Abstract
Reaction of nickel(II) chloride with sodium cyanate and 2,6-dimethylpyrazine leads to single crystals of the title compound, [Ni(NCO)2(C6H8N2)4]. The nickel(II) cation is located about a centre of inversion and is octahedrally coordinated by two cyanate anions and four 2,6-dimethylpyrazine ligands, forming discrete complexes.
Related literature
For the background to this work relating to complexes with thiocyanato and selenocyanato and N-donor ligands, see: Boeckmann & Näther (2010 ▶); Wriedt et al. (2009 ▶); Boeckmann et al. (2010 ▶).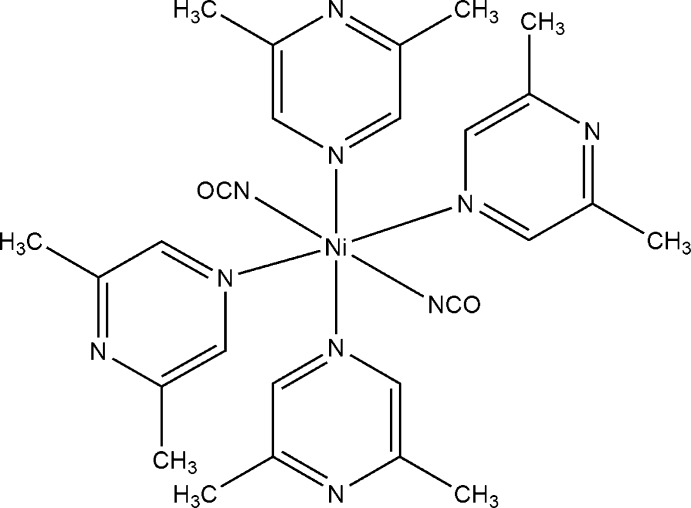
Experimental
Crystal data
[Ni(NCO)2(C6H8N2)4]
M r = 575.33
Monoclinic,

a = 24.932 (2) Å
b = 8.4963 (3) Å
c = 18.1748 (13) Å
β = 133.148 (7)°
V = 2808.9 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.73 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.07 × 0.04 × 0.03 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS-2 diffractometer
Absorption correction: numerical (X-SHAPE and X-RED32; Stoe & Cie 2008 ▶) T min = 0.888, T max = 0.969
8293 measured reflections
3341 independent reflections
2516 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.102
S = 1.01
3341 reflections
182 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-AREA; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2011 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: XCIF in SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027985/zl2488sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027985/zl2488Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Ni1—N1 | 2.0396 (19) |
| Ni1—N10 | 2.1475 (17) |
| Ni1—N20 | 2.1983 (15) |
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support by the DFG (project No. NA 720/3-1) and the State of Schleswig-Holstein. We thank Professor Dr. Bensch for access to his experimental facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently we have reported on the synthesis, structures and properties of new coordination polymers based on paramagnetic transition metals, small-sized anionic ligands such as thiocyanato and selenocyanato, and N-donor ligands. In the course of these investigations we found that new coordination compounds with bridging anionic ligands can be prepared by thermal decomposition of suitable precursor compounds, in which the anionic ligands are only terminally coordinated (Wriedt et al., 2009 and Boeckmann & Näther, 2010). In further investigations we also have shown that even metal formate coordination compounds can be prepared by this method (Boeckmann, Wriedt & Näther, 2010). In our current investigations we tried to prepare similar compounds based on transition metal cyanates with 2,6-dimethylpyrazine as a neutral co-ligand. Therefore, we have reacted nickel(II) chloride with sodium cyanate and 2,6-dimethylpyrazine which resulted in the formation of crystals of the title compound that were identified by single crystal X-ray diffraction.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound consists of one nickel(II) cation, which is located on a centre of inversion, one cyanato anion and two 2,6-dimethylpyrazine ligands in general positions (Fig. 1). In the crystal structure each nickel(II) cation is coordinated by two terminal N-bonded cyanato anions and four 2,6-dimethylpyrazine ligands into discrete complexes, and the coordination polyhedra around the Ni cations corresponds to a slightly distorted octahedra. The anionic ligands are trans to each other and because of sterical crowding the 2,6-dimethylpyrazine ligand is coordinated via the nitrogen atom that is not neighbouring the methyl groups. The Ni—N distances range from 2.0396 (19) Å to 2.1983 (15) Å with angles between 88.72 (6) ° and 180 ° (Table 1). The shortest intermolecular distances between the nickel(II) cations is 8.4963 (3) Å.
Experimental
Nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate (NiCl2×6H2O), sodium cyanate (NaNCO) and 2,6-dimethylpyrazine were obtained from Alfa Aesar. All chemicals were used without further purification. 0.15 mmol (35.5 mg) NiCl2×6H2O and 0.3 mmol (19.5 mg) NaNCO were reacted in 0.6 mmol (65 µL) 2,6-dimethylpyrazine. Green shaped single-crystals suitable for structure determination were obtained after one week at room temperature.
Refinement
C—H H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry (methyl H atoms were allowed to rotate but not to tip) and were refined isotropically with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) (1.5 for methyl H atoms) and C—H distances of 0.93 Å for aromatic and 0.96 Å for methyl H atoms using a riding model.
Figures
Fig. 1.
: Crystal structure of the title compound with labeling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50 % probability level. Symmetry code: i = -x + 3/2, -y + 3/2, -z + 1.
Crystal data
| [Ni(NCO)2(C6H8N2)4] | F(000) = 1208 |
| Mr = 575.33 | Dx = 1.360 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 8293 reflections |
| a = 24.932 (2) Å | θ = 2.7–28.0° |
| b = 8.4963 (3) Å | µ = 0.73 mm−1 |
| c = 18.1748 (13) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 133.148 (7)° | Block, green |
| V = 2808.9 (3) Å3 | 0.07 × 0.04 × 0.03 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS-2 diffractometer | 3341 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2516 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.047 |
| ω scan | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: numerical (X-SHAPE and X-RED32; Stoe & Cie 2008) | h = −25→32 |
| Tmin = 0.888, Tmax = 0.969 | k = −11→10 |
| 8293 measured reflections | l = −23→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.102 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0632P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3341 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 182 parameters | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ni1 | 0.7500 | 0.7500 | 0.5000 | 0.01887 (11) | |
| N20 | 0.64456 (8) | 0.8103 (2) | 0.34913 (11) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| N10 | 0.79329 (8) | 0.6983 (2) | 0.43337 (11) | 0.0231 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.68822 (10) | 0.4093 (3) | 0.46580 (14) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.71677 (9) | 0.5219 (2) | 0.47971 (13) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| N21 | 0.50923 (9) | 0.8818 (2) | 0.15700 (13) | 0.0270 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.82299 (10) | 0.5593 (3) | 0.44444 (15) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.8239 | 0.4804 | 0.4807 | 0.031* | |
| C23 | 0.62225 (10) | 0.9586 (2) | 0.31901 (15) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| H23 | 0.6526 | 1.0401 | 0.3631 | 0.028* | |
| N11 | 0.85370 (10) | 0.6399 (3) | 0.35157 (14) | 0.0364 (5) | |
| C22 | 0.55452 (10) | 0.9952 (3) | 0.22309 (15) | 0.0251 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.59907 (10) | 0.6966 (3) | 0.28228 (14) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| H20 | 0.6130 | 0.5918 | 0.3002 | 0.029* | |
| O1 | 0.65623 (11) | 0.2844 (2) | 0.45025 (18) | 0.0568 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.85283 (11) | 0.5294 (3) | 0.40292 (15) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.79369 (10) | 0.8085 (3) | 0.38110 (14) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.7725 | 0.9060 | 0.3708 | 0.032* | |
| C12 | 0.82493 (11) | 0.7812 (3) | 0.34183 (16) | 0.0330 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.88376 (15) | 0.3709 (3) | 0.4124 (2) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.8580 | 0.3295 | 0.3464 | 0.068* | |
| H14B | 0.8780 | 0.3006 | 0.4479 | 0.068* | |
| H14C | 0.9350 | 0.3812 | 0.4490 | 0.068* | |
| C15 | 0.82941 (15) | 0.9083 (4) | 0.2884 (2) | 0.0526 (8) | |
| H15A | 0.8799 | 0.9357 | 0.3276 | 0.079* | |
| H15B | 0.8029 | 0.9994 | 0.2800 | 0.079* | |
| H15C | 0.8082 | 0.8707 | 0.2234 | 0.079* | |
| C21 | 0.53149 (10) | 0.7326 (3) | 0.18668 (14) | 0.0272 (4) | |
| C25 | 0.53126 (11) | 1.1627 (3) | 0.19022 (17) | 0.0341 (5) | |
| H25A | 0.5382 | 1.1915 | 0.1461 | 0.051* | |
| H25B | 0.5604 | 1.2302 | 0.2483 | 0.051* | |
| H25C | 0.4803 | 1.1738 | 0.1552 | 0.051* | |
| C24 | 0.48127 (12) | 0.6054 (3) | 0.11260 (18) | 0.0405 (6) | |
| H24A | 0.4342 | 0.6160 | 0.0917 | 0.061* | |
| H24B | 0.5019 | 0.5045 | 0.1437 | 0.061* | |
| H24C | 0.4756 | 0.6143 | 0.0549 | 0.061* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.01411 (16) | 0.02221 (18) | 0.01902 (17) | −0.00050 (14) | 0.01083 (13) | 0.00029 (14) |
| N20 | 0.0161 (7) | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0022 (6) |
| N10 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0312 (9) | 0.0196 (7) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0111 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0202 (9) | 0.0288 (11) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0043 (8) | 0.0137 (8) | −0.0008 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0028 (7) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0032 (7) |
| N21 | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0244 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | 0.0147 (7) | 0.0044 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0234 (9) | 0.0324 (11) | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0017 (8) |
| C23 | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0290 (10) | 0.0244 (9) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0146 (8) | 0.0021 (8) |
| N11 | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0556 (13) | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0103 (8) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0102 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0344 (11) | 0.0270 (9) | 0.0061 (8) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0062 (8) |
| C20 | 0.0180 (8) | 0.0299 (10) | 0.0200 (9) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0116 (8) | 0.0001 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0535 (11) | 0.0307 (10) | 0.0848 (15) | −0.0174 (8) | 0.0467 (12) | −0.0082 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0245 (10) | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0183 (9) | 0.0020 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0204 (9) | 0.0361 (11) | 0.0240 (9) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0230 (9) | 0.0498 (15) | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0058 (8) | 0.0183 (8) | 0.0114 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0546 (16) | 0.0491 (14) | 0.0189 (12) | 0.0422 (13) | 0.0102 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0500 (14) | 0.0681 (19) | 0.0591 (17) | 0.0181 (14) | 0.0449 (14) | 0.0293 (15) |
| C21 | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0378 (13) | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0020 (8) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C25 | 0.0263 (10) | 0.0380 (13) | 0.0365 (11) | 0.0115 (9) | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0139 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0422 (14) | 0.0292 (10) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0102 (9) | −0.0066 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ni1—N1i | 2.0396 (19) | C22—C25 | 1.498 (3) |
| Ni1—N1 | 2.0396 (19) | C20—C21 | 1.395 (3) |
| Ni1—N10 | 2.1475 (17) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| Ni1—N10i | 2.1475 (17) | C11—C14 | 1.502 (3) |
| Ni1—N20 | 2.1983 (15) | C13—C12 | 1.389 (3) |
| Ni1—N20i | 2.1983 (15) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N20—C23 | 1.335 (3) | C12—C15 | 1.507 (3) |
| N20—C20 | 1.345 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N10—C10 | 1.334 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N10—C13 | 1.339 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1 | 1.113 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C1—O1 | 1.238 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| N21—C22 | 1.339 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| N21—C21 | 1.341 (3) | C21—C24 | 1.497 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.398 (3) | C25—H25A | 0.9600 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | C25—H25B | 0.9600 |
| C23—C22 | 1.400 (3) | C25—H25C | 0.9600 |
| C23—H23 | 0.9300 | C24—H24A | 0.9600 |
| N11—C11 | 1.334 (3) | C24—H24B | 0.9600 |
| N11—C12 | 1.347 (3) | C24—H24C | 0.9600 |
| N1i—Ni1—N1 | 180.00 (13) | N11—C11—C10 | 121.2 (2) |
| N1i—Ni1—N10 | 89.86 (7) | N11—C11—C14 | 117.3 (2) |
| N1—Ni1—N10 | 90.14 (7) | C10—C11—C14 | 121.5 (2) |
| N1i—Ni1—N10i | 90.14 (7) | N10—C13—C12 | 121.8 (2) |
| N1—Ni1—N10i | 89.86 (7) | N10—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| N10—Ni1—N10i | 180.000 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
| N1i—Ni1—N20 | 89.74 (7) | N11—C12—C13 | 121.1 (2) |
| N1—Ni1—N20 | 90.26 (7) | N11—C12—C15 | 117.1 (2) |
| N10—Ni1—N20 | 88.72 (6) | C13—C12—C15 | 121.7 (2) |
| N10i—Ni1—N20 | 91.28 (6) | C11—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| N1i—Ni1—N20i | 90.26 (7) | C11—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| N1—Ni1—N20i | 89.74 (7) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| N10—Ni1—N20i | 91.28 (6) | C11—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N10i—Ni1—N20i | 88.72 (6) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N20—Ni1—N20i | 180.000 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C23—N20—C20 | 116.73 (16) | C12—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C23—N20—Ni1 | 122.62 (13) | C12—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C20—N20—Ni1 | 120.64 (14) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C10—N10—C13 | 116.95 (19) | C12—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C10—N10—Ni1 | 122.49 (14) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C13—N10—Ni1 | 120.51 (15) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—O1 | 179.7 (2) | N21—C21—C20 | 121.5 (2) |
| C1—N1—Ni1 | 167.16 (17) | N21—C21—C24 | 117.32 (18) |
| C22—N21—C21 | 117.19 (17) | C20—C21—C24 | 121.1 (2) |
| N10—C10—C11 | 121.7 (2) | C22—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| N10—C10—H10 | 119.2 | C22—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.2 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| N20—C23—C22 | 122.01 (19) | C22—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| N20—C23—H23 | 119.0 | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C22—C23—H23 | 119.0 | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C11—N11—C12 | 117.2 (2) | C21—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| N21—C22—C23 | 121.1 (2) | C21—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| N21—C22—C25 | 117.86 (17) | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C23—C22—C25 | 121.1 (2) | C21—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| N20—C20—C21 | 121.5 (2) | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| N20—C20—H20 | 119.3 | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C21—C20—H20 | 119.3 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+3/2, −y+3/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2488).
References
- Boeckmann, J. & Näther, C. (2010). Dalton Trans. 39, 11019–11026. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Boeckmann, J., Wriedt, M. & Näther, C. (2010). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 1820–1828.
- Brandenburg, K. (2011). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2008). X-AREA, X-RED32 and X-SHAPE Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Wriedt, M., Jess, I. & Näther, C. (2009). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 1406–1413.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027985/zl2488sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812027985/zl2488Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



