Abstract
Iodide is required for thyroid hormone synthesis in mammals and other vertebrates. The role of both iodide and iodinated tyrosine derivatives is currently unknown in lower organisms, yet the presence of a key enzyme in iodide conservation, iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD), is suggested by genomic data from a wide range of multicellular organisms as well as some bacteria. A representative set of these genes has now been expressed, and the resulting enzymes all catalyze reductive deiodination of diiodotyrosine with kcat/Km values within a single order of magnitude. This implies a physiological presence of iodotyrosines (or related halotyrosines) and a physiological role for their turnover. At least for Metazoa, IYD should provide a new marker for tracing the evolutionary development of iodinated amino acids as regulatory signals through the tree of life.
Introduction
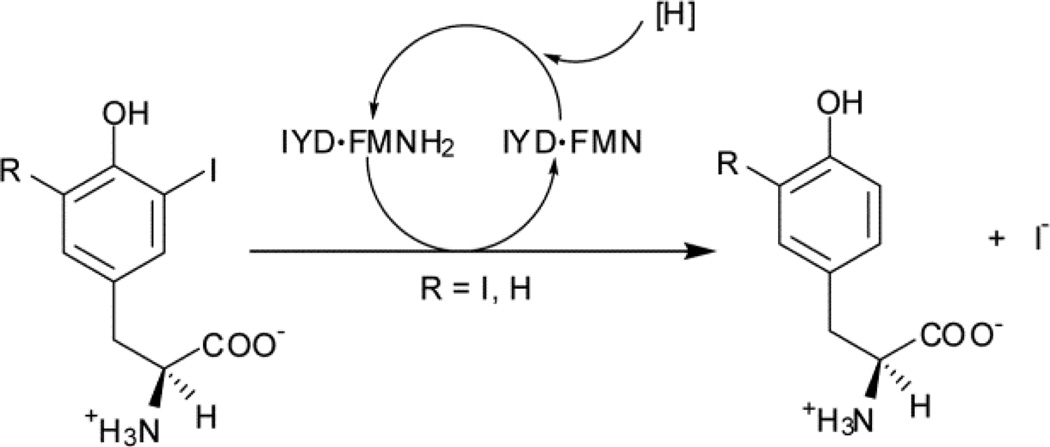
Reductive dehalogenation is rare in aerobic organisms and even more unusual in Metazoans.1,2 Only two enzymes are known to catalyze reductive dehalogenation in mammals, and both are critical for thyroid function. Iodothyronine deiodinase (ID) catalyzes deiodination of thyroid hormone (TH) to regulate its physiological activity3 while iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD) catalyzes deiodination of mono- and diiodotyrosine (MIT and DIT) for iodide salvage from these byproducts of TH synthesis (Fig. 1).4 Despite similarities in function, their origins are quite diverse. ID is a member of the thioredoxin structural superfamily5 and promotes deiodination of thyroxine with help of an active site selenocysteine.6 In contrast, IYD is a member of the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily (formerly referred to as the NADH oxidase/flavin reductase superfamily) and its catalysis relies on a flavin cofactor (FMN).7,8
Fig. 1.
Reductive deiodination of mono- and diiodotyrosine is promoted by iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD) and its bound cofactor, flavin mono- nucleotide (FMN and, in its reduced form, FMNH2).
IYD is unique in its recruitment of flavin to promote reductive dehalogenation in mammals.9 Sequence analysis of mammalian IYD detected an N-terminal membrane anchor, an intermediate domain and a large C-terminal catalytic domain that is homologous to flavoproteins associated with reduction of nitroaromatics among other types of substrates.10 The crystal structure of IYD11 revealed most similarity to a bacterial flavin destructase (BluB) responsible for synthesis of the lower ligand of vitamin B12.12 Together, IYD and BluB form a distinct subclass within their superfamily based on the position of their active site lid sequences.11,12 The remaining two subclasses represented by NADH oxidase (NOX) from Thermus thermophilus and flavin reductase P (FRP) from Vibrio harveyi utilize different regions of their primary structure to form active site lids.13,14 Emergence of a deiodinase from this collection of activities is far from obvious and made all the more interesting due to its unusual dependence on a flavin for dehalogenation and its contribution to iodide homeostasis and thyroid function in higher organisms. This enzyme also has the potential to serve as a marker to trace the origins of cell signaling by iodinated compounds that ultimately culminated in the development of the mammalian thyroid.
A prerequisite for tracing IYD through the tree of life is a robust set of structural determinants. Automated sequence analysis will typically assign a protein to the correct superfamily but is much less reliable in predicting its function.15 Additions to the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily are often broadly annotated as nitroreductases without regard to their potential catalytic diversity. The co-crystal structure of mouse (mm) IYD and MIT identified key residues that are expected to be diagnostic of deiodinase activity and not required by other activities within the superfamily.11 The side chains of E153, Y157, and K178 interact directly with the zwitterion portion of MIT and appear critical for function (Fig. 2).16 Although the mutation Y157F only diminished the kcat/Km of mmIYD for turnover of DIT by ~ 35%, the affinity for MIT was suppressed by 20-fold.16 More dramatic was the complete loss of catalytic activity and substrate affinity for the mutation E153Q.16 Comparable analysis of K178G was not possible since the resulting protein could not be expressed in a soluble form.
Fig. 2.
Active site region of iodotyrosine deiodinase from mouse is established by both subunits of its α2 dimer (preen and purple) and contains flavin (FMN), monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and the key residues stabilizing their complex (PDB ID 3GFD).
The amide nitrogen of A126 provides yet another interaction to the substrate of IYD by coordinating to its phenolic OH group. BluB contains a Gly at an equivalent site (G61) but lacks all key residues responsible for coordinating MIT.12 Another distinction is the T235 in IYD and the S167 in BluB that provide a side chain hydrogen bond to the O4 and N5 of FMN.11,12 No equivalent activation of FMN is evident in the remaining members of the superfamily. As described below, the residues corresponding to A126, E153, Y157, K178 and T235 of mmIYD now accurately predict deiodinase activity (Fig. 3). The presence of IYD extends well beyond initial expectations and includes diverse organisms not previously associated with a need for iodide conservation.
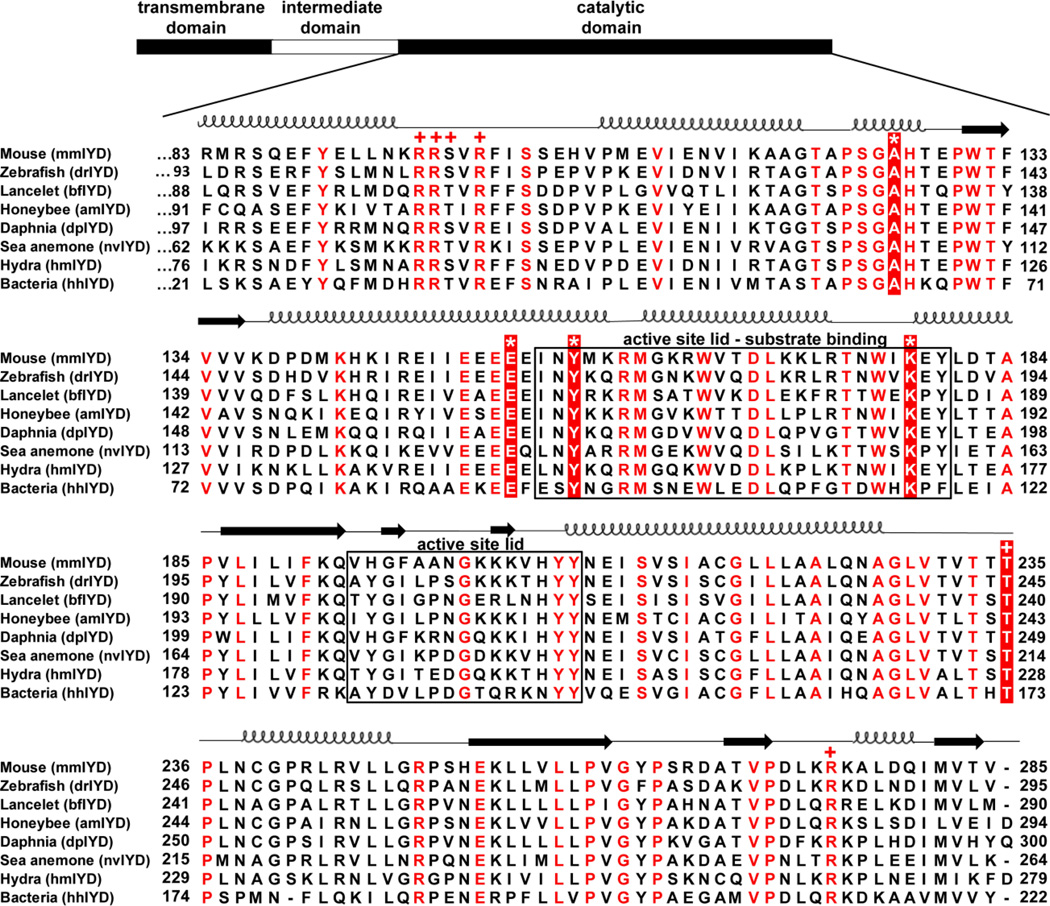
Fig. 3. Multiple sequence alignment of the catalytic domains of IYD homologs.
Alignment of homologs chosen for protein expression was generated using MUSCLE.45 Numbering of the amino acids for each protein is indicated on the left and right of the alignment. Residues in red (or white) are fully conserved, and the sequences forming the active site lids are indicated with a box. Key residues coordinating to substrate and FMN are indicated with an (*) and (+), respectively. Secondary structure elements are derived from the crystal structure of mmIYD bound to DIT (PDB ID 3GH8).11
Methods
Cloning of homologous genes
IYD homologs from zebrafish, lancelet and honeybee were truncated to remove their N-terminal membrane domains predicted by TMHMM (supplementary Table S1).17 Full length sequences were used for IYD homologs from daphnia, sea anemone, hydra and the bacterium Haliscomenobacter hydrossis (DSM 1100). Each gene included a C-terminal His6 tag and flanking 5’ BamHI and 3’ XhoI restriction sites. Genes were synthesized (Blue Heron Biotechnology and GenScript) and subcloned to create SUMO-fusions in the pSMT3 plasmid18 kindly provided, along with the expression vector for the SUMO-specific protease Ulp1, by Dr. C. Lima (Memorial Sloan-Kettering Institute).
Expression of IYD homologs
Rosetta 2(DE3) E. coli cells were transformed with the appropriate pSMT3 plasmid and grown in LB media containing kanamycin and chloramphenicol at 37°C with shaking to an OD600 of 0.6–0.8. The media was then cooled and supplemented with isopropyl-β-D-thiogalacto- pyranoside as summarized in supplementary Table S2. Cells were harvested, resuspended in lysis buffer (500 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM DTT, 10% glycerol and 50 mM sodium phosphate pH 8.0) and lysed by three passages through a French press cell at 1000 psi. The lysates were centrifuged at 40,000 g for 2 hrs.
Purification of IYD homologs
SUMO-IYD fusions were purified by Ni2+ affinity chromatography using HisPur Ni-NTA resin. Supernatant was loaded and washed with 5 column volumes of lysis buffer containing increasing concentrations of imidazole (20 mM, 60 mM and 100 mM). SUMO-IYD fusions were eluted with 250 mM imidazole and treated with Ulp1 (1:200 w/w). Proteins from zebrafish (drIYD), lancelet (bfIYD), honeybee (amIYD) and H. hydrossis (hhIYD) were further purified using a 1 ml HiTrap Ni2+ column. This was washed successively with 20 mM imidazole (10 ml), 60 mM imidazole (10 ml) and 100 mM imidazole (5 ml) in lysis buffer. The proteins were eluted with 250 mM imidazole in lysis buffer. Homologs from sea anemone (nvIYD), daphnia (dpIYD) and hydra (hmIYD) were dialyzed with 300 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, 10% glycerol and 50 mM sodium phosphate pH 8.0 and further purified by size exclusion chromatography using Sephacryl S-200 HR resin. A third affinity step using a HiTrap Ni2+ column as described above was necessary for dpIYD.
The amino acid sequence of the active dpIYD fragment was identified by N-terminal sequencing (JHMI sequencing and synthesis facility). The extinction coefficients (ε280) for the IYD homologs were determined from their amino acid sequence using ExPASy ProtParam.19 The concentration of FMN bound to enzyme was determined from A450 (ε450 12,500 M−1 cm−1),20 and the concentration of enzyme was determined from its A280 after correcting for FMN absorbance using A280/A450 of 1.57.
Estimation of enzyme concentration for hmIYD
Western blotting was used to confirm the presence of hmIYD in isolates exhibiting deiodinase activity (supplementary Fig. S2). Total protein concentration was determined by the BCA assay per manufacturer’s protocol (Pierce), and the percentage of hmIYD was determined by densitometric analysis of a Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel using ImageQuant TL. The concentration of hmIYD was estimated from its average MW (33.5 kDa) observed in supplementary Figs. S1B and S2B.
Assay for catalytic activity
The rate of [125I]-iodide release from [125I]-DIT was determined by a discontinuous assay reported previously.7,21 Values of kcat were calculated based on protein concentration as opposed to FMN occupancy since excess FMN is present in the activity assay. BluB (gift of Dr. M. E. Taga, UC Berkeley) was tested for native activity by a FMN depletion assay22 in the presence a FMN reductase (SsuE, gift of Dr. H. R. Ellis, Auburn University).
Results
Selection and sequence analysis of IYD homologs
Using the sequence of mmIYD as reference, BLAST23 identified homologous proteins within the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily from a wide range of organisms. Most sequences within the animal kingdom were annotated as deiodinases, but some from invertebrates lacked annotation, and most from bacteria were annotated as nitroreductases or simply as oxidoreductases. To test the predictive powers of the IYD determinants described above, genes from organisms representing distinct phyla and classes within Metazoa as well as one from Eubacteria were chosen for expression in E. coli (Fig. 4). The specific examples were selected based on a variety of criteria including an absence of domains superfluous to IYD activity and a minimal number of cysteines to avoid potential problems with protein folding. Organisms that have become representative of a phylum or class were also chosen when possible. Until very recently, few potential genes for IYD had been identified in bacteria, but a candidate from H. hydrossis seemed intriguing since this species is commonly found in waste water after sewage treatment.24 The selected homologs all contained the conserved residues of the active site lid region that distinguishes the IYD subgroup within the superfamily and those critical for substrate and FMN coordination (Fig. 3).11,16
Fig. 4. The tree of life.
A tree indicating the diversity of organisms in which IYD homologs were identified and chosen for expression. Phylum and class for each organism were obtained from the NCBI taxonomy browser.46 Branches are not drawn to scale.
Expression and purification of IYD homologs
Candidate proteins were expressed as fusions with SUMO to enhance their solubility. The final yields of drIYD, amIYD, nvIYD and hhIYD after purification ranged from 3 to 5 mg/L of growth media. Expression of bfIYD, dpIYD and hmIYD primarily formed inclusion bodies even under optimized conditions (supplementary Table S2), and yields of active enzyme were consequently less than 1 mg/L of growth media. The active fraction isolated for dpIYD was found to be truncated in situ by 55 amino acids from the N-terminus. Multiple proteins were evident after separation of the soluble fraction of SUMO-hmIYD by Ni2+ affinity chromatography. As evident from densitometry, only ~55% of the soluble protein was susceptible to Ulp1, the protease used to remove the SUMO fusion. This is consistent with misfolding of the expressed protein. Further purification using size exclusion chromatography yielded an active fraction containing multiple proteins including those derived from SUMO- hmIYD and host proteins as identified by Western blot and Coomassie staining (supplementary Fig. S2). A truncated SUMO-hmIYD comprising ca. 15% of the protein was detected in the active fraction by scanning densitometry. Difficulties in hmIYD expression likely arose from use of sequence information that has since been revised in the NCBI database. The updated version differs in the first 42 amino acids. All other IYD homologs were purified to homogeneity (supplementary Fig. S1), and most contained FMN at 95% occupancy. Only nvIYD and hmIYD had lower FMN occupancies of 55% and 59% respectively
Catalytic activity
All homologs showed deiodinase activity with DIT as a substrate. Their kcat/Km values were clustered between ca. 0.3 min−1 µM−1 to 3.5 min−1 µM−1 (Table 1). Their Km values ranged from 4 µM to 105 µM and kcat values ranged from 4.1 min−1 to 32 min−1. The sea anemone enzyme (nvIYD) generated the highest Km and kcat values, but the daphnia and hydra enzymes (dpIYD and hmIYD, respectively) generated the highest kcat/Km values. In contrast, the closest structural homolog of IYD (BluB) expressed no deiodinase activity above the limit of detection at Km ≥ 133 µM, kcat ≤ 0.06 min−1 and a kcat/Km ≤ 5 × 10−4 min−1 µM−1. Likewise, no BluB-like activity was previously observed for mmIYD after its reduced form was exposed to molecular oxygen,25 and physiological concentrations of reduced nicotinamides were not capable of driving efficient turnover of mmIYD as expected if it could express a flavin or nitroreductase activity.26
Table 1.
Iodotyrosinedeiodinase activity of homologs.
| Organism |
Km (µM)c |
kcat (min−1)c |
kcat/Km (min−1µM−1)c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse (mmIYD)a | 19 ± 3 | 6.9 ± 1.3 | 0.36 ± 0.09 |
| Zebrafish (drIYD) | 8 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 0.51 ± 0.07 |
| Lancelet (bfIYD) | 6 ± 3 | 7 ± 1 | 1.2 ± 0.6 |
| Honeybee (amIYD) | 29 ± 7 | 8 ± 1 | 0.28 ± 0.07 |
| Daphnia (dpIYD) | 7 ± 1 | 17.6 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.4 |
| Sea anemone (nvIYD) | 105±26 | 32 ± 4 | 0.30 ± 0.08 |
| Hydra (hmIYD)b | 4 ± 1 | 14 ± 1 | 3.5 ± 0.9 |
| Bacteria (hhIYD) | 6.6±0.9 | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
Parameters for mmIYD were previously reported.16
Parameters kcat and kcat/Km calculated from estimated enzyme concentration (see experimental procedures).
Significant figures were determined from the magnitude of associated uncertainties.
Discussion
All of the tested homologs expressed iodotyrosine deiodinase activity with kcat/Km values narrowly distributed over a single order of magnitude, and thus the key residues selected from the crystal structure of mmIYD (Fig. 2) are excellent criteria for predicting deiodinase activity within the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily. Phylogenetic analysis of the catalytic domains of the deiodinases, nitro-FMN reductases and BluB (Fig. 5) suggests a divergent evolution from a common prokaryotic ancestor. BluB, the closest structural relative of IYD, did not exhibit deiodinase activity although BluB and IYD have active site lids that derive from the same region of primary sequence11,12 and flavin chemistry that is poised for sequential one electron transfer processes.4 The same lid regions are not evident in NOX and FRP and instead other regions of their primary sequence form their active site lids. Such differences serve to distinguish the subclasses of enzymes within the supferfamily.11 NOX and FRP are also distinct from the IYD and BluB subclasses by promoting substrate reduction through an obligate two electron process.10
Fig. 5. Phylogenetic analysis focusing on the IYD branch of the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily.
A phylogenetic tree was generated by phylogeny.fr47 integrating MUSCLE,45 PhyML,48 and TreeDyn49 for multiple sequence alignment, phylogenetic analysis and tree rendering, respectively. Catalytic domains of IYD homologs and aligned regions of BluB (PDB ID 2ISJ), NOX (PDB ID 1NOX) and FRP (PDB ID 2BKJ) were used as input sequences. The branch lengths are proportional to the number of amino acid substitutions per aligned residue.
The presence of IYD in Craniata (Fig. 4) is easily explained by the presence of a thyroid gland, its associated TH and the concomitant need to salvage the scarce nutrient iodide.27 IYD and iodide salvage is also expected in the remaining branches of Chordata lacking the thyroid. For example, the genome of lancelet contains homologs of most genes required for generating TH and an endostyle that may represent a proto-thyroid.28 The presence of deiodinase activity in Arthropoda is very intriguing since there is no confirmed evidence for endogenous synthesis of TH29 although a limited number of reports suggest that TH can be obtained exogeneously29,30 and affect insect metabolism.31–33 The requirements for iodide recycling and the effects of iodinated amino acids on insect development has yet to be determined.33 IYD might even have an alternative role in catabolism of scleroproteins that often contain halogenated tyrosines.27
The physiological role of IYD in the cnidarians hydra and sea anemone is currently unknown, and no reports on their sensitivity to iodide, iodotyrosine or TH could be found. However, these materials are all capable of initiating strobilation (metamorphosis from polyp to medusa) in another cnidarian, the jellyfish Aurelia aurita.34 DIT was most effective in these studies and is consistent with a proposal that iodotyrosines could be evolutionary precursors of THs.35 This presents a possibility that IYD may assume a regulatory role by its ability to degrade this primitive iodinated signal.
An equivalent function cannot be extrapolated to bacteria (e.g., H. Hydrossis) even though certain strains have been shown to accumulate iodine.36,37 More likely, bacterial IYD serves a catabolic or detoxification role enabling the bacteria to adapt to environments containing iodinated compounds such as those created by algae blooms. Chlorinated and brominated derivatives may also be consumed by bacterial IYD since at least mmIYD is known to dehalogenate bromo- and chlorotyrosine.25
A recent BLAST search using stringencies lower than those of our original survey (including hits with expect values > 10−59) revealed over 200 bacteria contain proteins within the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily that should now be classified as deiodinases according to the criteria established in this study. Some species even contain genes from multiple subclasses of the nitro-FMN reductase superfamily. For example, IYD and a FMN reductase are present in Vibrio harveyi, a model bacterium for bioluminescence and quorum sensing studies.38,39 Similarly, IYD and a nitroreductase are present in Deinococcus peraridilitoris, a recent addition to the Deinococcus genus of bacteria resistant to ionizing radiation.40
A few candidate deiodinases are also evident in Archaea (e.g. Pyrococcus furiosus) although these consistently contain a Met at the site corresponding to A126 in mmIYD. Their presence may originate from lateral gene transfer between thermophilic bacteria that also contain the Ala to Met substitution.41 In contrast, no deiodinase gene has yet been discovered in Fungi. Even Neurospora crassa that relies significantly on flavoproteins for metabolism42 does not contain an IYD gene. The genes most related to IYD in fungi had very weak homologies as indicated by e values of greater than 9 ×10−6. Greater homologies were evident between FRP and its homologues in fungi (e ≥ 10−39). In contrast, no protein sequences from plants registered an e value of less than 0.2 when compared to IYD, BluB, NOX or FRP.
Conclusion
The successful identification of a specialized enzyme such as IYD in diverse organisms demonstrates the importance of experimental data to support the functional assignment of a flavoprotein.42,43 IYD revealed an origin that is much more ancient than would be anticipated by its iodide salvage activity in mammals and may indicate requirements for iodide or iodinated molecules in most multicellular organisms. The enzyme is now ready to join the ranks of other TH-associated proteins in describing the evolution of TH signaling.28,44
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Ellis, Lima and Taga for providing essential materials for this study, Dr. Stephen Mount for many helpful discussions and support from NIH grant RO1 DK084186 to SER.
Footnotes
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: NCBI accession numbers for IYD homologs chosen for expression; optimized conditions for expressing IYD homologs; SDS-PAGE gel images of purified IYD homologs; identification of active IYD from hydra (hmIYD); deiodination rate dependence on DIT concentration for IYD homologs. See DOI: 10.1039/b000000x/
References
- 1.Mohn WW, Tiedje JM. Microbiol. Rev. 1992;56:482–507. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.3.482-507.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pandey J, Heipieper HJ, Chauhan A, Arora PK, Prakash D, Takeo M, Jain RK. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011;92:597–607. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3254-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.St. Germain DL, Galton VA, Hernandez A. Endocrinology. 2009;150:1097–1107. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rokita SE, Adler JM, McTamney PM, Watson JA., Jr Biochimie. 2010;92:1227–1235. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Callebaut I, Curcio-Morelli C, Mornon JP, Gereben B, Buettner C, Huang S, Castro B, Fonseca TL, Harney JW, Larsen PR, Bianco AC. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:36887–36896. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305725200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berry MJ, Kieffer JD, Harney JW, Larsen PR. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:14155–14158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Friedman JE, Watson JA, Lam DWH, Rokita SE. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:2812–2819. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510365200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goswami A, Rosenberg IN. J. Biol. Chem. 1979;254:12326–12330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rokita SE. In: Handbook of Flavoproteins. Hille R, Miller SM, Palfey B, editors. Vol. 1. Berlin: DeGruyter; 2013. pp. 337–350. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roldán MD, Pérez-Reinado E, Castillo F, Moreno-Vivián C. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008;32:474–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Thomas S, McTamney PM, Adler JM, LaRonde-LeBlanc N, Rokita SE. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:19659–19667. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.013458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taga ME, Larsen NA, Howard-Jones AR, Walsh CT, Walker GC. Nature. 2007;446:449–453. doi: 10.1038/nature05611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hecht HJ, Erdmann H, Park HJ, Sprinzl M, Schmid RD. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995;2:1109–1114. doi: 10.1038/nsb1295-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tanner JJ, Lei B, Tu SC, Krause KL. Biochemistry. 1996;35:13531–13539. doi: 10.1021/bi961400v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schnoes AM, Brown SD, Dodevski I, Babbit PC. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2009;5:e1000605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Buss JM, McTamney PM, Rokita SE. Protein. Sci. 2012;21:351–361. doi: 10.1002/pro.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer ELL. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;303:567–580. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mossessova E, Lima CD. Mol. Cell. 2000;5:865–876. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud S, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A. Walker JM. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2005. pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jacek K. Methods Enzymol. 1971;18:253–285. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rosenberg IN, Goswami A. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:488–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yu T-Y, Mok KC, Kennedy KJ, Valton J, Anderson KS, Walker GC, Taga ME. Protein. Sci. 2012;21:839–849. doi: 10.1002/pro.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kotay SM, Datta T, Choi J, Goel R. Water Res. 2011;45:694–704. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McTamney PM, Rokita SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:14212–14213. doi: 10.1021/ja906642n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Watson JA, Jr, McTamney PM, Adler JM, Rokita SE. ChemBioChem. 2008;9:504–506. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Valverde-R. C, Orozco A, Becerra A, Jeziorski MC, Villalobos P, Solis-S JC. Int. Rev. of Cytology. 2004;234:143–199. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)34004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Paris M, Brunet F, Markov GV, Schubert M, Laudet V. Dev. Genes Evol. 2008;218:667–680. doi: 10.1007/s00427-008-0255-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Eales JG. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997;214:302–317. doi: 10.3181/00379727-214-44098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Heyland A, Moroz LL. J. Exp. Biol. 2005;208:4355–4361. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Thyagaraja BS, Masler EP, Kelly TJ, Borkovec AB. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1993;104A:247–253. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Davey KG. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000;30:877–884. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(00)00061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Flatt T, Moroz LL, Tatar M, Heyland A. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2006;46:777–794. doi: 10.1093/icb/icl034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Silverstone M, Galton VA, Ingbar SH. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1978;34:132–140. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(78)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Crockford SJ. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2009;49:155–166. doi: 10.1093/icb/icp053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Amachi S, Mishima Y, Shinoyama H, Muramatsu Y, Fujii T. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;71:741–745. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.2.741-745.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li H-P, Brinkmeyer R, Jones WL, Zhang S, Xu C, Schwehr KA, Santschi PH, Kaplan DI, Yeager CM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77:2153–2160. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02164-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bassler BL, Wright M, Showalter RE, Silverman MR. Mol. Microbiol. 1993;9:773–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Surette MG, Miller MB, Bassler BL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999;96:1639–1644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rainey FA, Ferreira M, Nobre MF, Ray K, Bagaley D, Earl AM, Battista JR, Gómez-Silva B, McKay CP, da Costa MS. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007;57:1408–1412. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64956-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nelson KE, Clayton RA, Gill SR, Gwinn ML, Dodson RJ, Haft DH, Hickey EK, Peterson JD, Nelson WC, Ketchum KA, McDonald L, Utterback TR, Malek JA, Linher KD, Garrett MM, Stewart AM, Cotton MD, Pratt MS, Phillips CA, Richardson D, Heidelberg J, Sutton GG, Fleischmann RD, Eisen JA, White O, Salzberg SL, Smith HO, Venter JC, Fraser CM. Nature. 1999;399:323–329. doi: 10.1038/20601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Macheroux P, Kappes B, Ealick SE. FEBS J. 2011;278:2625–2634. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim J, Copley SD. Biochemistry. 2013;52:2905–2913. doi: 10.1021/bi4003343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Heyland A, Hodin J, Reitzel AM. Bioessays. 2005;27:64–75. doi: 10.1002/bies.20136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Edgar RC. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sayers EW, Barrett T, Benson DA, Bryant SH, Canese K, Chetvernin V, Church DM, DiCuccio M, Edgar R, Federhen S, Feolo M, Geer LY, Helmberg W, Kapustin Y, Landsman D, Lipman DJ, Madden TL, Maglott DR, Miller V, Mizrachi I, Ostell J, Pruitt KD, Schuler GD, Sequeira E, Sherry ST, Shumway M, Sirotkin K, Souvorov A, Starchenko G, Tatusova TA, Wagner L, Yaschenko E, Ye J. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:D5–D15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM, Gascuel O. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:W465–W469. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Guindon S, Dufayard J-F, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O. Syst. Biol. 2010;59:307–321. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syq010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chevenet F, Brun C, Banuls A-L, Jacq B, Christen R. BMC Bioinfomatics. 2006;7:439. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.