Abstract
Recent studies of five different phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylcholine (PC/PC) systems indicate that binary mixtures of phosphatidylcholines in which one component has a normalized chain length difference (delta C/CL) in the range of 0.09-0.40 and the other a delta C/CL in the range of 0.42-0.57 exhibit the phase behavior of a eutectic system. Here, delta C is the effective chain-length difference between the two acyl chains, and CL is the effective length of the longer of the two acyl chains for the same lipid molecule in the gel state. In each mixture, gel phase immiscibility occurs over a wide compositional range due to the difference in the gel phase acyl chain packing properties of each component. Although the mixtures differ in the location of their eutectic horizontal, with respect to temperature, all have a similar eutectic point that occurs at a composition of approximately 40 mol percent of the component with the delta C/CL value in the range of 0.42-0.57. Here, we extend these studies by systematically modifying the headgroup of C(17):C(17)PC and then analyzing the mixing behavior of the modified lipid with C(22):C(12)PC using DSC. Progressive demethylation of the C(17):C(17)PC headgroup leads to an increase in gel phase immiscibility and a decrease in the amount of C(22):C(12)PC that comprises the eutectic composition. The temperature defining the location of the eutectic horizontal, however, remains virtually unchanged in all three phase diagrams. Our results suggest that the eutectic composition is influenced by changes in gel phase acyl chain packing that are dependent on headgroup-headgroup interactions. In contrast, the eutectic nature of the phase diagram and the location of its solidus line are properties of acyl chain interactions that are independent of phospholipid headgroup-headgroup interactions.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bultmann T., Lin H. N., Wang Z. Q., Huang C. H. Thermotropic and mixing behavior of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines with molecular weights identical with that of L-alpha-dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7194–7202. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhry B. Z., Dalziel A. W. Phase transition properties of 1,2- and 1,3-diacylphosphatidylethanolamines with modified head groups. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4109–4117. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. The enzymatic synthesis of phosphatidylserine and purification by CM-cellulose column chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 20;488(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné J., Stamatatos L., Diacovo T., Hui S. W., Yeagle P. L., Silvius J. R. Physical properties and surface interactions of bilayer membranes containing N-methylated phosphatidylethanolamines. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4400–4408. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardam M., Silvius J. R. Intermixing of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine with phospho- and sphingolipids bearing highly asymmetric hydrocarbon chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 28;980(3):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Empirical estimation of the gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition temperatures for fully hydrated saturated phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):26–30. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Mixed-chain phospholipids and interdigitated bilayer systems. Klin Wochenschr. 1990 Feb 1;68(3):149–165. doi: 10.1007/BF01649079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Mason J. T., Huang C. Acyl chain interdigitation in saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5570–5577. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. N., Mannock D. A., McElhaney R. N., Turner D. C., Gruner S. M. Effect of fatty acyl chain length and structure on the lamellar gel to liquid-crystalline and lamellar to reversed hexagonal phase transitions of aqueous phosphatidylethanolamine dispersions. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):541–548. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. N., Wang Z. Q., Huang C. H. Differential scanning calorimetry study of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines with a common molecular weight identical with diheptadecanoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7063–7072. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. N., Wang Z. Q., Huang C. H. The influence of acyl chain-length asymmetry on the phase transition parameters of phosphatidylcholine dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 5;1067(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90021-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Huang C. Eutectic phase behavior of 1-stearoyl-2-caprylphosphatidylcholine and dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 8;946(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
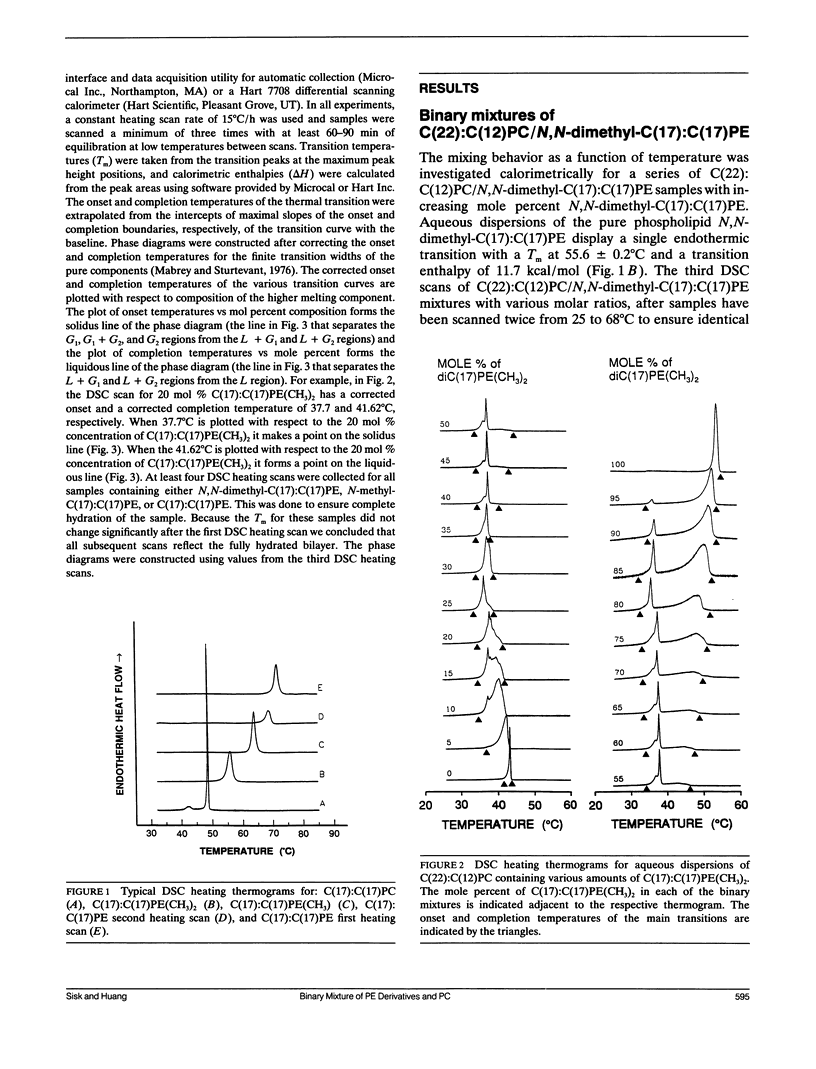
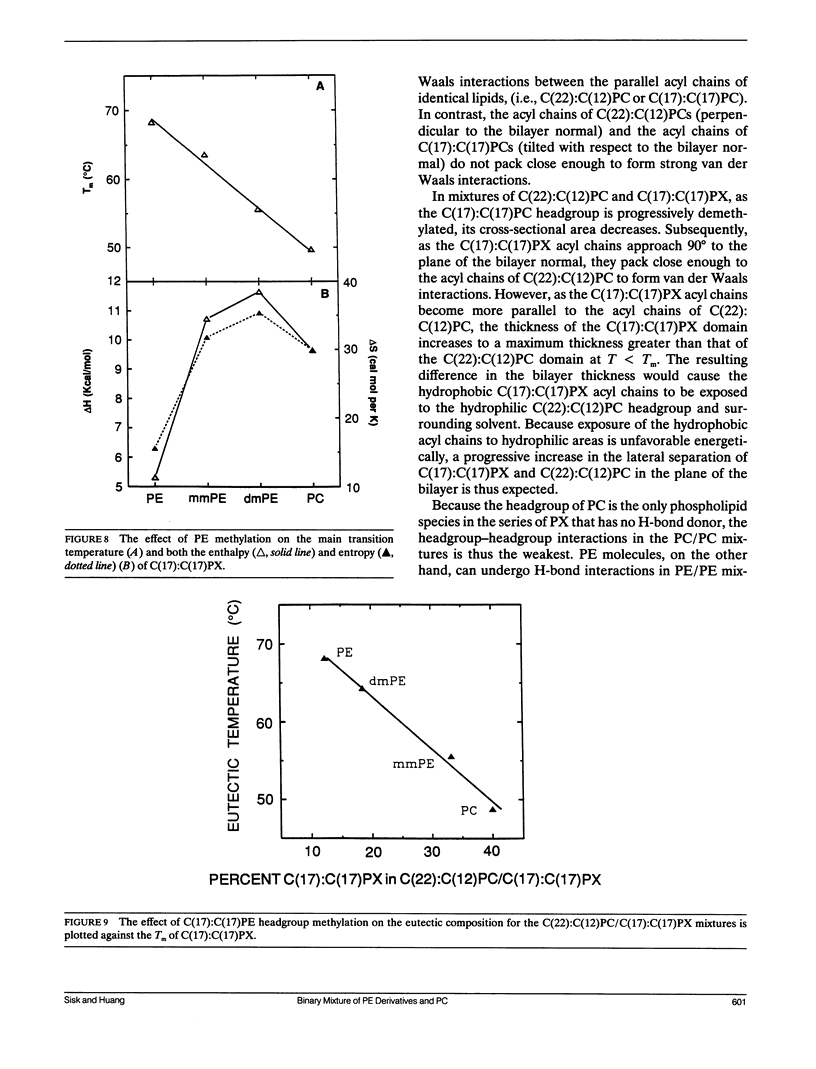
- Mabrey S., Sturtevant J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. T., Broccoli A. V., Huang C. A method for the synthesis of isomerically pure saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholines. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 1;113(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. T., Huang C., Biltonen R. L. Calorimetric investigations of saturated mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayer dispersions. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6086–6092. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattai J., Sripada P. K., Shipley G. G. Mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayers: structure and properties. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3287–3297. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J. Differences in hydrocarbon chain tilt between hydrated phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine bilayers. A molecular packing model. Biophys J. 1980 Feb;29(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Area per molecule and distribution of water in fully hydrated dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4948–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A., Ellington J. C., Jr, Porter N. A. New structural model for mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4038–4044. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulukutla S., Shipley G. G. Structure and thermotropic properties of phosphatidylethanolamine and its N-methyl derivatives. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2514–2519. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M., Harlos K., Marsh D. Metastability and polymorphism in the gel and fluid bilayer phases of dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine. Two crystalline forms in excess water. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3850–3854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah J., Sripada P. K., Shipley G. G. Structure and properties of mixed-chain phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4254–4262. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R., Brown P. M., O'Leary T. J. Role of head group structure in the phase behavior of amino phospholipids. 1. Hydrated and dehydrated lamellar phases of saturated phosphatidylethanolamine analogues. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4249–4258. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R. Solid- and liquid-phase equilibria in phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine mixtures. A calorimetric study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 28;857(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. A., Fink C. A., Kenworthy A. K., McIntosh T. J. The hydration pressure between lipid bilayers. Comparison of measurements using x-ray diffraction and calorimetry. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):538–546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82270-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisk R. B., Wang Z. Q., Lin H. N., Huang C. H. Mixing behavior of identical molecular weight phosphatidylcholines with various chain-length differences in two-component lamellae. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):777–783. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82420-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. L., Huang C. H. Interdigitated bilayer membranes. Prog Lipid Res. 1988;27(4):325–359. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(88)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. J., Keough K. M. Changes in phase transitions of phosphatidylethanolamine- and phosphatidylcholine-water dispersions induced by small modifications in the headgroup and backbone regions. FEBS Lett. 1974 Oct 1;47(1):158–161. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., Nagle J. F. Dilatometry and calorimetry of saturated phosphatidylethanolamine dispersions. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):187–192. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Stephenson F. A., Lin H. N., Huang C. H. Phase metastability and supercooled metastable state of diundecanoylphosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 4;943(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


