Abstract
1. Nerve terminals of the rat posterior pituitary were acutely dissociated and identified using a combination of morphological and immunohistochemical techniques. Terminal membrane currents were studied using the 'whole-cell' patch clamp technique and channels were studied using inside-out and outside-out patches. 2. In physiological solutions, but with 7 mM 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), depolarizing voltage clamp steps from different holding potentials (-90 or -50 mV) elicited a fast, inward current followed by a slow, sustained, outward current. This outward current did not appear to show any steady-state inactivation. 3. The threshold for activation of the outward current was -30 mV and the current-voltage relation was 'bell-shaped'. The amplitude increased with increasingly depolarized potential steps. The outward current reversal potential was measured using tail current analysis and was consistent with that of a potassium current. 4. The sustained potassium current was determined to be dependent on the concentration of intracellular calcium. Extracellular Cd2+ (80 microM), a calcium channel blocker, also reversibly abolished the outward current. 5. The current was delayed in onset and was sustained over the length of a 150 ms-duration depolarizing pulse. The outward current reached a peak plateau and then decayed slowly. The decay was fitted by a single exponential with a time constant of 9.0 +/- 2.2 s. The decay constants did not show a dependence on voltage but rather on intracellular Ca2+. The time course of recovery from this decay was complex with full recovery taking > 190 s. 6. 4-AP (7 mM), dendrotoxin (100 nM), apamin (40-80 nM), and charybdotoxin (10-100 nM) had no effect on the sustained outward current. In contrast Ba2+ (200 microM) and tetraethylammonium inhibited the current, the latter in a dose-dependent manner (apparent concentration giving 50% of maximal inhibition (IC50) = 0.51 mM). 7. The neurohypophysial terminal outward current recorded here corresponds most closely to a Ca(2+)-activated K+ current (IK(Ca)) and not to a delayed rectifier or IA-like current. It also has properties different from that of the Ca(2+)-dependent outward current described in the magnocellular neuronal cell bodies of the hypothalamus. 8. A large conductance channel is often observed in isolated rat neurohypophysial nerve terminals. The channel had a unit conductance of 231 pS in symmetrical 150 mM K+.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






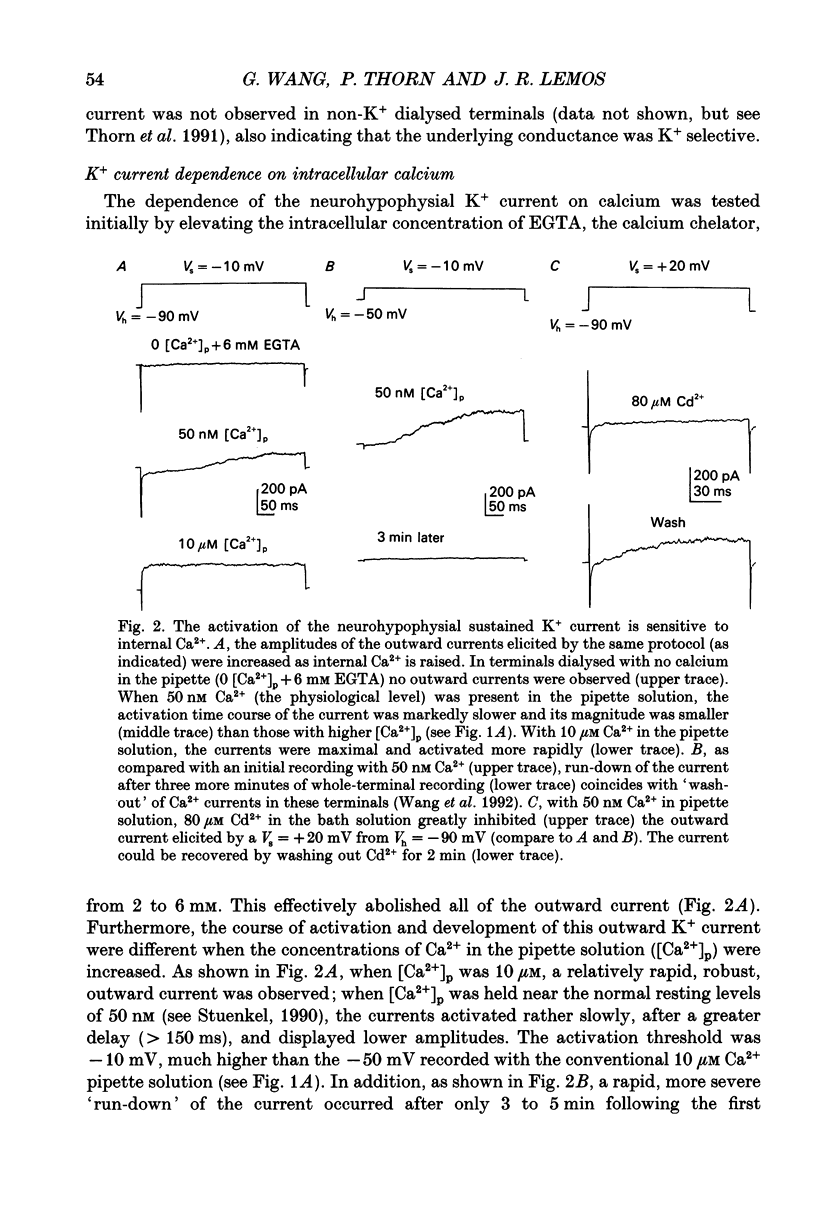



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
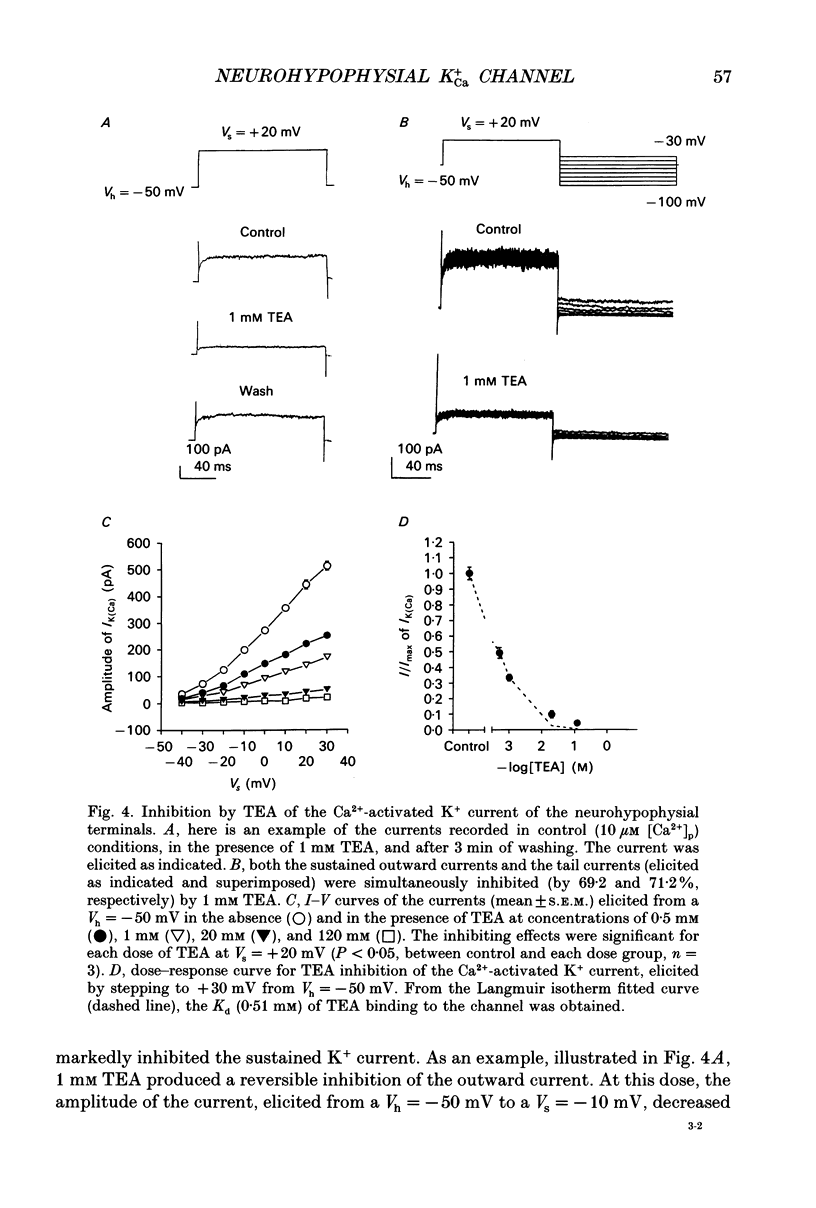
- Adler E. M., Augustine G. J., Duffy S. N., Charlton M. P. Alien intracellular calcium chelators attenuate neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1496–1507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01496.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. S., MacKinnon R., Smith C., Miller C. Charybdotoxin block of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Effects of channel gating, voltage, and ionic strength. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):317–333. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk D. A., Clark A., Jr, Hochmuth R. M. Analysis of lateral diffusion from a spherical cell surface to a tubular projection. Biophys J. 1992 Jan;61(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81810-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J., Brown D., Chapman C., Hancock P. D., Leng G. Reversible fatigue of stimulus-secretion coupling in the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:601–613. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A., Gainer H., Russell J. T. Effects of stimulus frequency and potassium channel blockade on the secretion of vasopressin and oxytocin from the neurohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Sep;46(3):258–267. doi: 10.1159/000124829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W. Activity-dependent modulation of nerve terminal excitation in a mammalian peptidergic system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Jan;14(1):28–30. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W. Intraterminal recordings from the rat neurohypophysis in vitro. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:247–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W. Transient calcium-dependent potassium current in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the rat supraoptic nucleus. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:331–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. Hormone release from isolated nerve endings of the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:55–70. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. The role of patterned burst and interburst interval on the excitation-coupling mechanism in the isolated rat neural lobe. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:45–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen O. Mediation of cell volume regulation by Ca2+ influx through stretch-activated channels. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):66–68. doi: 10.1038/330066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbett P., Legendre P., Mason W. T. Characterization of three types of potassium current in cultured neurones of rat supraoptic nucleus area. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:443–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):1–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Rudy B. Multiple types of voltage-dependent Ca2+-activated K+ channels of large conductance in rat brain synaptosomal membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):919–934. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83173-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. The function of calcium in the potassium permeability of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):653–654. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer H., Wolfe S. A., Jr, Obaid A. L., Salzberg B. M. Action potentials and frequency-dependent secretion in the mouse neurohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;43(5):557–563. doi: 10.1159/000124582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grega D. S., Macdonald R. L. Activators of adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP prolong calcium-dependent action potentials of mouse sensory neurons in culture by reducing a voltage-dependent potassium conductance. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):700–707. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Erxleben C. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels in Aplysia neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):27–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto Y., Ono K., Yoshida A., Akaike N. Delayed activation of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K channels in hippocampal neurons of the rat. Biophys J. 1989 Jul;56(1):207–212. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82665-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Konnerth A., Augustine G. J. Action potential broadening and frequency-dependent facilitation of calcium signals in pituitary nerve terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):380–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A., Perkel D. J. Calcium activates two types of potassium channels in rat hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1991 Jan;11(1):23–30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-01-00023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. G., Ritchie A. K. Large and small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in the GH3 anterior pituitary cell line. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Dec;410(6):614–622. doi: 10.1007/BF00581321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. G., Ritchie A. K. Tetraethylammonium blockade of apamin-sensitive and insensitive Ca2(+)-activated K+ channels in a pituitary cell line. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:117–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nordmann J. J., Cooke I. M., Stuenkel E. L. Single channels and ionic currents in peptidergic nerve terminals. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):410–412. doi: 10.1038/319410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nordmann J. J. Ionic channels and hormone release from peptidergic nerve terminals. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:53–72. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nowycky M. C. Two types of calcium channels coexist in peptide-releasing vertebrate nerve terminals. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1654–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.3059497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E., Marty A. Single channel activity associated with the calcium dependent outward current in Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Mar;389(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00584792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Action potential repolarization may involve a transient, Ca2+-sensitive outward current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):185–188. doi: 10.1038/300185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Reinhart P. H., White M. M. Charybdotoxin block of Shaker K+ channels suggests that different types of K+ channels share common structural features. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):997–1001. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Kinetic states and modes of single large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:79–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Latorre R., Reisin I. Coupling of voltage-dependent gating and Ba++ block in the high-conductance, Ca++-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Sep;90(3):427–449. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A. The early time course of potassium-stimulated calcium uptake in presynaptic nerve terminals isolated from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:251–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Dayanithi G., Lemos J. R. Isolated neurosecretory nerve endings as a tool for studying the mechanism of stimulus-secretion coupling. Biosci Rep. 1987 May;7(5):411–426. doi: 10.1007/BF01362504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Desmazes J. P., Georgescauld D. The relationship between the membrane potential of neurosecretory nerve endings, as measured by a voltage-sensitive dye, and the release of neurohypophysial hormones. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):731–737. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Stuenkel E. L. Electrical properties of axons and neurohypophysial nerve terminals and their relationship to secretion in the rat. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:521–539. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Levitan I. B. A family of calcium-dependent potassium channels from rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1031–1041. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski M. A. Transient outward current (IA) in clonal anterior pituitary cells: blockade by aminopyridine analogs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;338(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00174859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg B. M., Obaid A. L. Optical studies of the secretory event at vertebrate nerve terminals. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:195–231. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuenkel E. L. Effects of membrane depolarization on intracellular calcium in single nerve terminals. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 8;529(1-2):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90815-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn P. J., Wang X. M., Lemos J. R. A fast, transient K+ current in neurohypophysial nerve terminals of the rat. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:313–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Multiple components of synaptosomal [3H]-gamma-aminobutyric acid release resolved by a rapid superfusion system. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):586–593. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Latorre R. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):543–568. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. M., Treistman S. N., Lemos J. R. Direct identification of individual vasopressin-containing nerve terminals of the rat neurohypophysis after 'whole-cell' patch-clamp recordings. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Mar 11;124(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90838-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Treistman S. N., Lemos J. R. Two types of high-threshold calcium currents inhibited by omega-conotoxin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:181–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Adler M. Tetraethylammonium blockade of calcium-activated potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00585303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


