Abstract
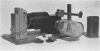
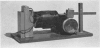
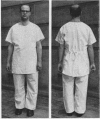
Investigations into the factors affecting dust concentrations in the breathing zone of pottery operatives have shown that cotton overalls constitute a serious source of dust. Attempts to overcome this difficulty by treatment of the material were not successful, so other types of materials were investigated. Terylene was found to have outstandingly desirable properties; types of “terylene” material and designs of clothing were defined. Factory tests showed that with this new protective clothing reductions of up to 65% in breathing zone dust concentrations were achieved. This type of clothing is now being officially recommended by the Joint Standing Committee for the Pottery Industry.
Full text
PDF