Abstract
In the title compound, C15H15NO3, the carbazole skeleton includes an ethoxycarbonyl group at the 3-position. In the indole ring system, the benzene and pyrrole rings are nearly coplanar, forming a dihedral angle of 0.89 (4)°. The cyclohexenone ring has an envelope conformation. In the crystal, intermolecular N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three dimensional network. A weak C—H⋯π interaction is also observed.
Related literature
For background to tetrahydrocarbazole systems present in indole-type alkaloids, see: Saxton (1983 ▶). For related structures, see: Hökelek et al. (1994 ▶, 1998 ▶, 1999 ▶, 2009 ▶); Patır et al. (1997 ▶); Hökelek & Patır (1999 ▶); Çaylak et al. (2007 ▶); Uludağ et al. (2009 ▶). For the use of 4-oxo-tetrahydrocarbazole in the syntheses of biologically active species, see: Kumar et al. (2008 ▶); Ergün et al. (2002 ▶); Li & Vince (2006 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15NO3
M r = 257.28
Orthorhombic,

a = 9.1057 (3) Å
b = 12.7031 (4) Å
c = 21.3874 (5) Å
V = 2473.89 (13) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.43 × 0.26 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.960, T max = 0.981
12029 measured reflections
2993 independent reflections
2258 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.102
S = 1.04
2993 reflections
177 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg3 is the centroid of the C5A/C5–C8,C8A ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N9—H9⋯O2i | 0.885 (16) | 2.044 (16) | 2.9103 (15) | 166.0 (15) |
| C3—H3⋯O1ii | 1.00 | 2.41 | 3.4053 (17) | 173 |
| C11—H11A⋯Cg3iii | 0.99 | 2.86 | 3.7358 (15) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Anadolu University and the Medicinal Plants and Medicine Research Centre of Anadolu University, Eskişehir, Turkey, for the use of X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Tetrahydrocarbazole systems are present in the framework of a number of indole-type alkaloids of biological interest (Saxton, 1983). The structures of tricyclic, tetracyclic and pentacyclic ring systems with dithiolane and other substituents of the tetrahydrocarbazole core, have been reported previously (Hökelek et al., 1994; Patır et al., 1997; Hökelek et al., 1998; Hökelek et al., 1999; Hökelek & Patır, 1999). Although 4-oxo-tetrahydrocarbazoles rarely occur in nature, they have been increasingly important intermediates in the syntheses of indole or carbazole alkaloids and various biologically active heterocyclic compounds because of their unique structures. For instance, 4-oxo-tetrahydrocarbazole was used in the syntheses of antiemetic drugs, central nervous system active drugs and NPY-1 antagonists (Kumar et al., 2008). They have also been used in the syntheses of indole alkaloids (Ergün et al., 2002). Tetrahydrocarbazolone based antitumor active compounds and inhibitors of HIV integrase were synthesized from 4-oxo-tetrahydrocarbazoles (Li & Vince, 2006). The present study was undertaken to ascertain the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
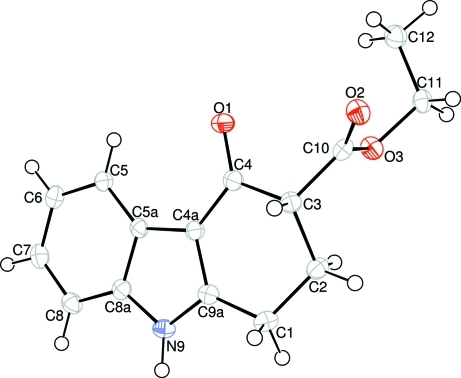
The molecule of the title compound contains a carbazole skeleton with an ethoxycarbonyl group at the 3 position, (Fig. 1), where the bond lengths are close to standard values (Allen et al., 1987) and generally agree with those in the previously reported compounds. In all structures atom N9 is substituted.
An examination of the deviations from the least-squares planes through individual rings shows that rings B (C4a/C5a/C8a/N9/C9a) and C (C5a/C5—C8/C8a) are nearly coplanar [with a maximum deviation of -0.012 (1) Å for atom C5a] with dihedral angle of B/C = 0.89 (4)°. Ring A (C1—C4/C4a/C9a) adopts envelope conformation with atom C2 displaced by -0.632 (2) Å from the plane of the other rings atoms, as in 3a,4,10,10b-tetrahydro-2H-furo[2,3-a]carbazol-5(3H)-one (Çaylak et al., 2007), 3,3-ethylenedithio-3,3a,4,5,10,10b-hexahydro-2H-furo[2,3-a]carbazole (Uludağ et al., 2009) and ethyl 1-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-carbazole-3-carboxylate (Hökelek et al., 2009).
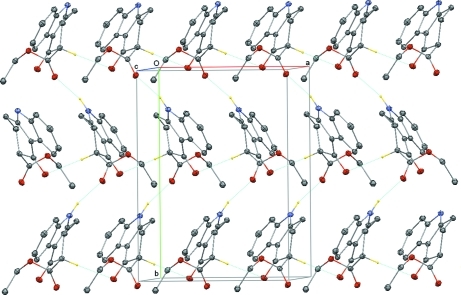
In the crystal, intermolecular N—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three dimensional network (Table 1 and Fig. 2). There also exists a weak C—H···π interaction (Table 1).
Experimental
A solution of 2,3-dichloro -5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone (9.36 g, 41.20 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml, 90%) was added dropwise to a solution of ethyl 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H -carbazole-3-carboxylate (5.00 g, 20.60 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (50 ml, 90%) at 268 K. The reaction mixture was stirred for 10 min at 268 K, and then the solution was poured into sodium hydroxide (500 ml, 10%) and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed. The residue was purified by chromatography using silica gel and ethyl acetate. After the solvent was evaporated, the product was crystallized from ether to yield colourless blocks of (I) (yield; 0.58 g, 11%, m.p. 396 K).
Refinement
H9 atom is located in a difference Fourier synthesis and refined isotropically. The remaining C-bound H-atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.95, 1.00, 0.99 and 0.98 Å, for aromatic, methine, methylene and methyl H-atoms, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = k × Ueq(C), where k = 1.5 for methyl H-atoms and k = 1.2 for all other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of the crystal packing of the title compound. The N—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines [H-atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity].
Crystal data
| C15H15NO3 | F(000) = 1088 |
| Mr = 257.28 | Dx = 1.382 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 3293 reflections |
| a = 9.1057 (3) Å | θ = 2.9–28.3° |
| b = 12.7031 (4) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 21.3874 (5) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 2473.89 (13) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.43 × 0.26 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2993 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2258 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −11→9 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.981 | k = −16→8 |
| 12029 measured reflections | l = −20→28 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.044P)2 + 0.6029P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2993 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 177 parameters | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.27325 (11) | 0.49989 (7) | 0.23207 (4) | 0.0234 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.13644 (11) | 0.53475 (7) | 0.37765 (4) | 0.0226 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.31033 (11) | 0.40993 (7) | 0.36958 (4) | 0.0220 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.01764 (17) | 0.22360 (9) | 0.25890 (6) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.0260 | 0.1466 | 0.2651 | 0.026* | |
| H1B | −0.0879 | 0.2422 | 0.2578 | 0.026* | |
| C2 | 0.09311 (17) | 0.28148 (9) | 0.31263 (7) | 0.0218 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.1906 | 0.2495 | 0.3202 | 0.026* | |
| H2B | 0.0340 | 0.2730 | 0.3511 | 0.026* | |
| C3 | 0.11251 (16) | 0.39973 (9) | 0.29874 (6) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| H3 | 0.0122 | 0.4306 | 0.2936 | 0.024* | |
| C4 | 0.19696 (16) | 0.42026 (9) | 0.23804 (6) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| C4A | 0.17494 (15) | 0.34286 (9) | 0.18970 (6) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.30954 (16) | 0.40632 (10) | 0.08810 (6) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.3511 | 0.4689 | 0.1048 | 0.024* | |
| C5A | 0.22407 (15) | 0.34016 (9) | 0.12551 (6) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.33239 (17) | 0.37872 (11) | 0.02632 (7) | 0.0231 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.3903 | 0.4232 | 0.0005 | 0.028* | |
| C7 | 0.27209 (17) | 0.28667 (10) | 0.00100 (7) | 0.0244 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.2901 | 0.2697 | −0.0416 | 0.029* | |
| C8 | 0.18676 (17) | 0.22010 (10) | 0.03698 (7) | 0.0229 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.1457 | 0.1576 | 0.0200 | 0.027* | |
| C8A | 0.16323 (15) | 0.24812 (10) | 0.09904 (7) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| N9 | 0.08119 (13) | 0.19804 (9) | 0.14526 (5) | 0.0202 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.0272 (18) | 0.1408 (13) | 0.1399 (7) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| C9A | 0.08866 (15) | 0.25402 (9) | 0.19910 (6) | 0.0181 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.18566 (16) | 0.45682 (10) | 0.35239 (6) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.39176 (16) | 0.45682 (10) | 0.42153 (7) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.4609 | 0.4042 | 0.4388 | 0.025* | |
| H11B | 0.3222 | 0.4767 | 0.4551 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.47603 (17) | 0.55264 (10) | 0.40117 (7) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.5356 | 0.5785 | 0.4361 | 0.037* | |
| H12B | 0.4071 | 0.6076 | 0.3881 | 0.037* | |
| H12C | 0.5403 | 0.5342 | 0.3661 | 0.037* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0241 (6) | −0.0053 (4) | 0.0006 (5) | −0.0008 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0223 (4) | 0.0220 (6) | 0.0049 (4) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0027 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0210 (4) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0045 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | −0.0024 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0174 (6) | 0.0265 (8) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0036 (6) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0251 (8) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0216 (8) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0007 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0213 (8) | 0.0171 (6) | 0.0204 (7) | 0.0022 (5) | −0.0005 (6) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0188 (8) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0027 (5) | −0.0041 (6) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C4A | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0003 (5) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0015 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0199 (8) | −0.0003 (5) | −0.0031 (6) | 0.0019 (5) |
| C5A | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0030 (5) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0005 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0227 (8) | 0.0261 (7) | 0.0206 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0047 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0268 (9) | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0210 (6) | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0026 (5) | −0.0036 (6) | −0.0036 (5) |
| C8A | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0184 (6) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0031 (5) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0009 (5) |
| N9 | 0.0205 (7) | 0.0164 (5) | 0.0236 (7) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0028 (4) |
| C9A | 0.0157 (7) | 0.0165 (5) | 0.0222 (7) | 0.0029 (5) | −0.0014 (6) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0185 (6) | 0.0190 (7) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0040 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0241 (6) | 0.0178 (7) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0246 (9) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0008 (6) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0003 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C4 | 1.2338 (15) | C5A—C5 | 1.3972 (19) |
| O2—C10 | 1.2136 (15) | C5A—C8A | 1.4123 (17) |
| O3—C10 | 1.3336 (17) | C6—C7 | 1.4008 (19) |
| O3—C11 | 1.4626 (16) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C9A | 1.4844 (19) | C7—C8 | 1.382 (2) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C1 | 1.5276 (19) | C8A—C8 | 1.391 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | N9—C8A | 1.3928 (18) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | N9—C9A | 1.3550 (17) |
| C3—C2 | 1.5413 (17) | N9—H9 | 0.886 (17) |
| C3—C4 | 1.531 (2) | C10—C3 | 1.5121 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 1.0000 | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C4—C4A | 1.4409 (18) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C4A—C5A | 1.4442 (19) | C12—C11 | 1.5033 (19) |
| C4A—C9A | 1.3897 (17) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.383 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C10—O3—C11 | 117.33 (10) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.9 | C7—C6—H6 | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.9 | C6—C7—H7 | 119.5 |
| C9A—C1—C2 | 109.08 (11) | C8—C7—C6 | 121.04 (14) |
| C9A—C1—H1A | 109.9 | C8—C7—H7 | 119.5 |
| C9A—C1—H1B | 109.9 | C7—C8—C8A | 117.48 (13) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.3 | C7—C8—H8 | 121.3 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.07 (11) | C8A—C8—H8 | 121.3 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.2 | N9—C8A—C5A | 107.69 (12) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.2 | C8—C8A—N9 | 130.03 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.2 | C8—C8A—C5A | 122.28 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.2 | C8A—N9—H9 | 125.5 (10) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.9 | C9A—N9—C8A | 109.67 (11) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 107.4 | C9A—N9—H9 | 124.7 (10) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 112.77 (11) | N9—C9A—C1 | 125.01 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 107.4 | N9—C9A—C4A | 109.36 (12) |
| C10—C3—C2 | 111.82 (11) | C4A—C9A—C1 | 125.62 (12) |
| C10—C3—C4 | 109.90 (11) | O2—C10—O3 | 123.78 (13) |
| C10—C3—H3 | 107.4 | O2—C10—C3 | 124.50 (13) |
| O1—C4—C3 | 120.68 (12) | O3—C10—C3 | 111.71 (11) |
| O1—C4—C4A | 124.31 (13) | O3—C11—C12 | 111.62 (11) |
| C4A—C4—C3 | 114.98 (11) | O3—C11—H11A | 109.3 |
| C4—C4A—C5A | 130.93 (12) | O3—C11—H11B | 109.3 |
| C9A—C4A—C4 | 121.94 (12) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.3 |
| C9A—C4A—C5A | 107.06 (11) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.3 |
| C5A—C5—H5 | 120.7 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.0 |
| C6—C5—C5A | 118.59 (13) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—C5A—C4A | 134.64 (12) | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C5A—C8A | 119.13 (12) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C8A—C5A—C4A | 106.21 (11) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.47 (14) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C10—O3—C11—C12 | −77.69 (15) | C5A—C4A—C9A—C1 | 178.62 (12) |
| C11—O3—C10—O2 | −0.64 (19) | C5A—C4A—C9A—N9 | −0.36 (15) |
| C11—O3—C10—C3 | −179.50 (10) | C5A—C5—C6—C7 | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—C9A—N9 | 159.90 (13) | C4A—C5A—C5—C6 | −178.78 (14) |
| C2—C1—C9A—C4A | −18.93 (18) | C8A—C5A—C5—C6 | −0.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1—C9A | 47.43 (15) | C4A—C5A—C8A—N9 | 0.09 (14) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | −56.21 (16) | C4A—C5A—C8A—C8 | 179.53 (13) |
| C10—C3—C2—C1 | 179.34 (12) | C5—C5A—C8A—N9 | −178.68 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | −149.89 (13) | C5—C5A—C8A—C8 | 0.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4A | 32.36 (16) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.3 (2) |
| C10—C3—C4—O1 | −24.40 (17) | C6—C7—C8—C8A | 0.0 (2) |
| C10—C3—C4—C4A | 157.85 (11) | N9—C8A—C8—C7 | 178.76 (13) |
| O1—C4—C4A—C5A | −3.9 (2) | C5A—C8A—C8—C7 | −0.5 (2) |
| O1—C4—C4A—C9A | 179.48 (13) | C8A—N9—C9A—C1 | −178.57 (12) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C5A | 173.73 (13) | C8A—N9—C9A—C4A | 0.42 (15) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C9A | −2.87 (18) | C9A—N9—C8A—C5A | −0.31 (15) |
| C4—C4A—C5A—C8A | −176.82 (14) | C9A—N9—C8A—C8 | −179.70 (14) |
| C4—C4A—C5A—C5 | 1.7 (3) | O2—C10—C3—C2 | −126.61 (14) |
| C9A—C4A—C5A—C5 | 178.65 (15) | O2—C10—C3—C4 | 107.35 (15) |
| C9A—C4A—C5A—C8A | 0.16 (14) | O3—C10—C3—C2 | 52.23 (15) |
| C4—C4A—C9A—N9 | 176.95 (12) | O3—C10—C3—C4 | −73.80 (13) |
| C4—C4A—C9A—C1 | −4.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg3 is the centroid of the C5A/C5–C8,C8A ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N9—H9···O2i | 0.885 (16) | 2.044 (16) | 2.9103 (15) | 166.0 (15) |
| C3—H3···O1ii | 1.00 | 2.41 | 3.4053 (17) | 173 |
| C11—H11A···Cg3iii | 0.99 | 2.86 | 3.7358 (15) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x−1/2, y, −z+1/2; (iii) −x−1/2, y−1/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5881).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Çaylak, N., Hökelek, T., Uludağ, N. & Patır, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3913–o3914.
- Ergün, Y., Patır, S. & Okay, G. (2002). J. Heterocycl. Chem., 39, 315–317.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Hökelek, T., Dal, H., Tercan, B., Göçmentürk, M. & Ergün, Y. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1702–o1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hökelek, T., Gündüz, H., Patır, S. & Uludağ, N. (1998). Acta Cryst. C54, 1297–1299.
- Hökelek, T. & Patır, S. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 675–677.
- Hökelek, T., Patır, S., Gülce, A. & Okay, G. (1994). Acta Cryst. C50, 450–453.
- Hökelek, T., Patır, S. & Uludağ, N. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 114–116.
- Kumar, A., Singh, D., Jadhav, A., Pandya, N. D., Panmand, S. D. & Thakur, R. G. (2008). US Patent Appl. US 2008/0009635 A1.
- Li, X. & Vince, R. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14, 2942–2955. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Patır, S., Okay, G., Gülce, A., Salih, B. & Hökelek, T. (1997). J. Heterocycl. Chem., 34, 1239–1242.
- Saxton, J. E. (1983). Editor. Heterocyclic Compounds, Vol. 25, The Monoterpenoid Indole Alkaloids, ch. 8 and 11. New York: Wiley.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Uludağ, N., Öztürk, A., Hökelek, T. & Erdoğan, Ü. I. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o595–o596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811018678/hb5881Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report