Abstract
Background
A rare disease is that an individual with a non-chimeric karyotype of 45,X develops into a male. We explored the genetic aetiology of an infertile male with an apparent 45,X karyotype, which was subsequently verified as cryptic translocation between chromosomes Y and 15.
Methods
DNA was extracted from the patient's peripheral blood. A range of genetic testing was performed, including conventional chromosomal karyotyping, short tandem repeat (STR) analysis for azoospermia factor (AZF) region, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with specific probes groups of DXZ1/DYZ3, DYZ3/D15Z1/PML and SRY/D15Z1/PML, and chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) for genomic copy number variations (CNVs).
Results
The patient was found to have an apparent 45,X karyotype. STR analysis showed that he possessed a short arm of the Y chromosome, including the SRY gene; however, he was missing the long arm of the Y chromosome, including AZFa + b + c and Yqter. A FISH assay of DXZ1 and DYZ3 probes showed a green signal of the X centromere and a red of the Y centromeric signal on a D-group-sized chromosome. By FISH assaying with D15Z1 and DYZ3 probes, chromosomes 15 and Y centromeric signals appeared closely on a single chromosome, as the PML control probe ascertained. A further FISH assay with D15Z1 and SRY probes revealed a signal of the SRY gene at the end of one arm of chromosome 15. The result of the CMA indicated a deletion with an approximate size of 45.31 Mb spanning from Yq11 to Yter.
Conclusion
Our study enriched the karyotype-phenotype correlation of Y and 15 chromosomes translocation. It strengthened the critical roles of molecular genetic techniques in identifying the chromosomal breakpoints and regions involved. Genetic aetiology can guide early intervention in childhood and assisted reproduction in adulthood.
Keywords: 45,X male; Y chromosome translocation; Sex-determining region Y gene; Azoospermia factor; Fluorescence in situ hybridization; Chromosomal microarray analysis
Background
Most individuals with a 45,X karyotype will develop into females with a Turner syndrome phenotype. However, very rare 45,X individuals are sterile males with testes. So far, fewer than 40 cases of 45,X males have been reported, and most of them have harboured chimeric XY cells [1, 2]. Only about 10 cases were discovered as 45,X males who do not possess the Y chromosome but translocation of the Y chromosome with an autosome [3–5]. The translocation rate of the Y chromosome and an autosomal is low to 1/2000 [5]. The Y chromosome harbours genes essential for testis development and function, such as the master gene for testis determination (SRY) and the genes residing in the azoospermia factor (AZF) regions. So, it is the most critical molecular genetic basis in male gender determination and fertility [6, 7]. There are two types of consequences of Y/autosome translocations: Individuals with balanced translocations usually have no abnormal clinical feature. However, Unbalanced translocations may have different clinical manifestations according to increased or decreased genetic material or damaged genes. For example, AZF region deletion of the Y chromosome is often presented as azoospermia and infertility [8]. Of note, about 70% of translocations between the Y and a telocentric chromosome involve chromosome 15, which may be attributable to the homology between heterochromatin sequences at 15p and Yq [9]. Furthermore, t(Y;15) is usually unbalanced, with most breakpoints occurring on 15p (15p11-13) and the heterochromatin region of Yq12. We hereby report on a male with an apparent 45,X karyotype, which was subsequently verified as cryptic translocation between chromosomes Y and 15.
Methods
Subject
The patient, a 27-year-old male, was referred to our hospital due to primary infertility. With a height of 166 cm (−0.5SD) and a weight of 51.5 kg (−1.2SD), the patient had a male appearance with a few whiskers and Adam’s apple. He was found to have a small testis measured approximately 8 mL on both sides. Sperms were not found on three routine semen examinations. The levels of sex hormones examined at another hospital were as follows: testosterone: 15.12 nmol/L (reference value: 4.94–32.01 nmol/L), prolactin: 168.09 nmol/L (reference value: 77.75–435.92 nmol/L), estradiol: 70.4 pmol/L (reference value: 40.4–161.5 pmol/L), luteinizing hormone: 5.33 IU/L (reference value: 0.57–12.07 IU/L), follicle-stimulating hormone 13.24 IU/L (reference value: 0.95–11.95 IU/L). His father and mother denied a family history of genetic disorders and consanguinity. No infertility problems or similar patients existed in their relatives. According to the recollection of the patient and his parents, the patient had no apparent abnormalities in the process of growth and development compared with other boys of the same age. He had never been had a growth hormone and sex hormone test until he came to our hospital. The karyotypes of his father and mother were 46, XY and 46, XX, respectively.
Specimen preparation
Peripheral blood samples of the patient and his parents were collected with heparin sodium and EDTA-Na2 anticoagulant tubes, respectively.
Chromosomal karyotyping analysis
Lymphocytes from heparin sodium anticoagulated blood were cultured, harvested, and loaded onto microscope slides for Giemsa staining using conventional methods. As previously described, a Zeiss (Germany) karyotype analysis system was adopted for chromosome counting and karyotype analysis [10]. Chromosome interpreted according to International System of Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN) criteria [11].
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted from EDTA-Na2 anticoagulated blood with a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Germany) by following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was qualified with a concentration over 30 ng/μL and an OD260/280 value between 1.8 to 2.0, as determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometer Nanodrop 1C (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
Analysis of AZF sequences
Y chromosome-specific sequences were detected using the short tandem repeats (STR) method. The PCR conditions were as follows: 94 °C for 2 min, 98 °C 10 s, 60 °C 30 s, 68 °C 30 s, 25 cycles; 72 °C for 10 min. The amplicons were subjected to capillary electrophoresis on an ABI 3500Dx gene analyzer. Then, the data were analyzed by using GeneMapper software. These specific STR loci are selected mainly based on sex chromosome ploidy and AZF microdeletion analysis. Sex chromosome ploidy was obtained by analyzing these STR loci. The STR loci of ZFX and ZFY are used to detect the number of X and Y chromosomes; Yqp to measure the ratio of Yq and Yp, Xqp to measure the ratio of Xq and Xp; C03Yp and C03Xq to detect the copy number of Yp and Xq, taking chromosome 3 as a reference. AZF microdeletion was informed through detecting the classical loci of sY84, sY86, sY127, sY134, sY254, sY255 of the AZF region in Yq. The TAF9b gene located on chromosome 3 is highly conserved, so taking it as a reference, the X chromosome can be accurately counted. The absence of the Y chromosome can be judged compared to the X chromosome.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis
FISH assay with D18Z1, DXZ1 and DYZ3 probes
Metaphase cells derived from cultured peripheral blood lymphocytes were hybridized with D18Z1, DXZ1 and DYZ3 probes (China Medical Technologies, Inc. Beijing, China), which targeted the DNA stretches of 18, X, and Y centromeres, respectively. Glass slides were denatured at 78 °C for 10 min and hybridized at 42 °C for more than 16 h. After that, the signals were observed under a fluorescence microscope.
FISH assay with PML, D15Z1 and DYZ3 probes
Metaphase cells loaded upon glass slides were hybridized with the PML, D15Z1 and DYZ3 probes. The hybridization buffer and the DYZ3 probe were mixed with a proportion of 4:1 and applied to the cell-loaded glass slides. Denaturation and hybridization were carried out by following the standard procedure.
FISH assay with PML, D15Z1 and SRY probes
The procedure was the same as the prior step, only differed with the preparation of the hybridization mix, in which the buffer and the SRY probe were mixed at a proportion of 9:1.
Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA)
500–1000 μg of genomic DNA and the same amount of reference DNA were used for the experiment. After digestion, the labelled patient sample was mixed with the reference and hybridized to a SurePrint G3 CGH + SNP (180 K) chip. Fluorescence signals were scanned with an Agilent DNA Microarray Scanner. Data were extracted from the chip image with Agilent Feature Extraction Software and converted into log-ratios. Copy number variants (CNVs) were analyzed with Agilent CytoGenomics Software (Agilent Technologies, USA). Candidate variants were queried with relevant online databases such as OMIM (https://omim.org/), DGV (http://dgv.tcag.ca/dgv/), Decipher (https://decipher.sanger.ac.uk/), ClinGen (https://www.clinicalgenome.org/) and ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/).
Comparison of the clinical phenotypes of patients with a 45,X,t (Y;15) karyotype
Cases with 45,X,dic(Y;15) karyotype has been searched for in the previous report, and their clinical phenotypes were compared.
Results
Cytogenetic analysis
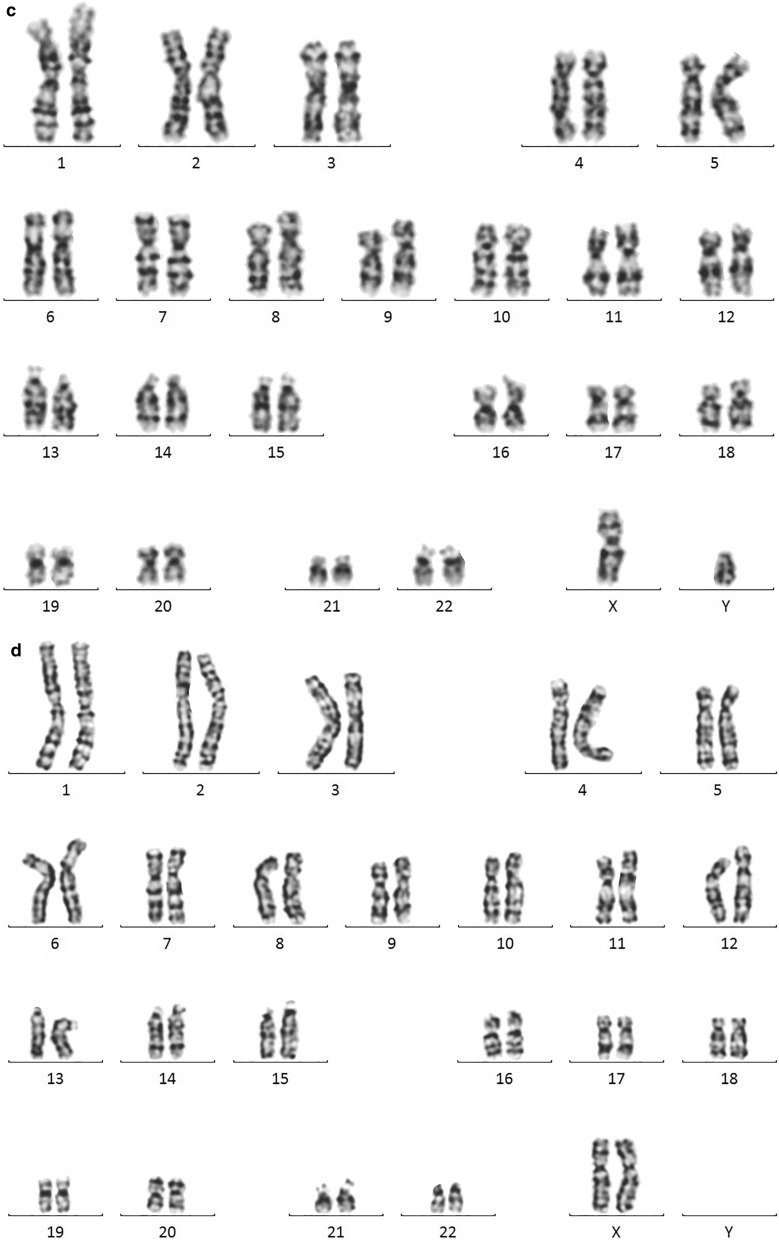
The patient’s father and mother had a karyotype of 46,XY and 46,XX, respectively. In contrast, the patient had an apparent 45,X karyotype (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
a: Karyogram of the t(Y;15) male patient. The der(15) and X chromosomes are indicated by arrows. b: Ideograms of chromosomes Y, 15, and dic(Y;15). The Y centromere and 15 centromere of the dicentric chromosome are indicated by arrows. c: 46,XY karyogram of the patient's father. d: 46,XX karyogram of the patient's mother
STR analysis
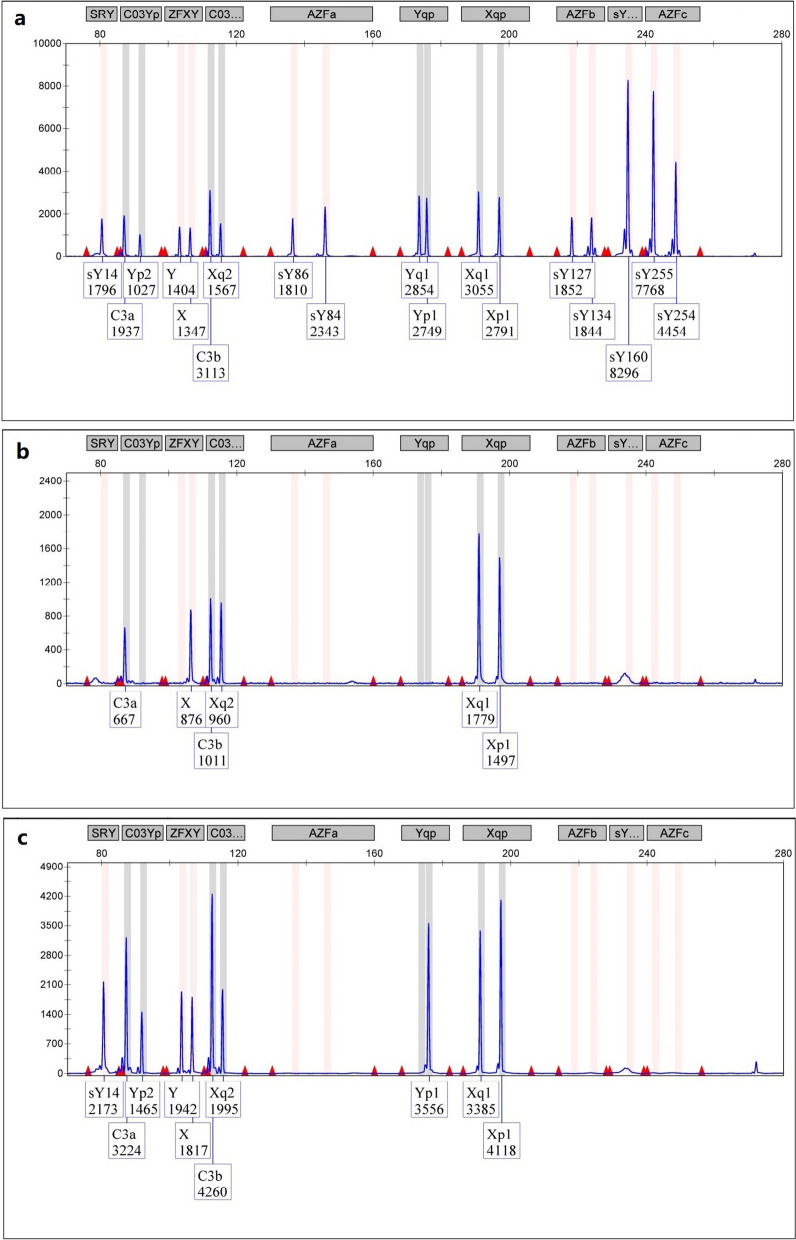
STR analysis showed that the patient was positive for the SRY gene mapped to Yp but negative for the AZFa + b + c and Yqter sequences of Yq. He had only possessed a single copy of Xp, Xq, and Yp (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Capillary electrophoresis diagram for the detection of AZF sequences. a: Normal male; b: Normal female; c: 45,X male. A fluorescence peak representing the SRY sequence was seen, but those for the AZFa, AZFb, AZFc, and SY160 were absent, suggesting loss of the whole long arm of the Y chromosome
FISH analysis
FISH with the D18Z1, DXZ1 and DYZ3 probes
FISH with D18Z1/DXZ1/DYZ3 centromeric probes showed two blue, one green, and one red signal, respectively. However, the red signal of the Y centromere was observed on one of the D-group-sized telochromosomes in the patient’s metaphase cells (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.

a: FISH image of metaphase cells of the patient detected with the X and Y centromeric probes. The green signal indicated the centromere of the X chromosome, while the red signal indicated the Y chromosome material on a D-group-telocentromeric chromosome; b: FISH image of metaphase cells of the patient's father detected with the 18, X and Y centromeric probes. The blue, green, red signals are indicated the 18, X, Y chromosomes
FISH with the PML, D15Z1 and DYZ3 probes
FISH with the PML, D15Z1 and DYZ3 probes has revealed one green, one aqua blue, and one red signal in one of the D-group-sized telochromosomes, respectively. The aqua blue and red signals of D15Z1 and DYZ3 were in close proximity, which indicated that chromosome 15 of the patient was dicentric and has contained materials from chromosomes 15 and Y (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.

FISH image of metaphase cells of the patient detected with centromeric probes for chromosomes 15 and Y. The green signal is from the PML probe mapped to 15q24.1, the red signal is from the DYZ3 probe mapped to the centromere of Y, and the aqua blue signal is from the D15Z1 probe (15q10) closely located on the same chromosome
FISH with the PML, D15Z1 and SRY probes
A further FISH assay with the PML, D15Z1 and SRY probes revealed fluorescence signals for all three probes on the same telocentromeric chromosome, including an aqua blue signal of D15Z1, a green signal of PML on chromosome 15, and an orange signal of SRY. The SRY probe signal was observed on the opposite arm of the PML probe at 15q24.1, which suggested the SRY gene has translocated to 15p (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.

FISH image of metaphase cells of the patient detected with probes for chromosome 15 and the SRY region. The green signal is from the PML probe mapped to 15q24.1, the orange signal from the SRY probe (Yp11.31) and the aqua blue signal from the D15Z1 probe (15q10) are located on the same chromosome
Result of CMA analysis
The CMA result of the patient was arr[GRCh37] Yq11.21q11.23(13988156_59301502) × 0, i.e. 45.31 Mb (Fig. 6). We postulated the deletion range from Yq11.21 to Yqter because the microarray chip contained no probe for the heterochromatin region from Yq11.23 to Yqter. The above result was also in keeping with the STR analysis, which showed no peaks for the AZF sequences at Yq and the SY160 sequence at Yqter.
Fig. 6.
CMA result of the patient. The Yq region was absent in the patient. The red bar indicates the area of deletion
Comparison of the clinical phenotypes of individuals with a 45,X,dic(Y;15) karyotype
Table 1 has summarized the clinical features of individuals with a 45,X,dic(Y;15) karyotype as shown; variation of the breakpoints has resulted in discrepancies in the deletion regions on chromosomes Y and 15. Patients 2, 3, and 4 had lost no genetic material; therefore, they had no abnormal phenotypes. Patient 5 showed severe oligoasthenospermia due to partial deletion of AZFc (sY254). Patients 6 and 7 had lost the entire long arm of the Y chromosome (including the AZFa + b + c regions), similar to our patient. They showed abnormal phenotypes, such as spermatogenous and testicular dysplasia.
Table 1.
Summary of chromosomal breakpoints and clinical phenotypes of individuals with a 45,X,dic(Y;15) karyotype
| Case | References | Chromosomal karyotype | Clinical phenotype | Analytical method | Whether the derivative chromosome contains the Y centromere | Whether the derivative chromosome contains the 15 centromere |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Present study | 45,X,dic(Y;15)(q11;p11).ish dic(Y;15)(SRY + ,DYZ3 + ;D15Z1 + ,PML +) | A 27-years-old male, with a weight 51.5 kg and a height of 160 cm, had small testes. Laboratory tests found normal level of testosterone, high level of follicle-stimulating hormone. He had azoospermia due to deletion of AZFa + b + c loci, but had a 45,X karyotype | Karyotyping, FISH, Multiplex PCR, CMA | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | Subrt et al. [15] | 45,X,t(Y;15)(Yqter → Yp11::15q11 → 15qter) | Four males from four consecutive generations of a pedigree harbored 45,X,t(Y;15) translocations but with a normal phenotype | Karyotyping | Yes | No |
| 3 | Mahmut [18] | 45,X,t(Y;15)(q12;q11) | The karyotypes of father and mother were 46,XY, t(15;20)(q11; 13) and 46,XX, respectively, but the fetus was a 45,X,t(Y;15) male, and no abnormal phenotype was observed up to one year after birth | Karyotyping, FISH | Yes | No |
| 4 | White et al. [19] | 45,X,dic(Y;15)(q11.23;p11.1) | The karyotype of the fetus was the same as that of the father, and no abnormal phenotype was observed | Karyotyping, FISH Microsatellite analysis | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | Lin et al. [22] | 45,X, der(15)(?::p11.2 → qter)dn. ish psu dic(Y;15)(q12;p11.2)(D15Z1 + , SNRPN + , PML + ; SRY + ,DYZ3 + , DYZ1 +) | A 33-year-old male had normal intelligence, growth and development, testicular size and sex hormones level but infertility. He had severe oligoasthenospermia due to partial AZFc (sY254) deletion | Karyotyping, FISH, Multiplex PCR | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | Antonio et al. [8] | 45,X,der(15)(Ypter → q22.21::15p11.2 → qter) | A 41-year-old male, 58 kg in weight and 157 cm in height, had small testis, epididymis dystrophy. Laboratory tests found low testosterone, high gonadotropin, azoospermia, and deletion of AZFa + b + c loci | Karyotyping, FISH, Y microdeletion analysis | Yes | Yes |
| 7 | Schempp [23] | 45,X,t(Y;15)(p10;p12) | A 19-year-old male had a weight of 54 kg and a height of 154 cm. He had normal mental development and no deformity. He had a de novo translocation between chromosomes Y and 15. His primary anomaly is azoospermia | Different chromosome staining | Yes | Yes |
Discussion
Among the previously reported 45,X,t(Y;15) male cases, only a few were non-chimeric. Our patient's results showed no other cells except for 45,X after analyzing two hundred cultured lymphocyte cells with karyotype and FISH methods as previous reports [1, 2]. Meanwhile, metaphase cells were analyzed with FISH probes of chromosome Y and chromosome 15. They showed the translocation of Yp onto one of 15 chromosomes. Some were initially detected with a 15p + karyotype but later confirmed as 45,X,t(Y;15) by molecular methods [12–14]. Of note, some of these translocations were inherited from parents with a normal phenotype [15–17]. As summarized by Table 1, variation of the breakpoint sites in these 45,X,t(Y;15) males has resulted in their phenotypes' heterogeneity. The individual with a loss of heterochromatin had a normal phenotype [15, 18, 19]. By contrast, individuals with loss of euchromatin had various clinical phenotypes. Loss of the AZFc region at Yq presented severe oligoasthenospermia [20], while the AZFa, AZFb and AZFc regions manifested azoospermia, testicular dysplasia and other phenotypes [8, 21].
The contribution of genetic testing performed here was different for the patient's diagnosis. Karyotyping was used to count chromosomes and assess chimaera. CMA analyses were adopted to map the deletion region accurately and exclude deletion and duplication of other genomic regions. STR was proper for AZF region microdeletions. FISH was helpful for the breakpoint location of the Y-15 chromosomal translocation. The cause of the patient's azoospermia has been ultimately verified. It was attributable to the unbalanced translocation between chromosomes 15 and Y, resulting in the deletion of the AZFa + b + c region on Yq. Therefore, combining these genetic techniques is our recommendation for clinicians to diagnose similar patients.
In the present study, the patient appeared to have no Y chromosome but was found to carry an unbalanced Y → 15 translocation by molecular genetic testing. The translocation has resulted in the SRY gene of Yp exchange onto the short arm of chromosome 15. Two broken chromosomes containing the centromeric parts have formed a dicentric aberration. Dicentric chromosomes derived from translocations between chromosomes Y and 15 are rare [22]. As one of the centromeres was inactive or nonfunctional, the dicentric chromosome might behave and segregate as a monocentric chromosome during cell division [23, 24]. A translocation study between the Y and chromosome 21 found that the Y chromosome's centromere was preferentially inactivated in pseudodicrocentromeres [25]. However, it is not sure which centromere is active because we have not directly measured the activity. Moreover, it is not apparent from the morphology of the centromeres. The acentric fragments, including the short arm of chromosome 15 and the long arm of chromosome Y, are prone to lose during subsequent cell divisions. As a result, only 45 chromosomes were left. Cytogenetically, the derivative chromosome 15 containing a small fraction of Yp could not be easily distinguished from the normal ones.
The heterochromatin of 15pter should be lost when Yp translocates to 15p. However, the CMA has no probes assigned in the telocentric satellite region. The results of CMA analysis showed no loss of chromosome 15 genetic material. Several males carrying a Y-acrocentric chromosome translocation with a breakpoint between Yq11 and Yq12 were reported previously [26, 27]. In the present study, based on the results of molecular analysis, our patient's karyotype was verified as 45,X,dic(Y;15)(q11;p11).ish dic(Y;15)(SRY+ ,DYZ3+ ;D15Z1+ ,PML+). Results of the FISH assay indicated that the patient's chromosomal rearrangement had occurred de novo, as no abnormality was found with his father. It may be postulated that the two chromosomes had broken during the first meiosis of spermatogenesis or at a very early stage of zygote formation. Human embryos will develop towards the male gender as long as the SRY gene is present in the genome, even without the Y chromosome. That may also be the primary molecular basis for 45,X males [28, 29]. Based on molecular testing, the seemingly "pure" 45,X male may not exist. The SRY gene on autosomes derived from the Yp translocation could explain the male sex determination in such cases [30].
Similar to Hsu et al. report [30], the main clinical features of our patient were azoospermia and infertility. Several genes mapped to the AZF region of Yq, including USP9Y, DBY, PRY, RBMY, DAZ and BPY2, are involved in the formation, development, and maturation of sperms. Deletions of the AZF region have been the most common risk factor for male infertility [8, 31, 32]. Account for 10–15% of azoospermia and 5–10% of severe oligozoospermia [33]. The type and location of the AZF gene deletions are correlated with the severity of fertility disorders. AZFa deletion usually results in SCOS-only type I syndrome (SCOS type I) and azoospermia. AZFb deletion is associated with azoospermia caused by the cessation of meiosis. AZFc deletion has considerable clinical heterogeneity [8]. In the present study, the patient has lost Yq (including AZFa + b + c), and no sperm was found upon routine semen tests. Microspermatocentesis was not recommended for this patient because his testis did not produce any sperm as previous report [34]. He has no chance of having a biological child, so this translocation will not be passed on.
Infertile reasons for this 45,X,t(Y;15) male patient may be mainly attributed to the loss of spermatogenetic genes in the AZF region and the disability of the critical step of the sex-chromosomal pairing during the meiotic prophase [35–37]. We speculated that the failure of X–Y pairing led to germ cell loss because of the loss of the YPAR2 region and the translocation of the YPAR1 region.
Our study enriched the karyotype-phenotype correlation of Y and 15 chromosomes translocation and strengthened the critical roles of molecular genetic techniques in identifying the chromosomal breakpoints and regions involved. Early diagnosis can guide their clinical intervention by correcting the external genitalia, removing gonad dysplasia, hormone therapy, and assisted reproduction.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Cytogenetics Group of the Department of Medical Genetics and Prenatal Diagnosis for the karyotype analysis and Sixiang Chen for the CMA analysis.
Authors' contributions
Clinical data collection, genetic counselling and follow-up were performed by JL-L. SQ contributed to the study conception and design, analyzed and interpreted the patient data. XW performed the physical examination and modified the manuscript. JW made the clinical evaluation and give reproductive advice. ZZ, XC, YY, and MY proceeded with the molecular genetics experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Funds (CXZD01-2020) of Sichuan Provincial Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study is retrospective and did not require the ethical approval.
Consent for publication
The patient had provided his consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Shengfang Qin, Email: qinshengfang@126.com.
Jesse Li-Ling, Email: jliling@scu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Forabosco A, Carratu A, Assuma M, De Pol A, Dutrillaux B, Cheli E. Male with 45, X karyotype. Clin Genet. 1977;12(2):97–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb00908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Graham BH, Bacino CA. Male patient with non-mosaic deleted Y-chromosome and clinical features of Turner syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2003;119A(2):234–237. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.10147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bilen S, Okten A, Karaguzel G, Ikbal M, Aslan Y. A 45 X male patient with 7q distal deletion and rearrangement with SRY gene translocation: a case report. Genet Couns. 2013;24(3):299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Turleau C, Chavin-Colin F, de Grouchy J. A 45, X male with translocation of euchromatic Y chromosome material. Hum Genet. 1980;53(3):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00287044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nielsen J, Rasmussen K. Y/autosomal translocations. Clin Genet. 1976;9(6):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McLaren A. Sex determination. What makes a man a man? Nature. 1990;346(6281):216–217. doi: 10.1038/346216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Krausz C, Casamonti E. Spermatogenic failure and the Y chromosome. Hum Genet. 2017;136(5):637–655. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1793-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Colaco S, Modi D. Genetics of the human Y chromosome and its association with male infertility. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0330-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Metzler-Guillemain C, Mignon C, Depetris D, Guichaoua MR, Mattei MG. Bivalent 15 regularly associates with the sex vesicle in normal male meiosis. Chromosome Res. 1999;7(5):369–378. doi: 10.1023/a:1009268014387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu Y, Kong XD, Wu QH, Li G, Song L, Sun YP. Karyotype analysis in large-sample infertile couples living in Central China: a study of 14965 couples. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(4):547–553. doi: 10.1007/s10815-013-9964-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McGowan-Jordan J, Hantings RJ, Moore S. ISCN 2020: an international system for human cytogenomic nomenclature(2020) S. Karger: Medical and Scientific Publishers; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Neumann AA, Robson LG, Smith A. A 15p+ variant shown to be a t(Y;15) with fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Ann Genet. 1992;35(4):227–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhang LL, Lu BT, Yao J. Detection of a pedigree with a 15p+ chromosomal karyotype with Y-specific probes. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2010;27(6):712–713. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2010.06.030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhao L, Li H, Xue YQ, Pan JL, Wu YF, Lu M. Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization in the diagnosis of genetic diseases. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2004;21(6):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Subrt I, Blehová B. Robertsonian translocation between the chromosome Y and 15. Humangenetik. 1974;23(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00272514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chen-Shtoyerman R, Josefsberg Ben-Yehoshua S, Nissani R, Rosensaft J, Appelman Z. A prevalent Y;15 translocation in the Ethiopian Beta Israel community in Israel. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2012;136(3):171–174. doi: 10.1159/000336201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen PY, Yen JH, Cheng CF, Chen PC, Li YS, Li TY, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of the maternal derivative chromosome der(15)t(Y;15)(q12;p13) in a dizygotic twin pregnancy. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;28(4):176–179. doi: 10.1016/j.tcmj.2016.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yıldırım MS, Arslan AB, Zamani AG. Interchromosomal effect: report of a father and son, bearing different translocations of the same chromosome, and a review of the current literature. Andrologia. 2021;53(1):e13805. doi: 10.1111/and.13805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.White LM, Treat K, Leff A, Styers D, Mitchell M, Knoll JH. Exclusion of uniparental inheritance of chromosome 15 in a fetus with a familial dicentric (Y;15) translocation. Prenat Diagn. 1998;18(2):111–116. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199802)18:2<111::AID-PD224>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lin S, Xie Y, Wu J, Fang Q, Chen Z, Chen B. Cytogenetic and molecular study of a patient with severe oligozoospermia and asthenozoospermia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2014;31(1):65–68. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2014.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mancini A, Zollino M, Leone E, Grande G, Festa R, Lecce R, et al. A case of 45, X male: genetic reevaluation and hormonal and metabolic follow-up in adult age. Fertil Steril. 2008;90(5):2011.e17–21. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.07.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gal A, Weber B, Neri G, Serra A, Müller U, Schempp W, et al. A 45, X male with Y-specific DNA translocated onto chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet. 1987;40(6):477–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Earnshaw WC, Migeon BR. Three related centromere proteins are absent from the inactive centromere of a stable isodicentric chromosome. Chromosoma. 1985;92(4):290–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00329812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sullivan BA, Schwartz S. Identification of centromeric antigens in dicentric Robertsonian translocations: CENP-C and CENP-E are necessary components of functional centromeres. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4(12):2189–2197. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.12.2189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fisher AM, Al-Gazali L, Pramathan T, Quaife R, Cockwell AE, Barber JC, et al. Centromeric inactivation in a dicentric human Y;21 translocation chromosome. Chromosoma. 1997;106(4):199–206. doi: 10.1007/s004120050240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rosa MD, Brasi DD, Zarrilli S, Paesano L, Pivonello R, Agostino A, et al. Short stature and azoospermia in a patient with Y chromosome long arm deletion. J Endocrinol Invest. 1997;20(10):623–628. doi: 10.1007/BF03346921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alitalo T, Tiihonen J, Hakola P, de la Chapelle A. Molecular characterization of a Y;15 translocation segregating in a family. Hum Genet. 1988;79(1):29–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00291705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Amaro A, Mafra FA, Valada Pane CE, Kulikowski LD, Bianco B, Barbosa CP, et al. 45, X karyotype in an infertile man: how is this possible. Urol Int. 2015;94(4):488–490. doi: 10.1159/000365010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.de la Chapelle A, Page DC, Brown L, Kaski U, Parvinen T, Tippett PA. The origin of 45, X males. Am J Hum Genet. 1986;38(3):330–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hsu LY. Phenotype/karyotype correlations of Y chromosome aneuploidy with emphasis on structural aberrations in postnatally diagnosed cases. Am J Med Genet. 1994;53(2):108–140. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320530204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Motovali-Bashi M, Rezaei Z, Dehghanian F, Rezaei H. Multiplex PCR based screening for micro/partial deletions in the AZF region of Y-chromosome in severe oligozoospermic and azoospermic infertile men in Iran. Iran J Reprod Med. 2015;13(9):563–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tiepolo L, Zuffardi O. Localization of factors controlling spermatogenesis in the nonfluorescent portion of the human Y chromosome long arm. Hum Genet. 1976;34(2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00278879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yu XW, Wei ZT, Jiang YT, Zhang SL. Y chromosome azoospermia factor region microdeletions and transmission characteristics in azoospermic and severe oligozoospermic patients. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):14634–14646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hopps CV, Mielnik A, Goldstein M, Palermo GD, Rosenwaks Z, Schlegel PN. Detection of sperm in men with Y chromosome microdeletions of the AZFa, AZFb and AZFc regions. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(8):1660–1665. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deg348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Burgoyne PS, Mahadevaiah SK, Sutcliffe MJ, Palmer SJ. Fertility in mice requires X-Y pairing and a Y-chromosomal "spermiogenesis" gene mapping to the long arm. Cell. 1992;71(3):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90509-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ogata T, Wakui K, Kosho T, Muroya K, Yamanouchi Y, Takano T, Fukushima Y, Rappold G, Suzuki Y. Structural analysis of a rare rearranged Y chromosome and its bearing on genotype-phenotype correlation. Am J Med Genet. 2000;92(4):256–259. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(20000605)92:4<256::AID-AJMG6>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McKee BD, Wilhelm K, Merrill C, Ren X. Male sterility and meiotic drive associated with sex chromosome rearrangements in Drosophila. Role of X-Y pairing. Genetics. 1998;149(1):143–155. doi: 10.1093/genetics/149.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.