Abstract
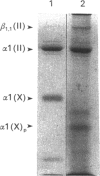
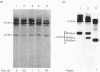
We isolated and characterized the intact native tissue form of type X collagen from the presumptive calcification region of lathyritic chick-embryo sterna and from organ cultures incubated in the presence of beta-aminopropionitrile (beta APN). The administration of beta-APN in vivo greatly increased the solubility of type X collagen and allowed the extraction of quantitative amounts of these molecules under non-denaturing non-proteolytic conditions. Biosynthetic studies in vitro showed that the addition of beta APN during labelling resulted in a 4-fold increase in the extractability of the newly synthesized type X collagen. Biochemical characterization of the intact type X collagen extracted from the tissues or biosynthesized in the organ cultures showed that type X collagen is composed of 59,000-Mr chains that do not undergo conversion into shorter polypeptides. Despite the marked solubilization of type X collagen upon administration of beta APN, a substantial proportion remained tissue-bound and could only be extracted by employing proteolytic digestion followed by disulphide bond reduction. These findings indicate that type X collagen in the tissues is stabilized by at least two different mechanisms, one involving beta APN-sensitive cross-links and the second through interactions with disulphide-bonded proteins. Limited proteolytic digestion with chymotrypsin of tissues containing 1.0 M-NaCl-insoluble type X collagen resulted in its complete solubilization. The majority of type X collagen molecules extracted with chymotrypsin were approx. 10% shorter than those obtained after limited pepsin digestion (Mr 40,000 versus Mr 45,000) and showed the selective loss of a single CNBr-cleavage peptide. These findings indicate the existence of chymotrypsin-sensitive sites within the triple-helical domain of the molecules.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayad S., Kwan A. P., Grant M. E. Partial characterization of type X collagen from bovine growth-plate cartilage. Evidence that type X collagen is processed in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80899-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Quarto N., Descalzi-Cancedda F., Cancedda R. The low molecular weight collagen synthesized by chick tibial chondrocytes is deposited in the extracellular matrix both in culture and in vivo. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):823–827. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01891.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Yankowski R., Reginato A. M. Quantitative analysis of type X-collagen biosynthesis by embryonic-chick sternal cartilage. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):357–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2330357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juva K., Prockop D. J. Modified procedure for the assay of H-3-or C-14-labeled hydroxyproline. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Kwan A. P., Holmes D. F., Schor S. L., Grant M. E. Type X collagen, a product of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):545–554. doi: 10.1042/bj2270545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LuValle P., Ninomiya Y., Rosenblum N. D., Olsen B. R. The type X collagen gene. Intron sequences split the 5'-untranslated region and separate the coding regions for the non-collagenous amino-terminal and triple-helical domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18378–18385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Gordon M., van der Rest M., Schmid T., Linsenmayer T., Olsen B. R. The developmentally regulated type X collagen gene contains a long open reading frame without introns. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5041–5050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reginato A. M., Lash J. W., Jimenez S. A. Biosynthetic expression of type X collagen in embryonic chick sternum cartilage during development. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2897–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington M. C., Bashey R. I., Brighton C. T., Jimenez S. A. Biosynthesis of a disulphide-bonded short-chain collagen by calf growth-plate cartilage. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):227–233. doi: 10.1042/bj2240227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington M. C., Bashey R. I., Brighton C. T., Jimenez S. A. Biosynthesis of a low molecular weight collagen by rabbit growth plate cartilage organ cultures. Coll Relat Res. 1983 May;3(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(83)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Mayne R., Jeffrey J. J., Linsenmayer T. F. Type X collagen contains two cleavage sites for a vertebrate collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4184–4189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]