Abstract
The retention of polar compounds, the separation of structural isomers and thermal stability make carbonaceous materials very attractive stationary phases for Liquid Chromatography (LC). Carbon clad zirconia (C/ZrO2), one of the most interesting, exhibits unparalleled chemical and thermal stability, but its characteristically low surface area (20 – 30 m2/g) limits broader application as a second dimension separation in two-dimensional liquid chromatography (2DLC) where high retentivity and therefore high stationary phase surface area are required. In this work, we used a high surface area commercial HPLC alumina (153 m2/g) as a support material to develop a carbon phase by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) at elevated temperature using hexane vapor as the carbon source. The loading of carbon was varied by changing the CVD time and temperature, and the carbon coated alumina (C/Al2O3) was characterized both physically and chromatographically. The resulting carbon phases behaved as a reversed phase similar to C/ZrO2. At all carbon loadings, C/Al2O3 closely matched the unique chromatographic selectivity of carbon phases, and as expected the retentivity was increased over C/ZrO2. Excess carbon – the amount equivalent to 5 monolayers - was required to fully cover the oxide support in C/Al2O3, but this was less excess than needed with C/ZrO2. Plate counts were 60,000 – 76,000/meter for 5 μm particles. Spectroscopic studies (XPS and FT-IR) were also conducted; they showed that the two materials were chemically very similar.
1. Introduction
Carbonaceous materials are very attractive for stationary phases in liquid chromatography (LC) because of their chemical and thermal stability and chromatographically unique selectivity [1–8]. Even though carbon phases are reversed phases, they also retain certain polar solutes that show little retention on conventional silica based reversed phases. Their uniqueness is also exhibited in their ability to retain very polarizable anions [9] and in their exceptional selectivity for various classes of stereo isomers [4,6]. For instance, nitrobenzene is significantly more retained on carbon phases than is toluene; this is never observed on conventional alkyl bonded phases. The ability to separate structural isomers or closely related solutes is also a unique property of carbon phases. Jackson et al. showed that certain aromatic stereoisomers could be separated on carbon but could not be separated on an octadecyl silica (ODS) column [4]. All these characteristics have broadened the utility of the carbon phases to separation of biological samples including drug metabolites [10,11] and to carbohydrate analysis [12].
In 1990, Carr and coworkers successfully developed carbon clad zirconia as a HPLC support [13]. This study was motivated by the unparalleled chemical, mechanical and thermal stability of zirconia compared to silica under extreme conditions (i.e. pH 1–14 at >100 °C) [14]. Carbon was deposited on the surface of zirconia (C/ZrO2) in a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process by flowing organic vapor over a bed of zirconia at the elevated temperature at low pressure (< 60 torr). It was shown that the carbon load depends on the temperature, the reaction time and the carbon source. The physical and chemical properties of C/ZrO2 were extensively explored [3,4,6–8,15], showing that C/ZrO2 retains the unique selectivity of carbon materials as described above but with enhanced mechanical stability. Jackson et al. showed the similarity in chromatographic selectivity between C/ZrO2 and porous graphitic carbon (Hypercarb), a commercial carbon phase [3,15]. These properties make C/ZrO2 an excellent candidate for use as the second dimension column for fast 2DLC, which has tremendous potential in separation for complex bioanalytes [16].
However, the second dimension column in 2DLC is optimally highly retentive so as to provide a high degree of sample focusing. In 2DLC separations, an analyte that elutes from the first dimension column is sequentially injected onto a second column (termed the second dimension). It is very important that the separation in the second dimension be fast so that the analyte peak on the first dimension can be sampled more than once; ideally more than three or four times. Furthermore, the total analysis time is limited by the run time of the second dimension separation. Thus, there is great need to improve the speed of the separation in the second dimension; for instance, Carr et al. recently developed a fast 2DLC system that uses higher temperatures (> 100 °C) to accelerate the second dimension. An ideal column for the second dimension must have 1) high chemical and packed bed stability, 2) orthogonal selectivity compared to the first dimension column and 3) have high retentivity for the analyte. Although C/ZrO2 meets the first two requirements, the intrinsically low surface area of commercial porous zirconia (20 – 30 m2/g) limits its retentivity. High retentivity is critical because analytes that are injected onto the second column from the first column are typically in a strong solvent environment. Furthermore, a large volume of sample is injected on a relatively low volume second dimension column (33 mm by 2.1 mm). This situation can lead to distorted peak shapes and thus, poor peak capacity and low analytical sensitivity if the second column fails to focus the analyte at the inlet of the column. Use of a stationary phase that is strongly hydrophobic helps to ameliorate this problem. Jackson el al. showed that carbon phases exhibit higher intrinsic hydrophobicity than ODS [15]. Thus, the use of a carbon phase is a partial solution to this problem due to its stronger retention of weakly retained analytes. An increase in phase ratio should also help as it will further increase retention factors.
Theoretically, the retentivity in adsorption chromatography is proportional to the total surface area of the stationary phase [17]. Since the retention mechanism of carbon phases is based on adsorption on the rigid carbon surface, we believe that use of a higher surface area substrate on which to deposit the carbon ought to enhance retentivity and thus improve the use of carbon based phases as the second dimension in 2DLC.
Many attempts have been made over the past three decades to prepare chromatographically useful carbon packing materials using a variety of substrates [18–20], but none enjoy the full combination of high surface area, mechanical strength and chemical homogeneity. Guiochon et al. modified graphitized carbon black by depositing a thin layer of pyrocarbon to improve the mechanical strength of carbon black and use it for HPLC [21]. Knox et al. developed a new method to synthesize a porous graphitic carbon (PGC) [22]; they impregnated a phenol-formaldehyde polymer in the pores of a silica “template”, subsequently pyrolyzed the polymer to produce a carbonaceous material, then, removed the silica template by alkali treatment, heating the residual carbon skeleton at 2500 °C to produce a graphitic carbon. PGC is the most successful carbon packing material for HPLC. Although the PGC support has been widely used for various applications, it has some drawbacks including a costly manufacturing process and lesser mechanical strength than C/ZrO2 [8,23]. Silica has also used as a template to develop a graphitized carbon monolithic column [24]. Leboda et al. developed a different method in which a metal catalyst was impregnated on silica to catalyze the chemical decomposition of a hydrocarbon [25,26]. Several other studies have shown that carbon can be deposited directly on silica either by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) without catalysts by using certain species as the carbon source [27,28] or by pyrolysis of pre-adsorbed oligomers [23]. Unfortunately, all the resulting materials suffered from low available carbon surface area, heterogeneous surface chemistries, and significantly tailed peaks and poor efficiencies in general.
In this study, we have developed a high surface area carbon phase on porous HPLC grade alumina (Al2O3) by depositing carbon using a CVD process related to that used to develop C/ZrO2. The reaction took place at elevated temperatures (≥ 700 °C) and at atmospheric pressure.We subsequently evaluated its physical and chromatographic properties. We chose alumina for this work because it is a well known active catalyst for cracking hydrocarbons [29] and has comparable chemical stability to that of zirconia [30]. Because this material has a higher surface area compared to zirconia, we expected that the resulting material would have a higher retentivity while maintaining similar selectivity. Thus, in the work presented here, the C/ZrO2 is used as a bench mark to compare retentivity and selectivity. We also examined its potential use for the 2DLC by using indolic metabolites which were of interest to us in our 2DLC studies.
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
HPLC grade hexanes from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, M), USA) were used as the CVD carbon source. All chemicals, reagent grade or better, used for the chromatographic study were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Di(phenethyl)amide isomers were provided by Prof. T. R. Hoye at the University of Minnesota. Standards of amphetamines drugs (1 mg/ml in methanol, were from Cerilliant (Round Rock, TX, USA)) Four indolic metabolites standards were prepared as described by Stoll [16]. They include Indole-5-hydroxy-typtamine (IHT), Indole-3-acetyl-ε-L-lysinee (IAL), Indole-3-ethanol (IE) and Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA). HPLC eluents comprise HPLC grade acetonitrile from Burdick and Jackson (Muskegon, MI, USA) and HPLC grade water that was prepared in-house from a Barnstead Nanopure II deionizing system (Dubuque, IA, USA). This water was boiled to remove carbon dioxide and filtered through a 0.45 μm nylon filtration apparatus (Lida Manufacturing Inc., Kenosha, WI, USA) prior to use.
2.2. Carbon phase preparation
Aluspher 5 μm porous alumina (Al2O3) was a gift of Merck KGaA, (Darmstadt, Germany). 1 g of Al2O3 was placed in a baffled quartz heated reactor (Model HTR 11/75 Carbolite, Aston Lane, Hope, England) that oscillates between 0 and 180 ° to mix Al2O3 particles during the CVD process (see Fig. 1). Two gas controllers taken from a HP 5890 Gas Chromatography (Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA) were used to maintain gas flow at 200 ml/min for both directions.
Figure 1.
Schematic of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) apparatus. 1 and 2 are gas controllers for each direction (200 cc/min.)
Previous work on C/ZrO2 in this laboratory showed that saturated hydrocarbons provide carbon phases with better efficiency and symmetrical peak shapes compared to unsaturated hydrocarbons [7]. Thus, we used hexane vapor as the carbon source in this study. The whole system is flushed with high purity nitrogen (99.99% purity) before elevating the temperature. Flowing hexane vapor is introduced by bubbling high purity nitrogen through a reservoir of the hexanes. The vapor is then passed over Al2O3 at 700 or 800 °C for 1.5 to 6 hours to deposit carbon. After deposition the oven temperature is allowed to drop slowly to room temperature while maintaining the makeup nitrogen flow to remove gaseous byproducts produced during the CVD process. Carbon coated alumina was sent for analysis of its carbon content (Atlantic Microlabs, Norcross, GA, USA).
2.3. Column packing
The columns were packed by procedures very similar to what have been reported elsewhere [16]. C/ZrO2 (3 μm, carbon loading = 8 %), obtained from ZirChrom Separations Inc. (Anoka, MN, USA), was packed by the same procedure as described above.
2.4. Chromatographic studies
All chromatographic data were collected by a HP 1090 LC system controlled by Chemstation software version A.10.01 (Agilent Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). The instrument is equipped with an autosampler, thermostatting column compartment and photodiode array UV detector (DAD). All solutes were detected at 210 nm unless otherwise noted. Column dead times were measured from the retention time of acetone. All retention data are an average of triplicate runs.
2.5. Conductivity measurement
The electrical conductivity of the pyrolyzed carbon on alumina was measured using the circuit shown in Fig. 2. A hole was drilled through both sides of a plastic tube to create a cavity. The particles were placed in the cavity and screws were used to densely pack the materials for maximum interparticle contact. The reference resistance (Rs) was adjusted until the reading voltage (VAB) dropped to half of the reference voltage (Vs) reading. Then, the sample resistance (Rx) was calculated with Eq. (1).
Figure 2.

Schematic of the device used to measure the resistivity of various carbon materials including C/ZrO2, C/Al2O3, and graphite. The circuit consists of a reference voltage (Vs,); a measured voltage (VAB,); the reference resistance (Rs,); the sample resistance (Rx); A and B are connected to the potentiometer that has input impedance of > 100 GΩ.
| (1) |
Voltages were measured by an EMF 16 potentiometer (Lawson Labs Inc., Malvern, PA) controlled with EMF Suite 1.02 software (Fluorous Innovations, Arden Hills, MN) at room temperature (25 °C). The circuit was tested using the resistance of bare Al2O3 and graphite (≥ 99.0 % C, ≤ 20 μm) obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The resistance of the bare alumina was greater than the maximum measurable resistance (1010 Ω).
2.6. N2 adsorption
The pore structure of the alumina before and after carbon deposition was characterized by nitrogen sorption performed on a Micromeritics ASAP 2000 sorptometer (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA). The specific surface area of the particles was computed using the BET method [31]. Approximate pore size distributions were computed using the BJH method [32].
2.7. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and transmission FT-IR spectroscopy
The samples (24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2) were sent for XPS analysis (Characterization Facility of the University of Minnesota, MN, USA). The XPS measurements were performed on an SSX-100 system (Surface Science Instruments) quipped with a monochromated Al Kα X-ray source, a hemispherical sector analyzer (HSA) and a resistive anode detector. FT-IR spectra in the mid-IR range (4000 – 400 cm−1) were obtained on a Nicolet Magna-IR 760 spectrometer using potassium bromide pellets of the samples (0.1 % w/w) including 24% C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2 in a nitrogen atmosphere. The same weight percent of decanophenone in the pellet was used as a control.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Reproducibility of carbon deposition on Al2O3
Table 1 compares the batch-to-batch reproducibility and chromatographic properties of several preparations of carbon coated alumina (C/Al2O3). Three replicate coatings gave an average of 23.3 % of carbon load with 6 % standard deviation. We evaluated the resulting materials chromatographically by measuring the efficiency and retention of nitrohexane, toluene and nitrobenzene. As is shown in the table, this carbon stationary phase gave reproducible efficiency (12 % RSD) and retention (6 – 10 % RSD). Fig. 3 shows that we can obtain reasonably symmetric peak shapes of nitroalkanes on 24 % C/Al2O3. Nitroalkanes are used to evaluate the column because they provide maximum efficiency and the least peak tailing. Given the chromatographic data and the reasonably reproducible coating process, it is clear that these materials are potentially useful as packing materials for HPLC.
Table 1.
Reproducibility of carbon deposition process
| Batch 1 | Batch 2 | Batch 3 | Average | SD | % RSD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % C w/wa | 24.4 | 23.8 | 21.7 | 23.3 | 1.4 | 6 |
| Plate count/mb | 69,580 | 59,860 | 76,480 | 68,640 | 8450 | 12 |
| k′ of nitrohexanec | 17.7 | 20.7 | 17.4 | 18.6 | 1.8 | 10 |
| k′ of toluened | 5.2 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 5.4 | 0.3 | 6 |
| k′ of nitrobenzened | 19.5 | 23.8 | 22.2 | 21.8 | 2.2 | 10 |
6 h CVD at 700 °C.
Plate count for nitrohexane. LC conditions: F = 0.4 ml/min, T = 40 °C, 50 mm × 2.1 mm i.d. column.
35/65 MeCN/water.
50/50 MeCN/water.
Figure 3.
Chromatogram for a homolog series of nitroalkanes. LC conditions: 35/65 MeCN/water, T = 40 °C, F = 0.4 ml/min. 50 × 2.1 mm id. column, solutes: nitropropane, nitrobutane, nitropentane and nitrohexane (100 μg/ml), 1 μl injection.
3.2. Effect of CVD conditions on the property of the material
3.2.1. Physical and chemical characteristics
Surface coverage
Carbon load increased with deposition time and reactor temperature. We obtained 40 % (w/w) carbon at 800 °C in 6 h as compared to 24 % (w/w) at 700 °C for the same time. For chromatographic application it is necessary to fully cover the Al2O3. The amount of carbon needed to fully cover the Al2O3 was ascertained by using benzoic acid as a probe as per the method of Trammell [33]. Effective blockage of benzoic acid-binding sites on the oxide is critical as such sites strongly interact with any Lewis base analytes such as carboxylic acids, resulting in low analyte recovery or broadening and tailing peaks. Benzoic acid did not elute after adsorption on the 6 and 14 % carbon indicating poor coverage of alumina, but it was fully eluted on 24 % and 40 % carbon (data not shown). This suggests that 24 % C/Al2O3 may have the optimum amount of carbon on Al2O3 to fully cover the oxide surface without excessively reducing surface area. This will be borne out by other techniques.
Pore size distribution
Table 2 summarizes the amount of carbon deposited under different conditions and the BET pore characteristics. Clearly, the surface area and the pore volume decrease with increasing carbon load. A carbon load of 40 % (w/w) removes about 80 % of the initial surface area and leaves only 13 % of the original pore volume. Thus, it is critical to find the optimal carbon load that maximizes retentivity before the loss of the pore area and volume cause a decrease.
Table 2.
Ch aracteristics of different carbon load on Al2O3
| CVD conditions | % C (w/w) | Carbona (μmol/m2) | HypotheticalCarbon thicknessb (monolayer) | SBETc (m2/g) | Pore volumed (cm3/g) | Nominal BET pore diametere (nm) | log (resistance, Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare | na | na | na | 153 | 0.38 | 10.0 | >10 |
| 700 °C 1.5 h | 6 | 30 | 1 | 119 | 0.29 | 9.7 | 9.4 |
| 700 °C 6 h | 24 | 133 | 5 | 92 | 0.18 | 7.8 | 2.1 |
| 800 °C 6 h | 40 | 218 | 8 | 31 | 0.05 | 5.9 | 2.6 |
(% C) × (106)/{(100) × (SBET of Bare) × (12.011)}.
NA × π (1.42 × 10−10)2 × (result from a)/(106) [8]. This is the number of monolayers in a hypothetical uniform-thickness coating, with no pore size effect. Assumption: graphitic carbon, 1.42 Å for carbon bond length and homogeneous coating process.
Surface area (SBET).
Pore volume obtained from single total pore volume less than 140, 198, 251, 125 nm diameter at P/Po of 0.986, 0.990, 0.992 and 0.984, respectively (from top to bottom).
Nominal pore diameter of an equivalent single cylinder, calculated by 4 × (pore volume)/SBET. The pore size distributions (Fig. 4) are much more meaningful, but we include this figure for comparison with other materials (for which this figure is often cited).
On the basis of the BET data, assuming a uniform coating process and that the carbon has graphite-density, we estimate the % C that is theoretically required to form one hypothetical monolayer of carbon (see Table 2). As a result, 6 % (w/w) of carbon load obtained by 700 °C for 1.5 h is expected to provide full coverage of Al2O3. However, as mentioned above, 24 % carbon, which corresponds to about 5 monolayers of carbon, was required to fully block access to the Al2O3 substrate. This suggests that the carbon coating by our CVD method is not in fact uniform. However, it should be noted that 8 % carbon must be loaded on ZrO2 to fully block access to the substrate and, at its lower surface area, this is equivalent to about 11 monolayers. A carbon load of 24 % resulted in the loss of 40 % of the surface area in C/Al2O3; this is a rather reasonable loss when compared to the loss of 88 % of the surface area after 3 % carbon is loaded on zirconia [26].
To better understand how nonuniform the carbon coating is, we plotted pore area and pore volume distributions from nitrogen adsorption and desorption data in Fig. 4. The adsorption and desorption curves are considered to reflect the size distribution of pore bodies and pore throat, respectively [34]. Low carbon loads (6 %) had little effect on the pore structures as both small and large pore sizes were only slightly decreased. However, high carbon loads considerably changed both the area and volume distributions. Noticeable shifts of the distribution peaks towards smaller pore sizes are observed indicating a decrease of the average pore diameter. Uniform coating of carbon would not cause a shift in this manner. Thus, the observed shift confirms that carbon deposition on Al2O3 is not uniform.
Figure 4.
Differential pore size distribution for pore volume and surface area for various carbon load computed by the BJH method from nitrogen adsorption (upper) and desorption (lower) data. (*) bare Al2O3; (◇) 6 %; (□) 24 %; (▲) 40 % C/Al2O3
Nonuniform deposition of pyrolytic carbon is not surprising; several review papers explain nonuniform coating thickness and even patchiness at early stages of coating [35,36]. However, the rather large excess carbon (equivalent of 5 hypothetical monolayers) required to fully block access of species which adsorb irreversibly on Al2O3 could cause pore plugging, which would be quite detrimental to the performance of a chromatographic support. Thus, we used Reeder’s models [34] to test the geometry of carbon deposition. Though these models were developed to understand coatings resulting from the solution deposition of a polymer in a porous body, we believe that the models are geometrically applicable to explain whether in our process excess carbon well beyond a hypothetical monolayer is needed and yet does not block the narrowest pores. Reeder’s first two models are 1) uniform thickness of layers through all pores (model 1) and 2) nonuniform thickness of layers for different size of pores (model 2), but with constant volume fraction deposition in the pores - thicker in larger pores, but with constant proportion of coating thickness to pore diameter. The differential pore distribution plots for pore volume and surface area based on the models are shown in Fig. 5.As compared in Fig. 4 – 5, the actual changes in the area and volume distributions with increasing carbon load is closer to model 2. Apparently in our samples carbon deposited nonuniformly in the pores with thicker layers in larger pores; this confirms that the excess carbon is not necessarily blocking small pores. This also helps explain why it requires excess carbon to make sure the smaller pores are adequately covered – consistent with our observation that we must use as much carbon as would be required for 5 hypothetical monolayers.
Figure 5.
Differential pore size distribution for pore volume (upper) and surface area (lower) for various carbon load on Al2O3 using the models: A, model 1 of smooth coating of uniform thickness; B, model 2 of smooth coating thicker in larger pores (i.e. not uniform thickness, but instead with uniform volume fraction of carbon in pores; carbon thickness/pore diameter constant for all values of pore diameter). See Fig. 4 for symbols.
Electrical resistivity
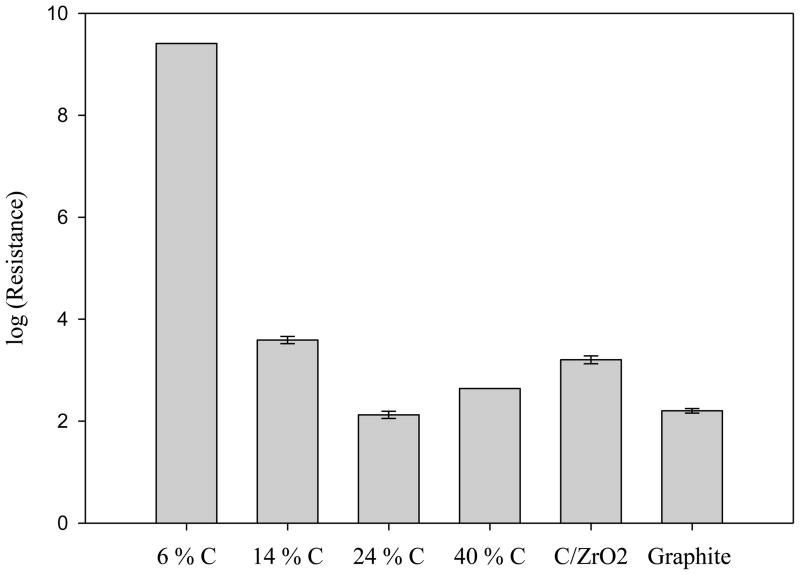
Fig. 6 presents a comparison of the resistivity of the different carbon coated particles with C/ZrO2 and graphite. Since the carbon is a conductor and alumina is not, we expect those materials that have a lower fraction of the alumina covered by carbon will have higher resistivity as the carbon layer will be less continuous. The resistance clearly decreased upon increasing the amount of carbon deposited. The 14 % carbon material showed higher resistivity than did 24 % carbon, but little additional change in resistance was seen above a load of 24 %. This again suggests that 24 % carbon is adequate to fully cover Al2O3. Olesik et al. showed that lower resistance of carbon phases exhibits higher polarizability leading to increased retentivity [23]. As 24 % C/Al2O3 shows comparable resistivity to graphite, this material retains considerable sp2 hybridization. It also has a lower resistance than C/ZrO2, which may imply a higher degree of sp2 hybridization and thus a higher degree of polarizability of the carbon on C/Al2O3.
Figure 6.
Plot of log (resistance, ohms) for various carbon materials. See Fig. 2 and Eq. 1 for the calculation of the resistance. Bars indicate a standard deviation obtained from triplicate measurement (no error bar if not measured at least three times).
Spectroscopic characterization
XPS was conducted on the 24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2. Both samples are sufficiently conductive and no charge neutralization was applied. Due to the thinness of the carbon coating, oxygen from both the alumina and zirconia dominated the spectra. As a result, the O 1s spectra from both samples were attributed to the metal oxides. Fig. 7 compares the C 1s spectra for the 24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2; it shows rather sharp (FWHM = 2.3 eV) and strong peaks at 284.6 and 284.4 eV, respectively. On the whole the C 1s spectra predominantly have the same character as a combination of graphite and diamond like carbon [37]. The peaks are asymmetric and are comparable to the spectra reported for pyrolytic carbon [38]. The broad and tailed region of the C 1s spectra at around 286 – 289 eV could be due to minor C-O and C=O components [39]. However, overall the C 1s spectra show great similarity in the chemical environment of these carbons and an insignificant amount of oxygen incorporated in both carbon surfaces. We further ran these carbon samples by FT-IR by preparing pellets with potassium bromide. However, we could not see any peaks of carbon-oxygen functional groups whereas the same weight % of decanophenone in the pellet showed a very significant carbonyl signal.
Figure 7.
XPS C 1s spectra for (a) 24 % C/Al2O3 and (b) C/ZrO2
3.2.2. Chromatographic characteristics
Carbon phases are known to be reversed phases. The nature of the surface can be examined by measuring the hydrophobic selectivity, which is the slope of log k′ vs. the number of methylene groups (nCH2) for a homolog series of solutes.
| (2) |
Positive slopes and a linear relationship are expected for all reversed phases. The slope (B) can be used to calculate the free energy of transfer per methylene group from the mobile phase to the stationary phase (ΔGCH2 = −2.3BRT; R is gas constant and T is the temperature) [40]. Thus, bigger slopes indicate stronger affinity of stationary phases for a methylene group.
The log k′ of two different homolog series was plotted against nCH2 for C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2 (see Fig. 8). The slopes, intercepts and free energies of transfer per methylene group with their standard deviations are listed in Table 3. All the carbon phases including the lowest carbon load obviously behave as a reversed phase. A slight deviation from linearity for the alkylbenzenes, which is not observed on the conventional octadecyl bonded silica phase (ODS), is one of the unique properties of carbon phases attributed to the different retention mechanisms of carbon and ODS materials [6,15]. The intercepts and slopes show that all carbon loadings, C/Al2O3 have similar methylene affinity as C/ZrO2. Retentivity for both homolog series increases with carbon load up to 14 % carbon, stays about the same at 24 %, and then decreases from 24 to 40 %.
Figure 8.
Plot of logk′ vs. number of methylene groups for (a) nitroalkane homologs (nitropropane, nitrobutane, nitropentane and nitrohexane); (b) alkylbenzene homologs (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, propylbenzene and butylbenzene). LC conditions: F = 0.4 ml/min., T = 40 °C and (a) 35/65 MeCN/water; (b) 50/50 MeCN/water. (○) C/ZrO2 (33 × 2.1 mm id. column); (◇) 6 %; (◽) 14 %; (□) 24 %; (▲) 40 % C/Al2O3 (50 × 2.1 mm id. column)
Table 3.
The slopes, intercept and ΔGCH2 obtained from different carbon phases. See Fig. 8 for LC conditions
| Nitroalkanea |
Alkylbenzeneb |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (B) | Intercept | R2 | ΔGCH2c | Slope (B) | Intercept | R2 | ΔGCH2c | |
| C/ZrO2 | 0.322 ± 0.002 | −1.349 ± 0.003 | 0.99995 | −461 ± 3 | 0.235 ± 0.002 | −0.412 ± 0.007 | 0.99992 | −336 ± 3 |
| 6% C | 0.359 ± 0.003 | −1.38 ± 0.01 | 0.99990 | −514 ± 4 | 0.306 ± 0.002 | −0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.99997 | −438 ± 2 |
| 14% C | 0.368 ± 0.003 | −0.99 ± 0.01 | 0.99987 | −526 ± 4 | 0.327 ± 0.006 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.99971 | −468 ± 8 |
| 24% C | 0.376 ± 0.003 | −1.02 ± 0.01 | 0.99986 | −538 ± 4 | 0.304 ± 0.001 | 0.230 ± 0.004 | 0.99998 | −435 ± 2 |
| 40% C | 0.375 ± 0.003 | −1.39 ± 0.01 | 0.99989 | −536 ± 4 | 0.312 ± 0.008 | −0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.99937 | −446 ± 11 |
The slope and intercept of the linear regression of log k′ vs. nCH2 based on the data in Fig. 8(a).
The slope and intercept of the linear regression of log k′ vs. nCH2 based on the data from ethylbenzene to butylbenzene in Fig. 8(b).
The free energy of transfer per methylene group calculated from the slope.
The slopes of log k′ vs. homolog number plots on ODS phases for different homologs are typically almost indistinguishable [8], but they are clearly different on the various C/Al2O3 materials and C/ZrO2. We believe that this has more to do with the aromaticity of the alkylbenzenes as compared to the nitroalkanes as how the phenyl ring interacts with the carbon surface. However, the difference in slope between the nitroalkanes and the alkylbenzenes is significantly smaller on the C/Al2O3 materials than on C/ZrO2. Since the slope of such plots is independent of the specific surface area, this strongly suggests that the chemical and/or physical nature of the carbon surfaces is different although we could hardly detect any chemical difference by XPS. For the alkylbenzenes the difference in the slopes for the three C/Al2O3 phases is smaller than the difference in slope of the C/Al2O3 relative to the C/ZrO2.
Although there was no further increase in retentivity above 14 % carbon, we further increased the carbon load to block solute secondary interactions with Lewis acid sites on Al2O3.
Comparison of the 24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2, both of which show full blockage of substrate, indicates that it takes fewer monolayers of carbon to fully cover Al2O3 (about 5 monolayers required) than ZrO2 (about 11 required). However, the 24 % carbon phase provides much higher retentivity than does C/ZrO2 under the same elution conditions. This improvement is not due to the higher % carbon on Al2O3. The carbon load per unit surface area is higher on C/ZrO2 (290 μmol/m2) than that on the C/Al2O3 (133 μmol/m2). Rather we attribute it to the difference in total surface area. We calculated the total surface area for both materials in the same size column based on the BET surface area and the density of Al2O3 and ZrO2 [30]. A column packed with 24 % C/Al2O3 has 2.4 folds more surface area than a column packed with C/ZrO2. In fact the increase in the retentivity of the C/Al2O3 relative to C/ZrO2 is higher than the ratio of the surface areas. This could be attributed to the higher affinity of C/Al2O3 for methylene group as indicated by the higher free energy of transfer which implies a greater hydrophobicity for C/Al2O3 as compared to C/ZrO2. We infer from the lower resistivity of 24 % C/Al2O3 as compared to C/ZrO2 that the C/Al2O3 has a higher polarizability which we believe may contribute to the increased retentivity.
Since the relative retentivity depends on the type of compound used, it may be also due to different degree of surface oxidation although both metal oxide based materials are prepared by very similar methods. It is well known that surface of carbon generally contain hetero atoms like oxygen, which induce various types of surface oxides [41,42]. However, as shown by the XPS data above and very similar selectivity of these carbon (see Fig. 9), the difference in oxygen content is likely not large.
Figure 9.
Plot of log (k′/k′benezene) vs. benzene substituted compounds. LC conditions: F = 0.4 ml/min., T = 40 °C, 50/50 MeCN/water. (○) C/ZrO2 (33 × 2.1 mm id. column); (◇) 6 %; (◽) 14 %; (□) 24 % C/Al2O3 (50 × 2.1 mm id. column); (*) ODS (50 × 2.1 mm id. column)
We chose a series of monosubstituted (polar and nonpolar) benzene derivatives to compare the chemical selectivity of the carbon phases. Various benzene derivatives had been used to show the unique selectivity of C/ZrO2 compared to the octadecyl bonded silica phase (ODS) [3]. We obtained the retention factor of 18 benzene derivatives on all of the carbon phases and on the ODS under the same elution conditions and calculated the retention factor of the derivatives relative to that of benzene. This normalization eliminates the phase ratio (see Fig. 9). The derivatives are arranged in the order of increasing retention on ODS. As shown in Fig. 9, the elution order of these solutes on all carbon phases is the same but differs radically from that on ODS. This indicates a dramatic difference in the chemical selectivity of the carbon phases from that of ODS. All the C/Al2O3 phases provide very similar chemical selectivity to that of C/ZrO2 although there are small differences among the C/Al2O3 materials and C/ZrO2. In particular 24 % C/Al2O3 behaves more like the C/ZrO2 phase than do the 6 and 14 % C/Al2O3 phases. We believe this is likely due to the incomplete coverage of Al2O3 at the low carbon loads.
In addition, we wanted to see if C/Al2O3 matches C/ZrO2 in superior resolving power towards structural isomers [4]. We selected three different pairs of isomers (see Table 4). ODS shows poor separation of these compounds as seen by the selectivity (α), however, the 24 % C/Al2O3 can easily separate these isomers under the same conditions, which is consistent with the C/ZrO2.
Table 4.
Separation of structural isomers on C/Al2O3 and ODS.a
| αb | ODS | C/Al2O3c |
|---|---|---|
| 1-Phenyl-3-propanol/1-phenly-1-propanold | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| Di(phenethyl)amidese | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| cis-/trans-stilbenee | 1.0 | 15 |
F = 0.4 ml/min, T = 40 °C.
The ratio of two retention factor.
24% carbon load.
50/50 MeCN/water.
60/40 MeCN/water. 50 mm × 2.1 mm i.d. for both columns.
C/Al2O3 also shows a subtle enhancement of retentivity for polar compounds that is highly desirable for the application of the carbon phases to drug metabolites. Amphetamines, a weakly retained family of drugs on conventional reversed phases, were injected on both the 24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2 under the same gradient condition. As shown in Fig. 10, the C/Al2O3 provides at most about a 3-fold increase in retention although the increment of retentivity depends on the analyte.
Figure 10.
Ratio of the retention time of basic drugs on 24 % C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2. LC conditions: A, 20 mM perchloric acid; B, MeCN; 10 – 80 % MeCN, in 0–2.5 min. F = 1 ml/min. T = 40 °C, 33 × 2.1 mm id. column for both. PMA, p-Methoxyamphetamine; MDA, 3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine; PMMA, p-Methoxy-methamphetamine; MDMA, Methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine; MDEA, 3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine; MBDB, 3,4-Methylenedioxy-alpha-ethyl-N-methylphenethylamine
We hypothesized that improved retentivity would help analytes to be focused at the inlet of the second dimension column in the fast 2DLC, thus alleviating the detrimental effect of strong injected solvent on peak distortion. Accordingly, we ran conditions similar to those used in the second dimension of 2DLC on both carbon phases (see Fig. 11) to examine the potential use of C/Al2O3 in 2DLC. Mixtures of 4 indolic metabolites were prepared in progressively stronger eluents from 20 to 80 % (v/v) acetonitrile in water, and a relatively large volume (25 μl) of each mixture was injected on both columns. The gradient conditions on C/Al2O3 were adjusted to have the first (IHT) and the last (IBA) indoles eluted in the similar time window as on the C/ZrO2. As a result, the C/Al2O3 column required much stronger initial and final eluent conditions indicating its higher retentivity for the indoles than that of the C/ZrO2 column. The overlays of chromatograms from samples made up in different solvent compositions compare the effect of the strong injected solvent on the peak shapes on both carbon phases. The considerable peak distortion of the early eluting indoles was observed on both phases. However, there was almost no effect of the strong injected solvent on the later eluting peaks from the C/Al2O3 column whereas the effect was apparent in all of the peaks on the C/ZrO2. This comparison clearly demonstrates not only the need for high retentivity of column on the second dimension in the 2DLC but also the improvement made by the C/Al2O3. As the C/Al2O3 exhibits similar selectivity but enhanced retentivity compared to C/ZrO2, we believe that the C/Al2O3 will be an excellent alternative for the second dimension column in the 2DLC.
Figure 11.
Chromatograms of mixture of 4 indolic metabolites on (a) C/ZrO2 and (b) 24% C/Al2O3. LC conditions: A, 20 mM perchloric acid in water; B, MeCN; 8 – 35 % B in 0 –3.5 min for (a); 15– 60 % B in 0– 3.5 min for (b); F = 1 ml/min, T = 80 °C, 220 nm, 25 μl injection, 33 × 2.1 mm id. column for both. The analyte diluents (B/A) are 20/80 (black solid line), 40/60 (red dashed line), 80/20 (blue dotted line)
4. Conclusions
A new CVD carbon phase based on high surface area Al2O3 using hexanes vapor as a carbon source has been developed. This carbon packing material offers reasonable chromatographic efficiency and can be prepared reproducibly. We obtained various carbon loads on Al2O3 by varying the CVD conditions, and all carbon loadings gave both hydrophobic and polar selectivity similar to C/ZrO2. About 24 % (w/w) carbon (5 monolayers) was necessary to obtain maximum retentivity, balancing full coverage of the underlying Al2O3 against excessive loss of surface area, but it should be noted that commercial 8 % (w/w) C/ZrO2 has the equivalent of 11 monolayers of carbon.
A carbon load of 24% on Al2O3 gives more retention than 8 % C/ZrO2. We obtained even more retention than would be expected based on the increase in the ratio of the total surface area. We attribute this to stronger interactions of the new carbon phase with solutes possibly due to its higher polarizability and polarity. Although the increment of retention varied depending on the test solute, C/Al2O3 overall exhibited higher retentivity for both polar and nonpolar solutes compared to C/ZrO2. This improvement helped to lessen peak distortion caused by injection of the large volume of sample solvent. Comparison of the relative retention factor of various solutes including stereoisomeric compounds between C/Al2O3 and C/ZrO2 showed great similarity in selectivity patterns. The new carbon packing material is very promising as a packing material for HPLC and should be quite suitable for use as the second dimension in 2DLC.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Institute of Health (GM 054585) and the Institute of Technology Characterization Facility, University of Minnesota, part of the NSF-funded Materials Research Facilities Network (www.mrfn.org) for XPS data. We also thank Prof. A. Stein at University of Minnesota for FT-IR use and Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) and ZirChrom Separations Inc. (Anoka, MN, USA) for the donation of porous alumina and carbon clad zirconia, respectively.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Forgacs E, Cserhati T. Chromatographia. 1992;33:356. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Forgacs E, Cserhati T. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 1995;14:23. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jackson PT, Carr PW. J Chromatogr A. 2002;958:121. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(02)00392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jackson PT, Kim TY, Carr PW. Anal Chem. 1997;69:5011. doi: 10.1021/ac970561h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Knox JH, Kaur B, Millward GR. J Chromatogr. 1986;352:3. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Weber TP, Carr PW. Anal Chem. 1990;62:2620. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Weber TP, Carr PW, Funkenbusch EF. J Chromatogr A. 1990;519:31. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Weber TP, Jackson PT, Carr PW. Anal Chem. 1995;67:3042. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Elfakir C, Chaimbault P, Dreux M. J Chromatogr A. 1998;829:193. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barrett DA, Pawula M, Knaggs RD, Shaw PN. Chromatographia. 1998;47:667. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Forgacs E, Cserhati T. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1998;18:15. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(98)00159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koizumi K. J Chromatogr A. 1996;720:119. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(94)01274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Funkenbusch EF, Carr PW, Hanggi DA, Weber TP. Regents of the University of Minnesota. USA: 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rigney MP, Funkenbusch EF, Carr PW. J Chromatogr. 1990;499:291. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jackson PT, Schure MR, Weber TP, Carr PW. Anal Chem. 1997;69:416. doi: 10.1021/ac960453f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stoll DR, Cohen JD, Carr PW. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1122:123. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.04.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Colin H, Guiochon G. J Chromatogr. 1977;137:19. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Knox JH, Ross P. Adv Chromatogr. Vol. 37. New York: 1997. p. 73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Unger KK. Anal Chem. 1983;55:361A. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Leboda R, Lodyga A, Charmas B. Mater Chem Phys. 1998;55:1. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Colin H, Eon C, Guiochon G. J Chromatogr. 1976;119:41. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gilbert MT, Knox JH, Kaur B. Chromatographia. 1982;16:138. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Engel TM, Olesik SV, Callstrom MR, Diener M. Anal Chem. 1993;65:3691. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liang C, Dai S, Guiochon G. Anal Chem. 2003;75:4904. doi: 10.1021/ac030146r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gierak A, Leboda R. J Chromatogr. 1989;483:197. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Leboda R, Gierak A, Hubicki Z, Lodyga A. Mater Chem Phys. 1991;30:83. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Colin H, Guiochon G. J Chromatogr. 1976;126:43. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Leboda R. Chromatographia. 1981;14:524. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Knoezinger H, Ratnasamy P. Catal Rev - Sci Eng. 1978;17:31. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nawrocki J, Dunlap C, McCormick A, Carr PW. J Chromatogr A. 2004;1028:1. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.11.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E. J Am Chem Soc. 1938;60:309. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP. J Am Chem Soc. 1951;73:373. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Trammell BC, Hillmyer MA, Carr PW. Anal Chem. 2001;73:3323. doi: 10.1021/ac010032k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Reeder DH, Li J, Carr PW, Flickinger MC, McCormick AV. J Chromatogr A. 1997;760:71. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(96)00623-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bourrat X. World of Carbon. 2003;2:159. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Delhaes P. Carbon. 2002;40:641. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Taki Y, Takai O. Thin Solid Films. 1998;316:45. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ogenko VM, Dubrovina LV, Goldun OV, Volkov SV, Senkevich AI, Danilenko NI. Inorganic Materials. 2006;42:515. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kinoshita K. Carbon, Electrochemical and Physicochemical Properties. John Wiley & Sons; New York: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Melander WR, Horvath C. Chromatographia. 1982;15:86. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Barton SS, Boulton GL, Harrison BH. Carbon. 1972;10:395. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Morimoto T, Miura K. Langmuir. 1985;1:658. [Google Scholar]