Abstract
In an effort to assess connective tissue biosynthetic activity in human liver disease, collagen proline hydroxylase (a key enzyme in collagen biosynthesis) and the uptake of 35S sulphate (a precursor of sulphated mucopolysaccharides) were measured in hepatic tissue obtained mainly by percutaneous biopsy.
A procedure is described for the quantitation of collagen proline hydroxylase in cryostat sections which allows for the simultaneous histopathological examination of the liver specimen. A three to eightfold increase in the activity of this enzyme was found in four cirrhotic livers compared with the mean value of four normal livers and two biopsies from patients with Gilbert's syndrome. Elevated hydroxylase levels were found also in five patients with hepatic dysfunction but without cirrhosis (four alcoholics and one patient with persistent hepatitis associated with serum smooth muscle antibody). It is suggested that the hepatic level of collagen proline hydroxylase may be a useful quantitative index of fibroblastic activity in human liver disease.
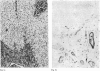
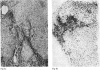
Autoradiographic studies of radioactive sulphate uptake in biopsy specimens from patients with chronic liver disease showed an exaggerated incorporation of isotope not only at sites of established fibrogenesis but also in the walls of sinusoids throughout the liver.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. A., Prockop D. J. The thermal transition of a non-hydroxylated form of collagen. Evidence for a role for hydroxyproline in stabilizing the triple-helix of collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90961-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman L., Lieber C. S. Hepatic collagen metabolism: effect of alcohol consumption in rats and baboons. Science. 1972 May 19;176(4036):795–795. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4036.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galambos J. T. Acid mucopolysaccharides and cirrhosis of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jul;51(1):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant M. E., Prockop D. J. The biosynthesis of collagen. 3. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 10;286(6):291–300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202102860604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halme J., Jäskeläinen M. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase of the mouse uterus during pregnancy and post-partum involution. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):367–369. doi: 10.1042/bj1160367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halme J., Uitto J., Kahanpä K., Karhunen P., Lindy S. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase activity in experimental pulmonary fibrosis of rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Apr;75(4):535–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. J., Jr, Udenfriend S. Soluble collagen proline hydroxylase and its substrates in several animal tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):198–202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S., Harsch M., Rosenbloom J. Hydroxyproline stabilizes the triple helix of chick tendon collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):106–114. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90960-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Langness U., Udenfriend S. Immunological evidence for an inactive precursor of collagen proline hydroxylase in cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1585–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., O'Hare R. P., Patrick R. S. Stimulation of the collagen biosynthetic pathway by factors isolated from experimentally-injured liver. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):121–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Patrick R. S. The role of perisinusoidal cells in hepatic fibrogenesis. An electron microscopic study of acute carbon tetrachloride liver injury. Lab Invest. 1972 Apr;26(4):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Patrick R. S. The synthesis of sulphated mucopolysaccharide in mouse liver following carbon tetrachloride injury. I. Autoradiographic studies. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Dec;50(6):521–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Rhoads R. E., Udenfriend S. The substrate recognition site of collagen proline hydroxylase: the hydroxylation of -X-Pro-Gly- sequences in bradykinin analogs and other peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Udenfriend S. Hydroxylation of proline residues in collagen nascent chains. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jul;139(1):104–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mussini E., Hutton J. J., Jr, Udenfriend S. Collagen proline hydroxylase in wound healing, granuloma formation, scurvy, and growth. Science. 1967 Aug 25;157(3791):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3791.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Uenfriend S. Hepatic fibrosis. Correlation of biochemical and morphologic investigations. Am J Med. 1970 Nov;49:707–721. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., Udenfriend S. Purification and properties of collagen proline hydroxylase from newborn rat skin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Aug;139(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Prockop D. J. Protocollagen proline hydroxylase in normal liver and in hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 1969 Apr;56(4):744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]