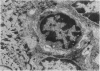
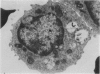
Abstract
We have isolated Fc receptor bearing cells from murine epidermis and examined these cells using both structural and functional methods. From 60 to 70% of these cells are Ia positive, phagocytic and express Mac 1 and F4.80 markers. They do not have Birkbeck granules in their cytoplasm. In functional studies these cells are not active as inducer cells in allogeneic and mitogen responses. The results do not support direct homology between these Langerhans cells and the interdigitating dendritic cell. Thus within the epidermis these cells may be more closely related to a macrophage, possibly involved in antigen uptake.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Tamaki K., Sachs D. H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):324–326. doi: 10.1038/282324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Balfour B. M., Armstrong J. A., Griffiths S. Functional anatomy of lymph nodes. II. Peripheral lymph-borne mononuclear cells. Anat Rec. 1978 Jan;190(1):5–21. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake P., Clark E. A., Khorshidi M., Sunshine G. H. Production and characterization of cytotoxic Thy-1 antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. Detection of T cell subsets. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Nov;9(11):875–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptak W., Rozycka D., Askenase P. W., Gershon R. K. Role of antigen-presenting cells in the development and persistence of contact hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):362–375. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells mature into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):526–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Nussenzweig M. C. Dendritic cells: features and functions. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:127–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Clement L., Green I., Shevach E. M. Immunologic functions of Ia-bearing epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2005–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunshine G. H., Katz D. R., Czitrom A. A. Heterogeneity of stimulator cells in the murine mixed leukocyte response. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):9–15. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki K., Stingl G., Gullino M., Sachs D. H., Katz S. I. Ia antigens in mouse skin are predominantly expressed on Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):784–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbecke G. J., Silberberg-Sinakin I., Flotte T. J. Langerhans cells as macrophages in skin and lymphoid organs. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):32–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilders M. M., Sminia T., Janse E. M. Ontogeny of non-lymphoid and lymphoid cells in the rat gut with special reference to large mononuclear Ia-positive dendritic cells. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):303–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]