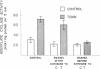Abstract
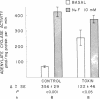
The effect of cholera toxin on adenylate cyclase from rat liver has been studied in a broken cell preparation. The activation of the enzyme in this in vitro preparation requires the addition of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to the incubation medium and the presence of cell components other than the membrane-bound adenylate cyclase. Once the activation of the cyclase is produced, the effect persists despite repeated washing or solubilization of the enzyme. The effect can be obtained with concentrations of cholera toxin as low as 0.4 nM after 15 min of incubation at 22 degrees C, and stimulation can be detected after only 5 min of incubation at 37 degrees C. The activation of the enzyme is still apparent after at least 2 h at 0 degrees C. Preincubation with choleragenoid in vitro does not interfere with this effect of the toxin. Animals pretreated by an intravenous injection of cholera toxin do not respond to the in vitro addition of cholera toxin and NAD to the same extent as untreated animals; i.e., the effects overlap to suggest that the in vitro effect is the same as that in vivo. Responses to isoproterenol, glucagon, and NaF were also similar in the in vitro broken cell-activated system, as previously reported for the enzyme activated in vivo.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman B., Flores J., Witkum P. A., Sharp G. W. Studies on the mode of action of cholera toxin. Effects on solubilized adenylate cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1202–1205. doi: 10.1172/JCI107660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. C., Jr Cholera enterotoxin--recent investigations yield insights into transport processes. Am J Med. 1971 Jan;50(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Mode of action of cholera toxin: stabilization of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in turkey erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3299–3303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Involvement of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in the action of cholera toxin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2064–2068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T. Diphtheria toxin, protein synthesis, and the cell. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Kato I., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis by diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W. Action of cholera toxin on fluid and electrolyte movement in the small intestine. Annu Rev Med. 1973;24:19–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.24.020173.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S., Lipson L. C., Parkinson D. K. Action of cholera toxin to stimulate adenyl cyclase. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1971;84:200–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]