Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of physiological doses of hydrocortisone on synthesis and turnover of cell associated matrix (CAM) by human chondrocytes obtained from normal articular cartilage.
Methods: Human articular cartilage cells were obtained from visually intact cartilage of the femoral condyles of five donors and maintained in culture for one week to reach equilibrium in accumulated CAM compounds. 0, 0.05, 0.20, and 1.0 µg/ml hydrocortisone was added to the nutrient media during the entire culture period. Cells were liberated and levels of CAM aggrecan, type II collagen, and fibronectin, of intracellular IGF-1, IL1α and ß, and of their respective plasma membrane bound receptors IGFR1, IL1RI, and the decoy receptor IL1RII, were assayed by flow cytometry.
Results: In comparison with controls, hydrocortisone treated chondrocytes, at all concentrations, expressed significantly higher plasma membrane bound IGFR1. Intracellular IGF-1 levels remained unchanged. Together with these changes, reflecting an increased ability to synthesise extracellular matrix (ECM) macromolecules, hydrocortisone treated cells expressed significantly higher amounts of the plasma membrane bound decoy IL1RII. Concurrently, intracellular IL1α and ß levels and membrane bound IL1RI were down regulated. Levels of CAM aggrecan, type II collagen, and fibronectin were significantly up regulated in the chondrocytes treated with hydrocortisone.
Conclusion: 0.05 µg/ml hydrocortisone treated chondrocytes had decreased catabolic signalling pathways and showed an enhanced ability to synthesise ECM macromolecules. Because IL1 activity was decreased and the expression of IL1RII decoy receptor enhanced, more of the ECM macromolecules produced remained accumulated in the CAM of the chondrocytes. The effects were obtained at doses comparable with physiological plasma levels of hydrocortisone in humans.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (364.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
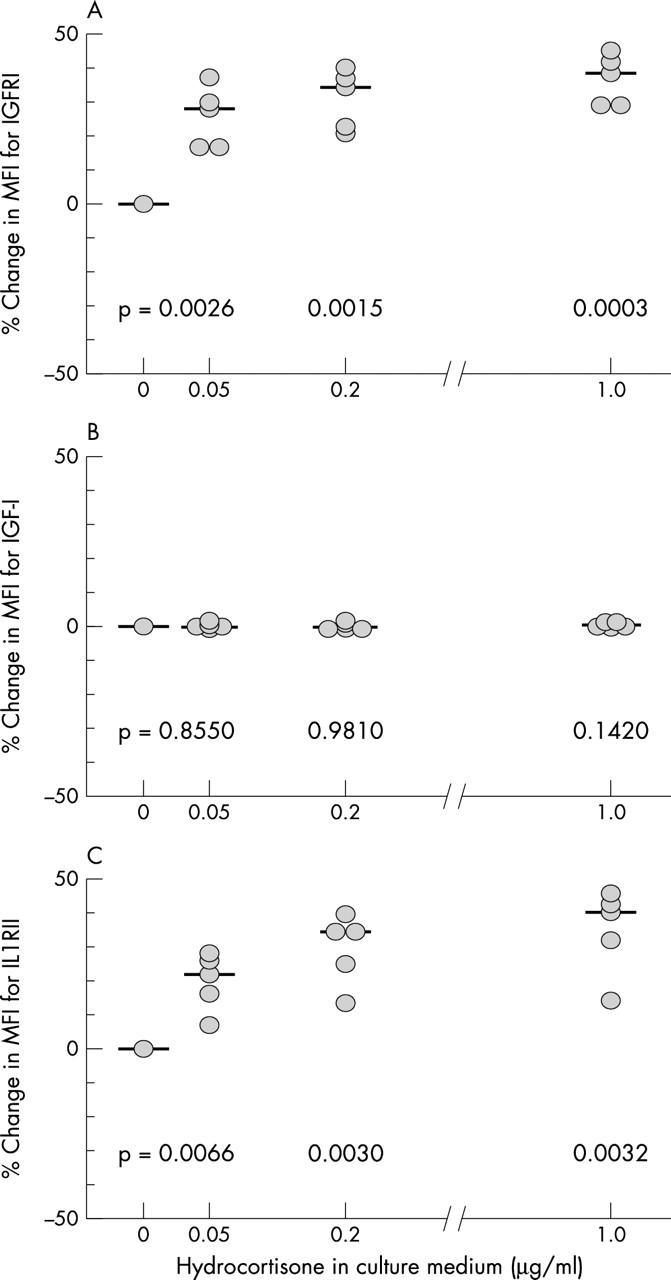
Effects of increasing doses of hydrocortisone on the IGF-1/IGFR1 autocrine pathway and on plasma membrane IL1RII. Percentage changes in chondrocyte MFI due to the binding of monoclonal antibodies specific for IGFR1 (A), IGF-1 (B), and IL1RII (C) are shown for varying doses of hydrocortisone in the culture medium. Each dot represents the mean value of the three results obtained in a single donor. Median values are indicated for each dose of hydrocortisone. Results of paired samples t test (p values) are given in the figure.
Figure 2 .
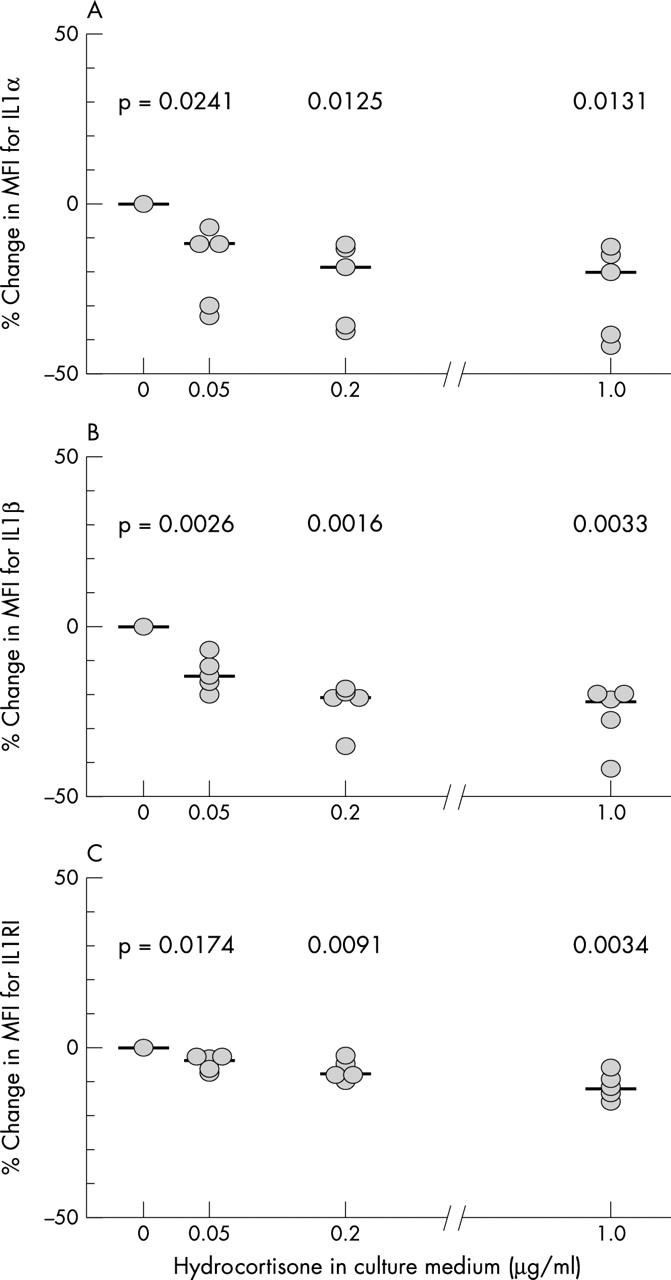
Effects of increasing doses of hydrocortisone on the IL1/IL1RI autocrine pathway. Percentage changes in chondrocyte MFI due to the binding of monoclonal antibodies specific for IL1α (A), IL1ß (B), and IL1RI (C) are shown for varying doses of hydrocortisone in the culture medium. Each dot represents the mean value of the three results obtained in a single donor. Median values are indicated for each dose of hydrocortisone. Results of paired samples t test (p values) are given in the figure.
Figure 3 .
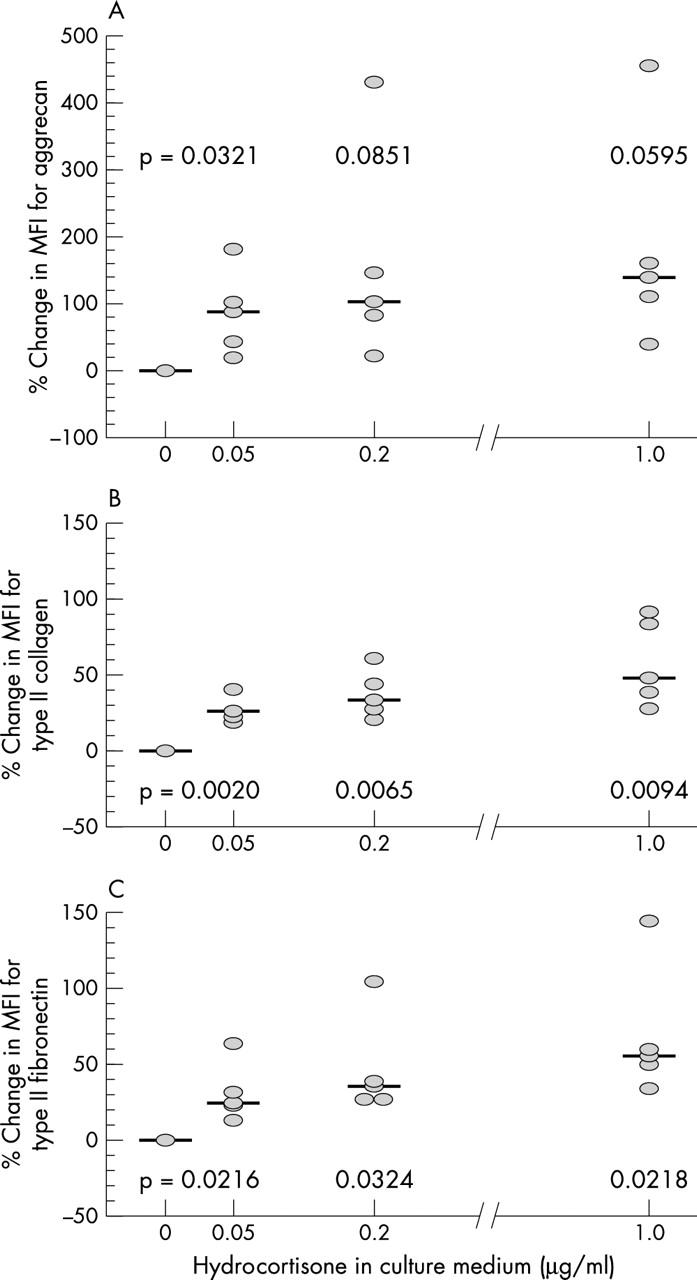
Effects of increasing doses of hydrocortisone on the levels of CAM aggrecan, type II collagen, and fibronectin. Percentage changes in chondrocyte MFI due to the binding of monoclonal antibodies specific for aggrecan (A), type II collagen (B), and fibronectin (C) are shown for varying doses of hydrocortisone in the culture medium. Each dot represents the mean value of the three results obtained in a single donor. Median values are indicated for each dose of hydrocortisone. Results of paired samples t test (p values) are given in the figure.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almqvist K. F., Wang L., Broddelez C., Verdonk R., Veys E. M., Verbruggen G. The influence of hydrocortisone on aggrecan metabolism in human articular chondrocyte cultures: comparison of two different matrices. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Nov-Dec;18(6):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arner E. C., Tortorella M. D. Signal transduction through chondrocyte integrin receptors induces matrix metalloproteinase synthesis and synergizes with interleukin-1. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Sep;38(9):1304–1314. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens F., Shepard N., Mitchell N. Alterations of rabbit articular cartilage by intra-articular injections of glucocorticoids. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Jan;57(1):70–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G., Goodfellow J. W. Disorganisation of the knees following intra-articular hydrocortisone injections. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1969 Aug;51(3):498–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M., Colombo C., Hickman L., O'Byrne E., Steele R., Steinetz B., Quintavalla J., Yokoyama N. A new model of osteoarthritis in rabbits. III. Evaluation of anti-osteoarthritic effects of selected drugs administered intraarticularly. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Nov;26(11):1380–1386. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers M. G., Bayliss M. T., Mason R. M. Chondrocyte cytokine and growth factor expression in murine osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997 Sep;5(5):301–308. doi: 10.1016/s1063-4584(97)80034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo C., Butler M., Hickman L., Selwyn M., Chart J., Steinetz B. A new model of osteoarthritis in rabbits. II. Evaluation of anti-osteoarthritic effects of selected antirheumatic drugs administered systemically. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Sep;26(9):1132–1139. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eymontt M. J., Gordon G. V., Schumacher H. R., Hansell J. R. The effects on synovial permeability and synovial fluid leukocyte counts in symptomatic osteoarthritis after intraarticular corticosteroid administration. J Rheumatol. 1982 Mar-Apr;9(2):198–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon G. V., Schumacher H. R. Electron microscopic study of depot corticosteroid crystals with clinical studies after intra-articular injection. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jan-Feb;6(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. T., Jr Behavior of articular chondrocytes in cell culture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971 Mar-Apr;75:248–260. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197103000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo J. F., Jourdian G. W., MacCallum D. K. Culture and growth characteristics of chondrocytes encapsulated in alginate beads. Connect Tissue Res. 1989;19(2-4):277–297. doi: 10.3109/03008208909043901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Masuda T., Susuda K., Ishii S., Abe K. Ultrastructure of the articular cartilage after systemic administration of hydrocortisone in the rabbit: an electron microscopic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980 Oct;(152):296–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J. Effects of cortisol on cell proliferation and proteoglycan synthesis and degradation in cartilage zones of the calf costochondral growth plate in vitro with and without rat plasma somatomedin activity. J Endocrinol. 1981 Mar;88(3):425–435. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0880425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. R., Mattmueller D. R., Steinberg J. J., Poppas D. P., Sledge C. B. Effect of steroid hormones on endotoxin-mediated cartilage degradation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Jan;79(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00229395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häuselmann H. J., Aydelotte M. B., Schumacher B. L., Kuettner K. E., Gitelis S. H., Thonar E. J. Synthesis and turnover of proteoglycans by human and bovine adult articular chondrocytes cultured in alginate beads. Matrix. 1992 Apr;12(2):116–129. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häuselmann H. J., Fernandes R. J., Mok S. S., Schmid T. M., Block J. A., Aydelotte M. B., Kuettner K. E., Thonar E. J. Phenotypic stability of bovine articular chondrocytes after long-term culture in alginate beads. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):17–27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itagane Y., Inada H., Fujita K., Isshiki G. Interactions between steroid hormones and insulin-like growth factor-I in rabbit chondrocytes. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1419–1424. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronick M. N., Grossman P. D. Immunoassay techniques with fluorescent phycobiliprotein conjugates. Clin Chem. 1983 Sep;29(9):1582–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tsou A. P., Chan H., Thomas J., Petrie K., Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit the transcription of the interleukin 1 beta gene and decrease the stability of interleukin 1 beta mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemare F., Steimberg N., Le Griel C., Demignot S., Adolphe M. Dedifferentiated chondrocytes cultured in alginate beads: restoration of the differentiated phenotype and of the metabolic responses to interleukin-1beta. J Cell Physiol. 1998 Aug;176(2):303–313. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199808)176:2<303::AID-JCP8>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. B., Ghosh P. Variation in proteoglycan metabolism by articular chondrocytes in different joint regions is determined by post-natal mechanical loading. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997 Jan;5(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/s1063-4584(97)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeser R. F., Shanker G., Carlson C. S., Gardin J. F., Shelton B. J., Sonntag W. E. Reduction in the chondrocyte response to insulin-like growth factor 1 in aging and osteoarthritis: studies in a non-human primate model of naturally occurring disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Sep;43(9):2110–2120. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9<2110::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutfi A. M., Kosel K. Effects of intra-articularly administered corticosteroids and salicylates on the surface structure of articular cartilage. J Anat. 1978 Oct;127(Pt 2):393–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Conger K. A. The acute effects of intra-articular hydrocortisone on articular cartilage in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Oct;48(7):1383–1388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Zarins A., Jaffe W. L. The effect of systemic corticosteroids on rabbit articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Nov-Dec;15(6):593–599. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel-Pelletier J., Cloutier J. M., Pelletier J. P. Neutral proteases in human osteoarthritic synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Sep;29(9):1112–1121. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire M. B., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Russell R. G. Production of collagenase and inhibitor (TIMP) by normal, rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovium in vitro: effects of hydrocortisone and indomethacin. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Dec;61(6):703–710. doi: 10.1042/cs0610703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie L. S., Horsburgh B. A., Ghosh P., Taylor T. K. Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on sulphated glycosaminoglycan synthesis in aged human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Dec;35(6):487–497. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.6.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos V., Fickert S., Müller B., Weber U., Sieper J. Immunohistological analysis of cytokine expression in human osteoarthritic and healthy cartilage. J Rheumatol. 1999 Apr;26(4):870–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz R. W., Davis W., Sammarco J., Mast W., Chase S. W. Experimentally induced corticosteroid arthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 May-Jun;13(3):236–243. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. C., DeBowes R. M., Gaughan E. M., Zhu C. F., Athanasiou K. A. The effects of intra-articular methylprednisolone and exercise on the mechanical properties of articular cartilage in the horse. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1998 Mar;6(2):106–114. doi: 10.1053/joca.1997.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Shinmei M., Tanaka O., Naka K., Kimura A., Nakanishi I., Bayliss M. T., Iwata K., Nagase H. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) in osteoarthritic cartilage and synovium. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):680–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papacrhistou G., Anagnostou S., Katsorhis T. The effect of intraarticular hydrocortisone injection on the articular cartilage of rabbits. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1997 Oct;275:132–134. doi: 10.1080/17453674.1997.11744766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Cloutier J. M., Martel-Pelletier J. In vitro effects of tiaprofenic acid, sodium salicylate and hydrocortisone on the proteoglycan metabolism of human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Rheumatol. 1989 May;16(5):646–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J. Cartilage degradation by neutral proteoglycanases in experimental osteoarthritis. Suppression by steroids. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1393–1401. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Cloutier J. M., Woessner J. F., Jr Proteoglycan-degrading acid metalloprotease activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage, and the effect of intraarticular steroid injections. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):541–548. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Howell D. S., Ghandur-Mnaymneh L., Enis J. E., Woessner J. F., Jr Collagenase and collagenolytic activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J. Protective effects of corticosteroids on cartilage lesions and osteophyte formation in the Pond-Nuki dog model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;32(2):181–193. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Mineau F., Raynauld J. P., Woessner J. F., Jr, Gunja-Smith Z., Martel-Pelletier J. Intraarticular injections with methylprednisolone acetate reduce osteoarthritic lesions in parallel with chondrocyte stromelysin synthesis in experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Mar;37(3):414–423. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG C. L., DUTHIE R. B., PIVA A. E. Charcot-like arthropathy following intra-articular hydrocortisone. JAMA. 1962 Sep 8;181:851–854. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050360037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. B., Gross A., Hall J. H. Hydrocortisone arthropathy--an experimental investigation. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Aug 19;97(8):374–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlopov B. V., Gumanovskaya M. L., Hasty K. A. Autocrine regulation of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) during osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):195–205. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<195::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbermann M., von der Mark K., Maor G., van Menxel M. Dexamethasone impairs growth and collagen synthesis in condylar cartilage in vitro. Bone Miner. 1987 Apr;2(2):87–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi Y., Björnsson B. T. Cortisol inhibits glycosaminoglycan synthesis in cultured rainbow trout cartilage. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1997 Oct;108(1):80–86. doi: 10.1006/gcen.1997.6950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takigawa M., Takano T., Nakagawa K., Sakuda M., Suzuki F. Hydrocortisone stimulation of proliferation and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in rabbit craniofacial chondrocytes in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1988;33(12):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(88)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen G., Veys E. M., Wieme N., Malfait A. M., Gijselbrecht L., Nimmegeers J., Almquist K. F., Broddelez C. The synthesis and immobilisation of cartilage-specific proteoglycan by human chondrocytes in different concentrations of agarose. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1990 Jul-Aug;8(4):371–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Jun, Elewaut Dirk, Veys Eric M., Verbruggen Gust. Insulin-like growth factor 1-induced interleukin-1 receptor II overrides the activity of interleukin-1 and controls the homeostasis of the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 May;48(5):1281–1291. doi: 10.1002/art.11061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Almqvist K. F., Broddelez C., Veys E. M., Verbruggen G. Evaluation of chondrocyte cell-associated matrix metabolism by flow cytometry. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001 Jul;9(5):454–462. doi: 10.1053/joca.2001.0412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Verbruggen G., Almqvist K. F., Elewaut D., Broddelez C., Veys E. M. Flow cytometric analysis of the human articular chondrocyte phenotype in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001 Jan;9(1):73–84. doi: 10.1053/joca.2000.0352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Raz E., Silbermann M. Effects of systemic glucocorticoids on the degradation of glycosaminoglycans in the mandibular condylar cartilage of newborn mice. Bone Miner. 1986 Sep;1(4):335–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Brandt K. D. Triamcinolone hexacetonide protects against fibrillation and osteophyte formation following chemically induced articular cartilage damage. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Nov;28(11):1267–1274. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Osch G. J., van der Veen S. W., Verwoerd-Verhoef H. L. In vitro redifferentiation of culture-expanded rabbit and human auricular chondrocytes for cartilage reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001 Feb;107(2):433–440. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200102000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B. Impact of NSAID and steroids on cartilage destruction in murine antigen induced arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991 Feb;27:122–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kraan P. M., Vitters E. L., Postma N. S., Verbunt J., van den Berg W. B. Maintenance of the synthesis of large proteoglycans in anatomically intact murine articular cartilage by steroids and insulin-like growth factor I. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Oct;52(10):734–741. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.10.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kraan P. M., Vitters E. L., Postma N. S., Verbunt J., van den Berg W. B. Maintenance of the synthesis of large proteoglycans in anatomically intact murine articular cartilage by steroids and insulin-like growth factor I. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Oct;52(10):734–741. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.10.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


