Abstract
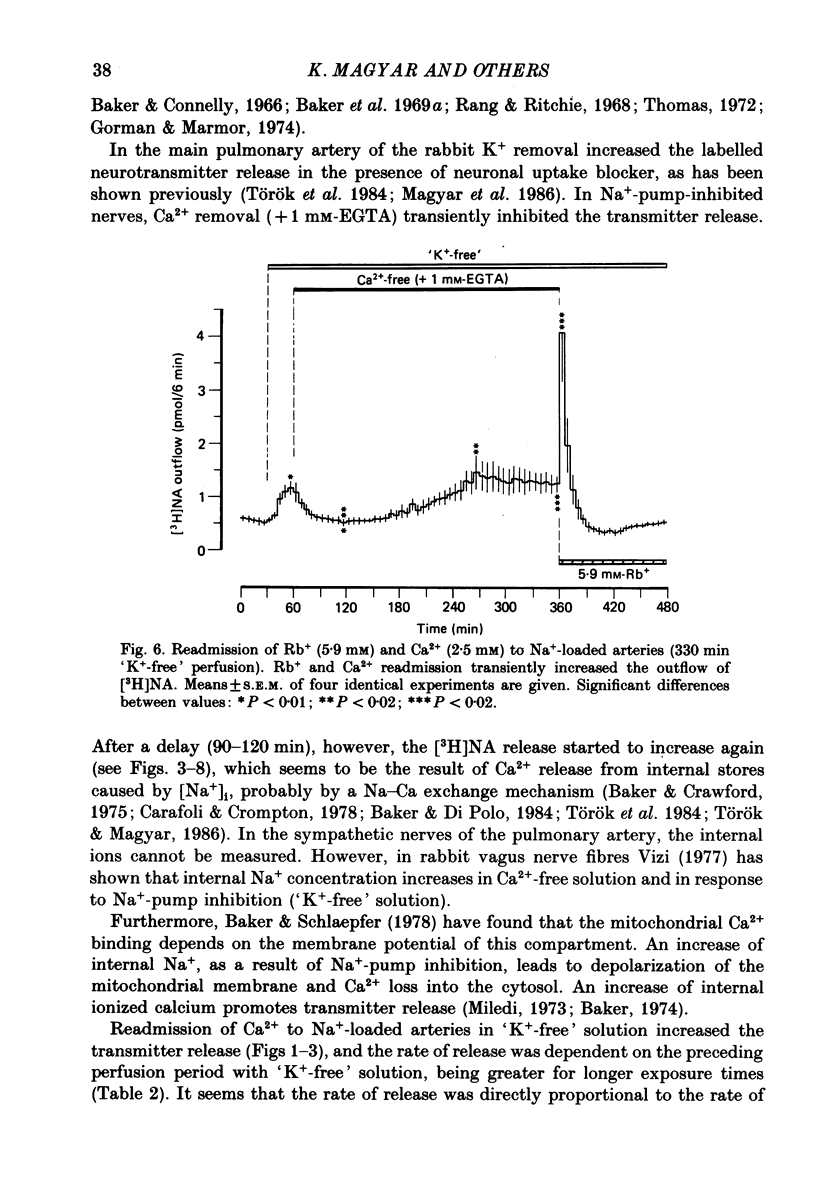
1. The release of [3H]noradrenaline ([3H]NA) from the isolated main pulmonary artery of the rabbit has been measured in the presence of neuronal (cocaine, 3 X 10(-5) M) and extraneuronal (corticosterone, 5 X 10(-5) M) uptake blockers. 2. K+ removal from the external medium increased the release of [3H]NA, an action transiently inhibited by Ca2+-free (+1 mM-EGTA) solution, i.e. after Ca2+ removal transmitter release was first abolished and then started to increase again after a delay lasting about 90-120 min. 3. Ca2+ readmission to arteries which had been kept in Ca2+- and 'K+-free' solution, markedly increased the [3H]NA release. The rate of transmitter release was dependent on the preceding perfusion period with 'K+-free' solution, being greater for longer exposure times. 4. When Ca2+ and K+ were readmitted together to K+-depleted and Na+-enriched preparations, the release of [3H]NA transiently increased. 5. If K+ was readmitted first, the subsequently applied Ca2+ was ineffective in producing transmitter release. 6. Different alkali metal ions (Rb+, Cs+ or Li+) were also readmitted as K+ substitutes together with Ca2+. In all cases the release of neurotransmitter transiently increased; however, the rate of release was dependent on the monovalent cation used. Thus, Rb+ ions were as effective as, Cs+ about one-third as effective as, and Li+ about one-fifth as effective as K+ in activating the Na+ pump. 7. It is concluded that in the absence of external Ca2+, and in response to Na+-pump inhibition, the release of Ca2+ from internal stores is responsible for the NA release observed. On readmission of Ca2+ the rate of transmitter release is dependent on the Na+ previously gained inside. Furthermore, the activity of the Na+ pump determines the rate of transmitter release through the Na-Ca exchange mechanism.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Allen T. J. The voltage-sensitivity of Na-Ca exchange in the squid axon. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;168:89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L., Steinhardt R. A. The influence of calcium on sodium efflux in squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):431–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Connelly C. M. Some properties of the external activation site of the sodium pump in crab nerve. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):270–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. A note of the mechanism by which inhibitors of the sodium pump accelerate spontaneous release of transmitter from motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):209–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Schlaepfer W. W. Uptake and binding of calcium by axoplasm isolated from giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:103–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. The regulation of intracellular calcium in giant axons of Loligo and Myxicola. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:250–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. The sodium pump. Endeavour. 1966 Sep;25(96):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0160-9327(66)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Kendrick N. C., Schweitzer E. S. Calcium buffering in presynaptic nerve terminals. I. Evidence for involvement of a nonmitochondrial ATP-dependent sequestration mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):15–41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W., Schweitzer E. S. Control of intracellular calcium in presynaptic nerve terminals. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2790–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Santiago E. M. Effects of internal and external cations and of ATP on sodium-calcium and calcium-calcium exchange in squid axons. Biophys J. 1977 Oct;20(1):79–111. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85538-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Starke K., Ehrl H., Endo T. A comparison of pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-adrenolytic drugs in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1977;2(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr Regulation of intracellular calcium in squid axons. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2778–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Okamoto K., Quastel D. M. The role of calcium in depolarization-secretion coupling at the motor nerve terminal. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):459–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipolo R. Effect of ATP on the calcium efflux in dialyzed squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Oct;64(4):503–517. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.4.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Feldman D. S. Effects of sodium pump inhibitors on spontaneous acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):498–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Starke K., Bangerter A., Taube H. D. Presynaptic receptor systems on the noradrenergic neurones of the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;296(3):229–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00498689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Marmor M. F. Long-term effect of ouabain and sodium pump inhibition on a neuronal membrane. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):49–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Willis W. D. The effects of depolarization of motor nerve terminals upon the release of transmitter by nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):381–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau E. M. The interaction of presynaptic polarization with calcium and magnesium in modifying spontaneous transmitter release from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):281–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Tov A., Rahamimoff R. A study of tetanic and post-tetanic potentiation of miniature end-plate potentials at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:247–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magyar K., Nguyen T. T., Török T. L., Tóth P. T. The action of excess potassium and calcium on ouabain-evoked [3H]-noradrenaline release from the rabbit pulmonary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):63–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw C. F., Somlyo A. V., Blaustein M. P. Probing for calcium at presynaptic nerve terminals. Fed Proc. 1980 Aug;39(10):2796–2801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. Tetanic and post-tetanic rise in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in low-calcium solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):245–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. A mechanism for Na/Ca transport. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):681–695. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato Y., Ohga A., Onoda Y. The effect of ouabain on noradrenaline output from peripheral adrenergic neurones of isolated guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:45–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis D. A. Cardiac glycosides and autonomic neurotransmission. J Auton Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;3(2):127–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1983.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Montel H., Gayk W., Merker R. Comparison of the effects of clonidine on pre- and postsynaptic adrenoceptors in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Alpha-sympathomimetic inhibition of Neurogenic vasoconstriction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;285(2):133–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00501149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Electrogenic sodium pump in nerve and muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):563–594. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török T. L., Magyar K. Ouabain-evoked [3H]noradrenaline release from the rabbit pulmonary artery in calcium-free solution. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Jan;71(1):105–114. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török T. L., Salamon Z., Nguyen T. T., Magyar K. Spontaneous [3H]noradrenaline release from the main pulmonary artery of the rabbit induced by sodium-pump inhibition. Q J Exp Physiol. 1984 Oct;69(4):841–865. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1984.sp002873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Termination of transmitter release by stimulation of sodium-potassium activated ATPase. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):261–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


