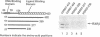Abstract
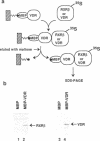
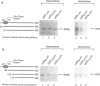
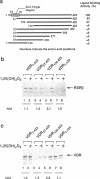
The vitamin D receptor mediates the signal of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by binding to vitamin D responsive elements in DNA as a homodimer or as a heterodimer composed of one vitamin D receptor subunit and one retinoid X receptor subunit. We have mapped the dimerization interfaces of the vitamin D receptor that is involved in homo- or heterodimer formation in the absence of DNA. While deletion of the first zinc finger region of vitamin D receptor diminished homodimerization activity, it did not affect heterodimerization. In contrast, a deletion just beyond the zinc finger region affected heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor, but not homodimerization. The zinc finger region alone could form a homodimer with full-length vitamin D receptor, but not a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor. The carboxy-terminal region was also necessary for heterodimer formation. This region showed only a weak dimerization activity in the absence of ligand, but this was dramatically increased in the presence of ligand for both homo- and heterodimerization. These results suggest that the vitamin D receptor has at least three dimerization interfaces whose functions are apparently distinguishable. These are located in the first zinc finger region, the region just beyond this zinc finger and in the carboxy-terminal region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer T. K., Hager G. L., Omichinski J. G. Sequence-specific DNA binding by glucocorticoid receptor "zinc finger peptides". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7560–7564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J., Alberts A. S., Brindle P., Claret F. X., Smeal T., Karin M., Feramisco J., Montminy M. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):226–229. doi: 10.1038/370226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester J. K., Maeda N., DeLuca H. F. Isolation and expression of rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester J. K., Wiese R. J., Maeda N., DeLuca H. F. Structure and regulation of the rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9499–9502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester J. K., Wiese R. J., Maeda N., DeLuca H. F. Structure and regulation of the rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9499–9502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg C., Bendik I., Wyss A., Meier E., Sturzenbecker L. J., Grippo J. F., Hunziker W. Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D. Nature. 1993 Feb 18;361(6413):657–660. doi: 10.1038/361657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheskis B., Freedman L. P. Ligand modulates the conversion of DNA-bound vitamin D3 receptor (VDR) homodimers into VDR-retinoid X receptor heterodimers. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3329–3338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy B., Green M. R. Eukaryotic activators function during multiple steps of preinitiation complex assembly. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):531–536. doi: 10.1038/366531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielian P. S., White R., Lees J. A., Parker M. G. Identification of a conserved region required for hormone dependent transcriptional activation by steroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Towers T. L. DNA binding properties of the vitamin D3 receptor zinc finger region. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Dec;5(12):1815–1826. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-12-1815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing N. H., Beekman J. M., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Members of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily interact with TFIIB (S300-II). J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17617–17623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Shales M., Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J., Greenblatt J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):588–590. doi: 10.1038/351588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok R. P., Lundblad J. R., Chrivia J. C., Richards J. P., Bächinger H. P., Brennan R. G., Roberts S. G., Green M. R., Goodman R. H. Nuclear protein CBP is a coactivator for the transcription factor CREB. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):223–226. doi: 10.1038/370223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi B. F., Xu W. X., Otwinowski Z., Freedman L. P., Yamamoto K. R., Sigler P. B. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with DNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):497–505. doi: 10.1038/352497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Chen J. Y., Chen Z., White J., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. The patterns of binding of RAR, RXR and TR homo- and heterodimers to direct repeats are dictated by the binding specificites of the DNA binding domains. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5029–5041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Scott R. A., Kerner S. A., O'Malley B. W., Pike J. W. Functional domains of the human vitamin D3 receptor regulate osteocalcin gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Apr;3(4):635–644. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-4-635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa J., Kitaura M., Matsumoto M., Imagawa M., Nishihara T. Difference and similarity of DNA sequence recognized by VDR homodimer and VDR/RXR heterodimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2902–2907. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa J., Matsumoto M., Sakoda K., Kitaura M., Imagawa M., Nishihara T. Vitamin D receptor zinc finger region binds to a direct repeat as a dimer and discriminates the spacing number between each half-site. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19739–19743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towers T. L., Luisi B. F., Asianov A., Freedman L. P. DNA target selectivity by the vitamin D3 receptor: mechanism of dimer binding to an asymmetric repeat element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6310–6314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Paulsen R. E., Padgett K. A., Milbrandt J. Participation of non-zinc finger residues in DNA binding by two nuclear orphan receptors. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):107–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1314418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechel C., Shen X. Q., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Dimerization interfaces formed between the DNA binding domains determine the cooperative binding of RXR/RAR and RXR/TR heterodimers to DR5 and DR4 elements. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1414–1424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechel C., Shen X. Q., Chen J. Y., Chen Z. P., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. The dimerization interfaces formed between the DNA binding domains of RXR, RAR and TR determine the binding specificity and polarity of the full-length receptors to direct repeats. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1425–1433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Salbert G., Lee M. O., Pfahl M. Mutations that alter ligand-induced switches and dimerization activities in the retinoid X receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4311–4323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]