Abstract
1. The coupling of D2 dopamine receptors and G-proteins has been examined in cholate-solubilized preparations of bovine caudate nucleus. 2. No receptor-G-protein coupling could be detected in solubilized preparations obtained in 0.3% cholate, but if this preparation is diluted 5-fold, coupling is re-established. 3. The dilution process was examined, and it was shown that the change in ionic strength was an important factor in modulating the observed receptor-G-protein interaction. 4. Ionic strength was shown, however, not to be the primary determinant of receptor-G-protein coupling. This is likely to be the formation, upon dilution of the preparation, of vesicles in which receptor and G-protein reassociate. 5. The formation of vesicles upon dilution was examined by a variety of techniques, including thermal-stability studies, gel filtration, centrifugation and electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF
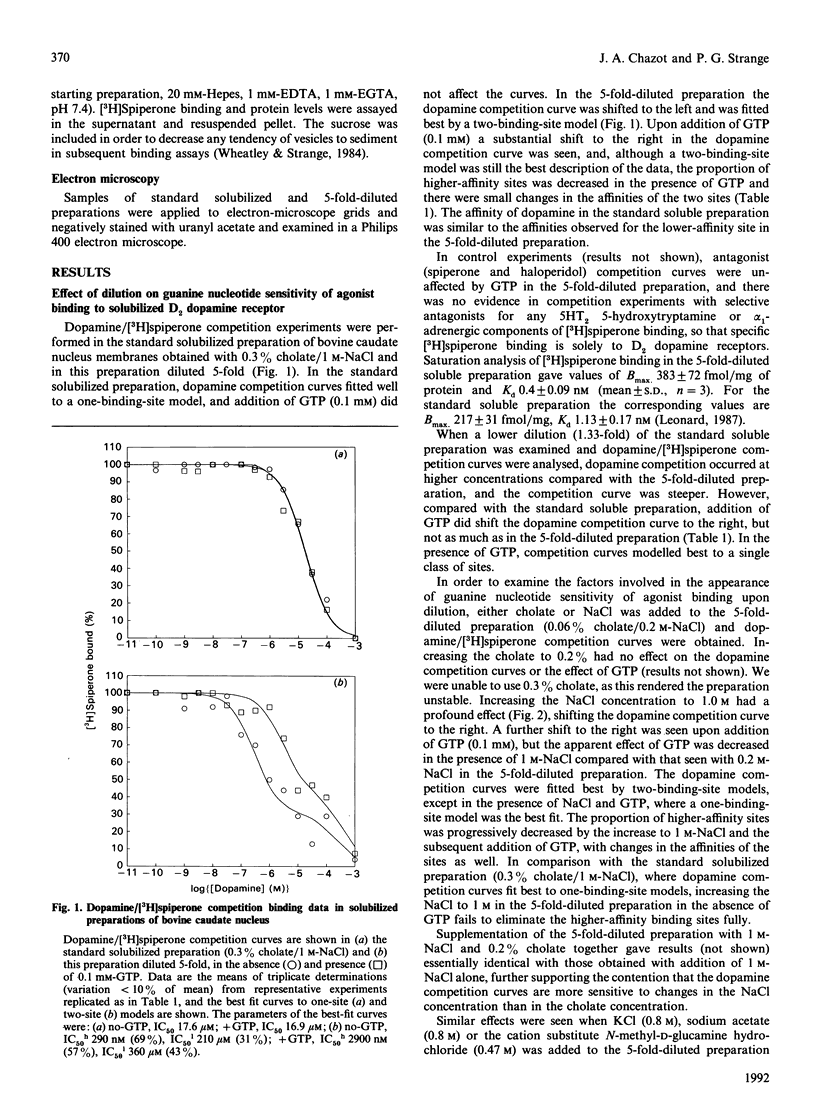

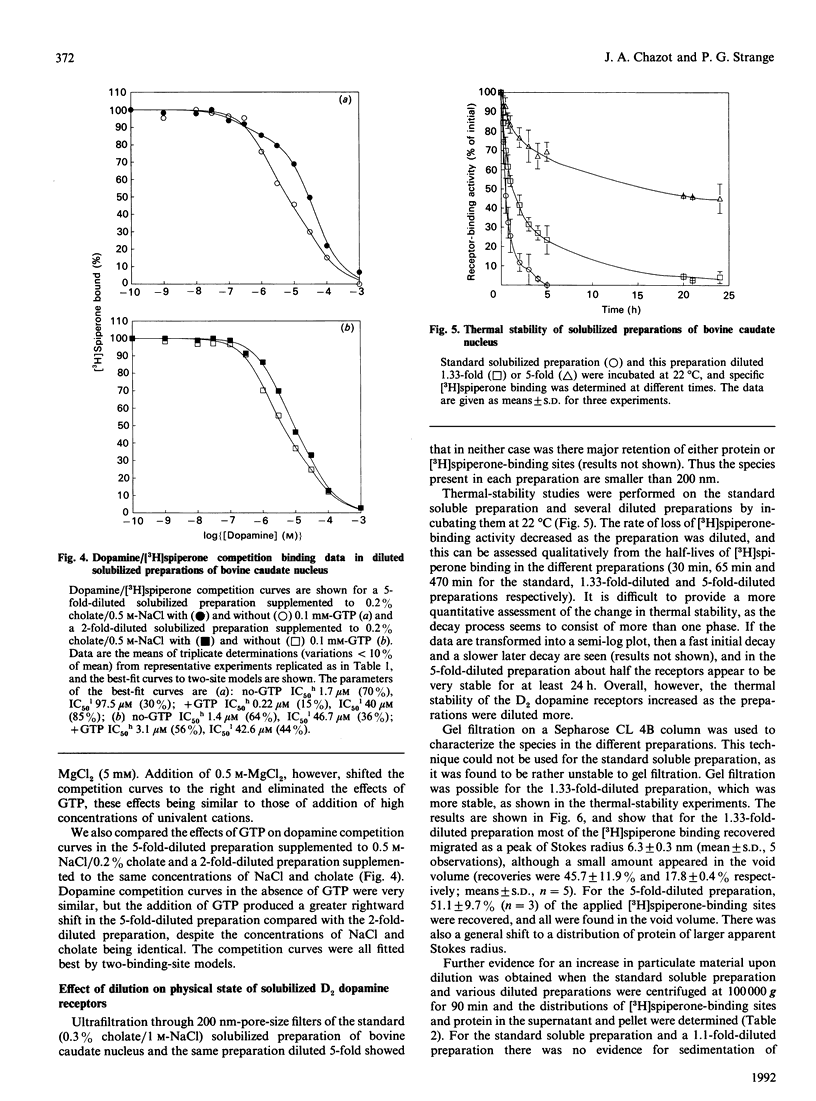



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Toso R., Sommer B., Ewert M., Herb A., Pritchett D. B., Bach A., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The dopamine D2 receptor: two molecular forms generated by alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4025–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Keyser J., De Backer J. P., Convents A., Ebinger G., Vauquelin G. D2 dopamine receptors in calf globus pallidus: agonist high- and low-affinity sites not regulated by guanine nucleotide. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):977–979. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Kilpatrick B. F., Caron M. G. Dopamine receptor of the porcine anterior pituitary gland. Evidence for two affinity states discriminated by both agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Kanety H., David C., Fuchs S. Purification of the D-2 dopamine receptor from bovine striatum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):602–609. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80885-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elazar Z., Siegel G., Fuchs S. Association of two pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins with the D2-dopamine receptor from bovine striatum. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2353–2357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Frankham P. A., Strange P. G. Use of cholate/sodium chloride for solubilisation of brain D2 dopamine receptors. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1526–1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi S. M., Ramwani J., Srivastava L. K., Rajakumar G., Ross G. M., Cullen M., Mishra R. K. Characterization of high-affinity dopamine D2 receptors and modulation of affinity states by guanine nucleotides in cholate-solubilized bovine striatal preparations. J Neurochem. 1986 Nov;47(5):1493–1502. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard M. N., Macey C. A., Strange P. G. Heterogeneity of D2 dopamine receptors in different brain regions. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):595–602. doi: 10.1042/bj2480595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard M. N., Williamson R. A., Strange P. G. The glycosylation properties of D2 dopamine receptors from striatal and limbic areas of bovine brain. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):877–883. doi: 10.1042/bj2550877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara K., Haga K., Berstein G., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Ohara K. The interaction between D-2 dopamine receptors and GTP-binding proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;33(3):290–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwani J., Mishra R. K. Purification of bovine striatal dopamine D-2 receptor by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8894–8898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Amlaiky N., Falardeau P., Caron M. G. Purification and characterization of the D2-dopamine receptor from bovine anterior pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18996–19002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Benovic J. L., Amlaiky N., Unson C., Milligan G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G. The D2-dopamine receptor of anterior pituitary is functionally associated with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4860–4867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senogles S. E., Spiegel A. M., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Caron M. G. Specificity of receptor-G protein interactions. Discrimination of Gi subtypes by the D2 dopamine receptor in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4507–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. The A1 adenosine receptor. Solubilization and characterization of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6728–6732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strange P. G. Aspects of the structure of the D2 dopamine receptor. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Sep;13(9):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Meldolesi J. Mechanisms of signal transduction at the dopamine D2 receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):74–77. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Guan H. C., Sunahara R. K., Seeman P., Niznik H. B., Civelli O. Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):610–614. doi: 10.1038/350610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., George S. R., Seeman P. Regulation of anterior pituitary D2 dopamine receptors by magnesium and sodium ions. J Neurochem. 1985 Dec;45(6):1842–1849. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb10542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley M., Strange P. G. Reconstitution of solubilised brain D2 dopamine receptors into phospholipid vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R. A., Worrall S., Chazot P. L., Strange P. G. Purification of brain D2 dopamine receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withy R. M., Mayer R. J., Strange P. G. Use of [3H]spiperone for labelling dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors in bovine caudate nucleus. J Neurochem. 1981 Nov;37(5):1144–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreggett K. A., De Léan A. The ternary complex model. Its properties and application to ligand interactions with the D2-dopamine receptor of the anterior pituitary gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):214–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



