Full text
PDF

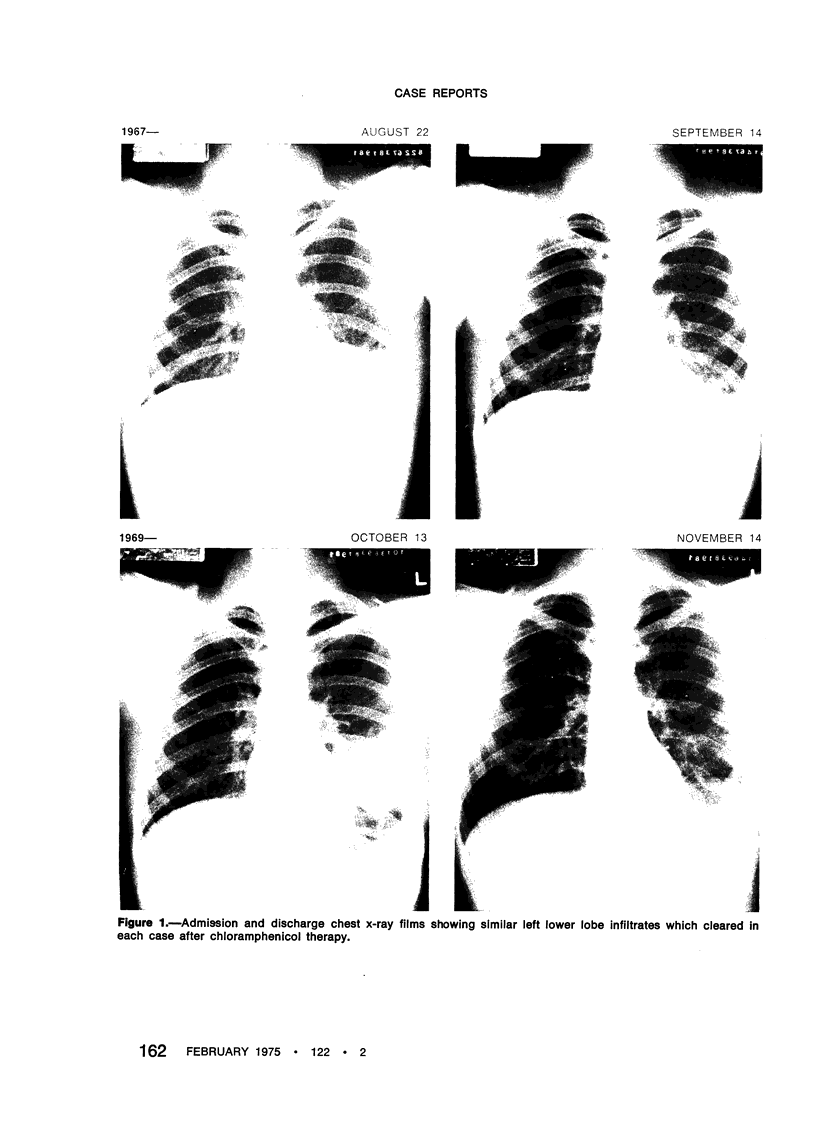


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acred P., Brown D. M., Knudsen E. T., Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. New semi-synthetic penicillin active against Pseudomonas pyocyanea. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):25–30. doi: 10.1038/215025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey R. H., Benner E. J. Necrotizing pneumonicitis due to the pseudomonad "eugonic oxidizer--group I". N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 15;279(7):361–362. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808152790706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. C., Douglas S. D., Fudenberg H. H. A selective neutrophil dysfunction syndrome: impaired killing of staphylococci. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1237–1243. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. D., Davis W. C., Fudenberg H. H. Granulocytopathies: pleomorphism of neutrophil dysfunction. Am J Med. 1969 Jun;46(6):901–909. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J., Burch W., Grimmett G., Orme K., Brewer D., Frost R., Fulkerson C. Successful treatment of Pseudomonas cepacia endocarditis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Nov;4(5):551–554. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.5.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Page A. R., Good R. A. Studies of the metabolic activity of leukocytes from patients with a genetic abnormality of phagocytic function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1422–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI105634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Park B. H., Malawista S. E., Quie P. G., Nelson D. L., Good R. A. Chronic granulomatous disease in females. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 30;283(5):217–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007302830501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Hook E. W. Leukocyte bactericidal activity in chronic granulomatous disease: correlation of bacterial hydrogen peroxide production and susceptibility to intracellular killing. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):531–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.531-532.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Hook E. W. Leukocyte function in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Studies on a seventeen year old boy. Am J Med. 1969 Sep;47(3):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattison R. A., Gooch W. M., 3rd, Guelzow K. W., South M. A. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood in a 17-year-old boy. J Pediatr. 1970 Jun;76(6):890–894. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. R., Sabbaj J., Weinstein L. Bacteriological, pharmacological, and clinical studies of carbenicillin. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Feb;125(2):282–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., Kaplan E. L., Page A. R., Gruskay F. L., Malawista S. E. Defective polymorphonuclear-leukocyte function and chronic granulomatous disease in two female children. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):976–980. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. N., Soothill J. F. Chronic granulomatous disease: quantitative clinicopathological relationships. Arch Dis Child. 1970 Feb;45(239):24–32. doi: 10.1136/adc.45.239.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



