Abstract
Objective: To compare the clinical assessment of overall inflammatory activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with grey scale and power Doppler (PD) ultrasonography (US).
Methods: Ninety four consecutive patients with RA were included. Demographic and clinical data, C reactive protein (CRP) level, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were recorded for each patient. The presence of tenderness, swelling, and a subjective swelling score from 1 to 3 were independently assessed by two rheumatologists, who reached a consensus in 60 joints examined in each patient. All patients underwent a US examination by a third blinded rheumatologist, using PD. US joint effusion, synovitis, and PD signal were graded from 1 to 3 in the 60 joints. Joint count and joint index for effusion, synovitis, and PD signal were recorded. A 28 joint count for clinical and US variables was calculated. Interobserver reliability of the US examination was evaluated by a fourth blinded rheumatologist.
Results: US showed significantly more joints with effusion (mean 15.2) and synovitis (mean 14.6) than clinical examination (mean 11.5, p<0.05). A significant correlation was found between joint count and joint index for swelling, US effusion, synovitis, and PD signal. The 28 joint count for effusion, synovitis, and PD signal correlated highly with the corresponding 60 joint counts. US findings correlated better with CRP and ESR than clinical measures. Interobserver reliability was better for US findings than for clinical assessment.
Conclusion: US is a sensitive method for assessing joint inflammatory activity in RA, complementary to clinical evaluation.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (111.8 KB).
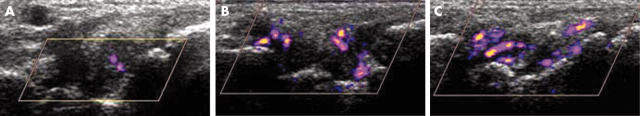
Figure 1.
Longitudinal sonographic image of the wrist joint with moderate effusion, moderate synovitis, and mild (A), moderate (B), and marked (C) colour signal.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alasaarela E. M., Alasaarela E. L. Ultrasound evaluation of painful rheumatoid shoulders. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1642–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alasaarela E., Leppilahti J., Hakala M. Ultrasound and operative evaluation of arthritic shoulder joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Jun;57(6):357–360. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.6.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alasaarela E., Tervonen O., Takalo R., Lahde S., Suramo I. Ultrasound evaluation of the acromioclavicular joint. J Rheumatol. 1997 Oct;24(10):1959–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Kamradt T., Sandrock D., Loreck D., Fritz J., Wolf K. J., Raber H., Hamm B., Burmester G. R., Bollow M. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1232–1245. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1232::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostino Maria-Antonietta, Said-Nahal Roula, Hacquard-Bouder Cécile, Brasseur Jean-Louis, Dougados Maxime, Breban Maxime. Assessment of peripheral enthesitis in the spondylarthropathies by ultrasonography combined with power Doppler: a cross-sectional study. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Feb;48(2):523–533. doi: 10.1002/art.10812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeseneer M., Jacobson J. A., Jaovisidha S., Lenchik L., Ryu K. N., Trudell D. R., Resnick D. Elbow effusions: distribution of joint fluid with flexion and extension and imaging implications. Invest Radiol. 1998 Feb;33(2):117–125. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt K., Fex E., Johnsson K., Geborek P. Hip involvement in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Jan;54(1):45–48. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberl D. R., Fasching V., Rahlfs V., Schleyer I., Wolf R. Repeatability and objectivity of various measurements in rheumatoid arthritis. A comparative study. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1278–1286. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteve-Vives J., Batlle-Gualda E., Reig A. Spanish version of the Health Assessment Questionnaire: reliability, validity and transcultural equivalency. Grupo para la Adaptación del HAQ a la Población Española. J Rheumatol. 1993 Dec;20(12):2116–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Chernoff M., Fried B., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Kieszak S., Lightfoot R. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):729–740. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiocco U., Cozzi L., Rubaltelli L., Rigon C., De Candia A., Tregnaghi A., Gallo C., Favaro M. A., Chieco-Bianchi F., Baldovin M. Long-term sonographic follow-up of rheumatoid and psoriatic proliferative knee joint synovitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Feb;35(2):155–163. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald O., Bresnihan B. Synovial membrane cellularity and vascularity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Jun;54(6):511–515. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.6.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Cookson J., Blades S., Coumbe A., Blake D. Quantitative assessment of the rheumatoid synovial microvascular bed by gadolinium-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Mar;57(3):152–157. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.3.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Cookson J., Blake D., Coumbe A., Blades S. Quantification of rheumatoid synovitis by magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1610–1617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi W., Cervini C. Ultrasonography in rheumatology: an evolving technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 May;57(5):268–271. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.5.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi W., Tittarelli E., Pirani O., Avaltroni D., Cervini C. Ultrasound examination of metacarpophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1993;22(5):243–247. doi: 10.3109/03009749309095131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratz S., Göbel D., Behr T. M., Herrmann A., Becker W. Correlation between radiation dose, synovial thickness, and efficacy of radiosynoviorthesis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Jun;26(6):1242–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hau M., Schultz H., Tony H. P., Keberle M., Jahns R., Haerten R., Jenett M. Evaluation of pannus and vascularization of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis by high-resolution ultrasound (multidimensional linear array). Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Nov;42(11):2303–2308. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199911)42:11<2303::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauzeur J. P., Mathy L., De Maertelaer V. Comparison between clinical evaluation and ultrasonography in detecting hydrarthrosis of the knee. J Rheumatol. 1999 Dec;26(12):2681–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iagnocco A., Coari G. Usefulness of high resolution US in the evaluation of effusion in osteoarthritic first carpometacarpal joint. Scand J Rheumatol. 2000;29(3):170–173. doi: 10.1080/030097400750002049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. A., Andresen R., Jaovisidha S., De Maeseneer M., Foldes K., Trudell D. R., Resnick D. Detection of ankle effusions: comparison study in cadavers using radiography, sonography, and MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998 May;170(5):1231–1238. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.5.9574591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevtic V., Watt I., Rozman B., Presetnik M., Logar D., Praprotnik S., Tomsic M., Sipek A., Kos-Golja M., Sepe A. Prognostic value of contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA MRI for development of bone erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;35 (Suppl 3):26–30. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_3.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane David, Balint Peter V., Sturrock Roger D. Ultrasonography is superior to clinical examination in the detection and localization of knee joint effusion in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2003 May;30(5):966–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim Z., Wakefield R. J., Conaghan P. G., Lawson C. A., Goh E., Quinn M. A., Astin P., O'Connor P., Gibbon W. W., Emery P. The impact of ultrasonography on diagnosis and management of patients with musculoskeletal conditions. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Dec;44(12):2932–2933. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200112)44:12<2932::aid-art481>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim Z., Wakefield R. J., Quinn M., Conaghan P. G., Brown A. K., Veale D. J., O'Connor P., Reece R., Emery P. Validation and reproducibility of ultrasonography in the detection of synovitis in the knee: a comparison with arthroscopy and clinical examination. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Feb;50(2):387–394. doi: 10.1002/art.20054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A., Mutazindwa T., Hassan A., al-Zuhair N. Unilateral traumatic adrenal haematoma presenting as pheochromocytoma. Eur J Radiol. 1998 Sep;28(2):133–135. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(97)00133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E. Review: angiogenesis: implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jun;41(6):951–962. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199806)41:6<951::AID-ART2>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M., Anttila P., Hämäläinen M., Isomäki H. Hip joint ultrasonography: correlation with intra-articular effusion and synovitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Jun;29(3):189–192. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.3.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M., Hermunen H. Intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment of the rheumatoid wrist. An ultrasonographic study. Scand J Rheumatol. 2001;30(5):268–270. doi: 10.1080/030097401753180336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M. Ultrasonography of the elbow joint. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(3):91–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02274820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. J., Heikal A., Maricic M. J., Krupinski E. A., Williams C. S. Ultrasonographic imaging of the hand and wrist in rheumatoid arthritis. Skeletal Radiol. 1995 Nov;24(8):591–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00204858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maini R. N., Taylor P. C., Paleolog E., Charles P., Ballara S., Brennan F. M., Feldmann M. Anti-tumour necrosis factor specific antibody (infliximab) treatment provides insights into the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Nov;58 (Suppl 1):I56–I60. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.2008.i56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. J., Rubin J. M. Power Doppler: it's a good thing. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1997 Feb;18(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/s0887-2171(97)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazarian L. N., Rawool N. M., Martin C. E., Schweitzer M. E. Synovial fluid in the hindfoot and ankle: detection of amount and distribution with US. Radiology. 1995 Oct;197(1):275–278. doi: 10.1148/radiology.197.1.7568837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. S., Adler R. S., Bude R. O., Rubin J. M. Detection of soft-tissue hyperemia: value of power Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 Aug;163(2):385–389. doi: 10.2214/ajr.163.2.8037037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. S., Laing T. J., McCarthy C. J., Adler R. S. Power Doppler sonography of synovitis: assessment of therapeutic response--preliminary observations. Radiology. 1996 Feb;198(2):582–584. doi: 10.1148/radiology.198.2.8596870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Court-Payen M., Gideon P., Wieslander S., Cortsen M., Lorenzen I., Henriksen O. Ultrasonography in arthritis of the knee. A comparison with MR imaging. Acta Radiol. 1995 Jan;36(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvistgaard E., Røgind H., Torp-Pedersen S., Terslev L., Danneskiold-Samsøe B., Bliddal H. Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):690–693. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubaltelli L., Fiocco U., Cozzi L., Baldovin M., Rigon C., Bortoletto P., Tregnaghi A., Melanotte P. L., di Maggio C., Todesco S. Prospective sonographic and arthroscopic evaluation of proliferative knee joint synovitis. J Ultrasound Med. 1994 Nov;13(11):855–862. doi: 10.7863/jum.1994.13.11.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. A., Völker L., Zacher J., Schläfke M., Ruhnke M., Gromnica-Ihle E. Colour Doppler ultrasonography to detect pannus in knee joint synovitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Jul-Aug;18(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Breedveld F. C., Eberl G., Jones I., Leeming M., Wylie G. L., Kirkpatrick J. Validity and reliability of the twenty-eight-joint count for the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):38–43. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkudlarek M., Court-Payen M., Strandberg C., Klarlund M., Klausen T., Ostergaard M. Power Doppler ultrasonography for assessment of synovitis in the metacarpophalangeal joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2018–2023. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2018::AID-ART350>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkudlarek Marcin, Court-Payen Michel, Jacobsen Søren, Klarlund Mette, Thomsen Henrik S., Østergaard Mikkel. Interobserver agreement in ultrasonography of the finger and toe joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):955–962. doi: 10.1002/art.10877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield R. J., Green M. J., Marzo-Ortega H., Conaghan P. G., Gibbon W. W., McGonagle D., Proudman S., Emery P. Should oligoarthritis be reclassified? Ultrasound reveals a high prevalence of subclinical disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Apr;63(4):382–385. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.007062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther M., Harms H., Krenn V., Radke S., Faehndrich T. P., Gohlke F. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):331–338. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<331::AID-ANR50>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther Markus, Harms Harry, Krenn Veit, Radke Stephan, Kirschner Stephan, Gohlke Frank. Synovial tissue of the hip at power Doppler US: correlation between vascularity and power Doppler US signal. Radiology. 2002 Oct;225(1):225–231. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2251011272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holsbeeck M., van Holsbeeck K., Gevers G., Marchal G., van Steen A., Favril A., Gielen J., Dequeker J., Baert A. Staging and follow-up of rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. Comparison of sonography, thermography, and clinical assessment. J Ultrasound Med. 1988 Oct;7(10):561–566. doi: 10.7863/jum.1988.7.10.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M., van Riel P. L., van de Putte L. B. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J Rheumatol. 1993 Mar;20(3):579–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]