Abstract
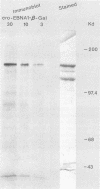
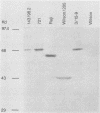
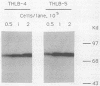
Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA-1) is the only viral protein required to support latent replication of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). To assess the likelihood that EBNA-1 regulates the amount of EBV DNA in a cell, we measured the average numbers of EBNA-1 molecules and EBV DNA molecules per cell in different clones of cells. The amount of EBNA-1 protein present in recently established lymphoblastoid cell lines was measured with affinity-purified anti-EBNA-1 antibodies, and viral DNA was measured by nucleic acid hybridization. The average levels of EBNA-1 protein varied little between these cell lines, whereas the average amount of viral DNA present varied substantially; consequently, these numbers were not correlated. There is no apparent relationship between amounts of EBNA-1 and viral DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Posttranslational processing of an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane protein expressed in cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):866–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.866-875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Andersson-Anvret M., Klein G., Lundin L., Killanger D. Relationship between amount of Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen per cell and number of EBV-DNA copies per cell. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):269–271. doi: 10.1038/266269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J., McCormick K. J., Andersson-Anvret M., Aman P., Killander D. Relationship between the amounts of EBV-DNA and EBNA per cell, clonability and tumorigenicity in two ebv-negative lymphoma lines and their EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Feb 15;31(2):163–169. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing J. C., Levine A. J. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (BamHI K antigen) is a single-stranded DNA binding phosphoprotein. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Purification and analysis of RNA polymerase II transcription factors by using wheat germ agglutinin affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Bach F. H., DeMars R. Gamma ray-induced loss of expression of HLA and glyoxalase I alleles in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C., Sugden B. Conservation and progressive methylation of Epstein-Barr viral DNA sequences in transformed cells. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):305–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.305-316.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton S., Levine A. J. Mapping genetic elements of Epstein-Barr virus that facilitate extrachromosomal persistence of Epstein-Barr virus-derived plasmids in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2533–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg S. Levels of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in lymphoblastoid cell lines are correlated with frequencies of spontaneous lytic growth but not with levels of expression of EBNA-1, EBNA-2, or latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):437–444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.437-444.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Raymond M. J., Ji I., Rebois R. V., Ji T. H. Photoaffinity labeling of the gonadotropin receptor with native, asialo, and deglycosylated choriogonadotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes G., Carson D. A., Valbracht J., Houghten R., Vaughan J. H. Human immune responses to synthetic peptides from the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternås L., Eliasson L., Lerner R., Klein G. Quantitation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) by a two-site enzyme immunoassay, in parallel with EBV-DNA. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Phelps M., Domoradzki J. Epstein-Barr virus DNA is amplified in transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.590-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Warren N. A promoter of Epstein-Barr virus that can function during latent infection can be transactivated by EBNA-1, a viral protein required for viral DNA replication during latent infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2644–2649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2644-2649.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Bacterial synthesis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 glycoprotein D antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jul;83(1 Suppl):102s–111s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12281828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G., Miller G. Recovery of Epstein-Barr virus from nonproducer neonatal human lymphoid cell transformants. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90490-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]