Abstract
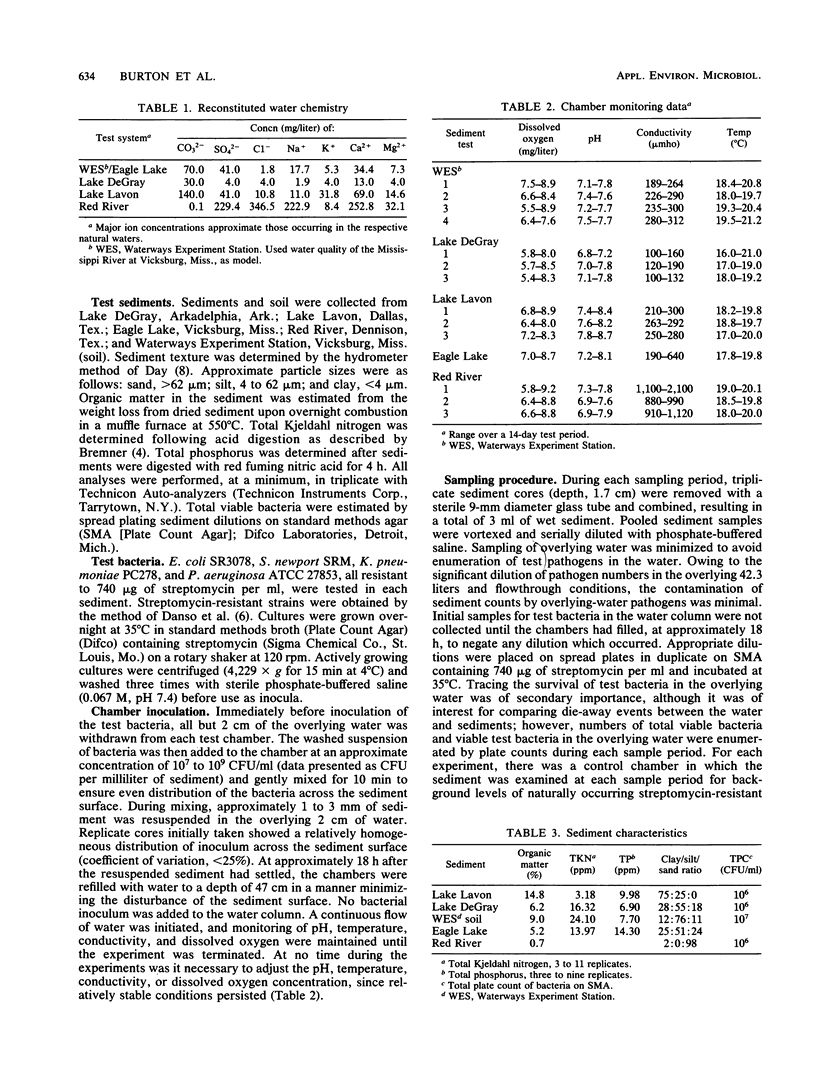
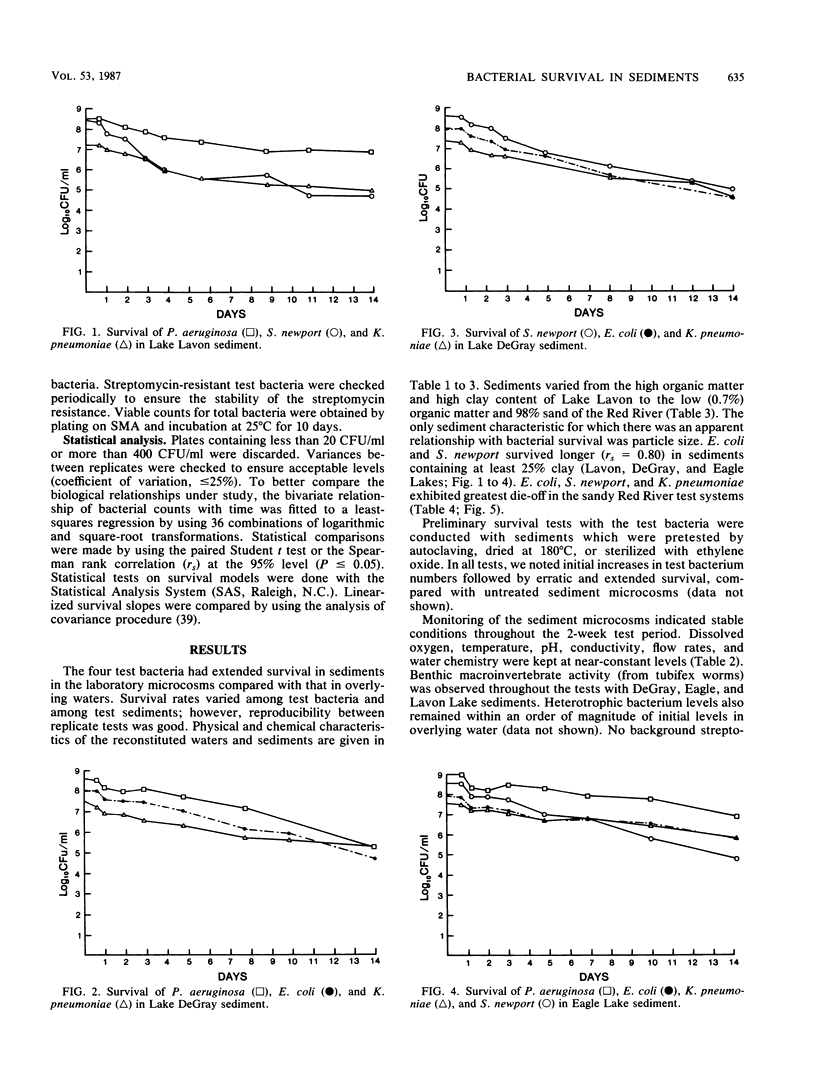
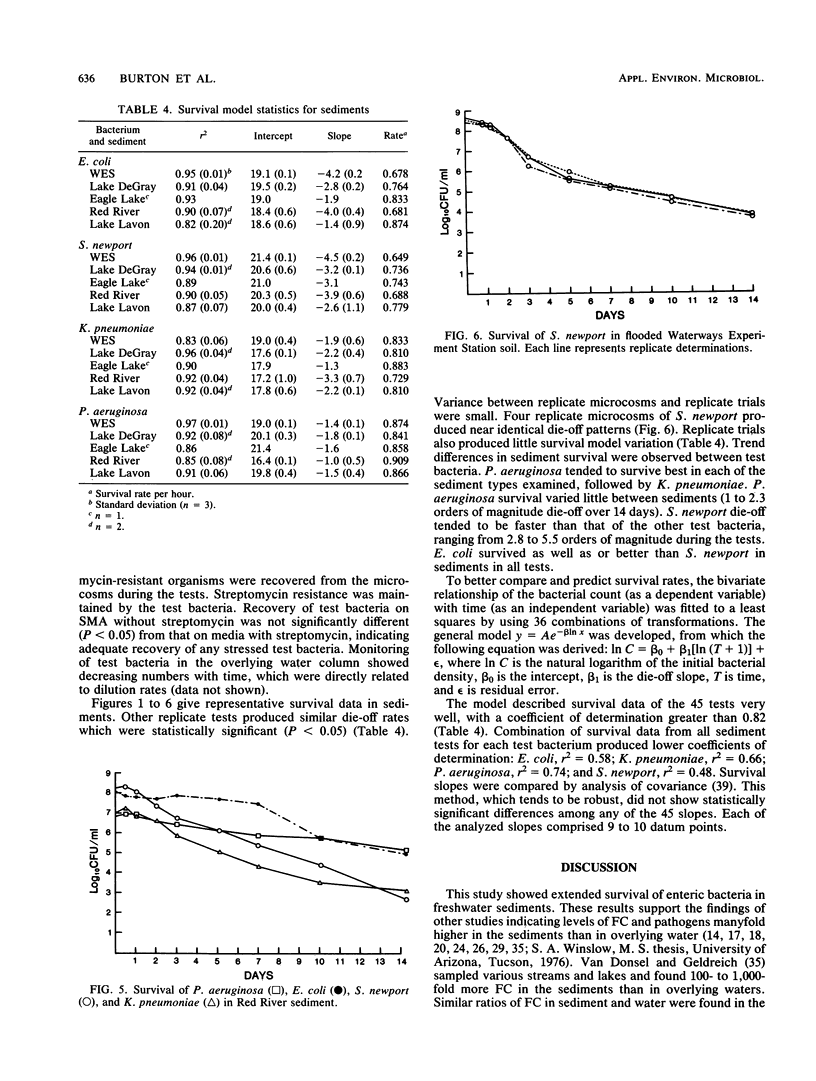
Four human-associated bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella newport, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, were tested for survival in five freshwater sediments. Bacterial survival in continuous-flow chambers was monitored over 14-day periods on sediments ranging from organically rich high-clay fractions to organically poor sandy fractions. Bacterial die-off ranged from 1 to 5 orders of magnitude in sediments. E. coli survived as long as or longer than S. newport. P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae tended to survive longer than E. coli. Survival of E. coli and S. newport was greater in sediments containing at least 25% clay. Good reproducibility allowed the development of linear models to describe die-off rates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard P. J. Longevity of Eberthella Typhosus in Various Soils. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1940 Sep;30(9):1077–1082. doi: 10.2105/ajph.30.9.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danso S. K., Habte M., Alexander M. Estimating the density of individual bacterial populations introduced into natural ecosytems. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Nov;19(11):1450–1451. doi: 10.1139/m73-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe L. L., Penrose W. R. "Bactericidal" property of seawater: death or debilitation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):829–833. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.829-833.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M. A., Aotaky A. E., Hargadon M. T. Effect of physical parameters on the in situ survival of Escherichia coli MC-6 in an estuarine environment. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):800–806. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.800-806.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG A. E. Survival of enteric organisms in sea water. Public Health Rep. 1956 Jan;71(1):77–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Best L. C., Kenner B. A., Van Donsel D. J. The bacteriological aspects of stormwater pollution. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1968 Nov;40(11):1861–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., McLeod J. S. Effect of sediments on the survival of Escherichia coli in marine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):114–120. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.114-120.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Adams W. N. Drug-resistant bacteria in Continental Shelf sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):861–862. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.861-862.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes D. J. Bacteriological water quality effects of hydraulically dredging contaminated upper Mississippi River bottom sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):782–789. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.782-789.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes D. J. Release of sediment-bound fecal coliforms by dredging. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):109–111. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.109-111.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Blake N. J. Relationship among fecal coliforms, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella spp. in shellfish. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.122-126.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E. Survival of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in estuarine waters and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):578–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.578-584.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurath G., Morita R. Y. Starvation-Survival Physiological Studies of a Marine Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1206–1211. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1206-1211.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBelle R. L., Gerba C. P., Goyal S. M., Melnick J. L., Cech I., Bogdan G. F. Relationships between environmental factors, bacterial indicators, and the occurrence of enteric viruses in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):588–596. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.588-596.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaLiberte P., Grimes D. J. Survival of Escherichia coli in lake bottom sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):623–628. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.623-628.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson E. A., Hornor S. G., Buck J. D. Pollution indicators and other microorganisms in river sediment. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1978 Jan;50(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett S., Bigley D. V., Grimes D. J. Distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a riverine ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):328–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.328-332.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. L., Alexander M. Role of resistance to starvation in bacterial survival in sewage and lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.410-415.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple K. L., Camper A. K., McFeters G. A. Survival of two enterobacteria in feces buried in soil under field conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):794–797. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.794-797.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos G. J., Swartz R. G. Survival of bacteria in seawater using a diffusion chamber apparatus in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):913–920. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.913-920.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


