Abstract
In the title compound, C21H20BrClN4O4S2, the benzene rings bridged by the sulfonamide group are tilted relative to each other by a dihedral angle of 70.2 (1)° and the dihedral angle between the sulfur-bridged pyrimidine and benzene rings is 69.5 (1)°. The molecular conformation is stabilized by a weak intramolecular π–π stacking interaction between the pyrimidine and the 4-chlorobenzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.978 (2) Å]. The morpholine ring adopts a chair conformation. In the crystal, molecules are linked into inversion dimers by pairs of C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds and these dimers are further connected by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a tape along the a axis.
Related literature
For related structures of sulfonamides, see: Rodrigues et al. (2011 ▶); Akkurt et al. (2011 ▶); Kant et al. (2012 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For ring conformations, see: Duax & Norton (1975 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H20BrClN4O4S2
M r = 571.89
Monoclinic,

a = 10.0311 (3) Å
b = 17.3096 (6) Å
c = 13.9223 (4) Å
β = 91.829 (3)°
V = 2416.16 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.02 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.3 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▶) T min = 0.438, T max = 0.668
26979 measured reflections
4744 independent reflections
3408 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.117
S = 1.03
4744 reflections
299 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.65 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2010 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N7—H7⋯O25i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.849 (4) | 148 |
| C20—H20⋯N19ii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.352 (5) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 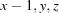 ; (ii)
; (ii) 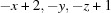 .
.
Acknowledgments
MK acknowledges the help of Bahubali College of Engineering for his research work. RK acknowledges the Department of Science & Technology for the single-crystal X-ray diffractometer sanctioned as a National Facility under project No. SR/S2/CMP-47/2003.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Bond lengths and angles in the title compound (Fig. 1) have normal values (Allen et al., 1987) and are comparable with the similar crystal structures (Rodrigues et al., 2011; Akkurt et al., 2011; Kant et al., 2012). The molecule is twisted at atom S1 with a C1—S1—N7—C8 torsion angle of 60.8 (3)°. The morpholine ring is exhibiting a chair conformation [asymmetry parameters are: ΔC2(N22—C23) = 2.53; ΔCs(N22—O25) = 1/5; Duax & Norton, 1975]. The two benzene rings (C1—C6/C8—C13) are tilted relative to each other by 70.2 (1)° and the dihedral angle between the sulfur bridged pyrimidine and benzene rings is 69.5 (1)°. The molecular conformation is stabilized by a weak intramolecular stacking interaction between the pyrimidine and the 4-chloro benzene rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.978 (2) Å, interplanar spacing = 3.340 Å, and centroid shift = 2.16 Å]. In the crystal, molecules are linked into dimers by pairs of C20—H20···N19 hydrogen bonds and these dimers are further linked by N7—H7···O25 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 and Fig. 2).
Experimental
The reaction of N-[2-(5-bromo-2-chloro-pyrimidin-4-ylsulfanyl)-4-methoxy-phenyl]-4-chloro-benzenesulfonamide (5.22 g, 0.01 mol) with morpholine (0.88 g, 0.01) were carried out in the presence of triethylamine and the reaction mixture was allowed to stir at room temperature for 6–7 h in dry dichloromethane. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. Upon completion, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and residue was extracted with ethyl acetate. The compound was purified by successive recrystallization from methanol (yield 80%, m.p. 462–464 K)
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and were treated as riding on their parent C and N atoms, with C—H distances of 0.93–0.97 Å and N—H distance of 0.86 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, N) or 1.5Ueq(methyl C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP view of the title molecule with the atom-labeling scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level. H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
A molecular packing view of the title compound down the a axis, showing intermolecular interactions. For clarity, hydrogen atoms which are not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C21H20BrClN4O4S2 | F(000) = 1160 |
| Mr = 571.89 | Dx = 1.572 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 9194 reflections |
| a = 10.0311 (3) Å | θ = 3.5–29.0° |
| b = 17.3096 (6) Å | µ = 2.02 mm−1 |
| c = 13.9223 (4) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 91.829 (3)° | Block, white |
| V = 2416.16 (13) Å3 | 0.3 × 0.2 × 0.2 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer | 4744 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3408 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1049 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.7° |
| w scans | h = −12→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2010) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.438, Tmax = 0.668 | l = −17→17 |
| 26979 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0505P)2 + 1.7709P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4744 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 299 parameters | Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.65 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Absorption correction: CrysAlis PRO, Oxford Diffraction Ltd., Version 1.171.34.40 (release 27–08-2010 CrysAlis171. NET) (compiled Aug 27 2010,11:50:40) Empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.5036 (3) | 0.16095 (19) | 0.0690 (2) | 0.0825 (9) | |
| O2 | 0.6714 (4) | 0.24236 (18) | −0.00871 (19) | 0.0816 (9) | |
| Br1 | 0.66487 (4) | 0.12100 (3) | 0.53546 (3) | 0.06449 (16) | |
| S2 | 0.69475 (8) | 0.25466 (5) | 0.37229 (6) | 0.0451 (2) | |
| S1 | 0.62576 (11) | 0.20307 (6) | 0.07413 (7) | 0.0605 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 1.06308 (15) | −0.03829 (9) | 0.18890 (14) | 0.1136 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.7553 (4) | 0.1383 (2) | 0.1103 (3) | 0.0516 (9) | |
| C2 | 0.8716 (5) | 0.1366 (3) | 0.0617 (3) | 0.0750 (12) | |
| H2 | 0.8858 | 0.1717 | 0.0125 | 0.090* | |
| C3 | 0.9679 (5) | 0.0824 (3) | 0.0860 (4) | 0.0851 (14) | |
| H3 | 1.0470 | 0.0803 | 0.0531 | 0.102* | |
| C4 | 0.9451 (4) | 0.0318 (3) | 0.1593 (4) | 0.0711 (12) | |
| C5 | 0.8317 (4) | 0.0349 (2) | 0.2101 (3) | 0.0647 (11) | |
| H5 | 0.8197 | 0.0012 | 0.2611 | 0.078* | |
| C6 | 0.7347 (4) | 0.0882 (2) | 0.1854 (3) | 0.0582 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.6561 | 0.0903 | 0.2190 | 0.070* | |
| N7 | 0.6095 (3) | 0.26564 (17) | 0.1598 (2) | 0.0492 (7) | |
| H7 | 0.5343 | 0.2686 | 0.1876 | 0.059* | |
| C8 | 0.7152 (3) | 0.31610 (19) | 0.1908 (2) | 0.0405 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.7703 (4) | 0.3677 (2) | 0.1266 (3) | 0.0503 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.7367 | 0.3699 | 0.0636 | 0.060* | |
| C10 | 0.8737 (4) | 0.4154 (2) | 0.1548 (3) | 0.0509 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.9106 | 0.4487 | 0.1105 | 0.061* | |
| C11 | 0.9235 (3) | 0.41437 (19) | 0.2487 (3) | 0.0461 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.8665 (3) | 0.36557 (19) | 0.3139 (2) | 0.0431 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.8964 | 0.3659 | 0.3779 | 0.052* | |
| C13 | 0.7647 (3) | 0.31593 (18) | 0.2847 (2) | 0.0382 (7) | |
| O14 | 1.0244 (3) | 0.46473 (15) | 0.2706 (2) | 0.0633 (7) | |
| C15 | 1.0716 (5) | 0.4676 (3) | 0.3673 (4) | 0.0833 (14) | |
| H15A | 0.9983 | 0.4774 | 0.4083 | 0.125* | |
| H15B | 1.1362 | 0.5083 | 0.3748 | 0.125* | |
| H15C | 1.1123 | 0.4191 | 0.3845 | 0.125* | |
| C16 | 0.8284 (3) | 0.18979 (17) | 0.3927 (2) | 0.0365 (7) | |
| N17 | 0.9356 (2) | 0.19637 (14) | 0.33991 (18) | 0.0367 (6) | |
| C18 | 1.0363 (3) | 0.14619 (18) | 0.3584 (2) | 0.0412 (8) | |
| N19 | 1.0348 (3) | 0.08998 (17) | 0.4253 (2) | 0.0555 (8) | |
| C20 | 0.9257 (4) | 0.0853 (2) | 0.4755 (3) | 0.0574 (10) | |
| H20 | 0.9215 | 0.0474 | 0.5227 | 0.069* | |
| C21 | 0.8188 (3) | 0.13305 (19) | 0.4616 (2) | 0.0424 (8) | |
| N22 | 1.1446 (3) | 0.15306 (17) | 0.3042 (2) | 0.0521 (7) | |
| C23 | 1.2648 (4) | 0.1067 (3) | 0.3206 (4) | 0.0713 (12) | |
| H23A | 1.2512 | 0.0708 | 0.3729 | 0.086* | |
| H23B | 1.2824 | 0.0769 | 0.2634 | 0.086* | |
| C24 | 1.3790 (4) | 0.1560 (3) | 0.3443 (4) | 0.0766 (13) | |
| H24A | 1.3669 | 0.1796 | 0.4066 | 0.092* | |
| H24B | 1.4591 | 0.1246 | 0.3486 | 0.092* | |
| O25 | 1.3958 (3) | 0.2151 (2) | 0.2743 (2) | 0.0899 (11) | |
| C26 | 1.2790 (4) | 0.2613 (3) | 0.2621 (4) | 0.0846 (15) | |
| H26A | 1.2934 | 0.2995 | 0.2125 | 0.101* | |
| H26B | 1.2632 | 0.2886 | 0.3215 | 0.101* | |
| C27 | 1.1609 (4) | 0.2154 (3) | 0.2354 (3) | 0.0649 (11) | |
| H27A | 1.0824 | 0.2482 | 0.2343 | 0.078* | |
| H27B | 1.1704 | 0.1940 | 0.1716 | 0.078* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0727 (19) | 0.083 (2) | 0.089 (2) | −0.0082 (16) | −0.0313 (16) | −0.0141 (18) |
| O2 | 0.127 (3) | 0.079 (2) | 0.0388 (15) | 0.0099 (19) | −0.0027 (15) | 0.0047 (14) |
| Br1 | 0.0599 (3) | 0.0763 (3) | 0.0583 (3) | −0.0100 (2) | 0.01681 (19) | 0.0202 (2) |
| S2 | 0.0322 (4) | 0.0552 (5) | 0.0482 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0061 (3) | 0.0165 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0729 (7) | 0.0615 (6) | 0.0461 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | −0.0126 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| Cl1 | 0.0878 (9) | 0.0894 (10) | 0.1623 (15) | 0.0286 (8) | −0.0144 (9) | −0.0113 (9) |
| C1 | 0.058 (2) | 0.049 (2) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0077 (17) | −0.0057 (17) | −0.0081 (17) |
| C2 | 0.082 (3) | 0.076 (3) | 0.068 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C3 | 0.069 (3) | 0.091 (4) | 0.096 (4) | 0.000 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| C4 | 0.064 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.091 (3) | 0.003 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C5 | 0.064 (3) | 0.048 (2) | 0.082 (3) | −0.010 (2) | −0.007 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C6 | 0.057 (2) | 0.054 (2) | 0.063 (2) | −0.0094 (19) | −0.0005 (19) | 0.001 (2) |
| N7 | 0.0450 (16) | 0.0564 (18) | 0.0462 (16) | −0.0007 (14) | −0.0001 (13) | 0.0004 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0393 (17) | 0.0421 (19) | 0.0405 (18) | 0.0066 (14) | 0.0061 (14) | 0.0035 (14) |
| C9 | 0.063 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0365 (18) | 0.0063 (18) | 0.0070 (16) | 0.0057 (16) |
| C10 | 0.057 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0012 (17) | 0.0192 (17) | 0.0131 (17) |
| C11 | 0.0397 (18) | 0.0387 (19) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0016 (15) | 0.0103 (16) | 0.0091 (16) |
| C12 | 0.0398 (17) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0454 (19) | 0.0028 (15) | −0.0019 (15) | 0.0102 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0346 (16) | 0.0376 (17) | 0.0426 (18) | 0.0048 (13) | 0.0061 (14) | 0.0103 (14) |
| O14 | 0.0573 (15) | 0.0597 (16) | 0.0730 (19) | −0.0169 (13) | 0.0053 (14) | 0.0132 (14) |
| C15 | 0.073 (3) | 0.086 (3) | 0.089 (3) | −0.032 (3) | −0.016 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| C16 | 0.0339 (16) | 0.0369 (17) | 0.0384 (17) | −0.0049 (13) | −0.0027 (13) | 0.0033 (14) |
| N17 | 0.0300 (13) | 0.0380 (15) | 0.0420 (15) | −0.0040 (11) | −0.0004 (11) | 0.0057 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0352 (17) | 0.0381 (18) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0063 (14) | −0.0007 (15) | 0.0013 (15) |
| N19 | 0.0500 (17) | 0.0424 (17) | 0.074 (2) | 0.0040 (14) | 0.0052 (16) | 0.0190 (15) |
| C20 | 0.060 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.065 (2) | −0.0005 (18) | 0.0028 (19) | 0.0229 (19) |
| C21 | 0.0440 (18) | 0.0411 (19) | 0.0425 (19) | −0.0075 (15) | 0.0064 (15) | 0.0137 (15) |
| N22 | 0.0364 (15) | 0.0505 (18) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0009 (13) | 0.0085 (14) | 0.0098 (16) |
| C23 | 0.048 (2) | 0.067 (3) | 0.099 (3) | 0.015 (2) | 0.013 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C24 | 0.042 (2) | 0.092 (3) | 0.095 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.032 (3) |
| O25 | 0.0371 (14) | 0.136 (3) | 0.096 (2) | −0.0163 (16) | −0.0023 (14) | 0.056 (2) |
| C26 | 0.064 (3) | 0.101 (4) | 0.088 (3) | −0.025 (3) | −0.010 (2) | 0.043 (3) |
| C27 | 0.040 (2) | 0.095 (3) | 0.060 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0070 (17) | 0.017 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—S1 | 1.426 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.386 (4) |
| O2—S1 | 1.427 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| Br1—C21 | 1.894 (3) | O14—C15 | 1.414 (5) |
| S2—C16 | 1.765 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| S2—C13 | 1.777 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| S1—N7 | 1.623 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| S1—C1 | 1.777 (4) | C16—N17 | 1.326 (4) |
| Cl1—C4 | 1.736 (5) | C16—C21 | 1.379 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.367 (6) | N17—C18 | 1.351 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.379 (5) | C18—N19 | 1.347 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (7) | C18—N22 | 1.348 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | N19—C20 | 1.320 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.368 (7) | C20—C21 | 1.363 (5) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.360 (6) | N22—C27 | 1.455 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (6) | N22—C23 | 1.461 (5) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C23—C24 | 1.458 (6) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C23—H23A | 0.9700 |
| N7—C8 | 1.430 (4) | C23—H23B | 0.9700 |
| N7—H7 | 0.8600 | C24—O25 | 1.426 (5) |
| C8—C13 | 1.384 (4) | C24—H24A | 0.9700 |
| C8—C9 | 1.391 (5) | C24—H24B | 0.9700 |
| C9—C10 | 1.374 (5) | O25—C26 | 1.424 (5) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C26—C27 | 1.465 (6) |
| C10—C11 | 1.384 (5) | C26—H26A | 0.9700 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | C26—H26B | 0.9700 |
| C11—O14 | 1.363 (4) | C27—H27A | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.378 (4) | C27—H27B | 0.9700 |
| C16—S2—C13 | 100.11 (14) | O14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—O2 | 120.05 (19) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—N7 | 105.76 (18) | O14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N7 | 108.56 (17) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 108.13 (18) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 106.19 (19) | N17—C16—C21 | 121.5 (3) |
| N7—S1—C1 | 107.62 (16) | N17—C16—S2 | 118.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.8 (4) | C21—C16—S2 | 119.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.1 (3) | C16—N17—C18 | 117.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 119.1 (3) | N19—C18—N22 | 118.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.6 (4) | N19—C18—N17 | 124.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.2 | N22—C18—N17 | 116.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.2 | C20—N19—C18 | 116.0 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.0 (4) | N19—C20—C21 | 123.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.5 | N19—C20—H20 | 118.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.5 | C21—C20—H20 | 118.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.7 (4) | C20—C21—C16 | 117.3 (3) |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 118.6 (4) | C20—C21—Br1 | 120.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—Cl1 | 119.7 (4) | C16—C21—Br1 | 122.2 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.6 (4) | C18—N22—C27 | 122.9 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | C18—N22—C23 | 122.7 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | C27—N22—C23 | 113.7 (3) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.3 (4) | C24—C23—N22 | 110.6 (4) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C24—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.4 | N22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C8—N7—S1 | 122.6 (2) | C24—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C8—N7—H7 | 118.7 | N22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| S1—N7—H7 | 118.7 | H23A—C23—H23B | 108.1 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 118.1 (3) | O25—C24—C23 | 112.0 (4) |
| C13—C8—N7 | 121.6 (3) | O25—C24—H24A | 109.2 |
| C9—C8—N7 | 120.3 (3) | C23—C24—H24A | 109.2 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.9 (3) | O25—C24—H24B | 109.2 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.5 | C23—C24—H24B | 109.2 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 107.9 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.6 (3) | C26—O25—C24 | 111.7 (3) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 | O25—C26—C27 | 112.4 (4) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 | O25—C26—H26A | 109.1 |
| O14—C11—C12 | 124.5 (3) | C27—C26—H26A | 109.1 |
| O14—C11—C10 | 116.4 (3) | O25—C26—H26B | 109.1 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 119.0 (3) | C27—C26—H26B | 109.1 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.3 (3) | H26A—C26—H26B | 107.8 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 | N22—C27—C26 | 110.0 (3) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 | N22—C27—H27A | 109.7 |
| C8—C13—C12 | 121.0 (3) | C26—C27—H27A | 109.7 |
| C8—C13—S2 | 120.8 (2) | N22—C27—H27B | 109.7 |
| C12—C13—S2 | 118.1 (2) | C26—C27—H27B | 109.7 |
| C11—O14—C15 | 117.3 (3) | H27A—C27—H27B | 108.2 |
| O14—C15—H15A | 109.5 | ||
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | 132.3 (3) | C11—C12—C13—S2 | −179.8 (2) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 2.2 (4) | C16—S2—C13—C8 | 111.6 (3) |
| N7—S1—C1—C2 | −113.9 (3) | C16—S2—C13—C12 | −70.9 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | −45.3 (3) | C12—C11—O14—C15 | −1.2 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −175.4 (3) | C10—C11—O14—C15 | 176.6 (4) |
| N7—S1—C1—C6 | 68.5 (3) | C13—S2—C16—N17 | −4.3 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 2.1 (6) | C13—S2—C16—C21 | 176.6 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −175.5 (4) | C21—C16—N17—C18 | −1.6 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (7) | S2—C16—N17—C18 | 179.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.6 (7) | C16—N17—C18—N19 | 0.8 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl1 | 178.4 (4) | C16—N17—C18—N22 | 179.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.4 (7) | N22—C18—N19—C20 | −179.2 (3) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −177.6 (3) | N17—C18—N19—C20 | −0.3 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.9 (6) | C18—N19—C20—C21 | 0.6 (6) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.3 (6) | N19—C20—C21—C16 | −1.4 (6) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 176.3 (3) | N19—C20—C21—Br1 | 178.9 (3) |
| O1—S1—N7—C8 | 176.2 (3) | N17—C16—C21—C20 | 1.9 (5) |
| O2—S1—N7—C8 | −53.7 (3) | S2—C16—C21—C20 | −179.0 (3) |
| C1—S1—N7—C8 | 60.8 (3) | N17—C16—C21—Br1 | −178.3 (2) |
| S1—N7—C8—C13 | −121.0 (3) | S2—C16—C21—Br1 | 0.8 (4) |
| S1—N7—C8—C9 | 59.7 (4) | N19—C18—N22—C27 | −175.0 (3) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 2.0 (5) | N17—C18—N22—C27 | 6.0 (5) |
| N7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.7 (3) | N19—C18—N22—C23 | −5.6 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.4 (5) | N17—C18—N22—C23 | 175.4 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—O14 | −178.8 (3) | C18—N22—C23—C24 | −118.5 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.0 (5) | C27—N22—C23—C24 | 51.7 (5) |
| O14—C11—C12—C13 | −179.6 (3) | N22—C23—C24—O25 | −53.3 (5) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 2.8 (5) | C23—C24—O25—C26 | 56.6 (6) |
| C9—C8—C13—C12 | −0.2 (5) | C24—O25—C26—C27 | −56.8 (5) |
| N7—C8—C13—C12 | −179.5 (3) | C18—N22—C27—C26 | 118.8 (4) |
| C9—C8—C13—S2 | 177.3 (2) | C23—N22—C27—C26 | −51.5 (5) |
| N7—C8—C13—S2 | −2.0 (4) | O25—C26—C27—N22 | 53.5 (5) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | −2.2 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N7—H7···O25i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.849 (4) | 148 |
| C20—H20···N19ii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.352 (5) | 149 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS5183).
References
- Akkurt, M., Mariam, I., Naseer, I., Khan, I. U. & Sharif, S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Duax, W. L. & Norton, D. A. (1975). Atlas of Steroid Structures, Vol. 1, New York: Plenum Press.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Kant, R., Gupta, V. K., Kapoor, K., Kumar, M., Mallesha, L. & Sridhar, M. A. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2590–o2591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2010). CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Rodrigues, V. Z., Foro, S. & Gowda, B. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812036689/is5183Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




