Abstract
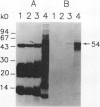
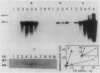
Molecular cloning of polygalacturonase (PG; EC 3.2. 1.15) from fruits of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill cv Rutgers) was accomplished by constructing a cDNA library from turning stage poly(A)+ RNA in λgtll and immunoscreening with polyclonal antibodies raised against purified PG2. Both PG cDNA and antibody probes were used to quantify changes in PG gene expression in pericarp from normal, mutant, and heterozygous genotypes. Results show that PG mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity sequentially peak at the turning, ripe, and red ripe stages of Rutgers pericarp ripening, respectively. PG gene expression was attenuated greatly (0-15% of normal on a gram fresh weight basis) for PG mRNA, protein, and enzyme activity in five ripening-impaired mutants (rin, nor, Nr, Gr, and Long Keeper) tested. Maximum expression of the PG gene in heterozygotes of rin, nor, Nr, Gr, and Long Keeper (crosses with Rutgers) at the mRNA level was about 25, 13, 17, 5, and 62% of the Rutgers turning stage, at the protein level was about 166, 110, 15, 6, and 104% of the Rutgers ripe stage, and at the enzyme activity level was about 69, 37, 4, 1, and 50% of the Rutgers red ripe stage, respectively. No PG gene expression was found in preclimacteric fruits or vegetative tissues. PG mRNA was localized on both free and membrane-bound polyribosomes of ripening pericarp. In addition to transcriptional regulation, mechanisms contributing to mRNA stability, delayed protein accumulation, and posttranslational modifications may play important roles in the overall accumulation of PG activity during fruit ripening.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggs M. S., Harriman R. W., Handa A. K. Changes in Gene Expression during Tomato Fruit Ripening. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):395–403. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crookes P. R., Grierson D. Ultrastructure of tomato fruit ripening and the role of polygalacturonase isoenzymes in cell wall degradation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1088–1093. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellapenna D., Kates D. S., Bennett A. B. Polygalacturonase Gene Expression in Rutgers, rin, nor, and Nr Tomato Fruits. Plant Physiol. 1987 Oct;85(2):502–507. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln J. E., Cordes S., Read E., Fischer R. L. Regulation of gene expression by ethylene during Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) fruit development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlow S. J., Handa A. K. Immuno slot-blot assay using a membrane which covalently binds protein. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jul 16;101(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menninger R. W. Editorial: Psychiatry 1976: time for a holistic medicine. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):603–604. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressey R., Avants J. K. Two forms of polygalacturonase in tomatoes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and protein metabolism in pea epicotyls : I. The aging process. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):809–816. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]