Abstract
The crystal of the title compound [systematic name: 4-(benzylamino)benzenesulfonamide], C13H14N2O2S, displays a hydrogen-bonded framework structure. Molecules are doubly N—H⋯O hydrogen bonded to one another via their NH2 groups and sulfonyl O atoms. These interactions generate a hydrogen-bonded ladder structure parallel to the a axis, which contains fused R 2 2(8) rings. The NH group serves as the hydrogen-bond donor for a second set of intermolecular N—H⋯O=S interactions.
Related literature
For the pharmacology and synthesis of the title compound, see Goissedet et al. (1936 ▶); Goissedet & Despois (1938 ▶); Mellon et al. (1938 ▶); Long & Bliss (1939 ▶). For related structures, see: Hursthouse et al. (1998 ▶, 1999a
▶,b
▶); Gelbrich et al. (2008 ▶); Davis et al. (1996 ▶); Costanzo et al. (1999 ▶); Kubicki & Codding (2001 ▶);Yathirajan et al. (2005 ▶); Denehy et al. (2006 ▶); Toumieux et al. (2006 ▶). For graph-set analysis, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).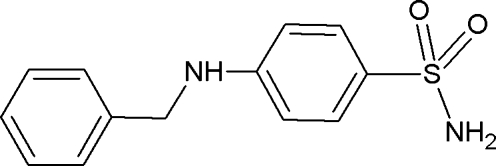
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H14N2O2S
M r = 262.32
Orthorhombic,

a = 7.8426 (1) Å
b = 10.5549 (11) Å
c = 14.6694 (3) Å
V = 1214.30 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.26 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius Roper CCD camera on κ-goniostat diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.950, T max = 0.962
11460 measured reflections
2364 independent reflections
2312 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.023
wR(F 2) = 0.061
S = 1.06
2364 reflections
176 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 972 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.01 (5)
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and COLLECT; data reduction: DENZO and COLLECT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and Mercury (Bruno et al., 2002 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H3N⋯O2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.0264 (16) | 160 (2) |
| N1—H2N⋯O1ii | 0.89 (2) | 2.09 (2) | 2.9613 (16) | 168 (2) |
| N1—H1N⋯O2iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.18 (1) | 3.0281 (16) | 172 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
TG gratefully acknowledges funding by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF), project M1135-N17.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound (synonyms: proseptazine, septazine, benzylsulfanilamide, chemodyn; CAS No. 104–22–3), first marketed in 1936, was one of the early antibacterial agents of the sulfonamide class (Goissedet et al., 1936; Goissedet & Despois, 1938; Mellon et al., 1938; Long & Bliss, 1939). The C–N–(C6H4)–S fragment of the molecule (see Fig. 1) is essentially planar, and the molecular geometry is characterized by the torsion angles N1–S1–C1–C2 and N2–C7–C8–C9 of 43.6 (1)° and -65.9 (2)°, respectively.
The crystal structure contains three independent intermolecular N—H···O=S bonds which lead to the formation of an H-bonded framework. Each molecule is doubly H-bonded, via its NH2 and sulfonyl groups, to two neighbouring molecules. These interactions generate an N—H···O=S-bonded ladder structure parallel to [100], which consists of fused R22(8) rings (Bernstein et al., 1995) and displays a 21 symmetry. This situation is illustrated in Fig. 2. The same one-dimensional structure has been found previously in only a few other compounds of the sulfonamide class, see Davis et al. (1996); Costanzo et al. (1999); Kubicki & Codding (2001);Yathirajan et al. (2005); Denehy et al. (2006); Toumieux et al. (2006).
The sulfonyl oxygen atom O2 accepts an additional H-bond from the NH group of a neighbouring molecule. This interaction links molecules which are related to one another by a 21 operation parallel to the c-axis (see Fig. 3).
Refinement
All H atoms were identified in a difference map. Secondary CH2 (C—H = 0.99 Å) and aromatic carbon atoms (C—H = 0.95 Å) were positioned geometrically and refined with Uiso = 1.2 Ueq(C). Hydrogen atoms attached to N and O were refined with restrained distances [N—H = 0.88 (2) Å]; and their Uiso parameters were refined freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary size.
Fig. 2.
Ladder structure parallel to [100] formed by H-bonds involving the NH2 group. The interactions between the NH group and O2 are indicated by arrows. O and H atoms directly engaged in N–H···O bonds are drawn as balls.
Fig. 3.
H-bonded framework structure viewed parallel to the a-axis, with H-bonds indicated by arrows.
Crystal data
| C13H14N2O2S | F(000) = 552 |
| Mr = 262.32 | Dx = 1.435 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 6120 reflections |
| a = 7.8426 (1) Å | θ = 2.9–27.5° |
| b = 10.5549 (11) Å | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| c = 14.6694 (3) Å | T = 120 K |
| V = 1214.30 (13) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius Roper CCD camera on κ-goniostat diffractometer | 2364 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Bruker-Nonius FR591 rotating anode | 2312 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 9.091 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2007) | k = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.950, Tmax = 0.962 | l = −18→18 |
| 11460 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.023 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.032P)2 + 0.3394P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.061 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.06 | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2364 reflections | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
| 176 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 3 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.021 (4) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 972 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: −0.01 (5) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.88925 (4) | 0.14891 (3) | 0.47921 (2) | 0.00933 (11) | |
| O1 | 1.04460 (12) | 0.09326 (9) | 0.51381 (7) | 0.0132 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.73029 (12) | 0.08853 (9) | 0.50432 (7) | 0.0127 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.88280 (16) | 0.29082 (11) | 0.51938 (8) | 0.0124 (3) | |
| H2N | 0.789 (2) | 0.3327 (18) | 0.5037 (13) | 0.027 (5)* | |
| H1N | 0.9760 (19) | 0.3323 (16) | 0.5125 (12) | 0.016 (4)* | |
| N2 | 0.94618 (16) | 0.14533 (12) | 0.07743 (8) | 0.0141 (3) | |
| H3N | 0.879 (2) | 0.0925 (18) | 0.0498 (13) | 0.032 (5)* | |
| C1 | 0.89793 (18) | 0.15385 (13) | 0.36038 (9) | 0.0103 (3) | |
| C2 | 1.00520 (19) | 0.23999 (13) | 0.31668 (10) | 0.0131 (3) | |
| H2 | 1.0688 | 0.2990 | 0.3518 | 0.016* | |
| C3 | 1.01965 (19) | 0.24017 (13) | 0.22311 (10) | 0.0135 (3) | |
| H3 | 1.0908 | 0.3008 | 0.1940 | 0.016* | |
| C4 | 0.92945 (17) | 0.15099 (14) | 0.17015 (9) | 0.0110 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.82057 (18) | 0.06548 (14) | 0.21519 (10) | 0.0115 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.7574 | 0.0057 | 0.1805 | 0.014* | |
| C6 | 0.80389 (18) | 0.06679 (13) | 0.30896 (9) | 0.0107 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.7291 | 0.0090 | 0.3383 | 0.013* | |
| C9 | 1.15434 (18) | 0.09176 (14) | −0.09378 (10) | 0.0145 (3) | |
| H9 | 1.2109 | 0.0486 | −0.0456 | 0.017* | |
| C7 | 1.03437 (19) | 0.24066 (13) | 0.02344 (10) | 0.0138 (3) | |
| H7A | 1.1487 | 0.2564 | 0.0497 | 0.017* | |
| H7B | 0.9696 | 0.3211 | 0.0251 | 0.017* | |
| C8 | 1.05223 (18) | 0.19639 (14) | −0.07416 (10) | 0.0119 (3) | |
| C10 | 1.1744 (2) | 0.04982 (15) | −0.18294 (11) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| H10 | 1.2445 | −0.0214 | −0.1957 | 0.022* | |
| C11 | 1.0911 (2) | 0.11273 (15) | −0.25348 (10) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| H11 | 1.1038 | 0.0840 | −0.3145 | 0.022* | |
| C12 | 0.9903 (2) | 0.21671 (15) | −0.23489 (11) | 0.0184 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.9340 | 0.2596 | −0.2832 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | 0.97056 (19) | 0.25909 (14) | −0.14530 (10) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.9013 | 0.3309 | −0.1329 | 0.018* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.00952 (18) | 0.01096 (17) | 0.00751 (17) | 0.00004 (13) | 0.00065 (13) | 0.00008 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0124 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0115 (5) | 0.0029 (4) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0120 (5) | −0.0022 (4) | 0.0026 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0110 (6) | 0.0127 (6) | 0.0136 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0009 (6) | −0.0031 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0090 (6) | −0.0072 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0005 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0105 (6) | 0.0132 (7) | 0.0073 (6) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0137 (7) | 0.0134 (7) | 0.0122 (7) | −0.0033 (6) | −0.0011 (6) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0136 (7) | 0.0125 (7) | −0.0049 (6) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0117 (6) | 0.0116 (6) | 0.0099 (6) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0109 (7) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | −0.0016 (5) | −0.0006 (5) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0106 (7) | 0.0099 (6) | 0.0117 (6) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0132 (7) | 0.0150 (7) | 0.0154 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | 0.0109 (7) | −0.0039 (6) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0016 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0117 (7) | 0.0128 (6) | 0.0112 (7) | −0.0047 (5) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0212 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | −0.0029 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0105 (7) | −0.0104 (6) | 0.0039 (6) | −0.0030 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0129 (8) | −0.0059 (6) | −0.0035 (6) | 0.0058 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0128 (7) | 0.0175 (8) | 0.0146 (7) | 0.0006 (6) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O1 | 1.4447 (10) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| S1—O2 | 1.4477 (10) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| S1—N1 | 1.6104 (12) | C9—C10 | 1.390 (2) |
| S1—C1 | 1.7452 (13) | C9—C8 | 1.394 (2) |
| N1—H2N | 0.889 (15) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1N | 0.858 (14) | C7—C8 | 1.5126 (19) |
| N2—C4 | 1.3677 (17) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C7 | 1.4553 (17) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| N2—H3N | 0.867 (15) | C8—C13 | 1.392 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3948 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.392 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.399 (2) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.380 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.411 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.397 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.407 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3817 (19) | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 117.25 (6) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.57 (13) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 106.02 (6) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.2 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 106.81 (6) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.2 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 109.28 (6) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.77 (14) |
| O2—S1—C1 | 107.51 (6) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 |
| N1—S1—C1 | 109.81 (6) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 |
| S1—N1—H2N | 113.2 (13) | N2—C7—C8 | 110.22 (11) |
| S1—N1—H1N | 113.9 (12) | N2—C7—H7A | 109.6 |
| H2N—N1—H1N | 114.9 (17) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.6 |
| C4—N2—C7 | 123.82 (12) | N2—C7—H7B | 109.6 |
| C4—N2—H3N | 115.7 (14) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.6 |
| C7—N2—H3N | 118.6 (14) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.88 (13) | C13—C8—C9 | 119.09 (14) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.14 (11) | C13—C8—C7 | 121.35 (13) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 119.89 (10) | C9—C8—C7 | 119.56 (13) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.57 (13) | C9—C10—C11 | 119.64 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.44 (13) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.08 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| N2—C4—C5 | 119.81 (13) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.27 (15) |
| N2—C4—C3 | 121.92 (13) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.27 (13) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.22 (13) | C8—C13—C12 | 120.15 (14) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C8—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | 43.59 (14) | N2—C7—C8—C9 | −65.94 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H3N···O2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.0264 (16) | 160.(2) |
| N1—H2N···O1ii | 0.89 (2) | 2.09 (2) | 2.9613 (16) | 168.(2) |
| N1—H1N···O2iii | 0.86 (1) | 2.18 (1) | 3.0281 (16) | 172.(2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, −y, z−1/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1; (iii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: EZ2246).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Edgington, P. R., Kessler, M., Macrae, C. F., McCabe, P., Pearson, J. & Taylor, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 389–397. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M. J., Jaroskova, L., Gauthier, D. A. & Maryanoff, B. E. (1999). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 10, 689–703.
- Davis, F. A., Boyd, R., Zhou, P., Abdul-Malik, N. F. & Carroll, P. J. (1996). Tetrahedron Lett. 37, 3267–3270.
- Denehy, E., White, J. M. & Williams, S. J. (2006). Chem. Commun. pp. 314–316. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Gelbrich, T., Bingham, A. L., Threlfall, T. L. & Hursthouse, M. B. (2008). Acta Cryst. C64, o205–o207. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Goissedet, P. E. C. & Despois, R. L. (1938). US Patent 2 111 768.
- Goissedet, P., Despois, R., Gailliot, P. & Mayer, R. (1936). C. R. Soc. Biol. 121, 1082–1084.
- Hooft, R. W. W. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Hursthouse, M. B., Threlfall, T. L., Coles, S. J. & Ward, S. C. (1998). University of Southampton, Crystal Structure Report Archive. doi:10.3737/ecrystals.chem.soton.ac.uk/158.
- Hursthouse, M. B., Threlfall, T. L., Coles, S. J. & Ward, S. C. (1999a). University of Southampton, Crystal Structure Report Archive. doi:10.3737/ecrystals.chem.soton.ac.uk/169.
- Hursthouse, M. B., Threlfall, T. L., Coles, S. J. & Ward, S. C. (1999b). University of Southampton, Crystal Structure Report Archive. doi:10.3737/ecrystals.chem.soton.ac.uk/170.
- Kubicki, M. & Codding, P. W. (2001). J. Mol. Struct. 561, 65–70.
- Long, P. H. & Bliss, E. A. (1939). The Clinical and Experimental Use of Sulfanilamide, Sulfapyridine and Allied Compounds New York: The Macmillan Company.
- Mellon, R. R., Gross, P. & Cooper, F. B. (1938). Sulfanilamide Therapy of Bacterial Infections Springfield, Illinois & Baltimore: Charles C. Thomas.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: AcademicPress.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2007). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Toumieux, S., Compain, P., Martin, O. R. & Selkti, M. (2006). Org. Lett. 8, 4493–4496. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Yathirajan, H. S., Narasegowda, R. S., Nagaraja, P. & Bolte, M. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o179–o181. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811019490/ez2246Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





