Abstract
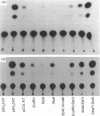
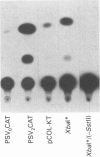
The transcriptional activity of plasmid pCOL-KT, in which human pro alpha 1 (I) collagen gene upstream sequences up to -804 and most of the first intron (+474 to +1440) drive expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene [Thompson, Simkevich, Holness, Kang & Raghow (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 2549-2556], was tested in a number of mesenchymal and non-mesenchymal cells. We observed that pCOL-KT was readily expressed in fibroblasts of human (IMR-90 and HFL-1), murine (NIH 3T3) and avian (SL-29) origin and in a human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line (A204), but failed to be expressed in human erythroleukaemia (K562) and rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells, indicating that the regulatory elements required for appropriate tissue-specific expression of the human pro alpha 1 (I) collagen gene were present in pCOL-KT. To delineate the nature of cis-acting sequences which determine the tissue specificity of pro alpha 1 (I) collagen gene expression, functional consequences of deletions in the promoter and first intron of pCOL-KT were tested in various cell types by transient expression assays. Cis elements in the promoter-proximal and intronic sequences displayed either a positive or a negative influence depending on the cell type. Thus deletion of fragments using EcoRV (nt -625 to -442 deleted), XbaI (-804 to -331) or SstII (+670 to +1440) resulted in 2-10-fold decreased expression in A204 and HFL-1 cells. The negative influences of deletions in the promoter-proximal sequences was apparently considerably relieved by deleting sequences in the first intron, and the constructs containing the EcoRV/SstII or XbaI/SstII double deletions were expressed to a much greater extent than either of the single deletion constructs. In contrast, the XbaI* deletion (nt -804 to -609), either alone or in combination with the intronic deletion, resulted in very high expression in all cells regardless of their collagen phenotype; the XbaI*/(-SstII) construct, which contained the intronic SstII fragment (+670 to +1440) in the reverse orientation, was not expressed in either mesenchymal or nonmesenchymal cells. Based on these results, we conclude that orientation-dependent interactions between negatively acting 5'-upstream sequences and the first intron determine the mesenchymal cell specificity of human pro alpha 1 (I) collagen gene transcription.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L. Enhancers: mechanisms of action and cell specificity. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:127–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Roush C. L., Gelinas R. E. DNA and chromatin structure of the human alpha 1 (I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14906–14913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Mathews L. S., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Dwarf mice produced by genetic ablation of growth hormone-expressing cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):453–461. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boast S., Su M. W., Ramirez F., Sanchez M., Avvedimento E. V. Functional analysis of cis-acting DNA sequences controlling transcription of the human type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13351–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Liska D. J., Apone S., Devarayalu S. Interactions between the promoter and first intron are involved in transcriptional control of alpha 1(I) collagen gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4851–4857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Morishima J. K., Devarayalu S., Gelinas R. E. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J. The first intron of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene contains several transcriptional regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1603–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Regulation of collagen gene expression. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;37:67–106. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60695-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., Rippe R. A., Veloz L. Analysis of the collagen alpha 1(I) promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6055–6064. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe I., Aycock R. S., Raghow R., Myers J. C., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. A hepatic fibrogenic factor stimulates the synthesis of types I, III, and V procollagens in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5408–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne D., Cutroneo K. R. Glucocorticoid coordinate regulation of type I procollagen gene expression and procollagen DNA-binding proteins in chick skin fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2736–2745. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Fine A., Farnsworth L. J., Poliks C., Polgar P. Phorbol ester-induced inhibition of collagen accumulation by human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13623–13628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Lemaire C., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Negative regulation contributes to tissue specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2558–2567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Eukaryotic transcription factors. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj2700281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liska D. J., Slack J. L., Bornstein P. A highly conserved intronic sequence is involved in transcriptional regulation of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Cell Regul. 1990 May;1(6):487–498. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.6.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Gay S. The collagens: an overview and update. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:3–41. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen A. S., Geddis A. E., Prockop D. J. High levels of expression of a minigene version of the human pro alpha 1 (I) collagen gene in stably transfected mouse fibroblasts. Effects of deleting putative regulatory sequences in the first intron. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1117–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Kobayashi S., Bornstein P. Transforming growth factor beta increases mRNA for matrix proteins both in the presence and in the absence of changes in mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1105–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Raghow R., Stricklin G. P., Poppleton H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Modulation of fibroblast functions by interleukin 1: increased steady-state accumulation of type I procollagen messenger RNAs and stimulation of other functions but not chemotaxis by human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):311–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Gossage D., Kang A. H. Pretranslational regulation of type I collagen, fibronectin, and a 50-kilodalton noncollagenous extracellular protein by dexamethasone in rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4677–4684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Gossage D., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Transcriptional regulation of type I collagen genes in cultured fibroblasts by a factor isolated from thioacetamide-induced fibrotic rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12718–12723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Kang A. H., Pidikiti D. Phenotypic plasticity of extracellular matrix gene expression in cultured hamster lung fibroblasts. Regulation of type I procollagen and fibronectin synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8409–8415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Transforming growth factor-beta increases steady state levels of type I procollagen and fibronectin messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1285–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Thompson J. P. Molecular mechanisms of collagen gene expression. Mol Cell Biochem. 1989 Mar 16;86(1):5–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00231686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez F., Di Liberto M. Complex and diversified regulatory programs control the expression of vertebrate collagen genes. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1616–1623. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2180769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein CIII gene expression is regulated by positive and negative cis-acting elements and tissue-specific protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6857–6864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe R. A., Lorenzen S. I., Brenner D. A., Breindl M. Regulatory elements in the 5'-flanking region and the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the mouse alpha 1 type I collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2224–2227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Karsenty G., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., de Crombrugghe B. A nuclear factor 1 binding site mediates the transcriptional activation of a type I collagen promoter by transforming growth factor-beta. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., de Crombrugghe B. Identification of a cell-specific transcriptional enhancer in the first intron of the mouse alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5590–5594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw C. M., Vergeer W. P., du Plooy S. J., Bernard M. P., Ramirez F., de Wet W. J. DNA sequences in the first intron of the human pro-alpha 1(I) collagen gene enhance transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15151–15157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood A. L., Bornstein P. Transcriptional control of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene involves orientation- and position-specific intronic sequences. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):895–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2650895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. L., Liska D. J., Bornstein P. An upstream regulatory region mediates high-level, tissue-specific expression of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2066–2074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. P., Simkevich C. P., Holness M. A., Kang A. H., Raghow R. In vitro methylation of the promoter and enhancer of Pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene leads to its transcriptional inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2549–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]