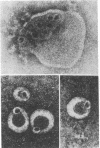
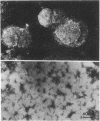
Abstract
The molecular basis of the membranolytic activity of the membrane attack complex (MAC) of complement was investigated. By using density gradient equilibrium ultracentrifugation, the binding of egg yolk lecithin to the isolated MAC and to its intermediate complexes and precursor proteins was measured. No stable phospholipid--protein complexes were formed with the MAC precursor components C5b--6, C7, C8, and C9. Stable complexes of phospholipid and protein were formed by C5b--7, C5b--8, C5b--9, and the MAC (C5b--9 dimer) and they exhibited densities of 1.2164, 1.184, 1.2055, and 1.2275 g/ml, respectively. The molar phospholipid/protein ratios for the four complexes were determined to be: C5b--7, 399:1, C5b--5, 841:1; C5b--9, 918:1; and C5b--9 dimer, 1460:1. Electron microscopy of the isolated phospholipid--protein complexes revealed no lipid bilayer structures. The magnitude of the phospholipid binding capacity of the MAC is consistent with the interpretation that the MAC forms phospholipid--protein mixed in micelles in lipid bilayers and biological membranes and thus causes formation of hydrophilic lipid channels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Skrabal P., Hauser H. Single bilayer vesicles prepared without sonication. Physico-chemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):322–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer structure in the membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., BARROW P., GOLDBERG B. Effect of antibody and complement on permeability control in ascites tumor cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:699–713. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadding U., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: isolation, description and mode of action. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):719–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. A., Kinsky C. B., Kinsky S. C. Immune response of a liposomal model membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):300–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Dourmashkin R. R. The lesions in cell membranes caused by complement. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:75–115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles G. H., Seeman P., Naylor D., Cinader B. Membrane lesions in immune lysis: surface rings, globule aggregates and transient openings. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):528–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kinoshita T., Okada M., Akiyama Y. Release of phospholipids from complement-mediated lesions on the surface structure of Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Inoue K., Okada M., Akiyama Y. Release of phospholipids from liposomal model membrane damaged by antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):73–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Munn E. A., Weissmanng Complement-mediated lysis of liposomes produced by the reactive lysis procedure. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):983–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-9 complex: subunit composition of the classical and alternative pathway-generated complex. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1431–1434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Purification of the sixth and seventh component of human complement without loss of hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: formation, isolation, and inhibition of its activity by lipoprotein and the S-protein of human serum. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Binding of desoxycholate, phosphatidylcholine vesicles, lipoprotein and of the S-protein to complexes of terminal complement components. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1025–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by C: exposure of hydrophobic sites on activated C proteins. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by complement: the effect of length and unsaturation of the acyl chains in liposomal bilayers and the effect of cholesterol concentration in sheep erythrocyte and liposomal membranes. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1996–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Steady-state analysis of tracer exchange across the C5b-9 complement lesion in a biological membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobschall D., McKeon C. Step conductance increases in bilayer membranes induced by antibody-antigen-complement action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 1;413(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]