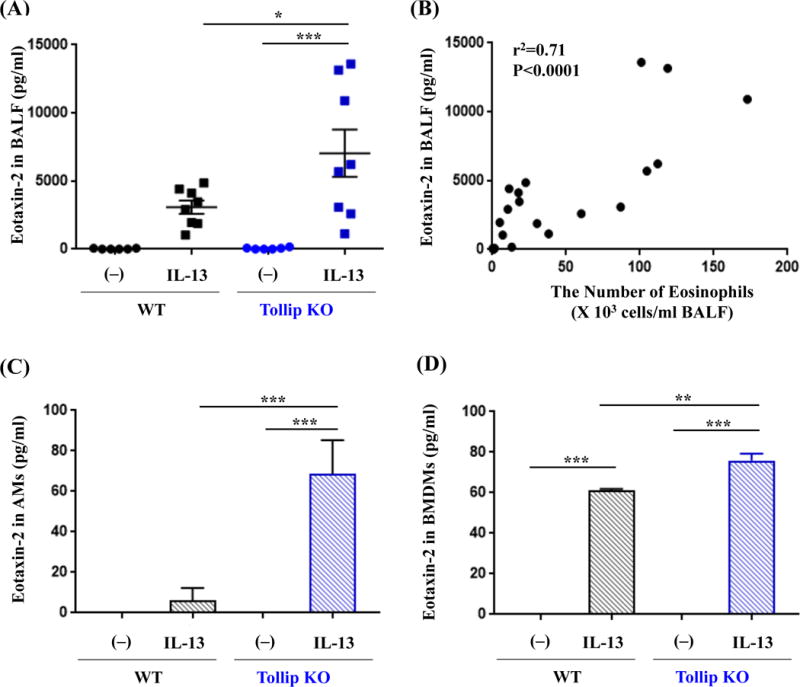
Tollip deficiency enhances IL-13-induced eotaxin-2 production in mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and macrophages. Tollip knockout (Tollip KO) and WT mice were treated with IL-13 and sacrificed at 24 hours after the last IL-13 treatment. (A) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in BALF. N=6–8 mice/group. (B) Scatterplot graph showing a positive correlation between the number of eosinophils and the level of eotaxin-2 protein in BALF. (C) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in culture medium of Tollip KO and WT mouse alveolar macrophages (AMs) stimulated with IL-13 for 48 hours. N=6 to 8 replicates from two independent experiments. (D) Eotaxin-2 protein measured in culture medium (± IL-13 for 24 hours) of bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) from Tollip KO and WT mice. N=9 replicates from three independent experiments. Data are expressed as means±SEM.
Tollip Suppresses IL-13-Induced Eotaxin-2 in Cultured Murine Macrophages
Because eotaxin-2 produced by macrophages is responsible for IL-13-mediated airway eosinophilia in a murine model [7], we determined the impact of Tollip expression on eotaxin-2 secretion by macrophages. To test if IL-13-exposed alveolar macrophages (AMs) from Tollip KO mice produce more eotaxin-2 than the WT cells, AMs were treated with rmIL-13. After IL-13 treatment, AMs from Tollip KO mice showed significantly higher levels of eotaxin-2 secretion than the WT mice (Fig. 3C).
As further mechanistic studies in murine AMs were difficult to pursue due to limited number of cells, we utilized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) from Tollip KO and WT mice. We confirmed that IL-13-treated BMDMs from Tollip KO mice produced higher levels of eotaxin-2 protein than those from the WT mice (Fig. 3D), which was consistent with the data in cultured AMs and BALF in vivo.
Tollip Decreases IL-13-Induced ST2L Expression and IL-13/IL-33-Mediated Eotaxin-2 Production in Murine BMDMs
How Tollip regulates eotaxin-2 expression under IL-13 stimulation remains unclear. A previous study using the BMDM culture system demonstrated the synergic effects of IL-13 in combination with IL-33, another key cytokine in the type 2 inflammation, on eotaxin expression, which is largely dependent on the induction of the IL-33 receptor ST2L by IL-13 [22]. Importantly, ST2L protein level was significantly higher in IL-13-treated BMDMs from the Tollip KO mice than the WT mice (Fig. 4A). As various cell types in the lung constitutively express IL-33, our data suggest that ST2L up-regulation associated with Tollip deficiency may enhance the crosstalk between IL-13 and IL-33 pathways, and further increase eotaxin expression and eosinophilic inflammation. Therefore, we stimulated BMDMs with IL-13 and IL-33 simultaneously and measured eotaxin-2 secretion. IL-13 and IL-33 stimulation in Tollip KO mouse BMDMs synergistically increased eotaxin-2 secretion, which was markedly (about 6-fold) inhibited by a ST2L neutralizing antibody (Fig. 4B). The contribution of ST2L to IL-13 and IL-33 mediated eotaxin-2 expression was further revealed by the finding that ST2L KO BMDMs produced significantly less eotaxin-2 than the WT cells (Fig. 4C). Moreover, as previous reports demonstrated that IL-33 amplifies IL-13-induced ST2L expression [22], we examined if Tollip deficiency enhances ST2L induction by IL-13 and IL-33. As shown in Fig. 4D, ST2L mRNA and protein were markedly induced by IL-13 and IL-33 in BMDMs from the Tollip KO mice.
Fig. 4.
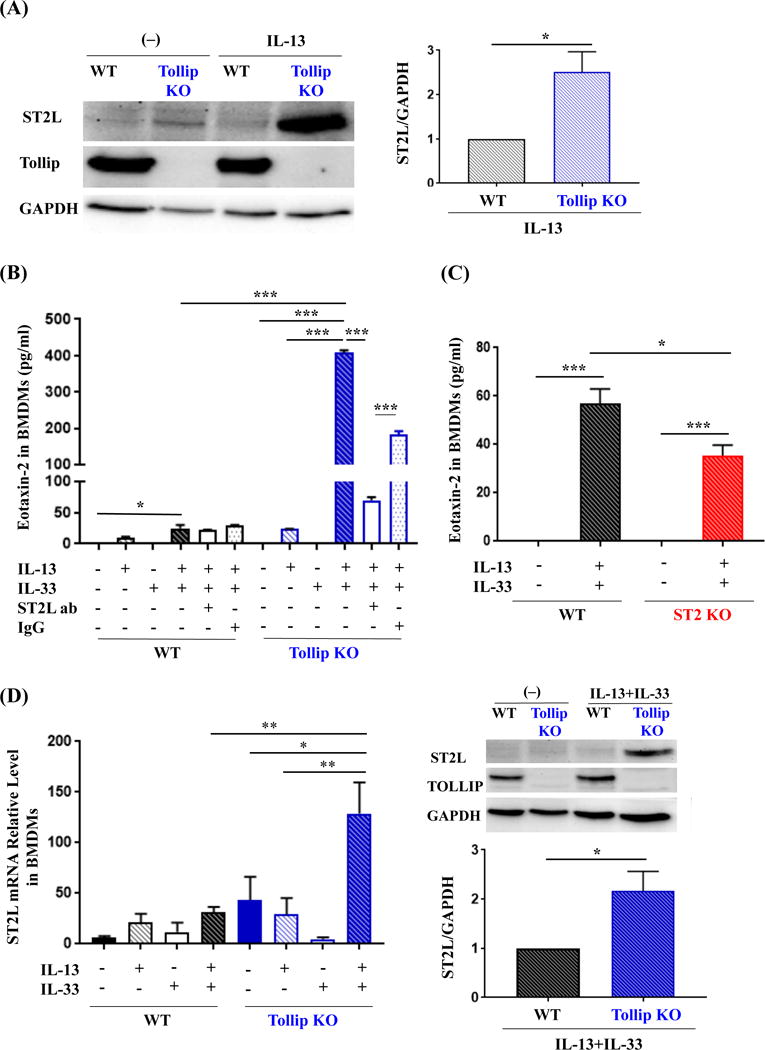
Tollip deficiency increases IL-13-induced ST2L expression, and eotaxin-2 production by IL-13 and IL-33 in murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs). (A) BMDMs from Tollip knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were incubated with IL-13 for 24 hours. Left panel – a representative Western blot image of IL-13-induced ST2L protein expression; Right panel – densitometric analysis of ST2L protein. (B) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in culture medium of Tollip KO and WT mouse BMDMs stimulated with IL-13, IL-33, and combination of IL-13 and IL-33 in the presence or absence of a ST2L neutralizing antibody (ST2L ab) or the IgG2B isotype control (IgG) for 24 hours. (C) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in culture medium of ST2 knockout (ST2 KO) and WT mouse BMDMs stimulated with IL-13 and IL-33 for 48 hours. (D) BMDMs from Tollip KO and WT mice were cultured with IL-13 and/or IL-33 for 24 hours. Left panel – ST2L mRNA relative levels; Right panel – a representative Western blot image of ST2L protein and densitometric analysis. Data are expressed as means±SEM. N=9 replicates from three independent experiments.
Tollip Down-regulates IL-13/IL-33-Induced Eotaxin-2 in Part by Inhibiting IRAK1 Activation
IL-33 is a member of the IL-1 family. Upon IL-33 stimulation, MyD88, IRAK1, IRAK4 and TRAF6 are all recruited to ST2L, which activates MAP kinase and NF-κB [23]. Tollip may negatively regulate IL-33 signaling pathway by inhibiting the activation of IRAK1 [24]. To determine if eotaxin-2 induction by IL-13 and IL-33 is regulated through IRAK1 activation, we measured eotaxin-2 production in IL-13 and IL-33 stimulated BMDMs of IRAK1 KO and WT mice. The dependence of eotaxin-2 expression on IRAK1 was supported by the lack of eotaxin-2 production in IL-13 and IL-33 stimulated BMDMs from IRAK1 KO mice as compared to the WT mice (Fig. 5A). Notably, Tollip KO BMDMs with IL-13 and IL-33 stimulation showed greater IRAK1 activation than WT cells (Fig. 5B), supporting Tollip’s inhibitory effect on IRAK1 activation and subsequent eotaxin-2 production.
Fig. 5.
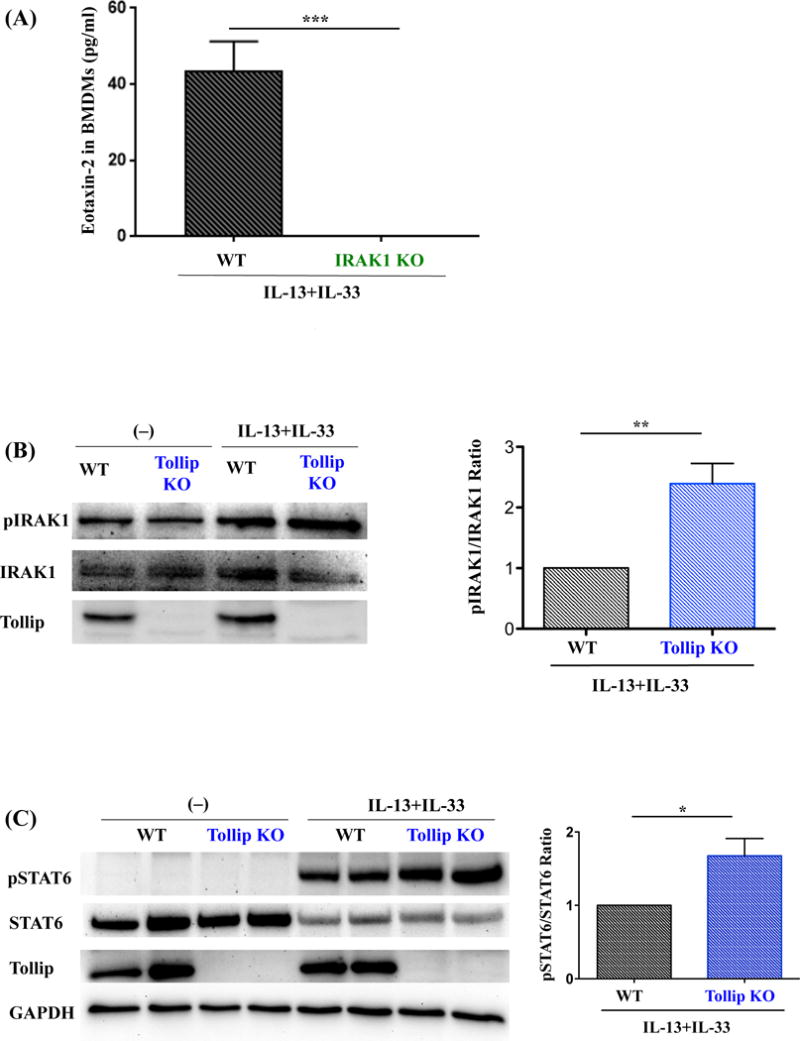
Role of IRAK1 and STAT6 in eotaxin-2 induction by IL-13 and IL-33 in murine bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs). (A) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in culture medium of IRAK1 knockout (IRAK1 KO) and WT mouse BMDMs stimulated with IL-13 and IL-33 for 48 hours. N=9 replicates from three independent experiments. (B) BMDMs from Tollip KO and WT mice were incubated with IL-13 and IL-33 for 24 hours. Left panel – a representative Western blot image of phosphorylated IRAK1 (pIRAK1) and total IRAK1 proteins; Right panel – densitometric analysis of IRAK1 activation, as determined by the ratio of pIRAK1 and total IRAK1. N=9 replicates from three independent experiments. (C) Left panel – a representative Western blot image of phosphorylated STAT6 (pSTAT6) and STAT6 in Tollip KO and WT mouse BMDMs stimulated with IL-13 and IL-33 for 60 minutes; Right panel – densitometric analysis of STAT6 activation, as determined by the ratio of pSTAT6 and total STAT6. N=3 replicates from two independent experiments. Data are expressed as means±SEM.
Having shown the inhibitory role of Tollip in IRAK1 activation, we determined if Tollip inhibited STAT6 activation, a pathway involved in IL-13-induced ST2L expression [25]. STAT6 activation was compared in BMDMs of WT and Tollip KO mice at 60 minutes after IL-13 and IL-33 co-stimulation to mimic the co-existence of these two cytokines in our IL-13 treatment mouse model. We found that STAT6 activation was moderately higher in BMDMs of Tollip KO mice than WT mice (Fig. 5C), suggesting an inhibitory role of Tollip in the early IL-13 signaling event.
IL-33 Protein Is Constitutively Secreted into The Mouse Airway, and Tollip Inhibits IL-33 mRNA Induction by IL-13 in AMs
As BMDMs from the Tollip KO mice increased eotaxin-2 secretion after IL-13 and IL-33 co-stimulation, we sought to determine if IL-33 protein levels in BALF were different between WT and Tollip KO mice. Although IL-33 protein was detectable in BALF of control mice, it was not further induced by IL-13 treatment (Fig. 6A) in WT or Tollip KO mice. As the murine macrophage is one of the major sources of IL-33 [26–30], we examined if IL-13 alone induced IL-33 expression in AMs. IL-33 mRNA was significantly induced by IL-13 in Tollip KO AMs, but not in WT AMs. The induction of IL-33 mRNA by IL-13 trended to be greater in AMs from the Tollip KO mice than the WT mice (Fig. 6B). However, IL-33 protein in culture medium from IL-13-treated AMs was undetectable by ELISA. AMs were stimulated with both IL-13 and IL-33 to mimic the co-existence of these two cytokines in our IL-13 treatment mouse model. Indeed, AMs from the Tollip KO mice, as compared to the WT mice, increased the production of eotaxin-2 (Fig. 6C), which was consistent with our data obtained from BMDMs (Fig. 4B).
Fig. 6.
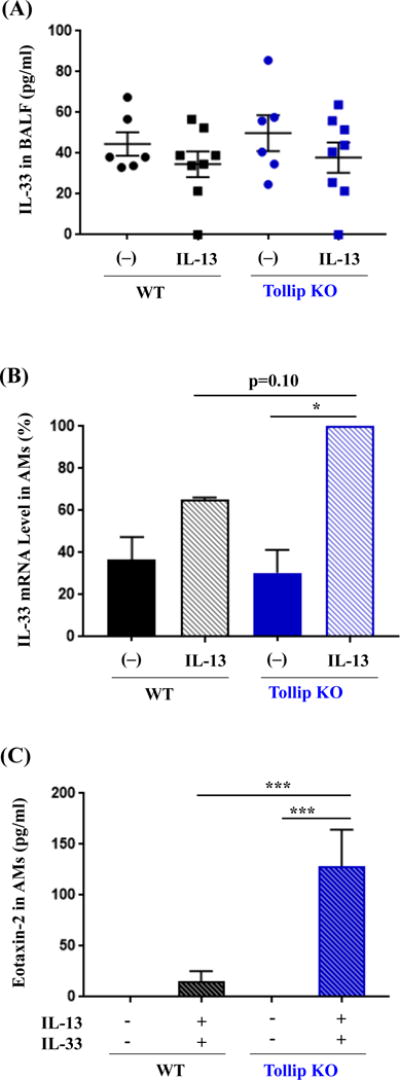
IL-33 expression in mouse bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and alveolar macrophages (AMs). (A) Tollip knockout (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice were treated with IL-13 and sacrificed at 24 hours after the last IL-13 treatment. IL-33 protein in BALF was measured by ELISA. N=6–8 mice/group. (B) AMs from Tollip KO and WT mice were incubated with IL-13 for 48 hours. IL-33 mRNA levels were expressed as % of IL-13-treated AMs from the Tollip KO mice. (C) Eotaxin-2 protein levels in culture medium of Tollip KO and WT mouse AMs with or without stimulation of IL-13 and IL-33 for 48 hours. Data are expressed as means±SEM. N=6 to 9 replicates from two to three independent experiments for culture of AMs.
Discussion
This is the first report demonstrating the regulation of in vivo lung eosinophilic inflammation by Tollip in the context of type 2 cytokine treatment. Our results suggest that Tollip deficiency promotes pulmonary eosinophilia by enhancing eotaxin-2 production. Major findings in this study include: 1) IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice show exaggerated pulmonary eosinophilia and eotaxin-2 production; and 2) Tollip KO murine macrophages stimulated with IL-13 alone or in combination with IL-33 are characterized by enhanced ST2L expression, IRAK1 activation, and eotaxin-2 production.
In this report, we clearly demonstrated that Tollip deficiency enhances IL-13-induced pulmonary eosinophilia along with eotaxin-2 secretion into the airway lumen. Although various mediators such as eotaxins and IL-5 are known to promote murine lung eosinophilic inflammation, how these mediators are regulated under a type 2 cytokine milieu remains poorly understood. In mouse lungs, AMs, in response to IL-13, serve as a major source of eotaxin-2 that contributes to sustained recruitment of eosinophils into the airway lumen [7]. Indeed, we found that eotaxin-2 production is higher in murine macrophages (AMs and BMDMs) from the Tollip KO mice than the wild-type mice. Once IL-13 binds to IL-13Rα1, STAT6 is activated and translocated to the nucleus where eotaxin-2 transcription is up-regulated [6]. We determined if Tollip modifies the activation of STAT6, and observed marginal enhancement of STAT6 activation by IL-13 in BMDMs from the Tollip KO mice, suggesting that Tollip may down-regulate eotaxin-2 in part through reducing STAT6 activation. While we do not know how Tollip exactly affects STAT6 activation, Tollip is known to modify several signaling pathways (e.g., IL-1βR and TGF-βR) by promoting degradation of ubiquitin-conjugated proteins [31–33]. Therefore, we propose that Tollip regulates the IL-13-STAT6 signaling pathway possibly by interacting with STAT6, but this awaits further confirmation.
One innovative aspect of our current study is to unravel the role of Tollip in inhibiting IL-13-mediated up-regulation of IL-33 receptor ST2L. IL-33, a member of the IL-1 cytokine family, is involved in asthma airway inflammation [34]. The binding of IL-33 to ST2L leads to IL-1R accessory protein (IL-1Racp) recruitment and formation of heterodimeric signaling complex that involves myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88), IRAK1, IRAK4 and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), and the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) [35]. ST2L expression is higher in endobronchial biopsies of severe asthmatics than healthy controls and mild/moderate asthmatics, and associated with multiple T2-high asthma biomarkers including blood eosinophils and eotaxin mRNA expression [36]. Notably, ST2L is induced by IL-13 in part through the STAT6 pathway [22,25]. Therefore, IL-33 has been shown to amplify eotaxin-2 production in IL-13 pretreated macrophages [22]. As Tollip is a negative regulator for TLR and IL-1R pathways by inhibiting IRAK1 activation [24], we tested if Tollip regulates the IL-13/IL-33/ST2L pathway, which was never evaluated before. Our data have extended previous reports [22] in that IL-13 particularly in the presence of IL-33 significantly increases ST2L expression and eotaxin-2 production in murine macrophages. Our study demonstrates for the first time that Tollip deficiency leads to greater induction of ST2L expression by IL-13 and/or IL-33 in macrophages. Moreover, we have found that Tollip deficiency results in greater induction of eotaxin-2 that is dependent on ST2L as Tollip’s inhibitory effect on eotaxin-2 is partially abrogated by a ST2L neutralizing antibody. Thus, greater ST2L expression on macrophages from Tollip KO mice renders the cells more sensitive to the stimulation of IL-33 that is constitutively expressed in the lung and can be further up-regulated by IL-13 treatment [26,37]. We are aware that, unlike the previous study [22], we did not observe a synergistic effect of IL-13 and IL-33 stimulation on ST2L expression in BMDMs from the wild-type mice. This may be explained by the use of a higher dose of IL-33 (20 ng/ml) in the previous study, and a lower dose of IL-33 (10 ng/ml) in our current study.
Having shown that IL-33/ST2L signaling is involved in eotaxin-2 production, we further evaluated the role of the downstream signaling event of this pathway in eotaxin expression in the context of Tollip. IRAK1 is an integral component of the IL-33/ST2L signaling, but its contribution to IL-13/IL-33-mediated eotaxin production is unknown. Our data suggest that Tollip deficiency allows greater IRAK1 activation, and that IRAK-1 deficiency significantly diminishes IL-13/IL-33-induced eotaxin-2 expression. Together, our data indicate that Tollip acts on several checking points to down-regulate eotaxin-2 expression in the IL-13/IL-33 setting. The relative contribution of these checking points to Tollip’s effects on eotaxin expression deserves further investigation.
Lung macrophages and epithelial cells produce IL-33 as an alarmin [26]. IL-33 is induced in alveolar macrophages of ovalbumin-challenged mice [28,38]. Intriguingly, we did not see increased IL-33 in BAL fluid of IL-13-treated Tollip KO mice as compared to the wild-type mice. Notably, in cultured alveolar macrophages from the Tollip KO mice but not the WT cells, there was significant induction of IL-33 mRNA by IL-13. However, IL-33 protein was not detectable in alveolar macrophage supernatants. Together, our findings suggest that Tollip has a minimal impact on IL-33 protein release during its regulation of lung eosinophilic inflammation. Instead, as described in the results section, IL-33 is constitutively released into the lung (e.g., airway lumen). We propose that greater induction of ST2L expression in lung cells (e.g., macrophages) of Tollip KO mice by IL-13 would increase the sensitivity of cells responding to endogenous/local IL-33, thereby promoting eosinophilic inflammation.
There are several limitations to the current study. First, because gene knockdown in human primary macrophages is very challenging, we were not able to knockdown Tollip in human primary AMs in order to translate our findings from mice to humans. Second, although lymphocyte recruitment is increased in Tollip KO vs. WT mice, we have not assessed its contribution to eosinophilic inflammation. Recent studies have indicated that type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) contribute to the persistence of airway eosinophilia in patients with severe asthma through localized production of IL-13 [39]. Therefore, dissecting the role of Tollip in regulating ILC2s would further reveal how Tollip affects lung eosinophilic inflammation. Finally, our mechanistic study was focused on macrophages. In our pilot study, we examined if airway epithelial cells are involved in Tollip’s function related to eosinophilic inflammation. As eotaxin-2 levels in cultured mouse tracheal epithelial cells were not detectable, we did not pursue the epithelial model for the mechanistic studies. However, future studies are warranted to determine the role of Tollip in regulating eotaxin expression by primary human airway epithelial cells.
In Fig. 7, we have proposed the novel mechanisms by which Tollip inhibits pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation. Briefly, IL-13-stimulated macrophages increase ST2L in part through STAT6 activation, and then eotaxin-2 expression in part through IRAK-1 activation in the context of lung constitutive and perhaps inducible IL-33 secretion. Tollip attenuates the activity of the IL-13/STAT6/ST2L/IL-33/IRAK-1/eotaxin axis in part by inhibiting STAT6 as well as IRAK-1 activation. As our previous study demonstrated that asthmatics carrying the Tollip rs5743899 AG/GG genotype (vs. the AA genotype) express less Tollip protein and greater airflow limitation (less FEV1/FVC), our current study likely offers an innovative and more precise approach to reduce airway inflammation in asthma patients. Enhancing Tollip expression or suppressing IRAK-1 activation in asthmatics carrying the rs5743899 AG or GG genotype may effectively reduce airway inflammation and improve pulmonary function.
Fig. 7.
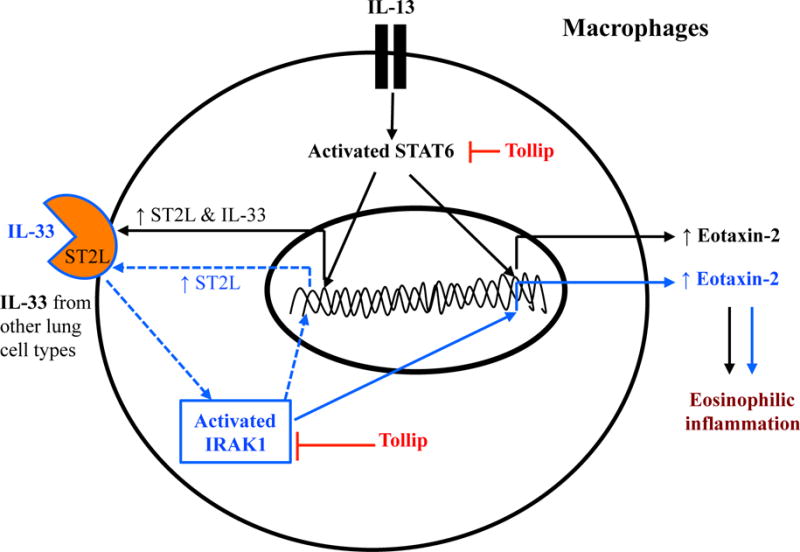
Proposed mechanisms whereby Tollip attenuates eotaxin-2 production and pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation. In lung cells such as macrophages, IL-13 induces eotaxin-2 expression in part through activating STAT6. Importantly, STAT6 activation will subsequently increase the expression of IL-33 receptor ST2L, which binds the pre-existing (constitutive) IL-33 in the lung to further induce eotaxin-2 expression and eosinophilic inflammation in part through activating IRAK1. Tollip inhibits eotaxin-2 and eosinophilic inflammation by suppressing the activity of IRAK1 as well as STAT6.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the National Institutes of Health, R01 HL122321, R01 AI106287, R01 HL125128 and U19AI125357.
Abbreviations
- AMs
Alveolar macrophages
- BALF
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- BMDMs
Bone marrow-derived macrophages
- BRC
Biological Research Center
- CCL24
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 24, also known as eotaxin-2
- DMEM
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- FBS
Fetal bovine serum
- IL-13
Interleukin-13
- IL-33
Interleukin-33
- IRAK1
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1
- ILC2s
Type 2 innate lymphoid cells
- KO
Knockout
- rmIL-13
Recombinant mouse IL-13
- rmIL-33
Recombinant mouse IL-33
- SNPs
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- T2-high
Type 2-high
- T2-low
Type 2-low
- TLR
Toll-like receptor
- Tollip
Toll-interacting protein
- WT
Wild-type
Footnotes
Disclosure Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Eder W, Ege MJ, von Mutius E. The asthma epidemic. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2226–2235. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra054308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tabatabaian F, Ledford DK, Casale TB. Biologic and New Therapies in Asthma. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2017;37:329–343. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2017.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carr TF, Berdnikovs S, Simon HU, Bochner BS, Rosenwasser LJ. Eosinophilic bioactivities in severe asthma. World Allergy Organ J. 2016;9:21. doi: 10.1186/s40413-016-0112-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zeiger RS, Schatz M, Li Q, Chen W, Khatry DB, Gossage D, Tran TN. High blood eosinophil count is a risk factor for future asthma exacerbations in adult persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:741–750. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2014.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moore WC, Hastie AT, Li X, Li H, Busse WW, Jarjour NN, Wenzel SE, Peters SP, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER. Sputum neutrophil counts are associated with more severe asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1557–1563.e1555. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rael EL, Lockey RF. Interleukin-13 signaling and its role in asthma. World Allergy Organ J. 2011;4:54–64. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e31821188e0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pope SM, Fulkerson PC, Blanchard C, Akei HS, Nikolaidis NM, Zimmermann N, Molkentin JD, Rothenberg ME. Identification of a cooperative mechanism involving interleukin-13 and eotaxin-2 in experimental allergic lung inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:13952–13961. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406037200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pope SM, Brandt EB, Mishra A, Hogan SP, Zimmermann N, Matthaei KI, Foster PS, Rothenberg ME. IL-13 induces eosinophil recruitment into the lung by an IL-5- and eotaxin-dependent mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:594–601. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.118600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jiang Z, Zhu L. Update on the role of alternatively activated macrophages in asthma. J Asthma Allergy. 2016;9:101–107. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S104508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Siddiqui S, Secor ER, Jr, Silbart LK. Broncho-alveolar macrophages express chemokines associated with leukocyte migration in a mouse model of asthma. Cell Immunol. 2013;281:159–169. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Balhara J, Gounni AS. The alveolar macrophages in asthma: a double-edged sword. Mucosal Immunol. 2012;5:605–609. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Capelluto DG. Tollip: a multitasking protein in innate immunity and protein trafficking. Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur. 2012;14:140–147. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shah JA, Vary JC, Chau TT, Bang ND, Yen NT, Farrar JJ, Dunstan SJ, Hawn TR. Human TOLLIP regulates TLR2 and TLR4 signaling and its polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. J Immunol. 2012;189:1737–1746. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang C, Jiang D, Francisco D, Berman R, Wu Q, Ledford JG, Moore CM, Ito Y, Stevenson C, Munson D, Li L, Kraft M, Chu HW. Tollip SNP rs5743899 modulates human airway epithelial responses to rhinovirus infection. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46:1549–1563. doi: 10.1111/cea.12793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moncayo-Nieto OL, Wilkinson TS, Brittan M, McHugh BJ, Jones RO, Conway Morris A, Walker WS, Davidson DJ, Simpson AJ. Differential response to bacteria, and TOLLIP expression, in the human respiratory tract. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2014;1:e000046. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Song Z, Yin J, Yao C, Sun Z, Shao M, Zhang Y, Tao Z, Huang P, Tong C. Variants in the Toll-interacting protein gene are associated with susceptibility to sepsis in the Chinese Han population. Critical care. 2011;15:R12. doi: 10.1186/cc9413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Noth I, Zhang Y, Ma SF, Flores C, Barber M, Huang Y, Broderick SM, Wade MS, Hysi P, Scuirba J, Richards TJ, Juan-Guardela BM, Vij R, Han MK, Martinez FJ, Kossen K, Seiwert SD, Christie JD, Nicolae D, Kaminski N, Garcia JG. Genetic variants associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis susceptibility and mortality: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1:309–317. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70045-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schimming TT, Parwez Q, Petrasch-Parwez E, Nothnagel M, Epplen JT, Hoffjan S. Association of toll-interacting protein gene polymorphisms with atopic dermatitis. BMC Dermatol. 2007;7:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-5945-7-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hollingsworth JW, Theriot BS, Li Z, Lawson BL, Sunday M, Schwartz DA, Walker JK. Both hematopoietic-derived and non-hematopoietic-derived {beta}-arrestin-2 regulates murine allergic airway disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010;43:269–275. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0198OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kinyanjui MW, Shan J, Nakada EM, Qureshi ST, Fixman ED. Dose-dependent effects of IL-17 on IL-13-induced airway inflammatory responses and airway hyperresponsiveness. J Immunol. 2013;190:3859–3868. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chu HW, Honour JM, Rawlinson CA, Harbeck RJ, Martin RJ. Effects of respiratory Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection on allergen-induced bronchial hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in mice. Infect Immun. 2003;71:1520–1526. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1520-1526.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kurowska-Stolarska M, Stolarski B, Kewin P, Murphy G, Corrigan CJ, Ying S, Pitman N, Mirchandani A, Rana B, van Rooijen N, Shepherd M, McSharry C, McInnes IB, Xu D, Liew FY. IL-33 amplifies the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway inflammation. J Immunol. 2009;183:6469–6477. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, Gorman DM, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J, Volpe F. Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nature cell biology. 2000;2:346–351. doi: 10.1038/35014038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yagami A, Orihara K, Morita H, Futamura K, Hashimoto N, Matsumoto K, Saito H, Matsuda A. IL-33 mediates inflammatory responses in human lung tissue cells. J Immunol. 2010;185:5743–5750. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nakae S, Morita H, Ohno T, Arae K, Matsumoto K, Saito H. Role of interleukin-33 in innate-type immune cells in allergy. Allergol Int. 2013;62:13–20. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.13-RAI-0538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ohno T, Oboki K, Kajiwara N, Morii E, Aozasa K, Flavell RA, Okumura K, Saito H, Nakae S. Caspase-1, caspase-8, and calpain are dispensable for IL-33 release by macrophages. J Immunol. 2009;183:7890–7897. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nabe T, Wakamori H, Yano C, Nishiguchi A, Yuasa R, Kido H, Tomiyama Y, Tomoda A, Kida H, Takiguchi A, Matsuda M, Ishihara K, Akiba S, Ohya S, Fukui H, Mizutani N, Yoshino S. Production of interleukin (IL)-33 in the lungs during multiple antigen challenge-induced airway inflammation in mice, and its modulation by a glucocorticoid. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;757:34–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ohno T, Oboki K, Morita H, Kajiwara N, Arae K, Tanaka S, Ikeda M, Iikura M, Akiyama T, Inoue J, Matsumoto K, Sudo K, Azuma M, Okumura K, Kamradt T, Saito H, Nakae S. Paracrine IL-33 stimulation enhances lipopolysaccharide-mediated macrophage activation. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18404. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Joshi AD, Oak SR, Hartigan AJ, Finn WG, Kunkel SL, Duffy KE, Das A, Hogaboam CM. Interleukin-33 contributes to both M1 and M2 chemokine marker expression in human macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2010;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Saha SS, Singh D, Raymond EL, Ganesan R, Caviness G, Grimaldi C, Woska JR, Jr, Mennerich D, Brown SE, Mbow ML, Kao CC. Signal Transduction and Intracellular Trafficking by the Interleukin 36 Receptor. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:23997–24006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.653378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brissoni B, Agostini L, Kropf M, Martinon F, Swoboda V, Lippens S, Everett H, Aebi N, Janssens S, Meylan E, Felberbaum-Corti M, Hirling H, Gruenberg J, Tschopp J, Burns K. Intracellular trafficking of interleukin-1 receptor I requires Tollip. Curr Biol. 2006;16:2265–2270. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhu L, Wang L, Luo X, Zhang Y, Ding Q, Jiang X, Wang X, Pan Y, Chen Y. Tollip, an intracellular trafficking protein, is a novel modulator of the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:39653–39663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.388009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cayrol C, Girard JP. IL-33: an alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2014;31:31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liew FY, Girard JP, Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:676–689. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Traister RS, Uvalle CE, Hawkins GA, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER, Wenzel SE. Phenotypic and genotypic association of epithelial IL1RL1 to human TH2-like asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:92–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.06.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Christianson CA, Goplen NP, Zafar I, Irvin C, Good JT, Jr, Rollins DR, Gorentla B, Liu W, Gorska MM, Chu H, Martin RJ, Alam R. Persistence of asthma requires multiple feedback circuits involving type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:59–68.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.11.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kurowska-Stolarska M, Kewin P, Murphy G, Russo RC, Stolarski B, Garcia CC, Komai-Koma M, Pitman N, Li Y, Niedbala W, McKenzie AN, Teixeira MM, Liew FY, Xu D. IL-33 induces antigen-specific IL-5+ T cells and promotes allergic-induced airway inflammation independent of IL-4. J Immunol. 2008;181:4780–4790. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Smith SG, Chen R, Kjarsgaard M, Huang C, Oliveria JP, O’Byrne PM, Gauvreau GM, Boulet LP, Lemiere C, Martin J, Nair P, Sehmi R. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:75–86.e78. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


