Abstract
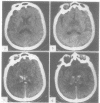
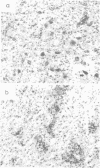
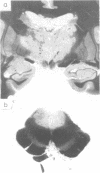
The clinical and pathological findings of a 31-year-old woman, in whom the diagnosis of Leigh's disease was made, are reported. CT scan examination with contrast enhancement showed symmetrical areas of low density, in both thalami, anterior limbs of internal capsules and corpus callosum. Longstanding chronic lesions involved the optic chiasma and the cerebral peduncles and consisted of myelin loss, status spongiosus, astrocytic gliosis and marked capillary proliferation. The neurons were spared. In the basal ganglia, internal capsules and corpus callosum, these lesions were more recent and consisted of focal necrosis, perivascular oedema and few lymphocytic perivascular cuffings.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FEIGIN I., WOLF A. A disease in infants resembling chronic Wernicke's encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 1954 Sep;45(3):243–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(54)80188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin I., Budzilovich G. N. Further observations on subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy in adults. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Jan;36(1):128–139. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197701000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin I., Goebel H. H. "Infantile" subacute necrotizing encephalopathy in the adult. Neurology. 1969 Aug;19(8):749–759. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.8.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Gardner-Medwin D. CT scan appearances in Leigh's disease (subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy). Neuroradiology. 1978;16:48–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00395200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger K., Seitelberger F. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (LEIGH). Ergeb Inn Med Kinderheilkd. 1970;29:155–219. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-95138-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo H., Lundberg P. O., Olsson Y. Familial subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy of the adult form (adult Leigh syndrome). Ann Neurol. 1979 Sep;6(3):200–206. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes J. J. Oncocytic transformation of choroid plexus epithelium. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;62(1-2):145–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00684932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIGH D. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy in an infant. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1951 Aug;14(3):216–221. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.14.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. J. Sur la délimitation clinicopathologique de l'encéphalopathie de Gayet-Wernicke et de la forme adulte de l'encéphalopathie de Leigh. Acta Neurol Belg. 1972 Sep-Oct;72(5):347–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montpetit V. J., Andermann F., Carpenter S., Fawcett J. S., Zborowska-Sluis D., Giberson H. R. Subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. A review and a study of two families. Brain. 1971;94(1):1–30. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake M., Takada G., Miyabayashi S., Arai N., Tada K., Morinaga S. Pyruvate decarboxylase deficiency in a patient with Leigh's encephalomyelopathy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1982 Aug;137(4):379–386. doi: 10.1620/tjem.137.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollivier A., Diebler C. Tomodensitométrie crânienne dans la maladie de Leigh. Une observation. Nouv Presse Med. 1980 Sep 20;9(33):2355–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W. J., Hutchison H. T., Berg B. O. Computerized tomography in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy (Leigh disease). Ann Neurol. 1981 Sep;10(3):268–271. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. C. Leigh's syndrome: the adult form of subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy with predilection for the brainstem. Neurology. 1973 Oct;23(10):1030–1038. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.10.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solheid C., Stoupel N., Martin J. J. La forme adulte à évolution chronique de l'encéphalopathie nécrosante de Leigh. Sa situation vis-à-vis des formes infanto-juvéniles. Acta Neurol Belg. 1971 May-Jun;71(3):282–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich J., Fankhauser-Mauri C. Subacute necrotizing encephalopathy (Leigh) in an adult. Eur Neurol. 1978;17(5):241–246. doi: 10.1159/000114952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetsell W. O., Jr, Plaitakis A. Leigh's disease in an adult with evidence of "inhibitor factor" in family members. Ann Neurol. 1978 Jun;3(6):519–524. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]