Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C17H16N2O3·0.5C4H8O2, pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link molecules into dimers with R 2 2(12) motifs, which are connected by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a supramolecular array in the ab plane. The 1,4-dioxane ring, which lies about an inversion center, adopts a chair conformation.
Related literature
For the biological activity of pyran and fused-pyran molecules, see: Bargagna et al. (1992 ▶); Symeonidis et al. (2009 ▶); Narender & Gupta (2009 ▶); Alvey et al. (2009 ▶); Gorlitzer et al. (1984 ▶); Han et al. (2008 ▶); Martinez & Marco (1997 ▶); Smith et al. (1998 ▶); Taylor et al. (1998 ▶). For related structures, see: Gourdeau et al. (2004 ▶); Foroumadi et al. (2007 ▶); Mohamed et al. (2012 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H16N2O3·0.5C4H8O2
M r = 340.37
Triclinic,

a = 8.0876 (4) Å
b = 9.2013 (4) Å
c = 12.1613 (6) Å
α = 94.376 (2)°
β = 102.827 (1)°
γ = 95.972 (2)°
V = 873.01 (7) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.35 × 0.25 × 0.22 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.973, T max = 0.980
14186 measured reflections
4108 independent reflections
3134 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.021
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.194
S = 1.07
4108 reflections
227 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯N2i | 0.86 | 2.27 | 3.123 (3) | 171 |
| N1—H1B⋯O3ii | 0.86 | 2.10 | 2.945 (2) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank Manchester Metropolitan University, the University of Sargodha and Erciyes University for guidance and for instrumental support of this study. We also extend our thanks to the Egyptian Government for their financial support of this project.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyran and fused pyran ring systems are biologically interesting compounds known for their antimicrobial and antifungal (Alvey, et al., 2009), antioxidant (Symeonidis et al., 2009), antileishmanial (Narender et al., 2009), antitumor (Han et al., 2008). In addition, fused chromene ring systems have platelet antiaggregating, local anesthetic (Bargagna et al. 1992) and antihistaminic activities (Gorlitzer et al. 1984). They also exhibit inhibitory effects on influenza virus sialidases (Smith et al. 1998; Taylor et al. 1998) and antiviral activities (Martinez & Marco, 1997). Such observations prompted us to report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound (I).
In (I), Fig. 1, the O2/C8—C10/C12/C13 4H-pyran and C12–C17 cyclohexene rings are puckered with puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) of QT = 0.187 (2) Å, θ = 72.2 (5) °, φ = 175.7 (6) ° and QT = 0.455 (2) ° A, θ = 122.9 (3) °, φ = 48.5 (3) °, respectively. The centroid of the solvent 1,4-dioxane ring (O4/C18/C19/O4a/C18a/C19a) lies about an inversion center. The 1,4-dioxane ring adopts a chair conformation [puckering parameters QT = 0.560 (5) Å, θ = 3.46 (3) °, φ = 0.00 °]. The values of the bond lengths and angles in (I) are in normal ranges and are comparable with those of related structures (Gourdeau et al., 2004; Foroumadi et al., 2007; Mohamed et al., 2012).
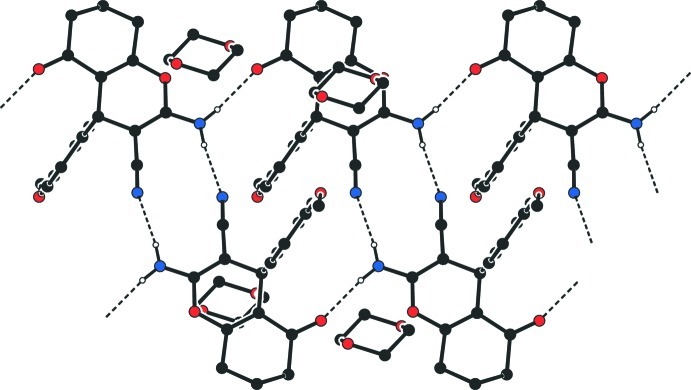
In the crystal, molecules are linked by the pairs of N—H···N hydrogen bonds, forming dimers, with an R22(12) motif (Bernstein et al., 1995; Table 1, Fig. 2). These dimers are connected through the N—H···O hydrogen bonds with each other (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
A mixture of (4-methoxybenzylidene)propanedinitrile (184 mg, 1 mmol), cyclohexane-1,3-dione (112 mg, 1 mmol) in presence of ethanolamine (61 mg) as catalyst was refluxed in ethanol (50 ml). The reaction mixture was monitored by TLC until completion after 7 h. A solid product was deposited on cooling at ambient temperature and collected by filtration. The crude product was washed with dioxane and recrystallized from ethanol/drops of dioxane to afford the title compound in 78% yield. Single crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were grown up on slow evaporation of its mixed solvent ethanol/dioxane (9:1) solution at room temperature over three days. M.pt: 435 K.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined by using a riding model, with N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), 0.96 Å (methyl), 0.97 Å (methylene) and 0.98 Å (methine), with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl-H and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, N) for other H-atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
View of the dimers formed by pairs of N—H···N hydrogen bonds (dashed lines), with an R22(12) motif, and the N—H···O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) which connect the dimers with each other, forming a two-dimensional array. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity. [Symmetry code: (a) 2 - x, 2 - y, 2 - z].
Crystal data
| C17H16N2O3·0.5C4H8O2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 340.37 | F(000) = 360 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.295 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.0876 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 420 reflections |
| b = 9.2013 (4) Å | θ = 3.6–22.5° |
| c = 12.1613 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| α = 94.376 (2)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 102.827 (1)° | Prism, light-yellow |
| γ = 95.972 (2)° | 0.35 × 0.25 × 0.22 mm |
| V = 873.01 (7) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4108 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3134 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.021 |
| Detector resolution: 0.81 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 1.7° |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −12→8 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.980 | l = −16→15 |
| 14186 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.194 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0997P)2 + 0.273P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4108 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 227 parameters | Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.39 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.1813 (2) | 0.42680 (19) | 0.00491 (15) | 0.0760 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.93204 (16) | 0.95097 (14) | 0.33842 (12) | 0.0512 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.36871 (18) | 0.99158 (15) | 0.37001 (14) | 0.0595 (5) | |
| N1 | 1.0877 (2) | 0.77420 (19) | 0.39337 (15) | 0.0563 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.8057 (3) | 0.5088 (2) | 0.49805 (19) | 0.0712 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.5009 (2) | 0.70436 (17) | 0.26984 (14) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.4984 (3) | 0.7302 (2) | 0.15944 (17) | 0.0531 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.3939 (3) | 0.6405 (2) | 0.06812 (18) | 0.0583 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.2893 (3) | 0.5219 (2) | 0.08782 (18) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.2917 (3) | 0.4941 (2) | 0.19793 (19) | 0.0563 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.3951 (2) | 0.58441 (19) | 0.28771 (17) | 0.0476 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.1568 (4) | 0.4634 (3) | −0.1082 (2) | 0.0809 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.6180 (2) | 0.79962 (17) | 0.37058 (14) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.7912 (2) | 0.74660 (18) | 0.40311 (14) | 0.0405 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.9333 (2) | 0.81758 (19) | 0.38054 (14) | 0.0420 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.8019 (2) | 0.6148 (2) | 0.45477 (17) | 0.0487 (6) | |
| C12 | 0.7895 (2) | 1.02140 (18) | 0.33096 (14) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.6429 (2) | 0.95783 (18) | 0.34927 (14) | 0.0403 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.5022 (2) | 1.04491 (19) | 0.35100 (15) | 0.0461 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.5308 (3) | 1.2042 (2) | 0.3328 (2) | 0.0634 (8) | |
| C16 | 0.6528 (3) | 1.2323 (2) | 0.2563 (2) | 0.0660 (8) | |
| C17 | 0.8203 (3) | 1.1737 (2) | 0.29963 (18) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.8992 (4) | 0.9746 (4) | 1.0758 (2) | 0.1475 (16) | |
| C18 | 0.8279 (5) | 0.9756 (5) | 0.9615 (4) | 0.1243 (19) | |
| C19 | 0.9322 (6) | 1.0707 (6) | 0.9113 (4) | 0.138 (2) | |
| H1A | 1.10620 | 0.69140 | 0.41900 | 0.0680* | |
| H1B | 1.16900 | 0.82900 | 0.37610 | 0.0680* | |
| H2 | 0.56870 | 0.81000 | 0.14570 | 0.0640* | |
| H3 | 0.39450 | 0.66020 | −0.00570 | 0.0700* | |
| H5 | 0.22270 | 0.41340 | 0.21170 | 0.0680* | |
| H6 | 0.39390 | 0.56470 | 0.36140 | 0.0570* | |
| H7A | 0.11860 | 0.55860 | −0.11240 | 0.1210* | |
| H7B | 0.07240 | 0.39170 | −0.15710 | 0.1210* | |
| H7C | 0.26270 | 0.46480 | −0.13150 | 0.1210* | |
| H8 | 0.56480 | 0.79380 | 0.43530 | 0.0460* | |
| H15A | 0.57660 | 1.26170 | 0.40550 | 0.0760* | |
| H15B | 0.42210 | 1.23650 | 0.29930 | 0.0760* | |
| H16A | 0.60040 | 1.18570 | 0.18050 | 0.0790* | |
| H16B | 0.67420 | 1.33710 | 0.25170 | 0.0790* | |
| H17A | 0.88530 | 1.17380 | 0.24150 | 0.0640* | |
| H17B | 0.88670 | 1.23700 | 0.36540 | 0.0640* | |
| H18A | 0.71550 | 1.00780 | 0.95170 | 0.1500* | |
| H18B | 0.81450 | 0.87690 | 0.92390 | 0.1500* | |
| H19A | 0.94160 | 1.17020 | 0.94680 | 0.1660* | |
| H19B | 0.87970 | 1.07000 | 0.83140 | 0.1660* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0761 (11) | 0.0640 (10) | 0.0702 (10) | −0.0133 (8) | −0.0058 (8) | −0.0056 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0475 (7) | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0657 (8) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0207 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0480 (8) | 0.0506 (8) | 0.0832 (10) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0217 (7) | 0.0084 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0429 (9) | 0.0552 (10) | 0.0748 (11) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0229 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0600 (11) | 0.0595 (11) | 0.1025 (16) | 0.0096 (8) | 0.0244 (10) | 0.0413 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0359 (8) | 0.0347 (8) | 0.0472 (9) | 0.0047 (6) | 0.0112 (7) | 0.0063 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0594 (12) | 0.0473 (10) | 0.0514 (10) | −0.0082 (8) | 0.0170 (9) | 0.0062 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0649 (13) | 0.0591 (12) | 0.0475 (10) | −0.0043 (10) | 0.0117 (9) | 0.0042 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0441 (10) | 0.0612 (12) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0016 (9) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0505 (11) | 0.0417 (10) | 0.0702 (13) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0124 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0454 (10) | 0.0423 (9) | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0148 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0762 (17) | 0.0896 (18) | 0.0618 (14) | 0.0016 (13) | −0.0056 (12) | −0.0107 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0407 (8) | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0071 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0423 (9) | 0.0372 (8) | 0.0413 (8) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0085 (7) | 0.0087 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0443 (9) | 0.0398 (8) | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0092 (7) | 0.0082 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0413 (9) | 0.0462 (10) | 0.0586 (11) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0104 (8) | 0.0144 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0499 (10) | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0420 (9) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0070 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0460 (9) | 0.0341 (8) | 0.0407 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0049 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0494 (10) | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0481 (10) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0041 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0664 (13) | 0.0403 (10) | 0.0882 (16) | 0.0107 (9) | 0.0234 (12) | 0.0150 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0820 (16) | 0.0462 (11) | 0.0748 (14) | 0.0089 (10) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0245 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0659 (12) | 0.0391 (9) | 0.0605 (11) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0251 (10) | 0.0135 (8) |
| O4 | 0.125 (2) | 0.236 (4) | 0.0879 (17) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0352 (16) | 0.018 (2) |
| C18 | 0.105 (3) | 0.152 (4) | 0.107 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.020 (3) |
| C19 | 0.114 (3) | 0.200 (5) | 0.111 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.022 (2) | 0.069 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C4 | 1.364 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.461 (2) |
| O1—C7 | 1.417 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.501 (3) |
| O2—C10 | 1.366 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.516 (3) |
| O2—C12 | 1.369 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.511 (3) |
| O3—C14 | 1.216 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C18 | 1.383 (5) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C19i | 1.446 (6) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C10 | 1.330 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C11 | 1.143 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1B | 0.8600 | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9800 |
| C1—C8 | 1.521 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.388 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.379 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C13 | 1.499 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.417 (7) |
| C8—C9 | 1.511 (2) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.354 (2) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C11 | 1.410 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C12—C13 | 1.338 (2) | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C12—C17 | 1.491 (3) | ||
| C4—O1—C7 | 117.78 (19) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| C10—O2—C12 | 118.91 (14) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C18—O4—C19i | 108.6 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 120.00 | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C10—N1—H1B | 120.00 | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C10—N1—H1A | 120.00 | O1—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.77 (17) | O1—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| C6—C1—C8 | 119.84 (15) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C8 | 122.37 (15) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.88 (19) | H7B—C7—H7C | 110.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.41 (19) | O1—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| O1—C4—C5 | 116.23 (19) | C9—C8—H8 | 108.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.3 (2) | C13—C8—H8 | 108.00 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 124.49 (19) | C1—C8—H8 | 108.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.73 (19) | C14—C15—H15B | 109.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.93 (18) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.00 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 108.63 (14) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.00 |
| C1—C8—C13 | 112.38 (14) | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.00 |
| C1—C8—C9 | 111.95 (13) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 122.54 (15) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.00 |
| C10—C9—C11 | 119.42 (16) | C17—C16—H16A | 109.00 |
| C8—C9—C11 | 118.00 (14) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.00 |
| O2—C10—N1 | 110.30 (15) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.00 |
| N1—C10—C9 | 128.22 (17) | C17—C16—H16B | 109.00 |
| O2—C10—C9 | 121.48 (15) | C12—C17—H17A | 110.00 |
| N2—C11—C9 | 177.6 (2) | C12—C17—H17B | 110.00 |
| O2—C12—C13 | 122.91 (15) | C16—C17—H17B | 110.00 |
| C13—C12—C17 | 125.75 (17) | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.00 |
| O2—C12—C17 | 111.34 (16) | C16—C17—H17A | 110.00 |
| C8—C13—C14 | 118.19 (14) | O4—C18—C19 | 110.9 (4) |
| C8—C13—C12 | 122.27 (15) | O4i—C19—C18 | 110.8 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.54 (15) | O4—C18—H18A | 109.00 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.57 (16) | O4—C18—H18B | 109.00 |
| O3—C14—C13 | 121.28 (16) | C19—C18—H18A | 109.00 |
| O3—C14—C15 | 121.11 (17) | C19—C18—H18B | 109.00 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 112.24 (17) | H18A—C18—H18B | 108.00 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 111.57 (18) | C18—C19—H19A | 109.00 |
| C12—C17—C16 | 110.51 (18) | C18—C19—H19B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.00 | H19A—C19—H19B | 108.00 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.00 | O4i—C19—H19A | 109.00 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 | O4i—C19—H19B | 110.00 |
| C7—O1—C4—C3 | −9.3 (3) | C1—C8—C9—C10 | 105.99 (18) |
| C7—O1—C4—C5 | 171.1 (2) | C1—C8—C9—C11 | −71.4 (2) |
| C10—O2—C12—C17 | 171.59 (15) | C9—C8—C13—C14 | −161.46 (15) |
| C12—O2—C10—N1 | −172.95 (15) | C1—C8—C13—C14 | 74.12 (19) |
| C10—O2—C12—C13 | −8.8 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 17.3 (2) |
| C12—O2—C10—C9 | 7.4 (2) | C11—C9—C10—N1 | 5.4 (3) |
| C18i—O4i—C19—C18 | −58.0 (5) | C8—C9—C10—O2 | 7.6 (3) |
| C19i—O4—C18—C19 | −58.0 (5) | C8—C9—C10—N1 | −172.00 (17) |
| C8—C1—C2—C3 | 178.46 (19) | C11—C9—C10—O2 | −175.05 (16) |
| C8—C1—C6—C5 | −178.09 (17) | C17—C12—C13—C8 | 174.55 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | −6.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C8—C9 | −87.6 (2) | O2—C12—C17—C16 | 162.26 (16) |
| C2—C1—C8—C13 | 34.9 (2) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | −17.3 (3) |
| C6—C1—C8—C9 | 90.63 (19) | O2—C12—C13—C14 | 173.82 (15) |
| C6—C1—C8—C13 | −146.80 (16) | O2—C12—C13—C8 | −5.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (3) | C12—C13—C14—O3 | −178.26 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (3) | C8—C13—C14—O3 | 0.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | 179.8 (2) | C8—C13—C14—C15 | 178.31 (16) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | −179.37 (19) | O3—C14—C15—C16 | −151.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.0 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 31.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.8 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −54.6 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—C11 | 163.92 (15) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 46.9 (2) |
| C1—C8—C13—C12 | −107.09 (18) | O4—C18—C19—O4i | 59.3 (5) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −18.7 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···N2ii | 0.86 | 2.27 | 3.123 (3) | 171 |
| N1—H1B···O3iii | 0.86 | 2.10 | 2.945 (2) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5115).
References
- Alvey, L., Prado, S., Saint-Joanis, B., Michel, S., Koch, M., Cole, S. T., Tillequin, F. & Janin, Y. L. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem 44, 2497–2505. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bargagna, A., Longobardi, M., Mariani, E., Schenone, P. & Falzarano, C. (1992). Il Farmaco, 47, 345–355. [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Foroumadi, A., Dehghan, G., Samzadeh-Kermani, A., Arabsorkhi, F., Sorkhi, M., Shafiee, A. & Abodollahi, M. (2007). Asian J. Chem. 19, 1391–1396. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gorlitzer, K., Dehre, A. & Engler, E. (1984). Arch. Pharm. Weinheim Ger. 317, 526–530.
- Gourdeau, H., Leblond, L., Hamelin, B., Desputeau, C., Dong, K., Kianicka, I., Custeau, D., Boudreau, C., Geerts, L., Cai, S.-X., Drewe, J., Labrecque, D., Kasibhatla, S. & Tseng, B. (2004). Mol. Cancer Ther. 3, 1375–1384. [PubMed]
- Han, Q.-B., Yang, N.-Y., Tian, H.-L., Qiao, C.-F., Song, J.-Z., Chang, D. C., Chen, S.-L., Luo, K. Q. & Xu, H.-X. (2008). Phytochemistry, 69, 2187–2192. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A. G. & Marco, L. J. (1997). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 7, 3165–3170.
- Mohamed, S. K., Akkurt, M., Tahir, M. N., Abdelhamid, A. A. & Albayati, M. R. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1965–o1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Narender, T. & Gupta, S. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 3913–3916. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, W. P., Sollis, L. S., Howes, D. P., Cherry, C. P., Starkey, D. I. & Cobley, N. K. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 787–797. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Symeonidis, T., Chamilos, M., Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. J., Kallitsakis, M. & Litinas, K. E. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem Lett 19, 1139-1142. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R. N., Cleasby, A., Singh, O., Sharzynski, T., Wonacott, J. A., Smith, W. P., Sollis, L. S., Howes, D. P., Cherry, C. P., Bethell, R., Colman, P. & Varghese, J. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 798–807. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027729/tk5115Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report