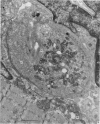
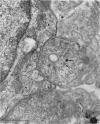
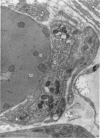
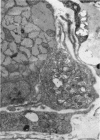
Full text
PDF





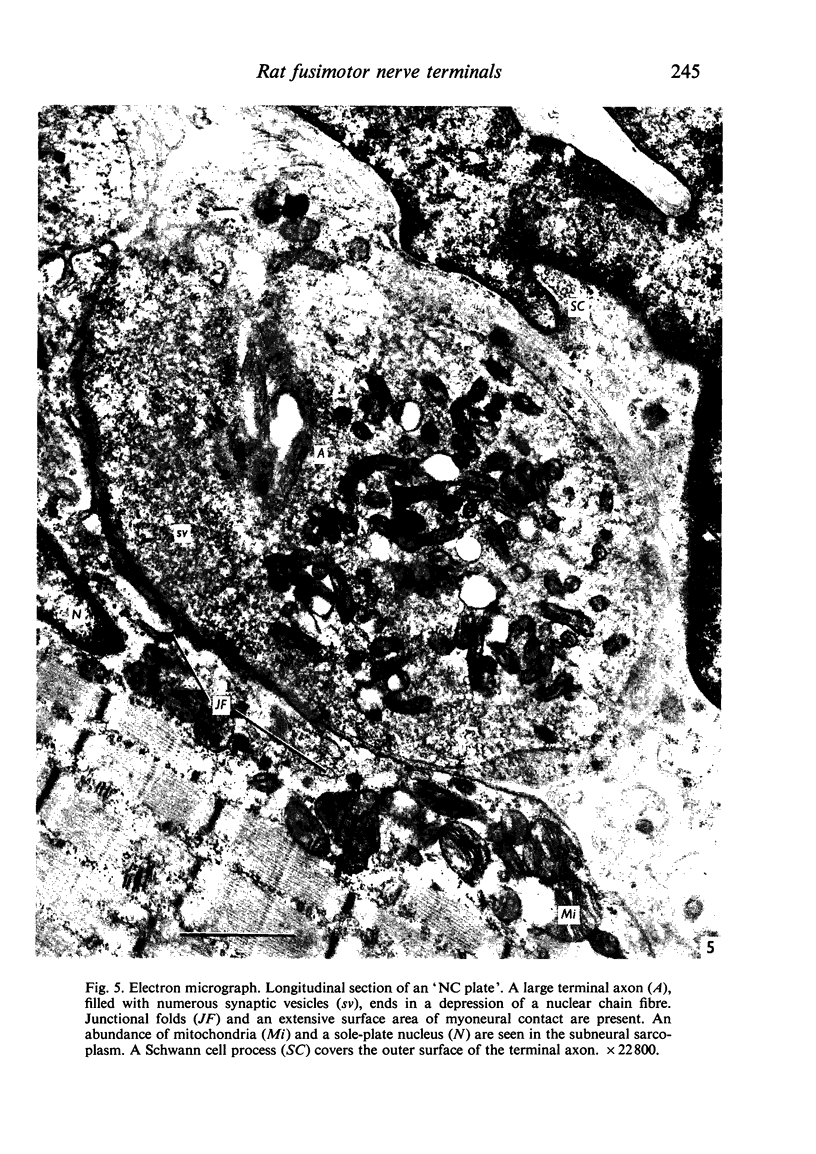







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. L'innervation motrice du muscle strié des vertébrés. Actual Neurophysiol (Paris) 1968;8:23–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Pages B. Intracellular recording from spindle muscle fibres of potentials elicited by static fusimotor axons in the cat. Life Sci. 1969 Apr 1;8(7):417–419. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER S., DANIEL P. M. MUSCLE SPINDLES IN MAN; THEIR MORPHOLOGY IN THE LUMBRICALS AND THE DEEP MUSCLES OF THE NECK. Brain. 1963 Sep;86:563–586. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvaja N., Marinozzi V., Pompeiano O. Muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscle of the adult cat. Electron microscopic observations and functional considerations. Arch Ital Biol. 1969 Oct;107(4):365–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diete-Spiff K. Tension development by isolated muscle spindles of the cat. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):31–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C. The electrical activity of mammalian intrafusal fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:169–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H. Muscle spindle innervation in the intertransverse caudal muscles of the rat. Experientia. 1969 Jun 15;25(6):604–606. doi: 10.1007/BF01896539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A., PILAR G. SLOW FIBRES IN THE EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:780–798. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. Two kinds of motor nerve endings on mammalian intrafusal muscle fibers revealed by the cholinesterase technique. Anat Rec. 1961 Feb;139:173–183. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091390209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig G. Die Nervenendigungen der Rattenmuskelspindel im elektronen- und plasenkontrastmikroskopischen Bild. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;96(2):275–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. The structure of vertebrate slow and twitch muscle fibers. Invest Ophthalmol. 1967 Jun;6(3):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Vertebrate slow muscle fibers. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):40–62. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUPFER C. Motor innervation of extraocular muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Oct;153:522–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr R. Untersuchungen an isolierten Muskelspindeln der Ratte nach Cholinesterasedarstellung und Sudanschwarz-Färbung. Ein Beitrag zur Frage der Morphologie und Verteilung motorischer Nervenendigungen in der Muskelspindel der Säuger. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;93(4):594–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovalle W. K., Jr Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The polar region. J Cell Biol. 1971 Oct;51(1):83–103. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porayko O., Smith R. S. Morphology of muscle spindles in the rat. Experientia. 1968 Jun 15;24(6):588–589. doi: 10.1007/BF02153790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Düring M., Andres K. H. Zur Feinstruktur der Muskelspindel von Mammalia. Anat Anz. 1969;124(5):566–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]