Abstract
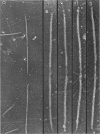
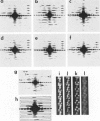
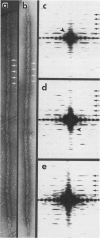
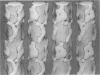
We have developed thick filament isolation methods that preserve the relaxed cross-bridge order of frog thick filaments such that the filaments can be analyzed by the convergent techniques of electron microscopy, optical diffraction, and computer image analysis. Images of the filaments shadowed by using either unidirectional shadowing or rotary shadowing show a series of subunits arranged along a series of right-handed near-helical strands that occur every 43 nm axially along the filament arms. Optical filtrations of images of these shadowed filaments show 4-5 subunits per half-turn of the strands, consistent with a three-stranded arrangement of the cross-bridges, thus supporting our earlier results from negative staining and computer-image analysis. The optical diffraction patterns of the shadowed filaments show a departure from the pattern expected for helical symmetry consistent with the presence of cylindrical symmetry and a departure of the cross-bridges from helical symmetry. We also describe a modified negative staining procedure that gives improved delineation of the cross-bridge arrangement. From analysis of micrographs of these negatively stained filament tilted about their long axes, we have computed a preliminary three-dimensional reconstruction of the filament that clearly confirms the three-stranded arrangement of the myosin heads.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caspar D. L., Cohen C., Longley W. Tropomyosin: crystal structure, polymorphism and molecular interactions. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):87–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellani L., Vibert P., Cohen C. Structure of myosin/paramyosin filaments from a molluscan smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):853–872. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowrashi P. K., Pepe F. A. Light meromyosin paracrystal formation. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):136–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R., Offer G. The location of C-protein in rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Mar 16;192(1109):451–461. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES R. E. A MOLECULAR THEORY OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION: CALCIUM-DEPENDENT CONTRACTIONS WITH HYDROGEN BOND FORMATION PLUS ATP-DEPENDENT EXTENSIONS OF PART OF THE MYOSIN-ACTIN CROSS-BRIDGES. Nature. 1963 Sep 14;199:1068–1074. doi: 10.1038/1991068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRosier D. J., Moore P. B. Reconstruction of three-dimensional images from electron micrographs of structures with helical symmetry. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):355–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Offer G. Shape and flexibility of the myosin molecule. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):505–519. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., NIEDERGERKE R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):971–973. doi: 10.1038/173971a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC PROTEIN FILAMENTS FROM STRIATED MUSCLE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Sep;7:281–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H., HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):973–976. doi: 10.1038/173973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C. A model of myosin crossbridge structure consistent with the low-angle x-ray diffraction pattern of vertebrate muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Jun;1(2):177–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00711798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C. X-ray evidence for conformational changes in the myosin filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 15;92(1):113–143. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Brown W. The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 14;30(2):383–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Faruqi A. R., Kress M., Bordas J., Koch M. H. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction studies of the myosin layer-line reflections during muscle contraction. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):637–684. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip W., Heuser J. Direct visualization of the myosin crossbridge helices on relaxed rabbit psoas thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 25;171(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer B., Szonyi E., Belcher C. D. "Hybrid" myosin filaments from smooth and striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 25;100(3):379–386. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. An electron microscopic and optical diffraction analysis of the structure of Limulus telson muscle thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):443–451. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. Determination of the handedness of the crossbridge helix of Limulus thick filaments. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):349–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00713042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Levine R. J., Stewart M. Electron microscopic and optical diffraction analysis of the structure of scorpion muscle thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):395–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensler R. W., Stewart M. Frog skeletal muscle thick filaments are three-stranded. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1797–1802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Kensler R. W., Reedy M. C., Hofmann W., King H. A. Structure and paramyosin content of tarantula thick filaments. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):186–195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Millman B. M. X-ray diffraction patterns from mammalian heart muscle. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 5;82(4):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic features in the amino acid sequence of nematode myosin rod. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 15;164(4):605–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F. Structure of the sheath of bacteriophage T4. I. Structure of the contracted sheath and polysheath. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):167–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. Relaxation of glycerinated muscle: low-angle x-ray diffraction studies. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Pepe F. A. Axial packing in light meromyosin paracrystals. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire J. M., Harford J. J., Edman A. C., Sjöström M. Fine structure of the A-band in cryo-sections. III. Crossbridge distribution and the axial structure of the human C-zone. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 15;155(4):467–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. H-protein and X-protein. Two new components of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):675–698. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polypeptide chains of intermediate molecular weight in myosin preparations. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 2;15(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. Structure of Limulus telson muscle thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):781–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Kensler R. W., Levine R. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of thick filaments from Limulus and scorpion muscle. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):402–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. A., Amos L. A. A new model for the geometry of the binding of myosin crossbridges to muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):297–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J., Elliott A. Effect of substrate on freeze-dried and shadowed protein structures. J Microsc. 1982 May;126(Pt 2):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varriano-Marston E., Franzini-Armstrong C., Haselgrove J. C. The structure and disposition of crossbridges in deep-etched fish muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Aug;5(4):363–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00818256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P., Craig R. Electron microscopy and image analysis of myosin filaments from scallop striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 5;165(2):303–320. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley N. G. The lattice spacing of crystalline catalase as an internal standard of length in electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Sep;24(5):454–464. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi N., O'Brien E. J., Matsubara I. Changes of thick filament structure during contraction of frog striated muscle. Biophys J. 1981 Jan;33(1):121–137. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84876-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]