Abstract
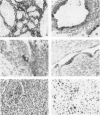
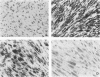
The presence of individual keratin polypeptides and desmoplakins was immunohistochemically studied in 25 spindle cell sarcomas of different types using acetone-fixed frozen sections. Results revealed that keratins 8 and 18 were present in a high number of tumors: 9 of 9 synovial sarcomas, 5 of 7 leiomyosarcomas, 5 of 5 malignant schwannomas, and 1 of 4 undifferentiated spindle cell sarcomas. In addition to keratins 8 and 18, the glandular component of synovial sarcoma showed prominent reactivity with antibodies to keratins 7 and 19. Also the glandular epithelial cells in synovial sarcoma showed desmoplakin immunoreactivity preferentially in a luminal distribution, but desmoplakin was absent in other spindle cell sarcomas. Furthermore keratin 13 was seen focally in 4 of 9 synovial sarcomas. In contrast, keratins 7, 13, and 19 were practically absent in leiomyosarcomas, malignant schwannomas, and undifferentiated spindle cell sarcomas. The widespread presence of keratins 8 and 18 in various spindle cell sarcomas may reflect aberrant keratin expression in mesenchymal cells, previously described in cultured transformed fibroblasts. The presence of keratins 7 and 19 and desmoplakin is highly associated with morphologically observable epithelial differentiation restricted to synovial sarcoma among spindle cell sarcomas.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. C., Theaker J. M., Banks P. M., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Cytokeratin expression in smooth muscle and smooth muscle tumours. Histopathology. 1987 May;11(5):477–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coindre J. M., de Mascarel A., Trojani M., de Mascarel I., Pages A. Immunohistochemical study of rhabdomyosarcoma. Unexpected staining with S100 protein and cytokeratin. J Pathol. 1988 Jun;155(2):127–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson J. M., Weiss L. M., Banks-Schlegel S. P., Pinkus G. S. Keratin proteins and carcinoembryonic antigen in synovial sarcomas: an immunohistochemical study of 24 cases. Hum Pathol. 1984 Jul;15(7):615–621. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Kapprell H. P., Franke W. W. The complement of desmosomal plaque proteins in different cell types. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1442–1454. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernobilsky B., Moll R., Leppien G., Schweikhart G., Franke W. W. Desmosomal plaque-associated vimentin filaments in human ovarian granulosa cell tumors of various histologic patterns. Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):476–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal antibodies to desmin, the muscle-specific intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01738.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal cytokeratin antibodies that distinguish simple from stratified squamous epithelia: characterization on human tissues. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1641–1647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Krepler R., Artlieb U., Gabbiani G., Rungger-Brändle E., Leoncini P., Franke W. W. Proteins of intermediate filaments. An immunohistochemical and biochemical approach to the classification of soft tissue tumors. Am J Pathol. 1983 Feb;110(2):193–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. Synovial sarcoma: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of epithelial differentiation in monophasic and biphasic tumors. Hum Pathol. 1986 Oct;17(10):996–1008. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Schiller D. L., Winter S., Jarasch E. D., Moll R., Denk H., Jackson B. W., Illmensee K. Differentiation-related patterns of expression of proteins of intermediate-size filaments in tissues and cultured cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):431–453. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Moll R., Moll I., Lee I., Schwechheimer K., Franke W. W. The intermediate filament complement of the spectrum of nerve sheath neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):463–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Boyd H. C., Chang Y., Ferguson M., Reichler B., Tippens D. Smooth muscle cells can express cytokeratins of "simple" epithelium. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies in vitro and in vivo. Am J Pathol. 1988 Aug;132(2):223–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. H., Rosenberg A. E., Dickersin G. R., Bhan A. K. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and keratin expression by benign and malignant nerve sheath tumors. Hum Pathol. 1989 Nov;20(11):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann H., Fouquet B., Franke W. W. Expression of intermediate filament proteins during development of Xenopus laevis. I. cDNA clones encoding different forms of vimentin. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):279–298. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huitfeldt H. S., Brandtzaeg P. Various keratin antibodies produce immunohistochemical staining of human myocardium and myometrium. Histochemistry. 1985;83(5):381–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00509196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar M., Gigi-Leitner O., Moll R., Franke W. W., Geiger B. Monoclonal antibodies to various acidic (type I) cytokeratins of stratified epithelia. Selective markers for stratification and squamous cell carcinomas. Differentiation. 1986;31(2):141–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Schwechheimer K., Moll R., Franke W. W. Attachment of vimentin filaments to desmosomal plaques in human meningiomal cells and arachnoidal tissue. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1072–1081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp A. C., Franke W. W. Spontaneous losses of control of cytokeratin gene expression in transformed, non-epithelial human cells occurring at different levels of regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90870-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruc N., Franke W. W. Transient coexpression of desmin and cytokeratins 8 and 18 in developing myocardial cells of some vertebrate species. Differentiation. 1988 Sep;38(3):177–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Bártek J., Purkis P. E., Leigh I. M. Keratin antigens in differentiating skin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:241–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M. Immunoreactivity for cytokeratin and epithelial membrane antigen in leiomyosarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Jun;112(6):637–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Badley R. A., Virtanen I. Expression of intermediate filaments in soft-tissue sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1982 Nov 15;30(5):541–546. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Rapola J. Immunohistochemical spectrum of rhabdomyosarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma-like tumors. Expression of cytokeratin and the 68-kD neurofilament protein. Am J Surg Pathol. 1989 Feb;13(2):120–132. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198902000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirra J. M., Wang S., Bhuta S. Synovial sarcoma with squamous differentiation of its mesenchymal glandular elements. A case report with light-microscopic, ultramicroscopic, and immunologic correlation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Oct;8(10):791–796. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198410000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Cowin P., Kapprell H. P., Franke W. W. Desmosomal proteins: new markers for identification and classification of tumors. Lab Invest. 1986 Jan;54(1):4–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton A. J., Thomas J. A., Isaacson P. G. Cytokeratin-specific monoclonal antibodies are reactive with tumours of smooth muscle derivation. An immunocytochemical and biochemical study using antibodies to intermediate filament cytoskeletal proteins. Histopathology. 1987 May;11(5):487–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., van Lessen G., Weber K., Klöppel G., Altmannsberger M. Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal carcinomas by using monoclonal antibodies specific for individual keratin polypeptides. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):497–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F., van Niekerk C., Poels L., Schaafsma E., Huijsmans A., Robben H., Schaart G., Vooijs P. Use of monoclonal antibodies to keratin 7 in the differential diagnosis of adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):641–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch W., Skalli O., Seemayer T. A., Gabbiani G. Intermediate filament proteins and actin isoforms as markers for soft tissue tumor differentiation and origin. I. Smooth muscle tumors. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jul;128(1):91–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Tseng S. C., Huang A. J., Cooper D., Schermer A., Lynch M. H., Weiss R., Eichner R. Monoclonal antibody studies of mammalian epithelial keratins: a review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:307–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley H., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Biochemical evidence that cytokeratins are present in smooth muscle. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Jun;69(3):433–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Microinjection of monoclonal antibodies specific for one intermediate filament protein in cells containing multiple keratins allow insight into the composition of particular 10 nm filaments. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;38(2):234–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Muijen G. N., Ruiter D. J., Warnaar S. O. Coexpression of intermediate filament polypeptides in human fetal and adult tissues. Lab Invest. 1987 Oct;57(4):359–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Heikinheimo K., Hormia M., Kivelä T., Laitinen L., Thornell L. E. Expression of intermediate filaments (IF) in tissues and cultured cells. Int J Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;33(1):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Kariniemi A. L., Paasivuo R. Diagnostic application of monoclonal antibodies to intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:635–648. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Swanson P. E., Scheithauer B. W., Manivel J. C. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. An immunohistochemical study of 62 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Apr;87(4):425–433. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.4.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]