Abstract
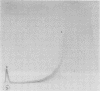
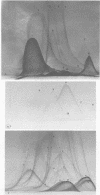
A pyridine extract antigen and a double-dialysis antigen (DDA) obtained from Thermoactinomyces candidus were analyzed by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. In addition, the heat lability, pronase sensitivity, and isolectric points of the components of the DDA were determined. By using antisera raised against crude pyridine extract antigen, two immunogenic components were resolved by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. A similar analysis of DDA using antisera raised against crude DDA revealed 15 immunogens. All but six components were heat labile, whereas pronase had little effect on the number of resolvable components. Intermediate gel crossed immunoelectrophoresis using antiserum raised to whole spores detected six immunogenic components, four of which were also detected by the anti-DDA serum. A total of 19 bands were obtained when the DDA was subjected to flatbed isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. The isoelectric points for the various components were found to range from 3.5 to 5.7. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis using isoelectric focusing in the first dimension yielded at least 16 immunogenic components. Six components with isoelectric points falling in the range of 4.5 to 6.4 were found to be resistant to heat. A comparison with antigens obtained from other thermophilic actinomycetes is presented.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke G. W., Carrington C. B., Strauss R., Fink J. N., Gaensler E. A. Allergic alveolitis caused by home humidifiers. Unusual clinical features and electron microscopic findings. JAMA. 1977 Dec 19;238(25):2705–2708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKIE H. A., RANKIN J. Farmer's lung; an acute granulomatous interstitial pneumonitis occurring in agricultural workers. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Jun 28;167(9):1069–1076. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990260011004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. N., Banaszak E. F., Barboriak J. J., Hensley G. T., Kurup V. P., Scanlon G. T., Schlueter D. P., Sosman A. J., Thiede W. H., Unger G. F. Interstital lung disease due to contamination of forced air systems. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Apr;84(4):406–413. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-4-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher S. M., Rondle C. J., Murray I. G. The extracellular antigens of Micropolyspora faeni: their significance in farmer's lung disease. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):401–409. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollick G. E., Hall N. K., Larsh H. W. Chemical and serological comparison of two antigen extracts of Thermoactinomyces candidus. Mykosen. 1979 Feb;22(2):49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1979.tb01711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N. A scheme for the identification of thermophilic actinomycetes associated with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.55-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N. Antigenic relationships among thermophilic actinomycetes. Sabouraudia. 1979 Jun;17(2):163–169. doi: 10.1080/00362177985380221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurup V. P., Fink J. N. Extracellular antigens of Micropolyspora faeni grown in synthetic medium. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):608–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.608-613.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey J. Thermoactinomyces sacchari sp. nov., a thermophilic actinomycete causing bagassosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jun;66(3):327–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-66-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. B., Salvaggio J. E. Characterization of Thermoactinomyces sacchari antigens. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):519–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.519-525.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J., Bannerman E. N., De Haller R., Wanner M. Farmer's lung: immunological response to a group of extracellular enzymes of Micropolyspora faeni. An experimental and field study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):401–406. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J., Bannerman E. N. Extracellular enzymes of Micropolyspora faeni found in moldy hay. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.7-12.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., JENKINS P. A., FESTENSTEIN G. N., GREGORY P. H., LACEY M. E., SKINNER F. A. FARMER'S LUNG. THERMOPHILIC ACTINOMYCETES AS A SOURCE OF "FARMER'S LUNG HAY" ANTIGEN. Lancet. 1963 Sep 21;2(7308):607–611. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90398-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., JENKINS P. A. PRECIPITIN (F.L.H.) TEST IN FARMER'S LUNG. Thorax. 1965 Jan;20:21–35. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C. Fractionation and chemical characterization studies on Micropolyspora faeni antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;221:199–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb28217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Zais D. P., Emanuel D. A. The frequency of precipitins to trichloroacetic acid-extractable antigens from thermophilic actinomycetes in farmer's lung patients and asymptomatic farmers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):23–28. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Zais D. P., Marx J. J., Jr, Treuhaft M. W. Comparative electrophoresis of the proteins and proteases in thermophilic actinomycetes. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Dec;90(6):1076–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabury J., Salvaggio J., Buechner H., Kundur V. G. Bagassois. 3. Isolation of thermophilic and mesophilic actinomycetes and fungi from molyd bagasse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):351–360. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck J. L., Roberts G. D. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):226–231. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.226-231.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen J., Axelsen N. H. A modified antigen--antibody crossed electrophoresis characterizing the specificity and titre of human precipiting against Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Jan;1(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treuhaft M. W., Roberts R. C., Hackbarth C., Emanuel D. A., Marx J. J., Jr Characterization of precipitin response to Micropolyspora faeni in farmer's lung disease by quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Apr;119(4):571–578. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walbaum S., Vaucelle T., Biguet J. Analyse de l'extrait de Micropolyspora faeni par immunoélectrophorèse en double dimension. Localisation des activités chymotrypsiques. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Apr;21(4):355–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel F. J., Emanuel D. A. Experimental studies of farmer's lung. N Y State J Med. 1965 Dec 15;65(24):3032–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]