Abstract
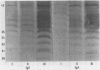
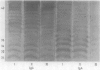
The occurrence of an outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicaemias on an oncology ward permitted an analysis of antibody responses in patients who were all orally exposed to the same source of infection. Seven patients became septicaemic. Serial serum samples were immunoblotted against the homologous strain. Responses were compared with those of 16 other patients with septicaemias caused by other strains and 10 healthy controls. All 18 survivors produced increasing IgG or IgA antibody, or both, against a 35,000 dalton band, whereas these antibodies were usually absent or fell in titre in the five fatal cases. These antibodies were also lacking in sera taken just before a patient became septicaemic. This band had the electrophoretic characteristics of the outer membrane porin protein F.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan C. S., Reynolds K. L., Brenner E. R. Analysis of 1,186 episodes of gram-negative bacteremia in non-university hospitals: the effects of antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):629–638. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A., Schoolnik G. K., Arko R. J. Protection against infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immunization with outer membrane protein complex and purified pili. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S132–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S. Evolving epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):156–159. doi: 10.1007/BF02013589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Passive protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in an experimental leukopenic mouse model. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):659–664. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.659-664.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Fürer E., Germanier R. Protection against fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound sepsis by immunization with lipopolysaccharide and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):795–799. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.795-799.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Pitt T. L., Fürer E., Germanier R. Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):508–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.508-513.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J. New insights into the epidemiology, pathogenesis and therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):153–155. doi: 10.1007/BF02013588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr, Parker M. G., Matthews J. M., Berg R. D. Use of a purified outer membrane protein F (porin) preparation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a protective vaccine in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):49–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.49-54.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haghbin M., Armstrong D., Murphy M. L. Controlled prospective trial of Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in children with acute leukemia. Cancer. 1973 Oct;32(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197310)32:4<761::aid-cncr2820320405>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mouat E. C., Speert D. P. Quantitation and identification of antibodies to outer-membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sera of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):220–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Mouat E. C. Immunotherapeutic potential of monoclonal antibodies against Pseudomonas aeruginosa protein F. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):224–227. doi: 10.1007/BF02013602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Antibody response of infected mice to outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.49-53.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y. Roles of exoenzymes and exotoxin in the pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the development of a new vaccine. Jpn J Exp Med. 1980 Jun;50(3):149–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Gupta J. L. Controlled trial of Pseudomonas immunoglobulin and vaccine in burn patients. Lancet. 1980 Dec 13;2(8207):1263–1265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92334-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J. S., Mutharia L. M., Hancock R. E., Høiby N., Lam K., Baek L., Costerton J. W. Immunogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane antigens examined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):88–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.88-98.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. C., Burnie J. P., Tabaqchali S. Immunoblot analysis of the serological response in systemic candidosis. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1415–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miler J. M., Spilsbury J. F., Jones R. J., Roe E. A., Lowbury E. J. A new polyvalent Pseudomonas vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Feb;10(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype strains. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):770–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus D. J., Morrison D., Andrews C., Lawrence E., Sell S. H., Wright P. F. Age-related response to two Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines. J Pediatr. 1982 Feb;100(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Longfield R. N., Karney W. W. Clinical significance of serum antibody responses to exotoxin A and type-specific lipopolysaccharides in patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Am J Med. 1983 Jun;74(6):980–987. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90795-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada S., Suzuki M., Kawamura T., Fujinaga S., Masuho Y., Tomibe K. Protection against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to lipopolysaccharides and outer membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):570–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Moody M., Young V. M. Relationship of colonization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa to development of Pseudomonas bacteremia in cancer patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:240–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Heard S. R., Richards M. A., Tabaqchali S. Gastrointestinal colonization and septicaemia with Pseudomonas aeruginosa due to contaminated thymol mouthwash in immunocompromised patients. J Hosp Infect. 1985 Dec;6(4):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(85)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Heard S. R., Richards M. A., Tabaqchali S. Outbreak of septicaemia due to contaminated mouthwash. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 8;289(6458):1584–1584. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6458.1584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Gordon J. Immunoblotting and dot immunobinding--current status and outlook. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Sep 4;72(2):313–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Meyer R. D., Armstrong D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine in cancer patients. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Oct;79(4):518–527. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-4-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]