Abstract
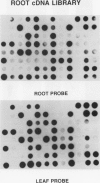
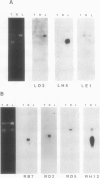
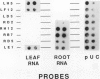
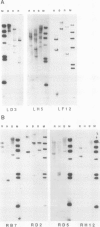
Four root-specific cDNA clones and their corresponding genomic clones have been isolated from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) by a novel differential hybridization procedure. The genes are expressed at high levels in roots and are not detectable in leaves. The cDNAs are encoded by small gene families of two to four members. Transcription experiments with isolated nuclei demonstrate that the genes are, at least in part, transcriptionally regulated. Constructions in which 1.4 kilobase pairs of 5′ flanking region of one of the root-specific genes was fused to a reporter gene (β-glucuronidase) were transformed into tobacco. β-Glucuronidase activity in transgenic plants was localized in the roots, demonstrating the cis-acting sequences regulating root-specific expression are present on the 5′ flanking region.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Watson B. D., Chiang C. C. Transformation of Tobacco, Tomato, Potato, and Arabidopsis thaliana Using a Binary Ti Vector System. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):301–305. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker S. J., Harada J. J., Goldberg R. B. Cellular localization of soybean storage protein mRNA in transformed tobacco seeds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):458–462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz D., Appleby C. A., Landsmann J., Dennis E. S., Trinick M. J., Peacock W. J. Functioning haemoglobin genes in non-nodulating plants. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):178–180. doi: 10.1038/331178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broglie R., Coruzzi G., Fraley R. T., Rogers S. G., Horsch R. B., Niedermeyer J. G., Fink C. L., Chua N. H. Light-regulated expression of a pea ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene in transformed plant cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):838–843. doi: 10.1126/science.6719112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortin M. G., Morrison N. A., Verma D. P. Nodulin-26, a peribacteroid membrane nodulin is expressed independently of the development of the peribacteroid compartment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):813–824. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Künstner P. W., Nguyen T., Verma D. P. Soybean nodulin genes: Analysis of cDNA clones reveals several major tissue-specific sequences in nitrogen-fixing root nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin M. B., Yancey S. B., Cline J., Revel J. P., Horwitz J. The major intrinsic protein (MIP) of the bovine lens fiber membrane: characterization and structure based on cDNA cloning. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamalay J. C., Goldberg R. B. Organ-specific nuclear RNAs in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2801–2805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B., Lamb C. J. Specific expression of a novel cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein gene in lateral root initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1639–1646. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner D. R., Raikhel N. V. Cloning and characterization of root-specific barley lectin. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):124–129. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Gene regulation by phytochrome. Trends Genet. 1988 Feb;4(2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Rapid restriction mapping of DNA cloned in lambda phage vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Parker R. C., Davidson N. Representation of DNA sequences in recombinant DNA libraries prepared by restriction enzyme partial digestion. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., VAN Montagu M., Herrera-Estrella L. Photosynthesis-associated gene families: differences in response to tissue-specific and environmental factors. Science. 1986 Jul 4;233(4759):34–38. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4759.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Schell J. Transgenic plants as tools to study the molecular organization of plant genes. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1176–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.237.4819.1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]